Abstract
Crit Care Sci. 2023;35(3):302-310
DOI 10.5935/2965-2774.20230141-pt
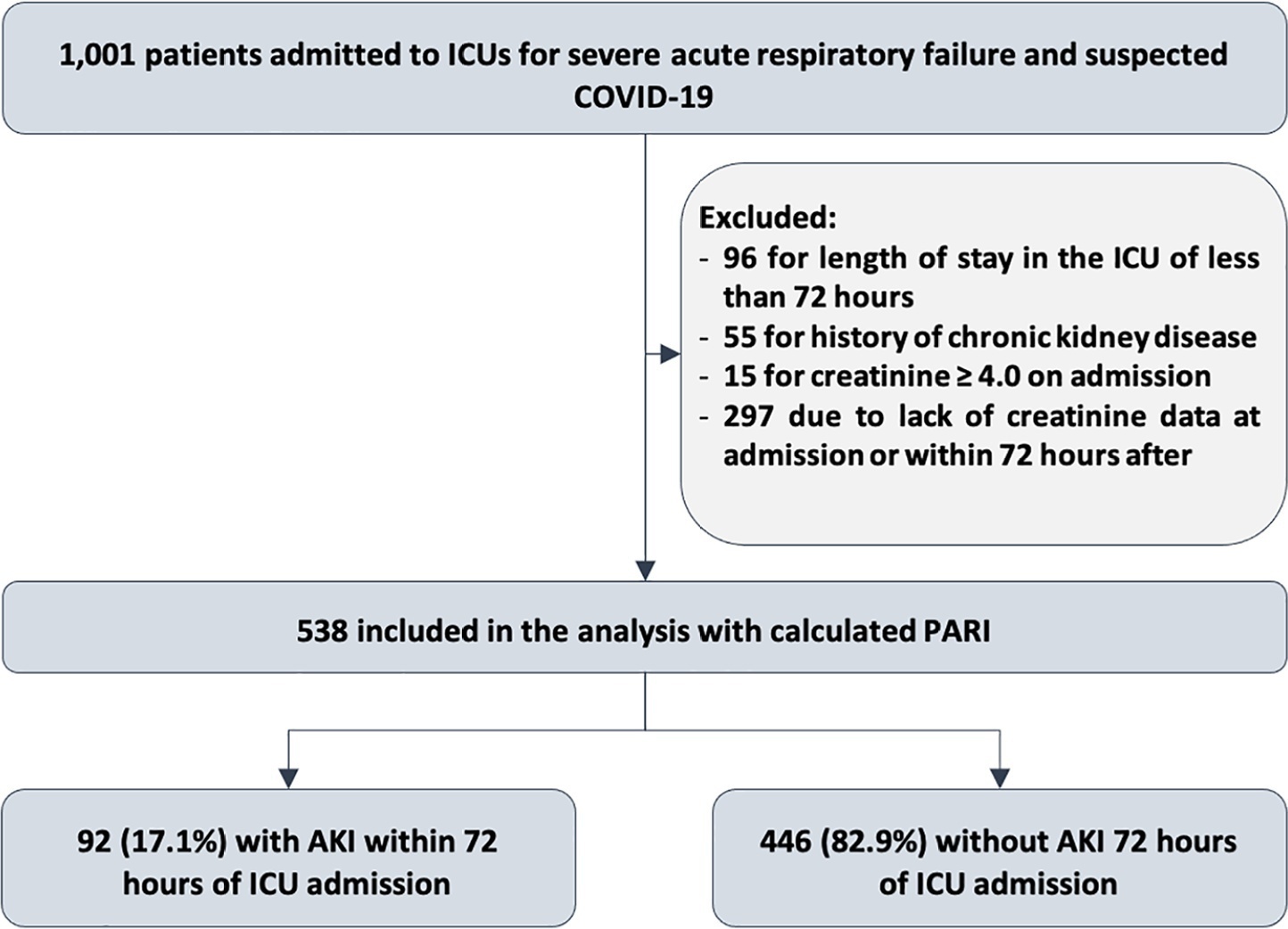
To evaluate the accuracy of the persistent AKI risk index (PARI) in predicting acute kidney injury within 72 hours after admission to the intensive care unit, persistent acute kidney injury, renal replacement therapy, and death within 7 days in patients hospitalized due to acute respiratory failure.
This study was done in a cohort of diagnoses of consecutive adult patients admitted to the intensive care unit of eight hospitals in Curitiba, Brazil, between March and September 2020 due to acute respiratory failure secondary to suspected COVID-19. The COVID-19 diagnosis was confirmed or refuted by RT-PCR for the detection of SARS-CoV-2. The ability of PARI to predict acute kidney injury at 72 hours, persistent acute kidney injury, renal replacement therapy, and death within 7 days was analyzed by ROC curves in comparison to delta creatinine, SOFA, and APACHE II.
Of the 1,001 patients in the cohort, 538 were included in the analysis. The mean age was 62 ± 17 years, 54.8% were men, and the median APACHE II score was 12. At admission, the median SOFA score was 3, and 83.3% had no renal dysfunction. After admission to the intensive care unit, 17.1% had acute kidney injury within 72 hours, and through 7 days, 19.5% had persistent acute kidney injury, 5% underwent renal replacement therapy, and 17.1% died. The PARI had an area under the ROC curve of 0.75 (0.696 - 0.807) for the prediction of acute kidney injury at 72 hours, 0.71 (0.613 - 0.807) for renal replacement therapy, and 0.64 (0.565 - 0.710) for death.
The PARI has acceptable accuracy in predicting acute kidney injury within 72 hours and renal replacement therapy within 7 days of admission to the intensive care unit, but it is not significantly better than the other scores.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2020;32(1):143-148
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20200020
In recent years and due, in part, to technological advances, the use of extracorporeal carbon dioxide removal systems paired with the use of extracorporeal membrane oxygenation has resurfaced. However, studies are lacking that establish its indications and evidence to support its use. These systems efficiently eliminate carbon dioxide in patients with hypercapnic respiratory failure using small-bore cannula, usually double-lumen cannula with a small membrane lung surface area. Currently, we have several systems with different types of membranes and sizes. Pump-driven veno-venous systems generate fewer complications than do arteriovenous systems. Both require systemic anticoagulation. The “lung-kidney” support system, by combining a removal system with hemofiltration, simultaneously eliminates carbon dioxide and performs continuous extrarenal replacement. We describe our initial experience with a combined system for extracorporeal carbon dioxide removal-continuous extrarenal replacement in a lung transplant patients with hypercapnic respiratory failure, barotrauma and associated acute renal failure. The most important technical aspects, the effectiveness of the system for the elimination of carbon dioxide and a review of the literature are described.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2019;31(2):258-261
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20190040
Rituximab safety and efficacy in patients with renal impairment have not been established, nor have the effects of hemodialysis on serum rituximab level. There are only a few published case reports assessing serum rituximab level pre- and postdialysis. No data have been published regarding the usage of rituximab in patients with continuous renal replacement therapy. The authors present a case of a 59-year-old female patient who presented with paraneoplastic tetraparesis. She was admitted to the intensive care unit due to alveolar hemorrhage with respiratory failure and acute kidney injury requiring continuous renal replacement therapy. After a diagnostic workup, the diagnosis of lymphoplasmacytic lymphoma was established. Therapy with rituximab and cyclophosphamide was started. Rituximab levels were determined in serum and dialysate. No rituximab was found in the dialysate. The patient died after 2 months in the intensive care unit from nosocomial pneumonia due to multidrug-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2018;30(3):264-285
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20180058
To investigate the existing capacity for renal replacement therapy and site-specific practices for managing acute kidney injury at centers participating in the BaSICS trial.
A questionnaire was provided to the chairs of 61 intensive care units enrolled in a randomized clinical trial in Brazil. A total of 124 physicians completed the questionnaire.
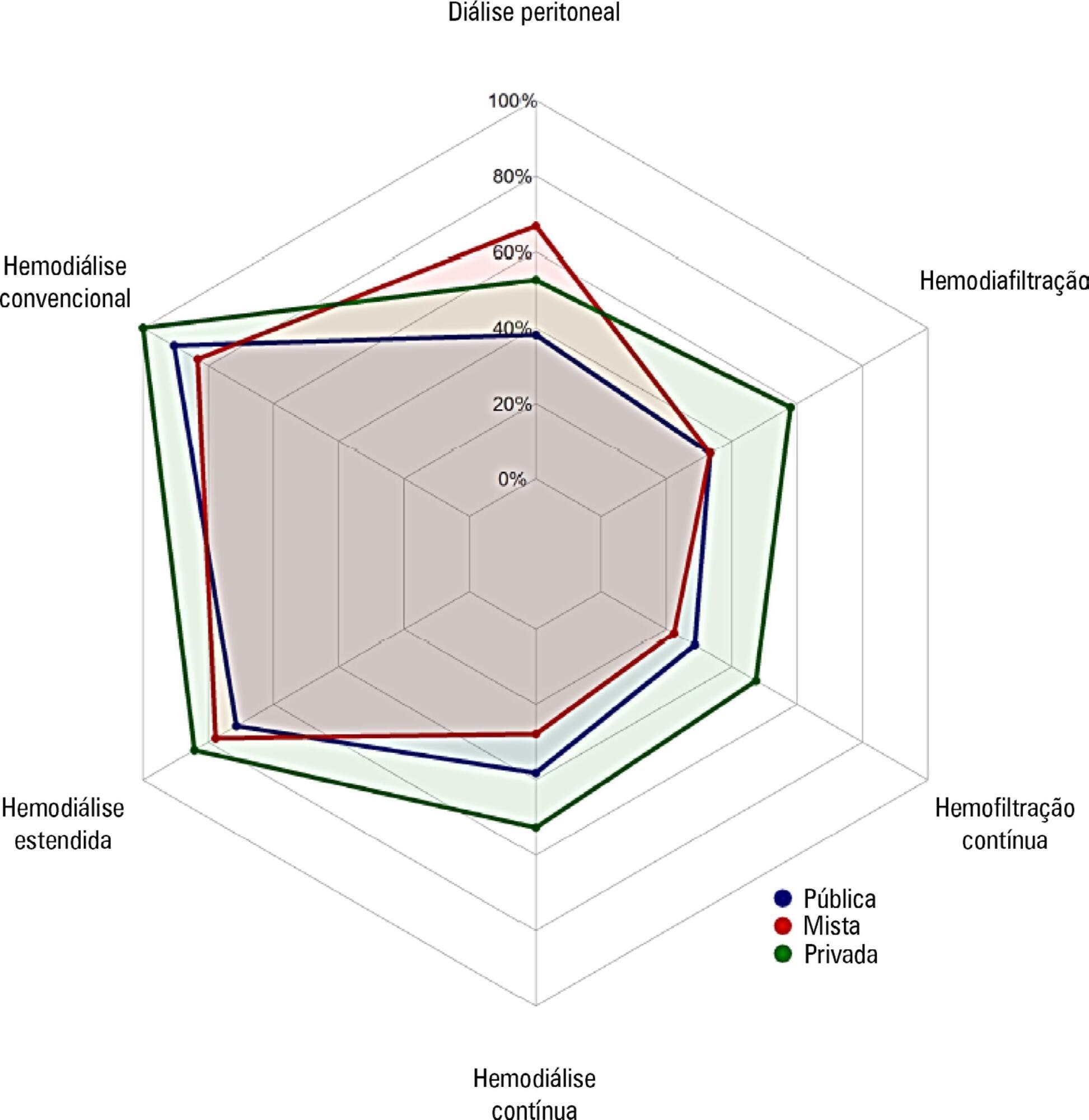
Approximately 15% of the patients admitted to the analyzed intensive care units received renal replacement therapy at the time of data collection. At least one renal replacement method was available in all of the analyzed units. Continuous methods were available more frequently at the private units than at the public units. The time from indication to onset of treatment was longer at the public units than at private units. The main obstacles to treatment initiation at public intensive care units were related to the availability of equipment and personnel, while the main bottleneck at private units was the nephrologist assessment. A considerable proportion of the participants stated that they would change their approach to renal replacement therapy if there were no limitations on the availability of methods in their units.
There was wide variation in the availability of resources for renal replacement therapy and in the management of acute kidney injury in Brazilian intensive care units. This information should be taken into account when planning clinical trials focused on this topic in Brazil.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2017;29(3):373-381
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20170051
Novel biomarkers can be suitable for early acute kidney injury diagnosis and the prediction of the need for dialysis. It remains unclear whether such biomarkers may also play a role in the prediction of recovery after established acute kidney injury or in aiding the decision of when to stop renal support therapy. PubMed, Web of Science and Google Scholar were searched for studies that reported on the epidemiology of renal recovery after acute kidney injury, the risk factors of recovery versus non-recovery after acute kidney injury, and potential biomarkers of acute kidney injury recovery. The reference lists of these articles and relevant review articles were also reviewed. Final references were selected for inclusion in the review based on their relevance. New biomarkers exhibited a potential role in the early diagnosis of acute kidney injury recovery. Urine HGF, IGFBP-7, TIMP-2 and NGAL may improve our ability to predict the odds and timing of recovery and eventually renal support withdrawal. Acute kidney injury recovery requires more study, and its definition needs to be standardized to allow for better and more powerful research on biomarkers because some of them show potential for the prediction of acute kidney injury recovery.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2016;28(1):70-77
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20160015
Identify prognostic factors related to mortality and non-recovery of renal function.
A prospective single-center study was conducted at the intensive care medicine department of a university hospital between 2012 and 2015. Patients with acute kidney injury receiving continuous renal replacement therapy were included in the study. Clinical and analytical parameters were collected, and the reasons for initiation and discontinuation of renal replacement therapy were examined.
A total of 41 patients were included in the study, of whom 43.9% had sepsis. The median Simplified Acute Physiology Score II (SAPSII) was 56 and the mortality was 53.7%, with a predicted mortality of 59.8%. The etiology of acute kidney injury was often multifactorial (56.1%). Survivors had lower cumulative fluid balance (median = 3,600mL, interquartile range [IQR] = 1,175 - 8,025) than non-survivors (median = 12,000mL, IQR = 6,625 - 17,875; p = 0.004). Patients who recovered renal function (median = 51.0, IQR = 45.8 - 56.2) had lower SAPS II than those who do not recover renal function (median = 73, IQR = 54 - 85; p = 0.005) as well as lower fluid balance (median = 3,850, IQR = 1,425 - 8,025 versus median = 11,500, IQR = 6,625 - 16,275; p = 0.004).
SAPS II at admission and cumulative fluid balance during renal support therapy were risk factors for mortality and non-recovery of renal function among critically ill patients with acute kidney injury needing renal replacement therapy.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2016;28(2):120-131
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20160026
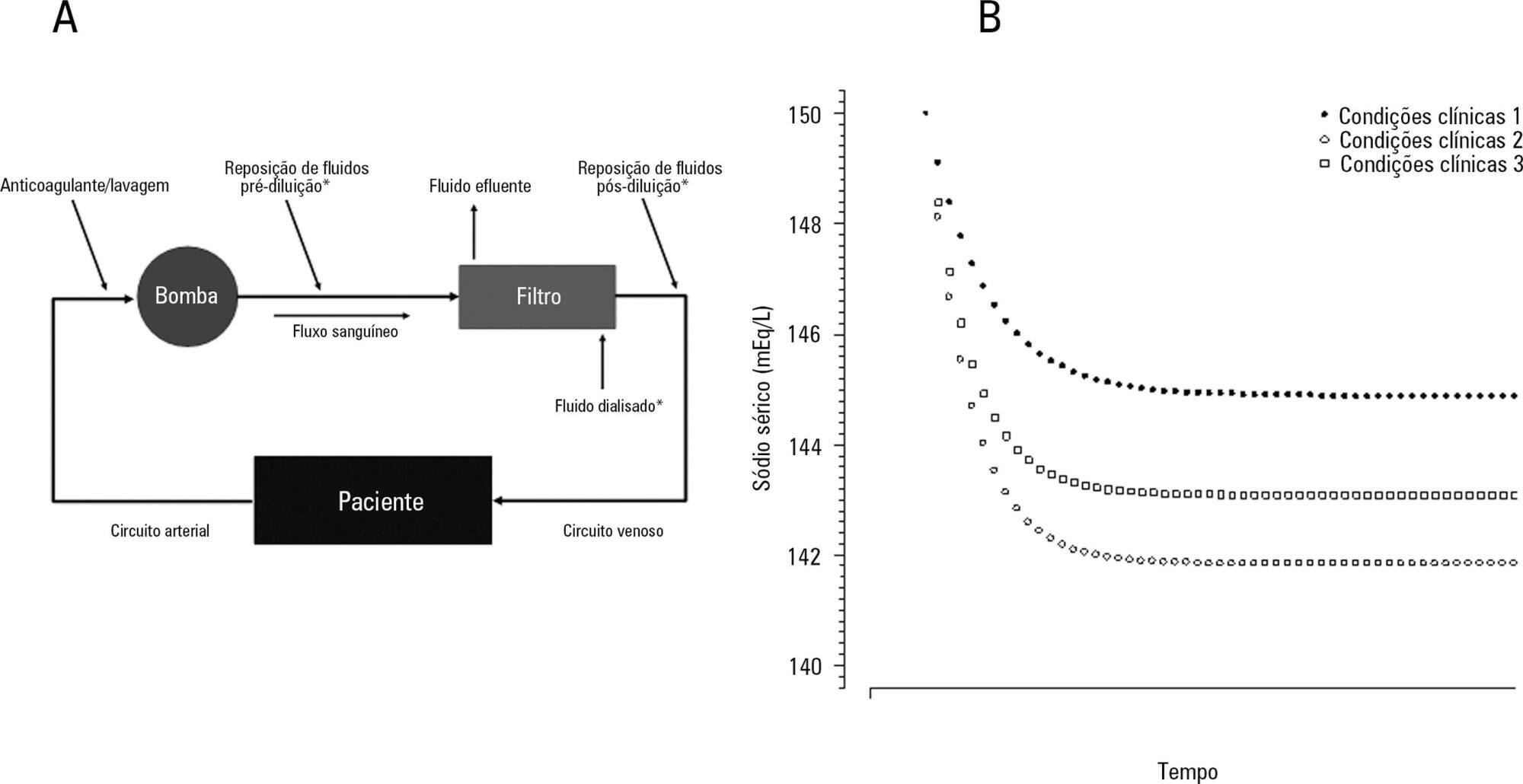
The aim of this study was to investigate the clinical and laboratorial factors associated with serum sodium variation during continuous renal replacement therapy and to assess whether the perfect admixture formula could predict 24-hour sodium variation.
Thirty-six continuous renal replacement therapy sessions of 33 patients, in which the affluent prescription was unchanged during the first 24 hours, were retrieved from a prospective collected database and then analyzed. A mixed linear model was performed to investigate the factors associated with large serum sodium variations (≥ 8mEq/L), and a Bland-Altman plot was generated to assess the agreement between the predicted and observed variations.
In continuous renal replacement therapy 24-hour sessions, SAPS 3 (p = 0.022) and baseline hypernatremia (p = 0.023) were statistically significant predictors of serum sodium variations ≥ 8mEq/L in univariate analysis, but only hypernatremia demonstrated an independent association (β = 0.429, p < 0.001). The perfect admixture formula for sodium prediction at 24 hours demonstrated poor agreement with the observed values.
Hypernatremia at the time of continuous renal replacement therapy initiation is an important factor associated with clinically significant serum sodium variation. The use of 4% citrate or acid citrate dextrose - formula A 2.2% as anticoagulants was not associated with higher serum sodium variations. A mathematical prediction for the serum sodium concentration after 24 hours was not feasible.
Search
Search in:
Case reports (56) Child (53) Coronavirus infections (34) COVID-19 (46) Critical care (115) Critical illness (54) Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (26) Infant, newborn (27) Intensive care (72) Intensive care units (256) Intensive care units, pediatric (31) mechanical ventilation (38) Mortality (76) Physical therapy modalities (28) Prognosis (61) Respiration, artificial (119) Respiratory insufficiency (26) risk factors (34) SARS-CoV-2 (28) Sepsis (98)