You searched for:"Rafaella Stradiotto Bernardelli"
We found (2) results for your search.-
Original Article
Typical phenotypes of patients with acute respiratory failure with and without COVID-19 and their relationship with outcomes: a cohort study
Crit Care Sci. 2023;35(4):355-366
Abstract
Original ArticleTypical phenotypes of patients with acute respiratory failure with and without COVID-19 and their relationship with outcomes: a cohort study
Crit Care Sci. 2023;35(4):355-366
DOI 10.5935/2965-2774.20230015-pt
Views15See moreABSTRACT
Objective:
To compare, within a cohort of patients with acute respiratory failure, the phenotypes of patients with and without COVID-19 in the context of the pandemic and evaluate whether COVID-19 is an independent predictor of intensive care unit mortality.
Methods:
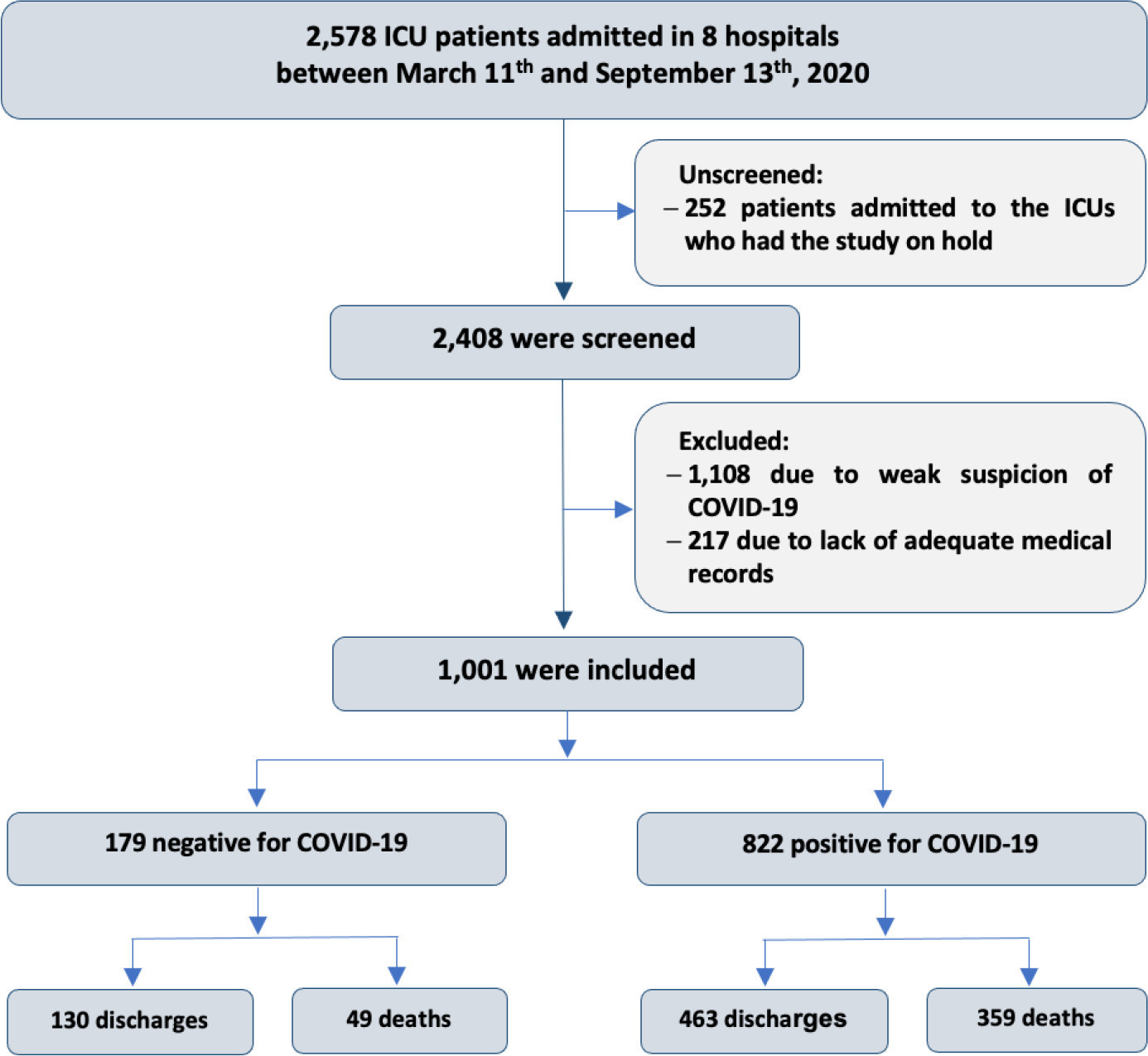
This historical cohort study evaluated 1001 acute respiratory failure patients with suspected COVID-19 admitted to the intensive care unit of 8 hospitals. Patients were classified as COVID-19 cases and non-COVID-19 cases according to real-time polymerase chain reaction results. Data on clinical and demographic characteristics were collected on intensive care unit admission, as well as daily clinical and laboratory data and intensive care unit outcomes.
Results:
Although the groups did not differ in terms of APACHE II or SOFA scores at admission, the COVID-19 group had more initial symptoms of fever, myalgia and diarrhea, had a longer duration of symptoms, and had a higher prevalence of obesity. They also had a lower PaO2/FiO2 ratio, lower platelet levels than non-COVID-19 patients, and more metabolic changes, such as higher levels of blood glucose, C-reactive protein, and lactic dehydrogenase. Patients with non-COVID-19 acute respiratory failure had a higher prevalence of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease/asthma and cardiopathy. Patients with COVID-19 stayed in the hospital longer and had more complications, such as acute kidney failure, severe acute respiratory distress syndrome and severe infection. The all-cause mortality rate was also higher in this group (43.7% in the COVID-19 group versus 27.4% in the non-COVID-19 group). The diagnosis of COVID-19 was a predictor of intensive care unit mortality (odds ratio, 2.77; 95%CI, 1.89 – 4.07; p < 0.001), regardless of age or Charlson Comorbidity Index score.
Conclusion:
In a prospective cohort of patients admitted with acute respiratory failure, patients with COVID-19 had a clearly different phenotype and a higher mortality than non-COVID-19 patients. This may help to outline more accurate screening and appropriate and timely treatment for these patients.
-
Original Article
Accuracy of the persistent AKI risk index in predicting acute kidney injury in patients admitted to the intensive care unit for acute respiratory failure
Crit Care Sci. 2023;35(3):302-310
Abstract
Original ArticleAccuracy of the persistent AKI risk index in predicting acute kidney injury in patients admitted to the intensive care unit for acute respiratory failure
Crit Care Sci. 2023;35(3):302-310
DOI 10.5935/2965-2774.20230141-pt
Views5ABSTRACT
Objective:
To evaluate the accuracy of the persistent AKI risk index (PARI) in predicting acute kidney injury within 72 hours after admission to the intensive care unit, persistent acute kidney injury, renal replacement therapy, and death within 7 days in patients hospitalized due to acute respiratory failure.
Methods:
This study was done in a cohort of diagnoses of consecutive adult patients admitted to the intensive care unit of eight hospitals in Curitiba, Brazil, between March and September 2020 due to acute respiratory failure secondary to suspected COVID-19. The COVID-19 diagnosis was confirmed or refuted by RT-PCR for the detection of SARS-CoV-2. The ability of PARI to predict acute kidney injury at 72 hours, persistent acute kidney injury, renal replacement therapy, and death within 7 days was analyzed by ROC curves in comparison to delta creatinine, SOFA, and APACHE II.
Results:
Of the 1,001 patients in the cohort, 538 were included in the analysis. The mean age was 62 ± 17 years, 54.8% were men, and the median APACHE II score was 12. At admission, the median SOFA score was 3, and 83.3% had no renal dysfunction. After admission to the intensive care unit, 17.1% had acute kidney injury within 72 hours, and through 7 days, 19.5% had persistent acute kidney injury, 5% underwent renal replacement therapy, and 17.1% died. The PARI had an area under the ROC curve of 0.75 (0.696 – 0.807) for the prediction of acute kidney injury at 72 hours, 0.71 (0.613 – 0.807) for renal replacement therapy, and 0.64 (0.565 – 0.710) for death.
Conclusion:
The PARI has acceptable accuracy in predicting acute kidney injury within 72 hours and renal replacement therapy within 7 days of admission to the intensive care unit, but it is not significantly better than the other scores.
Keywords:Acute kidney injuryCoronavirus infectionsCOVID-19DeathIntensive care unitsMortalityPrognosisRenal replacement therapyRespiratory insufficiencySARS-CoV-2See more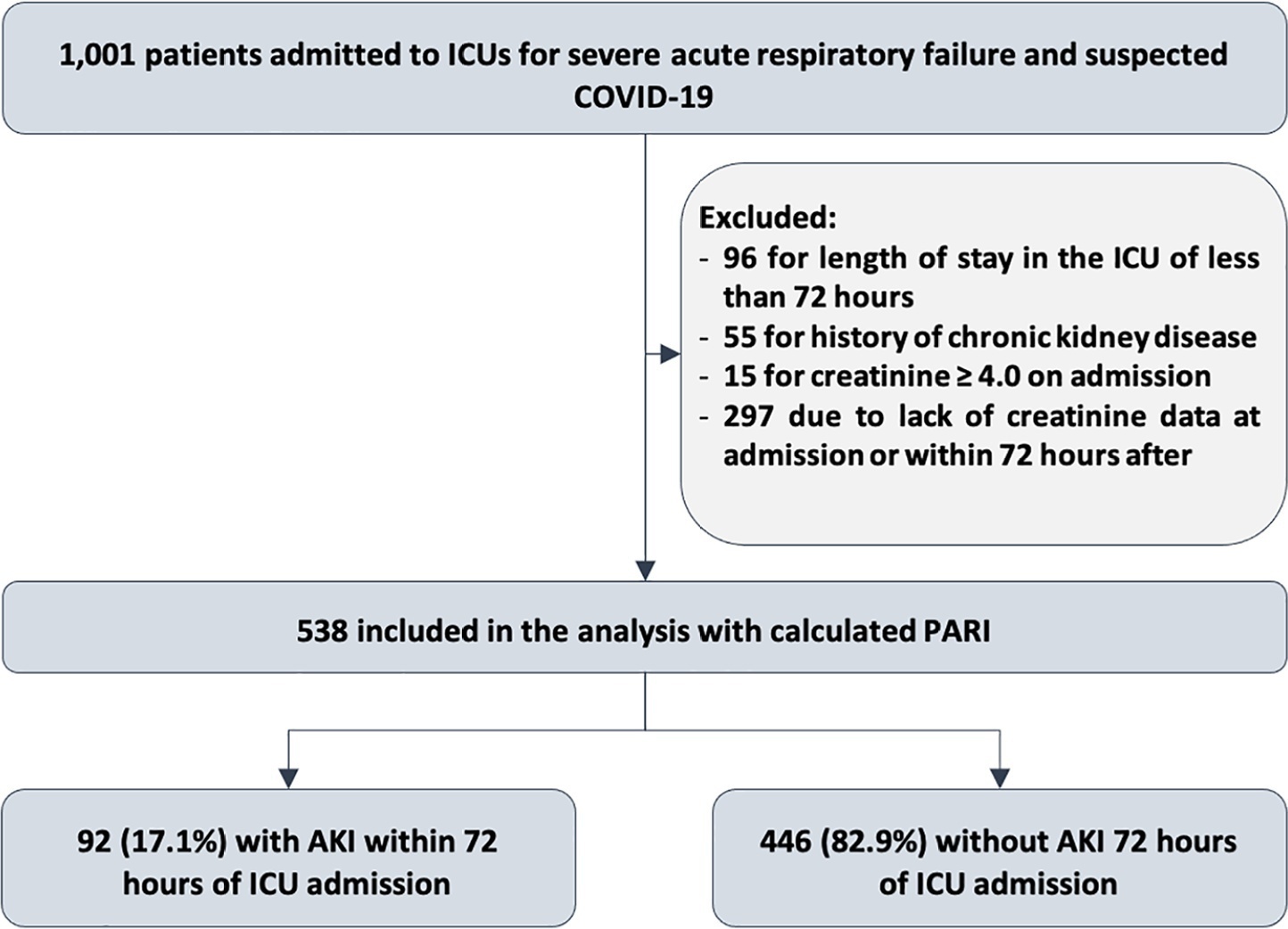
Search
Search in:
KEY WORDS
Case reports Child Coronavirus infections COVID-19 Critical care Critical illness Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation Infant, newborn Intensive care Intensive care units Intensive care units, pediatric mechanical ventilation Mortality Physical therapy modalities Prognosis Respiration, artificial Respiratory insufficiency risk factors SARS-CoV-2 Sepsis




