Abstract
Revista brasileira de terapia intensiva. 2013;25(3):251-257
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20130044
To assess the oxygenation behavior and ventilatory mechanics after hemodialysis in patients under ventilatory support.
The present study was performed in the general intensive care unit of a tertiary public hospital. Patients over 18 years of age under mechanical ventilation and in need of dialysis support were included. Each patient was submitted to 2 evaluations (pre- and post-dialysis) regarding the cardiovascular and ventilatory parameters, the ventilatory mechanics and a laboratory evaluation.
Eighty patients with acute or chronic renal failure were included. The analysis of the ventilatory mechanics revealed a reduction in the plateau pressure and an increased static compliance after dialysis that was independent of a reduction in blood volume. The patients with acute renal failure also exhibited a reduction in peak pressure (p=0.024) and an increase in the dynamic compliance (p=0.026), whereas the patients with chronic renal failure exhibited an increase in the resistive pressure (p=0.046) and in the resistance of the respiratory system (p=0.044). The group of patients with no loss of blood volume after dialysis exhibited an increase in the resistive pressure (p=0.010) and in the resistance of the respiratory system (p=0.020), whereas the group with a loss of blood volume >2,000mL exhibited a reduction in the peak pressure (p=0.027). No changes in the partial pressure of oxygen in arterial blood (PaO2) or in the PaO2/the fraction of inspired oxygen (PaO2/FiO2) ratio were observed.
Hemodialysis was able to alter the mechanics of the respiratory system and specifically reduced the plateau pressure and increased the static compliance independent of a reduction in blood volume.
Abstract
Revista Brasileira de Terapia Intensiva. 2009;21(2):124-128
DOI 10.1590/S0103-507X2009000200002
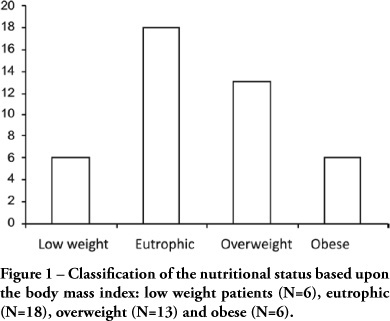
OBJECTIVE: Evaluate the nutritional status of patients with cardiac disease and concomitant renal dysfunction requiring renal replacement therapy. METHODS: Patients with cardiac disease and renal failure receiving renal replacement therapy, admitted to an intensive care unit, were submitted to nutritional evaluation, by use of anthropometric measurements and laboratory data. RESULTS: We studied 43 patients, mean age 64±15 years, 26 were men. The mean left ventricular ejection fraction was 0.36±0.16. Analysis of anthropometric measurements, based on body mass index disclosed that, 18 patients were normal, 6 were underweight and 19 were overweight or obese. Based on measurement of triceps skinfold thickness, 16 patients were considered normal and 27 had some degree of depletion. Measurements of midarm circumference and midarm muscular circumference showed 41 patients with some degree of depletion. Laboratory data revealed 28 patients with depletion based on albumin levels and 27 with depletion based on lymphocyte count. CONCLUSIONS: Malnutrition is common in critically ill patients with cardiac disease and renal failure receiving renal replacement therapy. Nutritional assessment based on body mass index did not prove to be a good index for diagnosis of nutritional disorders. The nutritional evaluation must be complemented in order to identify malnutrition and introduce early nutritional support.