Abstract
Crit Care Sci. 2023;35(3):320-327
DOI 10.5935/2965-2774.20230165-pt
To translate and cross-culturally adapt the Cornell Assessment of Pediatric Delirium anchor points from English to Brazilian Portuguese.
For the translation and cross-cultural adaptation of the anchor points, all steps recommended internationally were followed after authorization for use by the lead author. The stages were as follows: translation of the original version into Portuguese by two bilingual translators who were native speakers of the target language, synthesis of the versions, reverse translation by two translators who were native speakers of the source language, review and synthesis of the back-translation, review by a committee of experts and preparation of the final version.
The translation and cross-cultural adaptation of the anchor points was conducted in accordance with recommendations. The linguistic and semantic issues that arose were discussed by a committee of judges, with 91.8% agreement, as determined using a Likert scale, after changes by consensus. After reanalysis by the authors, there were no changes, resulting in the final version, which was easy to understand and administer.
The translation and cross-cultural adaptation of the anchor points of the Cornell Assessment of Pediatric Delirium scale into Portuguese spoken in Brazil were successful, maintaining the linguistic and semantic properties of the original instrument. The table of anchor points is easy to understand and will be helpful during the assessment of children younger than 24 months using the Cornell Assessment of Pediatric Delirium scale.
Abstract
Crit Care Sci. 2023;35(1):57-65
DOI 10.5935/2965-2774.20230350-pt
To assess Brazilian pediatric intensivists’ general knowledge of extracorporeal membrane oxygenation, including evidence for its use, the national funding model, indications, and complications.
This was a multicenter cross-sectional survey including 45 Brazilian pediatric intensive care units. A convenience sample of 654 intensivists was surveyed regarding their knowledge on managing patients on extracorporeal membrane oxygenation, its indications, complications, funding, and literature evidence.
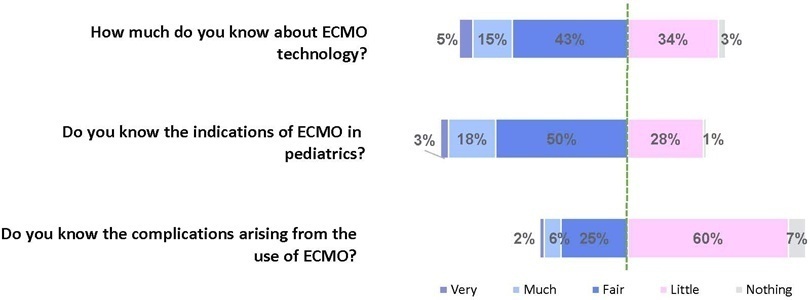
The survey addressed questions regarding the knowledge and experience of pediatric intensivists with extracorporeal membrane oxygenation, including two clinical cases and 6 optional questions about the management of patients on extracorporeal membrane oxygenation. Of the 45 invited centers, 42 (91%) participated in the study, and 412 of 654 (63%) pediatric intensivists responded to the survey. Most pediatric intensive care units were from the Southeast region of Brazil (59.5%), and private/for-profit hospitals represented 28.6% of the participating centers. The average age of respondents was 41.4 (standard deviation 9.1) years, and the majority (77%) were women. Only 12.4% of respondents had taken an extracorporeal membrane oxygenation course. Only 19% of surveyed hospitals have an extracorporeal membrane oxygenation program, and only 27% of intensivists reported having already managed patients on extracorporeal membrane oxygenation. Specific extracorporeal membrane oxygenation management questions were responded to by only 64 physicians (15.5%), who had a fair/good correct response rate (median 63.4%; range 32.8% to 91.9%).
Most Brazilian pediatric intensivists demonstrated limited knowledge regarding extracorporeal membrane oxygenation, including its indications and complications. Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation is not yet widely available in Brazil, with few intensivists prepared to manage patients on extracorporeal membrane oxygenation and even fewer intensivists recognizing when to refer patients to extracorporeal membrane oxygenation centers.
Abstract
Crit Care Sci. 2023;35(1):66-72
DOI 10.5935/2965-2774.20230312-pt
To evaluate whether a model of a daily fitness checklist for spontaneous breathing tests is able to identify predictive variables of extubation failure in pediatric patients admitted to a Brazilian intensive care unit.
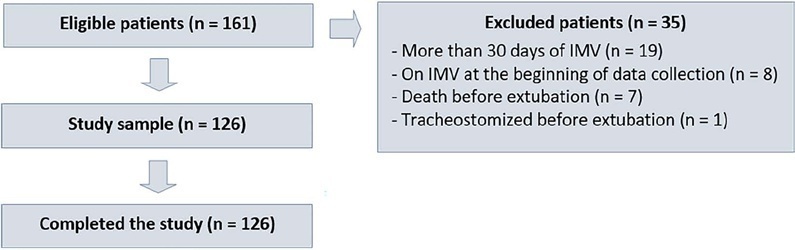
This was a single-center, cross-sectional study with prospective data collection. The checklist model comprised 20 items and was applied to assess the ability to perform spontaneous breathing tests.
The sample consisted of 126 pediatric patients (85 males (67.5%)) on invasive mechanical ventilation, for whom 1,217 daily assessments were applied at the bedside. The weighted total score of the prediction model showed the highest discriminatory power for the spontaneous breathing test, with sensitivity and specificity indices for fitness failure of 89.7% or success of 84.6%. The cutoff point suggested by the checklist was 8, with a probability of extubation failure less than 5%. Failure increased progressively with increasing score, with a maximum probability of predicting extubation failure of 85%.
The extubation failure rate with the use of this model was within what is acceptable in the literature. The daily checklist model for the spontaneous breathing test was able to identify predictive variables of failure in the extubation process in pediatric patients.
Abstract
Crit Care Sci. 2023;35(1):107-111
DOI 10.5935/2965-2774.20230305-pt
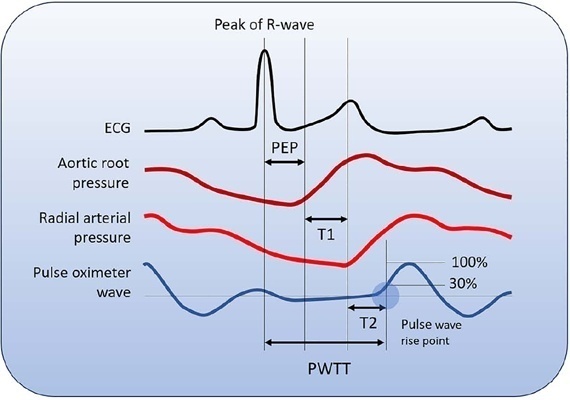
Cardiac output is an essential determinant of oxygen delivery, although unreliably measured on clinical examination and routine monitoring. Unfortunately, cardiac output monitoring is rarely performed in pediatric critical care medicine, with a limited availability of accurate methods for children. Herein, we report two pediatric cases in which noninvasive pulse-wave transit time-based cardiac output monitoring (esCCO, Nihon Kohden, Tokyo, Japan) was used. The esCCO system calculates cardiac output continuously by using the negative correlation between stroke volume and pulse wave transit time and requires only electrocardiogram monitoring, noninvasive blood pressure, and pulse oximetry signals. Before starting its use, esCCO should be calibrated, which can be done using patient information (gender, age, height, and body weight) or entering cardiac output values obtained by other methods. In both cases, when calibrations were performed using patient information, the agreement between esCCO and echocardiographic measurements was poor. However, after calibration with transthoracic echocardiography, the cardiac output values obtained by both methods remained similar after 2 hours and 18 hours. The results indicate that the esCCO system is suitable for use in children; however, further studies are needed to optimize its algorithm and determine its accuracy, precision, and trend in children.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2022;34(4):469-476
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20220429-en
To evaluate the effects of critical illness on the functional status of children aged zero to 4 years with or without a history of prematurity after discharge from the pediatric intensive care unit.
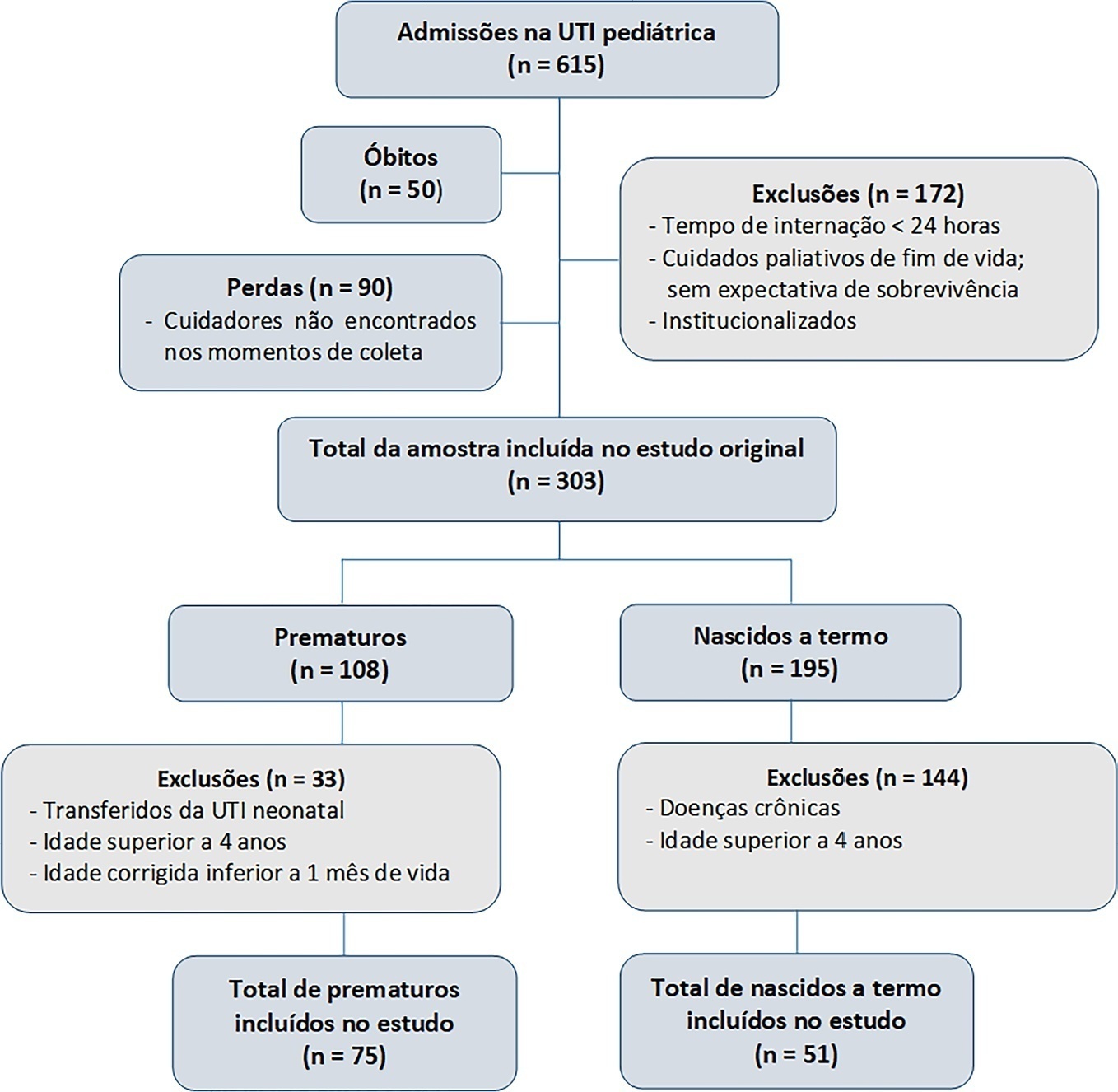
This was a secondary cross-sectional study nested in an observational cohort of survivors from a pediatric intensive care unit. Functional assessment was performed using the Functional Status Scale within 48 hours after discharge from the pediatric intensive care unit.
A total of 126 patients participated in the study, 75 of whom were premature, and 51 of whom were born at term. Comparing the baseline and functional status at pediatric intensive care unit discharge, both groups showed significant differences (p < 0.001). Preterm patients exhibited greater functional decline at discharge from the pediatric intensive care unit (61%). Among patients born at term, there was a significant correlation between the Pediatric Index of Mortality, duration of sedation, duration of mechanical ventilation and length of hospital stay with the functional outcomes (p = 0.05).
Most patients showed a functional decline at discharge from the pediatric intensive care unit. Although preterm patients had a greater functional decline at discharge, sedation and mechanical ventilation duration influenced functional status among patients born at term.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2022;34(2):295-299
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20220028-en
Posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome is a rare clinical and radiological syndrome characterized by vasogenic edema of the white matter of the occipital and parietal lobes, which are usually symmetrical, resulting from a secondary manifestation of acute dysfunction of the posterior cerebrovascular system. We describe a case of posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome secondary to SARS-CoV-2 infection in a 9-year-old boy who developed acute hypoxemic respiratory failure and required assisted mechanical ventilation. The child developed multisystem inflammatory syndrome, and he was monitored in the pediatric intensive care unit and was provided mechanical ventilation and vasoactive agents for hemodynamic support. Additionally, he developed pulmonary and extrapulmonary clinical manifestations along with neuropsychiatric manifestations that required close follow-up and were verified using brain magnetic resonance imaging for timely intervention. Currently, there are few reports of children with posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome associated with multisystem inflammatory syndrome.
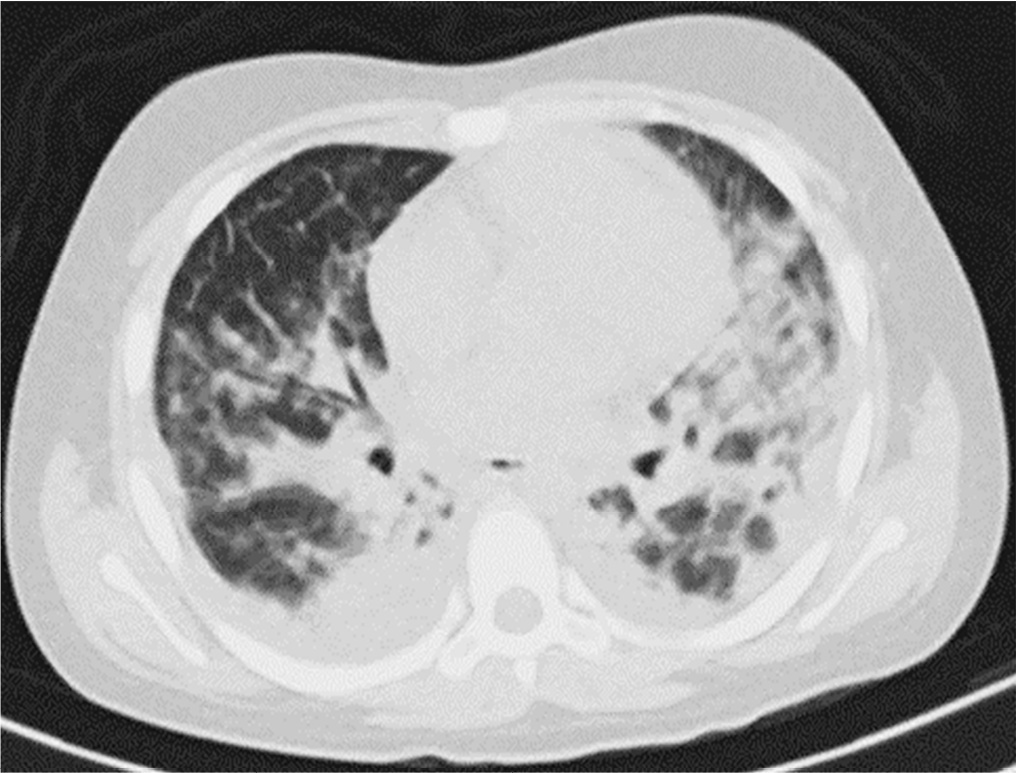
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2022;34(1):147-153
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20220009-en
To assess the percentage of vancomycin area under the curve/minimum inhibitory concentration target attainment in pediatric patients after the empirical dose regimen and to demonstrate the applicability of this method for vancomycin monitoring.
A retrospective cohort study was performed including pediatric patients with normal renal function admitted between January 2020 and December 2020. The one-compartment model with first-order kinetics was used to estimate the pharmacokinetic parameters, and the area under the curve was calculated by the trapezoidal rule. The therapeutic target was defined as area under the curve/minimum inhibitory concentration ≥ 400 and < 600. The Chi-squared test was applied to compare the percentage of target attainment over age groups, while the pharmacokinetic parameters were compared by the Kruskal-Wallis test with Dunn’s test for post hoc analyses. We considered significant p-values < 0.05.
In total, 42 pairs of vancomycin levels were analyzed from 17 patients enrolled in this study. After empirical vancomycin daily dosing, the therapeutic target was achieved in five (29%) patients; four patients (24%) had a supratherapeutic initial area under the curve/minimum inhibitory concentration value (> 600mg.h/L), and eight (47%) patients had subtherapeutic values (< 400mg.h/L). The most identified pathogens were Staphylococcus spp. (n = 7). Trough levels and areas under the curve showed moderate correlation values (R2 = 0.73). Acute kidney injury occurred in one (6%) patient.
Most patients did not reach the therapeutic target with a vancomycin empirical dose regimen, and the implementation of area under the curve-based dosing using two sample measurements allowed for real-time dose adjustments based on individuals’ pharmacokinetic parameters.
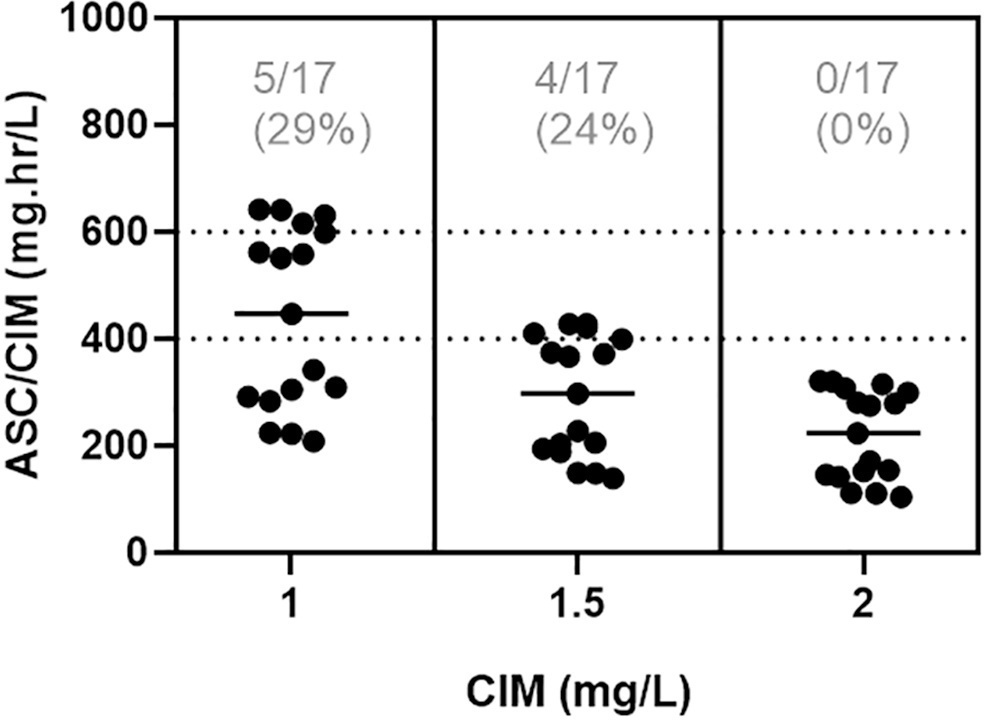
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2021;33(4):544-548
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20210082
To evaluate whether there was any impact on the number of pediatric extracorporeal membrane oxygenation runs and survival rates in the years subsequent to the 2009 pandemic.
We studied two different periods of extracorporeal membrane oxygenation support for respiratory failure in children by analyzing datasets from the Extracorporeal Life Support Organization. Autoregressive integrated moving average models were constructed to estimate the effect of the pandemic. The year 2009 was the year of intervention (the H1N1 epidemic) in an interrupted time series model. Data collected from 2001 - 2010 were considered preintervention, and data collected from 2010 - 2017 were considered postintervention.
There was an increase in survival rates in the period 2010 - 2017 compared to 2001 - 2010 (p < 0.0001), with a significant improvement in survival when extracorporeal membrane oxygenation was performed for acute respiratory failure due to viral pneumonia. The autoregressive integrated moving average model shows an increase of 23 extracorporeal membrane oxygenation runs per year, prior to the point of the level effect (2009). In terms of survival, the preslope shows that there was no significant increase in survival rates before 2009 (p = 0.41), but the level effect was nearly significant after two years (p = 0.05), with a 6% increase in survival. In four years, there was an 8% (p = 0.03) increase in survival, and six years after 2009, there was up to a 10% (p = 0.026) increase in survival.
In the years following 2009, there was a significant, global incremental increase in the extracorporeal membrane oxygenation survival rates for all runs, mainly due to improvements in the technology and treatment protocols for acute respiratory failure related to viral pneumonia and other respiratory conditions.
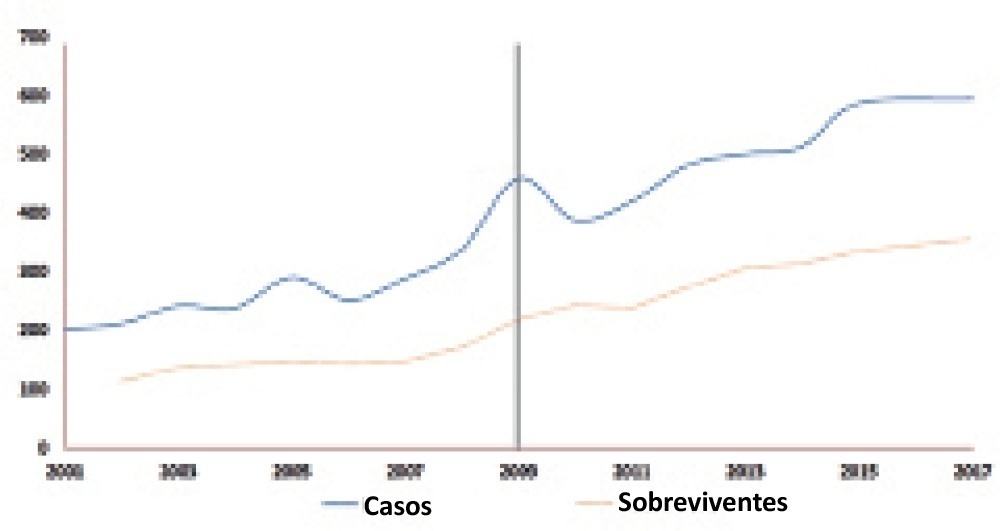
Search
Search in:
Case reports (56) Child (53) Coronavirus infections (33) COVID-19 (45) Critical care (115) Critical illness (54) Infant, newborn (27) Intensive care (72) Intensive care units (254) Intensive care units, pediatric (31) mechanical ventilation (38) Mortality (75) Physical therapy modalities (28) Prognosis (61) Respiration, artificial (117) Respiratory insufficiency (26) risk factors (34) SARS-CoV-2 (28) Sepsis (98) Septic shock (25)