Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2022;34(4):469-476
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20220429-en
To evaluate the effects of critical illness on the functional status of children aged zero to 4 years with or without a history of prematurity after discharge from the pediatric intensive care unit.
This was a secondary cross-sectional study nested in an observational cohort of survivors from a pediatric intensive care unit. Functional assessment was performed using the Functional Status Scale within 48 hours after discharge from the pediatric intensive care unit.
A total of 126 patients participated in the study, 75 of whom were premature, and 51 of whom were born at term. Comparing the baseline and functional status at pediatric intensive care unit discharge, both groups showed significant differences (p < 0.001). Preterm patients exhibited greater functional decline at discharge from the pediatric intensive care unit (61%). Among patients born at term, there was a significant correlation between the Pediatric Index of Mortality, duration of sedation, duration of mechanical ventilation and length of hospital stay with the functional outcomes (p = 0.05).
Most patients showed a functional decline at discharge from the pediatric intensive care unit. Although preterm patients had a greater functional decline at discharge, sedation and mechanical ventilation duration influenced functional status among patients born at term.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2021;33(2):276-281
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20210035
To evaluate serum uteroglobin-related protein 1 expression early after smoke inhalation injuries and its association with the severity of inhalation injury in burned patients.
Smoke or chemical inhalation injury is associated with morbidity and mortality. The consequences of inhalation result from an inflammatory response. Uteroglobin-related protein 1 is an anti-inflammatory protein and may improve lung inflammation. We hypothesized that uteroglobin-related protein 1 levels could reflect disease severity and predict outcome in patients with inhalation injury. Sixteen patients diagnosed with acute respiratory distress syndrome secondary to smoke inhalation injury were prospectively included in the study. Plasma was collected upon intensive care unit admission and within 24 hours of the inhalation injury. Bronchoscopies were carried out in all patients to assess the severity of inhalation injury within 72 hours. Uteroglobin-related protein 1 plasma levels were determined in duplicate with enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay.
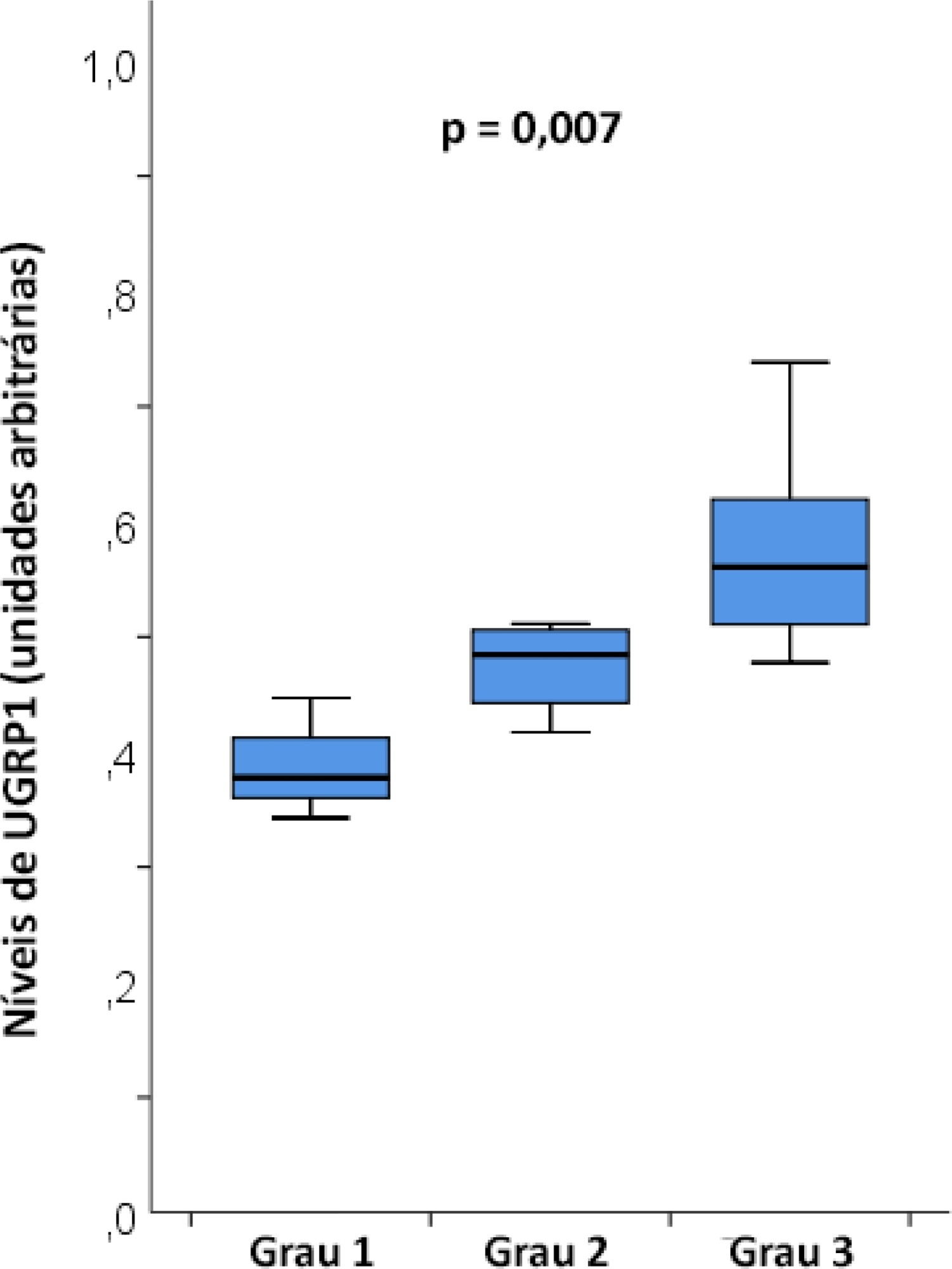
The mean age was 23 ± 5 years, and the inhalation injury distribution was as follows: three of grade 1, four of grade 2, and nine of grade 3. The level of uteroglobin-related protein 1 was related to inhalation severity (grade 1: 0.389 ± 0.053 arbitrary units versus grade 2: 0.474 ± 0.0423 arbitrary units versus grade 3: 0.580 ± 0.094 arbitrary units; p = 0.007).
Plasma levels of uteroglobin-related protein 1 are associated with the degree of lung inhalation injury.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2017;29(4):460-465
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20170066
To evaluate the functional status of pediatric patients after discharge from the pediatric intensive care unit using the Functional Status Scale and to compare the time of invasive mechanical ventilation, length of stay in the pediatric intensive care unit, and Pediatric Index of Mortality 2 results among individuals with different degrees of functional impairment.
A cross-sectional study was conducted on patients who were discharged from a pediatric intensive care unit. The functional evaluation by the Functional Status Scale was performed on the first day after discharge from the unit, and the Pediatric Index of Mortality 2 was used to predict the mortality rate at the time of admission to the pediatric intensive care unit.
The sample consisted of 50 individuals, 60% of which were male, with a median age of 19 [6 - 61] months. The overall score of the Functional Status Scale was 11.5 [7 - 15], and the highest scores were observed in the "motor function" 3 [1 - 4] and "feeding" 4 [1 - 4] domains. Compared to patients who were not readmitted to the pediatric intensive care unit, patients who were readmitted presented a worse overall score (p = 0.01), worse scores in the "motor function" (p = 0.01), "feeding" (p = 0.02), and "respiratory" (p = 0.036) domains, and a higher mortality rate according to the Pediatric Index of Mortality 2 (p = 0.025).
Evaluation of the functional status using the Functional Status Scale indicated moderate impairment in patients after discharge from the pediatric intensive care unit, mainly in the "motor function" and "feeding" domains; patients who were readmitted to the pediatric intensive care unit demonstrated worse overall functional, motor function, feeding and respiratory scores. Individuals with greater functional impairment had longer times of invasive mechanical ventilation and hospitalization in the pediatric intensive care unit.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2016;28(2):114-119
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20160025
To evaluate the variation in mobility during hospitalization in an intensive care unit and its association with hospital mortality.
This prospective study was conducted in an intensive care unit. The inclusion criteria included patients admitted with an independence score of ≥ 4 for both bed-chair transfer and locomotion, with the score based on the Functional Independence Measure. Patients with cardiac arrest and/or those who died during hospitalization were excluded. To measure the loss of mobility, the value obtained at discharge was calculated and subtracted from the value obtained on admission, which was then divided by the admission score and recorded as a percentage.
The comparison of these two variables indicated that the loss of mobility during hospitalization was 14.3% (p < 0.001). Loss of mobility was greater in patients hospitalized for more than 48 hours in the intensive care unit (p < 0.02) and in patients who used vasopressor drugs (p = 0.041). However, the comparison between subjects aged 60 years or older and those younger than 60 years indicated no significant differences in the loss of mobility (p = 0.332), reason for hospitalization (p = 0.265), SAPS 3 score (p = 0.224), use of mechanical ventilation (p = 0.117), or hospital mortality (p = 0.063).
There was loss of mobility during hospitalization in the intensive care unit. This loss was greater in patients who were hospitalized for more than 48 hours and in those who used vasopressors; however, the causal and prognostic factors associated with this decline need to be elucidated.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2015;27(3):220-227
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20150033
To analyze the epidemiological clinical profile of women with maternal near miss according to the new World Health Organization criteria.
A descriptive crosssectional study was conducted, in which the records of patients admitted to the obstetric intensive care unit of a tertiary hospital in Recife (Brazil) over a period of four years were analyzed. Women who presented at least one near miss criterion were included. The variables studied were age, race/color, civil status, education, place of origin, number of pregnancies and prenatal consultations, complications and procedures performed, mode of delivery, gestational age at delivery, and maternal near miss criteria. The descriptive analysis was performed using the program Epi-Info 3.5.1.
Two hundred fifty-five cases of maternal near miss were identified, with an overall ratio of maternal near miss of 12.8/1,000 live births. Among these cases, 43.2% of the women had incomplete primary education, 44.7% were primiparous, and 20.5% had undergone a previous cesarean section. Regarding specific diagnoses, there was a predominance of hypertensive disorders (62.7%), many of which were complicated by HELLP (hemolysis, elevated liver enzymes, and low platelets) syndrome (41.2%). The laboratory near miss criteria were the most often observed (59.6%), due mainly to the high frequency of acute thrombocytopenia (32.5%).
A high frequency of women who had a low level of education and who were primiparous was observed. According to the new criteria proposed by the World Health Organization, hypertensive pregnancy disorders are still the most common among maternal near miss cases. The high frequency of HELLP syndrome was also striking, which contributed to acute thrombocytopenia being the most frequent near miss criterion.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2013;25(1):49-55
DOI 10.1590/S0103-507X2013000100010
Recent evidence suggests that a negative protein balance secondary to severe disease is associated with increased morbidity. A loss of total body protein is inevitable in this scenario, even with an aggressive nutritional approach, primarily due to the catabolism of skeletal muscle fibers. The ubiquitin-proteasome system is the primary metabolic and biochemical mechanism involved in this process; paradoxically, this system consumes adenosine triphosphate as its energy source. It is possible that a neutral protein balance in these clinical situations is important for improving outcomes and achieving the caloric goals estimated or measured by indirect calorimetry. Recent studies have suggested that the use of higher protein concentrations in nutritional therapy for critically ill patients may help to reduce mortality. The purpose of this study was to review some of the nutrition therapy principles related to protein metabolism, evaluate the main assertions of the guidelines of specialty societies and review the recent studies that address these issues using critical insights from the authors' clinical experience.
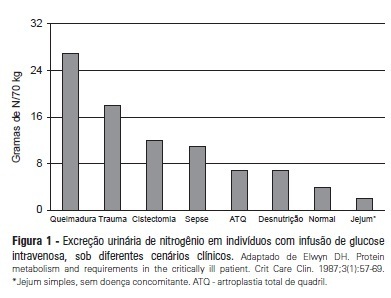
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2011;23(3):304-311
DOI 10.1590/S0103-507X2011000300008
OBJECTIVES: Ascending aortic dissection has a poor prognosis if it is not promptly corrected surgically. Even with surgical correction, postoperative management is feared because of its complicated course. Our aim was to describe the incidence of postoperative complications and identify the 1 and 6-month mortality rate of our ascending aortic dissection surgical cohort. Secondarily, a comparison was made between ascending aortic dissection patients and paired-matched patients who received urgent coronary artery bypass graft surgery. METHODS: A retrospective analysis of a prospectively-collected database from February 2005 through June 2008 revealed 12 ascending aortic dissection and 10 elective ascending aortic aneurysm repair patients. These patients were analyzed for demographic and perioperative characteristics. Ascending aortic dissection patients were compared to paired-matched coronary artery bypass graft surgery patients according to age (± 3 years), gender, elective/urgent procedure and surgical team. The main outcome was in-hospital morbidity, defined by postoperative complications, intensive care unit admission and hospital length of stay. RESULTS: Twenty-two patients received operations to correct ascending aortic dissections and ascending aortic aneurysms, while 246 patients received coronary artery bypass graft surgeries. Ascending aortic dissection patients were notably similar to ascending aortic aneurysm brackets, except for longer mechanical ventilation times and lengths of stay in the hospital. After matching coronary artery bypass graft surgery patients to an ascending aortic dissection group, the following significantly worse results were found for the Aorta group: higher incidence of postoperative complications (91% vs. 45%, p=0.03), and longer hospital length of stay (19 [11-41] vs. 12.5 [8.5-13] days, p=0.05). No difference in mortality was found at the 1-month (8.3%) or 6-month (16.6%) postoperative care date. CONCLUSION: Ascending aortic dissection correction is associated with an increased incidence of postoperative complications and an increased hospital length of stay, but 1 and 6-month mortality is similar to that of paired-matched coronary artery bypass graft surgery patients.
Search
Search in:
Case reports (56) Child (53) Coronavirus infections (34) COVID-19 (46) Critical care (116) Critical illness (54) Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (26) Infant, newborn (27) Intensive care (72) Intensive care units (256) Intensive care units, pediatric (31) mechanical ventilation (38) Mortality (76) Physical therapy modalities (28) Prognosis (61) Respiration, artificial (119) Respiratory insufficiency (26) risk factors (34) SARS-CoV-2 (28) Sepsis (98)