Abstract
Crit Care Sci. 2023;35(3):302-310
DOI 10.5935/2965-2774.20230141-pt
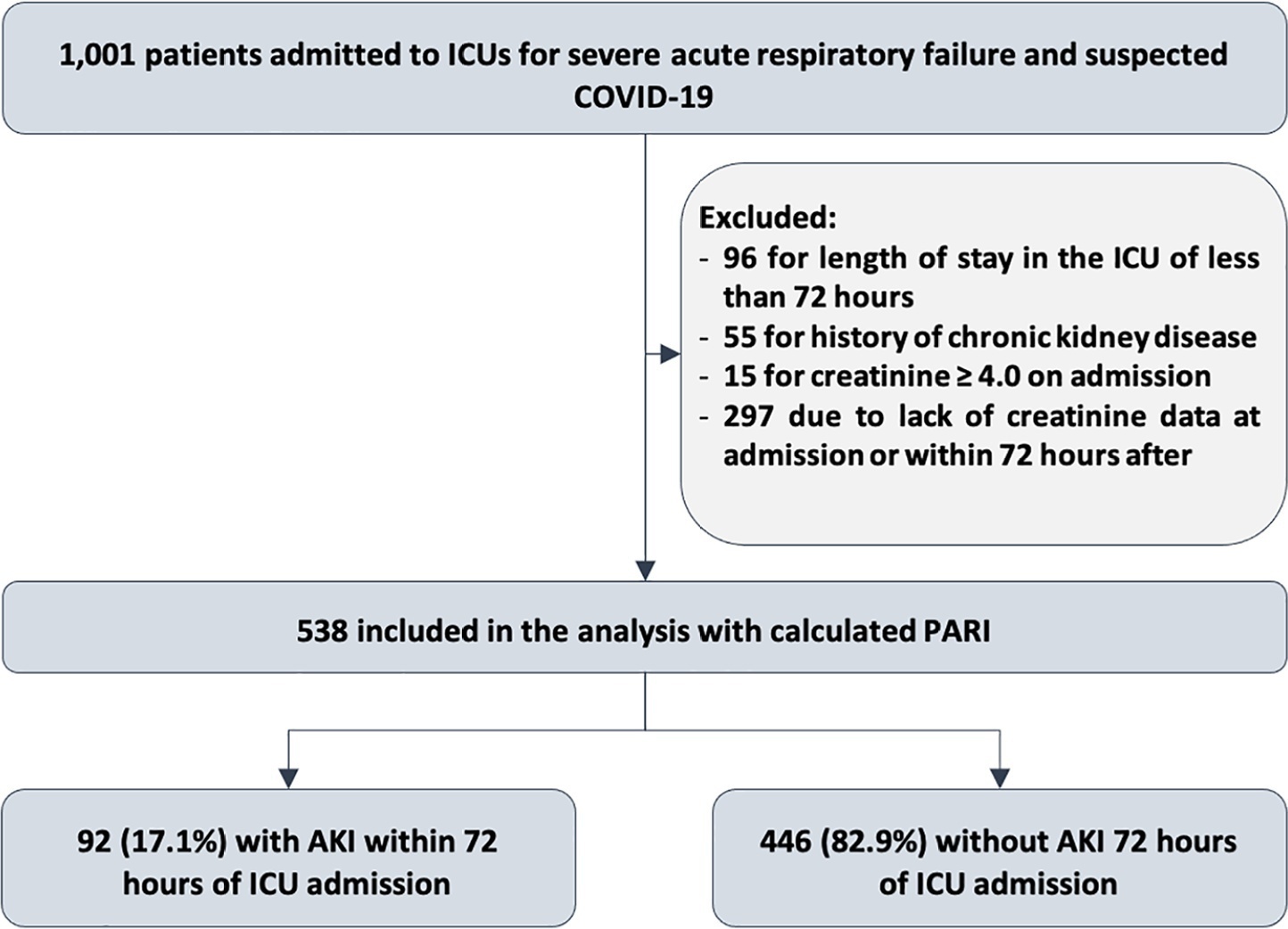
To evaluate the accuracy of the persistent AKI risk index (PARI) in predicting acute kidney injury within 72 hours after admission to the intensive care unit, persistent acute kidney injury, renal replacement therapy, and death within 7 days in patients hospitalized due to acute respiratory failure.
This study was done in a cohort of diagnoses of consecutive adult patients admitted to the intensive care unit of eight hospitals in Curitiba, Brazil, between March and September 2020 due to acute respiratory failure secondary to suspected COVID-19. The COVID-19 diagnosis was confirmed or refuted by RT-PCR for the detection of SARS-CoV-2. The ability of PARI to predict acute kidney injury at 72 hours, persistent acute kidney injury, renal replacement therapy, and death within 7 days was analyzed by ROC curves in comparison to delta creatinine, SOFA, and APACHE II.
Of the 1,001 patients in the cohort, 538 were included in the analysis. The mean age was 62 ± 17 years, 54.8% were men, and the median APACHE II score was 12. At admission, the median SOFA score was 3, and 83.3% had no renal dysfunction. After admission to the intensive care unit, 17.1% had acute kidney injury within 72 hours, and through 7 days, 19.5% had persistent acute kidney injury, 5% underwent renal replacement therapy, and 17.1% died. The PARI had an area under the ROC curve of 0.75 (0.696 - 0.807) for the prediction of acute kidney injury at 72 hours, 0.71 (0.613 - 0.807) for renal replacement therapy, and 0.64 (0.565 - 0.710) for death.
The PARI has acceptable accuracy in predicting acute kidney injury within 72 hours and renal replacement therapy within 7 days of admission to the intensive care unit, but it is not significantly better than the other scores.
Abstract
Crit Care Sci. 2023;35(2):177-186
DOI 10.5935/2965-2774.20230348-pt
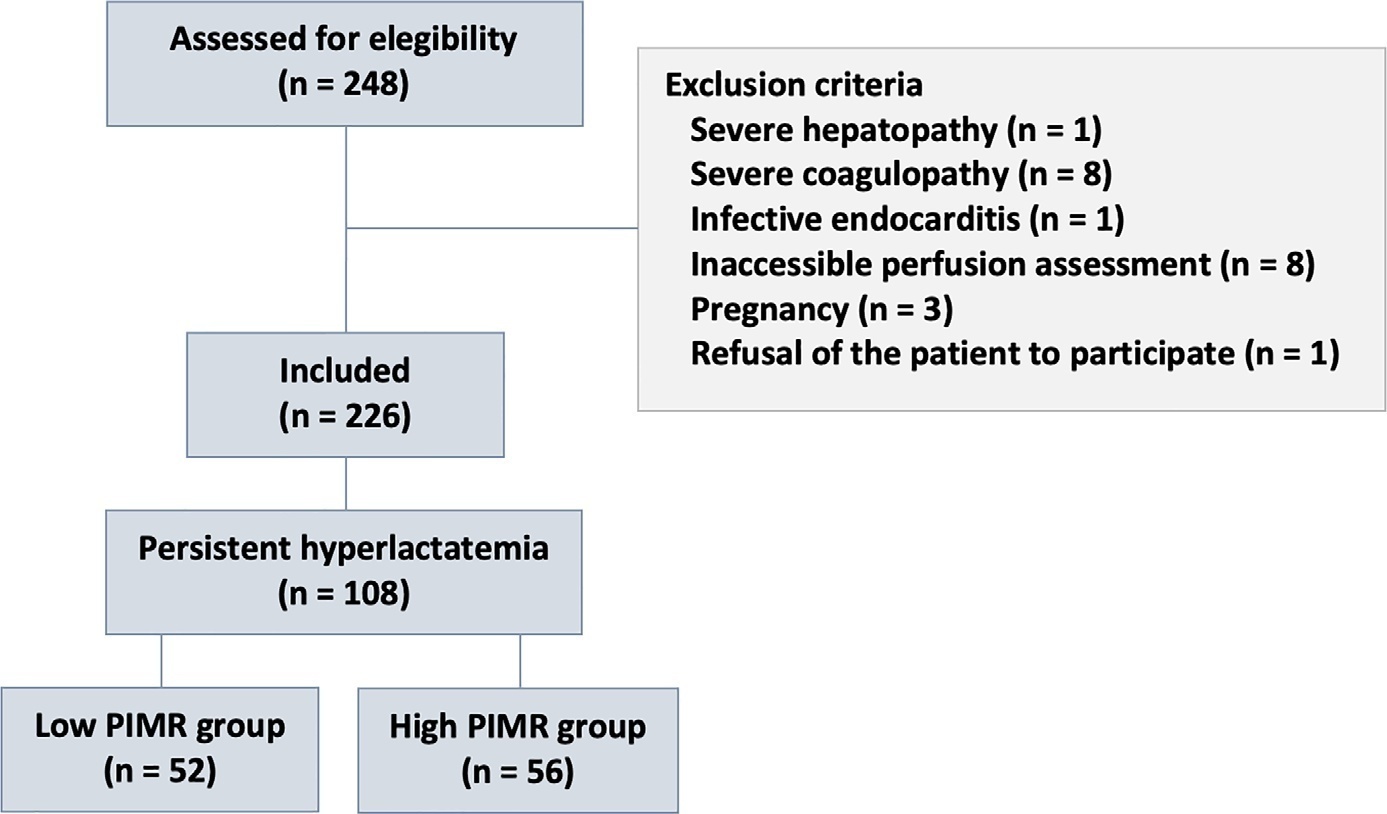
To measure the prognostic value of peripheral ischemic microvascular reserve in the context of persistent sepsis-induced hyperlactatemia and measure its influence on the temporal dynamics of lactate and the strength of association between these variables.
This post hoc analysis of the peripheral perfusion index/postocclusive reactive hyperemia trial, an observational cohort study that enrolled patients with sepsis who persisted with lactate levels ≥ 2mmol/L after fluid resuscitation (with or without shock). Peripheral ischemic microvascular reserve was evaluated using the association of the peripheral perfusion index and postocclusive reactive hyperemia techniques. The cutoff point of ∆ peripheral perfusion index peak values (%) defined the groups with low (≤ 62%) and high peripheral ischemic microvascular reserve (> 62%).
A total of 108 consecutive patients with persistent sepsis-induced hyperlactatemia were studied. The high peripheral ischemic microvascular reserve group showed higher 28-day mortality than the low peripheral ischemic microvascular reserve group (p < 0.01). The temporal dynamics of lactate within the first 48 hours showed a rapid decrease in lactate levels in the low peripheral ischemic microvascular reserve group (p < 0.01). However, this result was not reproduced in the linear mixed effects model. A weak correlation between peripheral ischemic microvascular reserve (%) and lactate level (mmol/L) was observed within the first 24 hours (r = 0.23; p < 0.05).
The prognostic value of high peripheral ischemic microvascular reserve was confirmed in the context of persistent sepsis-induced hyperlactatemia. Although there was a weak positive correlation between peripheral ischemic microvascular reserve value and lactate level within the first 24 hours of sepsis diagnosis, the low peripheral ischemic microvascular reserve group appeared to have a faster decrease in lactate over the 48 hours of follow-up.
Abstract
Crit Care Sci. 2023;35(2):196-202
DOI 10.5935/2965-2774.20230036-pt
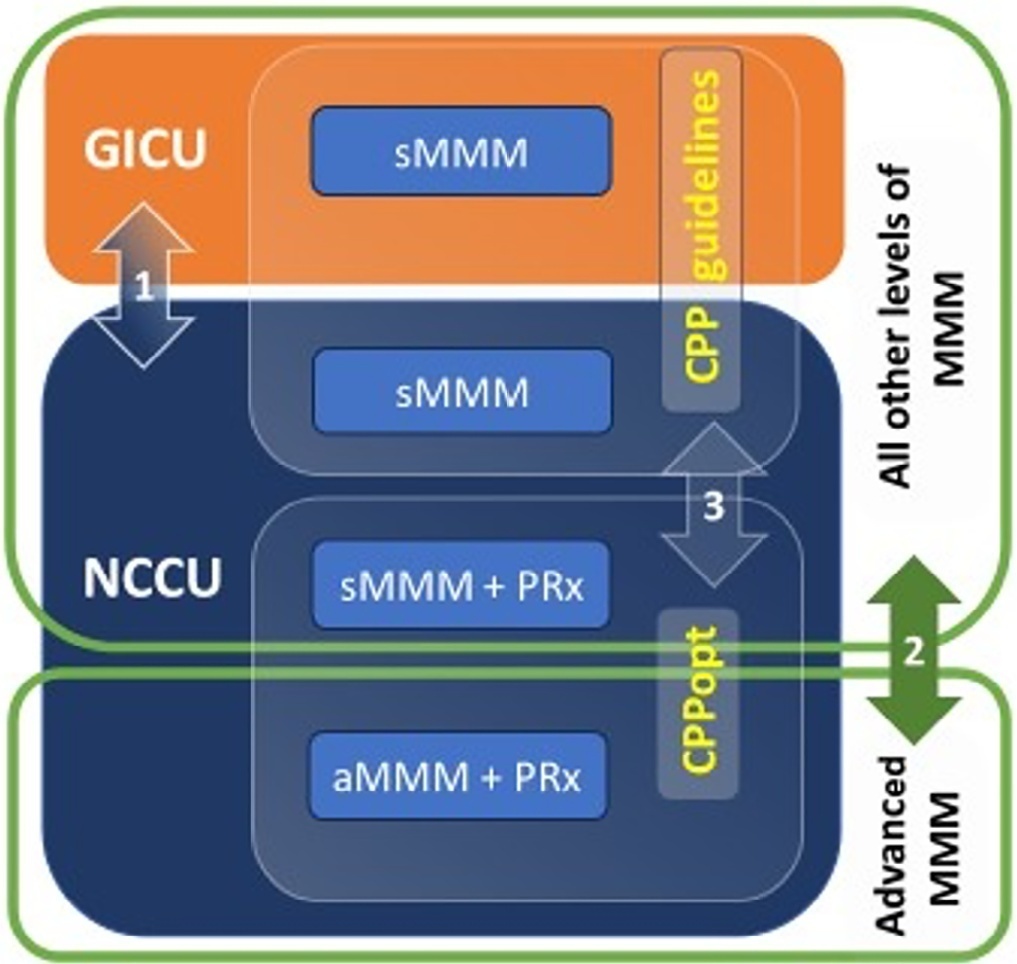
To evaluate the association between different intensive care units and levels of brain monitoring with outcomes in acute brain injury.
Patients with traumatic brain injury and subarachnoid hemorrhage admitted to intensive care units were included. Neurocritical care unit management was compared to general intensive care unit management. Patients managed with multimodal brain monitoring and optimal cerebral perfusion pressure were compared with general management patients. A good outcome was defined as a Glasgow outcome scale score of 4 or 5.
Among 389 patients, 237 were admitted to the neurocritical care unit, and 152 were admitted to the general intensive care unit. Neurocritical care unit management patients had a lower risk of poor outcome (OR = 0.228). A subgroup of 69 patients with multimodal brain monitoring (G1) was compared with the remaining patients (G2). In the G1 and G2 groups, 59% versus 23% of patients, respectively, had a good outcome at intensive care unit discharge; 64% versus 31% had a good outcome at 28 days; 76% versus 50% had a good outcome at 3 months (p < 0.001); and 77% versus 58% had a good outcome at 6 months (p = 0.005). When outcomes were adjusted by SAPS II severity score, using good outcome as the dependent variable, the results were as follows: for G1 compared to G2, the OR was 4.607 at intensive care unit discharge (p < 0.001), 4.22 at 28 days (p = 0.001), 3.250 at 3 months (p = 0.001) and 2.529 at 6 months (p = 0.006). Patients with optimal cerebral perfusion pressure management (n = 127) had a better outcome at all points of evaluation. Mortality for those patients was significantly lower at 28 days (p = 0.001), 3 months (p < 0.001) and 6 months (p = 0.001).
Multimodal brain monitoring with autoregulation and neurocritical care unit management were associated with better outcomes and should be considered after severe acute brain injury.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2022;34(4):492-498
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20220169-en
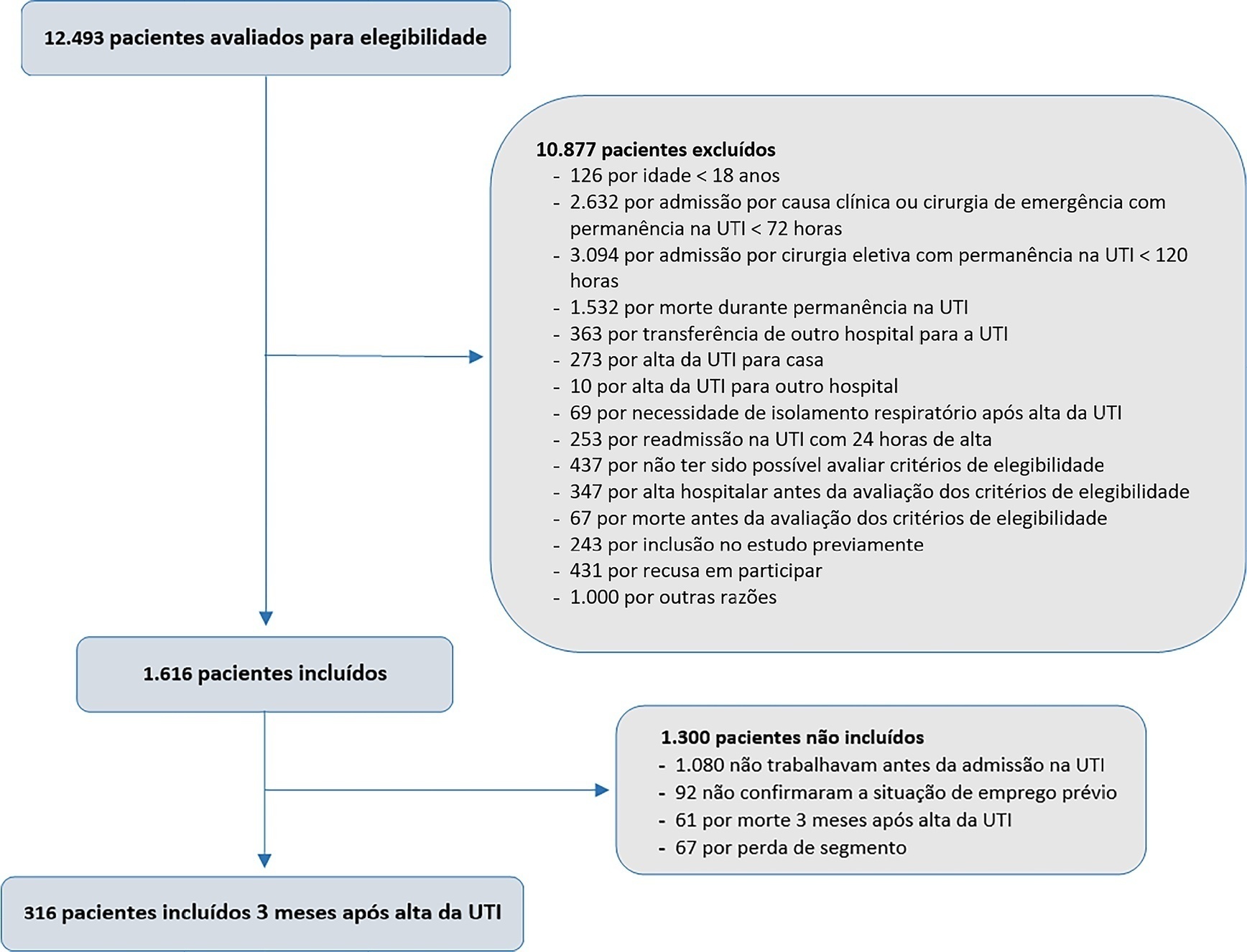
To describe the rate and factors related to nonreturn to work in the third month after discharge from the intensive care unit and the impact of unemployment, loss of income and health care expenses for survivors.
This was a prospective multicenter cohort study that included survivors of severe acute illness who were hospitalized between 2015 and 2018, previously employed, and who stayed more than 72 hours in the intensive care unit. Outcomes were assessed by telephone interview in the third month after discharge.
Of the 316 patients included in the study who had previously worked, 193 (61.1%) did not return to work within 3 months after discharge from the intensive care unit. The following factors were associated with nonreturn to work: low educational level (prevalence ratio 1.39; 95%CI 1.10 - 1.74; p = 0.006), previous employment relationship (prevalence ratio 1.32; 95%CI 1 10 - 1.58; p = 0.003), need for mechanical ventilation (prevalence ratio 1.20; 95%CI 1.01 - 1.42; p = 0.04) and physical dependence in the third month after discharge (prevalence ratio 1.27; 95%CI 1.08 - 1.48; p = 0.003). Survivors who were unable to return to work more often had reduced family income (49.7% versus 33.3%; p = 0.008) and increased health expenditures (66.9% versus 48.3%; p = 0.002). compared to those who returned to work in the third month after discharge from the intensive care unit.
Intensive care unit survivors often do not return to work until the third month after discharge from the intensive care unit. Low educational level, formal job, need for ventilatory support and physical dependence in the third month after discharge were related to nonreturn to work. Failure to return to work was also associated with reduced family income and increased health care costs after discharge.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2022;34(2):220-226
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20220019-en
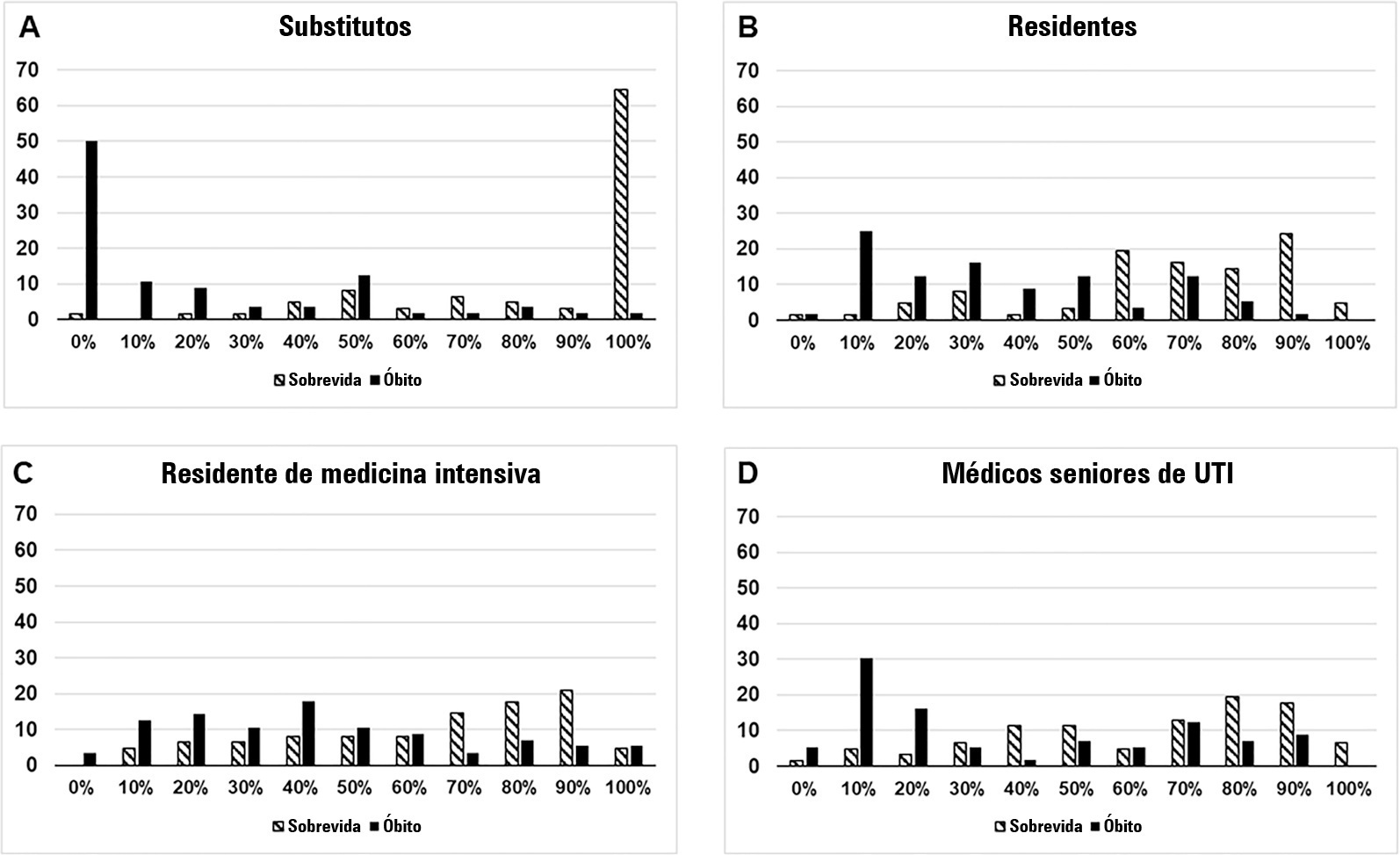
To compare the predictive performance of residents, senior intensive care unit physicians and surrogates early during intensive care unit stays and to evaluate whether different presentations of prognostic data (probability of survival versus probability of death) influenced their performance.
We questioned surrogates and physicians in charge of critically ill patients during the first 48 hours of intensive care unit admission on the patient’s probability of hospital outcome. The question framing (i.e., probability of survival versus probability of death during hospitalization) was randomized. To evaluate the predictive performance, we compared the areas under the ROC curves (AUCs) for hospital outcome between surrogates and physicians’ categories. We also stratified the results according to randomized question framing.
We interviewed surrogates and physicians on the hospital outcomes of 118 patients. The predictive performance of surrogate decisionmakers was significantly lower than that of physicians (AUC of 0.63 for surrogates, 0.82 for residents, 0.80 for intensive care unit fellows and 0.81 for intensive care unit senior physicians). There was no increase in predictive performance related to physicians’ experience (i.e., senior physicians did not predict outcomes better than junior physicians). Surrogate decisionmakers worsened their prediction performance when they were asked about probability of death instead of probability of survival, but there was no difference for physicians.
Different predictive performance was observed when comparing surrogate decision-makers and physicians, with no effect of experience on health care professionals’ prediction. Question framing affected the predictive performance of surrogates but not of physicians.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2022;34(2):262-271
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20220024-en
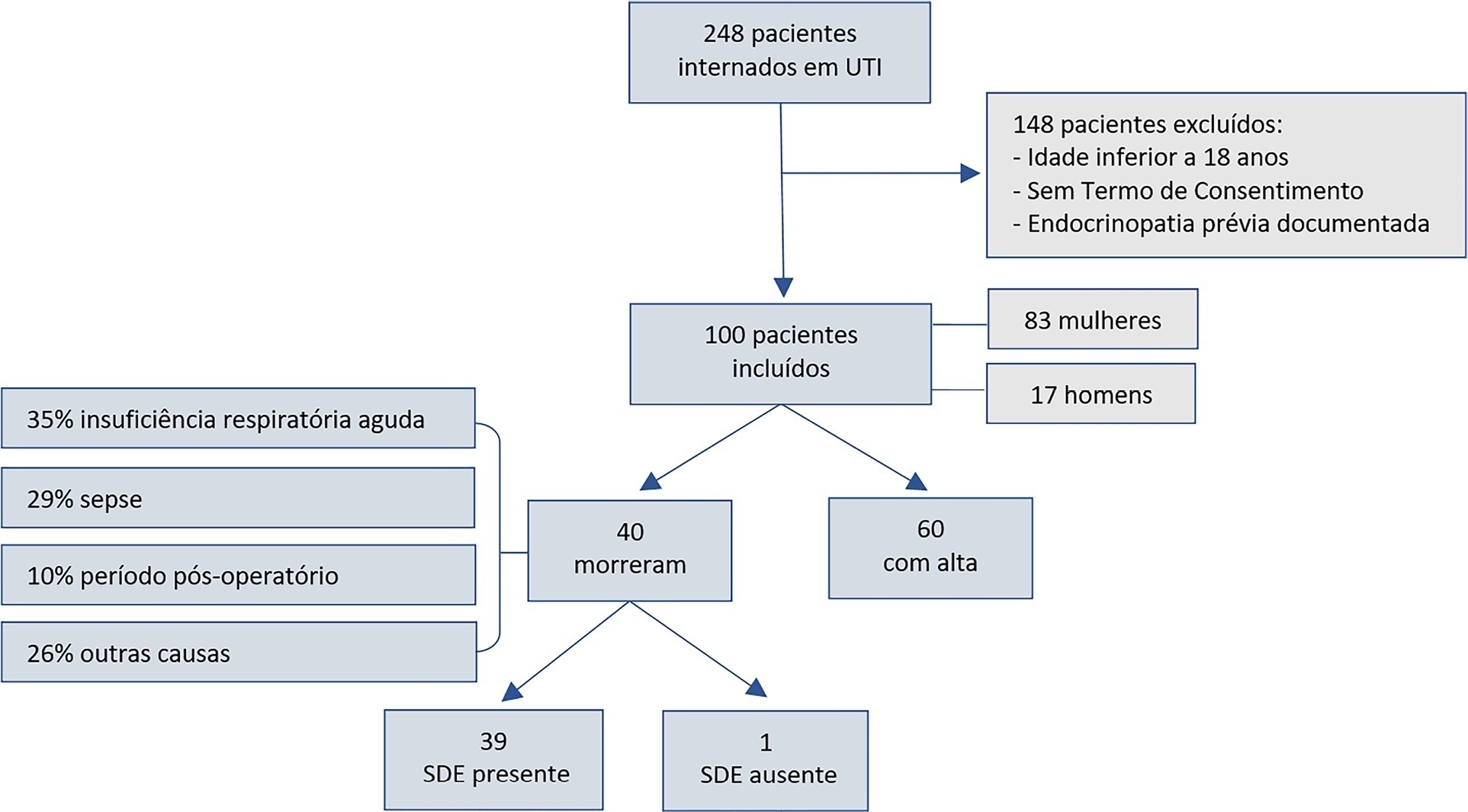
To assess euthyroid sick syndrome as a prognostic factor in patients in the intensive care unit; to detect factors that may affect mortality; and to develop an equation to calculate death probability.
This was a longitudinal, observational, nonconcurrent cohort study developed in the intensive care unit of Fundação Santa Casa de Misericórdia do Pará. One hundred adults with no prior documented endocrinopathy were submitted to a 20mL blood sample collection for the measurement of thyroid stimulating hormone, free tetraiodothyronine, free triiodothyronine and reverse triiodothyronine.
Most patients were female, aged 20 to 29 years. Most patients who died were older (median age of 48 years), and euthyroid sick syndrome was present in 97.5% of them. Euthyroid sick syndrome was related to death, comorbidities, age and length of stay in the intensive care unit (median of 7.5 days).
The main limitation of this study is the fact that it was conducted in a reference hospital for maternal and child care; therefore, there was a greater number of female patients and, consequently, a sampling bias existed. However, opportune measurement of free and reverse triiodothyronine levels in critical patients and application of the proposed equation are suggested.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2022;34(1):154-162
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20220010-en
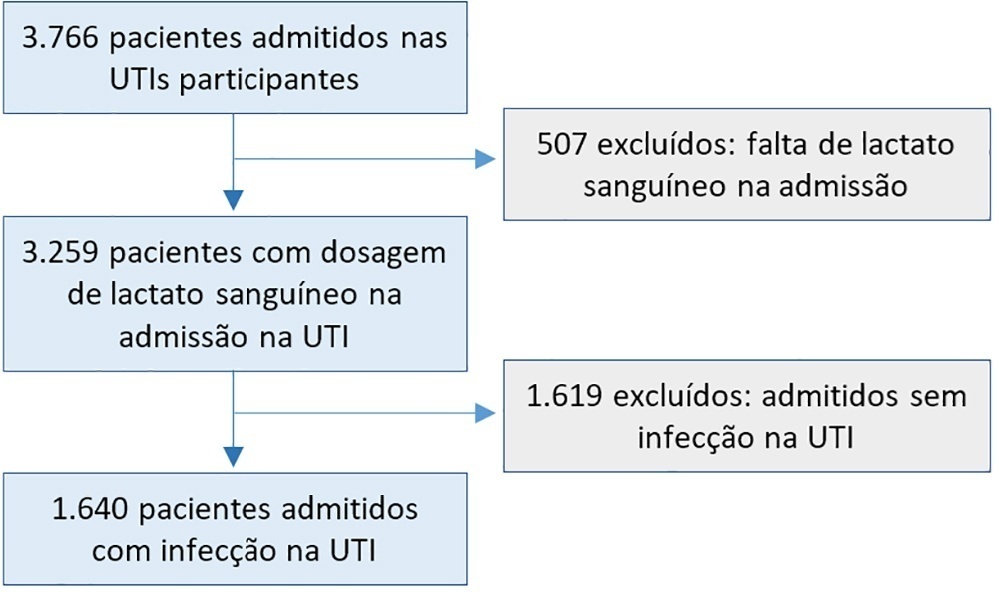
To evaluate the influence of patient characteristics on hyperlactatemia in an infected population admitted to intensive care units and the influence of hyperlactatemia severity on hospital mortality.
A post hoc analysis of hyperlactatemia in the INFAUCI study, a national prospective, observational, multicenter study, was conducted in 14 Portuguese intensive care units. Infected patients admitted to intensive care units with a lactate measurement in the first 12 hours of admission were selected. Sepsis was identified according to the Sepsis-2 definition accepted at the time of data collection. The severity of hyperlactatemia was classified as mild (2 - 3.9mmol/L), moderate (4.0 - 9.9mmol/L) or severe (> 10mmol/L).
In a total of 1,640 patients infected on admission, hyperlactatemia occurred in 934 patients (57%), classified as mild, moderate and severe in 57.0%, 34.4% and 8.7% of patients, respectively. The presence of hyperlactatemia and a higher degree of hyperlactatemia were both associated with a higher Simplified Acute Physiology Score II, a higher Charlson Comorbidity Index and the presence of septic shock. The lactate Receiver Operating Characteristic curve for hospital mortality had an area under the curve of 0.64 (95%CI 0.61 - 0.72), which increased to 0.71 (95%CI 0.68 - 0.74) when combined with Sequential Organ Failure Assessment score. In-hospital mortality with other covariates adjusted by Simplified Acute Physiology Score II was associated with moderate and severe hyperlactatemia, with odds ratio of 1.95 (95%CI 1.4 - 2.7; p < 0.001) and 4.54 (95%CI 2.4 - 8.5; p < 0.001), respectively.
Blood lactate levels correlate independently with in-hospital mortality for moderate and severe degrees of hyperlactatemia.
Search
Search in:
Case reports (56) Child (53) Coronavirus infections (33) COVID-19 (45) Critical care (115) Critical illness (54) ICU (25) Infant, newborn (27) Intensive care (72) Intensive care units (254) Intensive care units, pediatric (31) mechanical ventilation (38) Mortality (75) Physical therapy modalities (28) Prognosis (61) Respiration, artificial (117) Respiratory insufficiency (26) risk factors (34) SARS-CoV-2 (28) Sepsis (98)