You searched for:"Bruno Prata Martinez"
We found (6) results for your search.-
Original Article
Reproducibility of respiratory mechanics measurements in patients on invasive mechanical ventilation
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2020;32(3):398-404
Abstract
Original ArticleReproducibility of respiratory mechanics measurements in patients on invasive mechanical ventilation
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2020;32(3):398-404
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20200068
Views0See moreABSTRACT
Objective:
To evaluate the intra- and interexaminer reproducibility of measurements of the resistance and static and dynamic compliance of the respiratory system in patients on mechanical ventilation.
Methods:
This was an analytical study conducted with individuals aged ≥ 18 years who were on invasive mechanical ventilation and had no clinical diagnosis of respiratory system disease and/or chest abnormality. Three measurements of respiratory mechanics were performed with a 1-minute interval between them. The first and third measurements were performed by examiner A, the second by examiner B. The values for the resistance and static and dynamic compliance of the respiratory system were compared using the intraclass correlation coefficient.
Results:
A total of 198 measurements of respiratory mechanics were performed for 66 patients on mechanical ventilation. The patients had a mean age of 52.6 ± 18.6 years and a mean body mass index of 21.6 ± 2.1kg/m2; a surgical profile (61.5%) and female sex (53.8%) were predominant. Mean values were obtained for the three measurements of respiratory system resistance (A1: 15.7 ± 6.8cmH2O/L/s; B1: 15.7 ± 6.4cmH2O/L/s and A2: 15.9 ± 6.2cmH2O/L/s), respiratory system static compliance (A1: 42.1 ± 13.7mL/cmH2O; B1: 42.4 ± 14.6mL/cmH2O and A2: 42.2 ± 14.5mL/cmH2O) and respiratory system dynamic compliance (A1: 21.3 ± 7.3mL/cmH2O; B1: 21.4 ± 7.5mL/cmH2O and A2: 21.3 ± 6.2mL/cmH2O). The intraclass correlation coefficient was also calculated for respiratory system resistance (R = 0.882 and p = 0.001; R = 0.949 and p = 0.001 – interexaminer A1 versus B and B versus A2, respectively; R = 0.932 and p = 0.001 – intraexaminer); respiratory system static compliance (R = 0.951 and p = 0.001; R = 0.958 and p = 0.001 – interexaminer A1 versus B and B versus A2, respectively; R = 0.965 and p = 0.001 – intraexaminer) and respiratory system dynamic compliance (R = 0.957 and p = 0.001; R = 0.946 and p = 0.001 – interexaminer A1 versus B and B versus A2, respectively; R = 0.926 and p = 0.001 – intraexaminer).
Conclusion:
The measurements of resistance and static and dynamic compliance of the respiratory system show good intra- and interexaminer reproducibility for ventilated patients.
-
Original Articles
Assessment of the measurement properties of the Brazilian versions of the Functional Status Score for the ICU and the Functional Independence Measure in critically ill patients in the intensive care unit
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2019;31(4):521-528
Abstract
Original ArticlesAssessment of the measurement properties of the Brazilian versions of the Functional Status Score for the ICU and the Functional Independence Measure in critically ill patients in the intensive care unit
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2019;31(4):521-528
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20190065
Views1See moreABSTRACT
Objective:
To compare the measurement properties (internal consistency, intra and interrater reliability, construct validity, and ceiling and floor effects) of the Functional Status Score for the ICU (FSS-ICU) and the Functional Independence Measure (FIM-motor domain).
Methods:
In this study of measurement properties, the FSS-ICU and FIM were applied to 100 patients (72.1 ± 15.9 years; 53% male; Sequential Organ Failure Assessment = 11.0 ± 3.5 points, Simplified Acute Physiology Score 3 = 50.2 ± 16.8 points) in an intensive care unit at baseline and after 2 hours by physiotherapist 1 (test and retest) and 30 minutes after baseline by physiotherapist 2. The measurement properties evaluated were internal consistency (Cronbach’s alpha), intra- and interrater reliability (intraclass correlation coefficient), agreement (standard error of measurement) and minimum detectable change at a 90% confidence level, ceiling and floor effects (frequency of maximum and minimum scores) and construct validity (Pearson’s correlation).
Results:
The FSS-ICU and FIM presented adequate internal consistency (Cronbach’s alpha, FSS-ICU = 0.95 and FIM = 0.86), intra-and interrater reliability for overall FSS-ICU and FIM score (ICC > 0.75), agreement (minimum detectable change at a 90% confidence level: FSS-ICU and FIM = 1.0 point; standard error of measurement: FSS-ICU = 2% and FIM = 1%) and construct validity (r = 0.94; p < 0.001). However, the FSS-ICU and FIM presented ceiling effects (maximum score for 16% of patients for the FSS-ICU and 18% for the FIM).
Conclusion:
The FSS-ICU and FIM present adequate measurement properties to assess functionality in critically ill patients, although they present ceiling effects.
-
Original Article
Mobility decline in patients hospitalized in an intensive care unit
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2016;28(2):114-119
Abstract
Original ArticleMobility decline in patients hospitalized in an intensive care unit
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2016;28(2):114-119
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20160025
Views0See moreABSTRACT
Objective:
To evaluate the variation in mobility during hospitalization in an intensive care unit and its association with hospital mortality.
Methods:
This prospective study was conducted in an intensive care unit. The inclusion criteria included patients admitted with an independence score of ≥ 4 for both bed-chair transfer and locomotion, with the score based on the Functional Independence Measure. Patients with cardiac arrest and/or those who died during hospitalization were excluded. To measure the loss of mobility, the value obtained at discharge was calculated and subtracted from the value obtained on admission, which was then divided by the admission score and recorded as a percentage.
Results:
The comparison of these two variables indicated that the loss of mobility during hospitalization was 14.3% (p < 0.001). Loss of mobility was greater in patients hospitalized for more than 48 hours in the intensive care unit (p < 0.02) and in patients who used vasopressor drugs (p = 0.041). However, the comparison between subjects aged 60 years or older and those younger than 60 years indicated no significant differences in the loss of mobility (p = 0.332), reason for hospitalization (p = 0.265), SAPS 3 score (p = 0.224), use of mechanical ventilation (p = 0.117), or hospital mortality (p = 0.063).
Conclusion:
There was loss of mobility during hospitalization in the intensive care unit. This loss was greater in patients who were hospitalized for more than 48 hours and in those who used vasopressors; however, the causal and prognostic factors associated with this decline need to be elucidated.
-
Original Article
Influence of different degrees of head elevation on respiratory mechanics in mechanically ventilated patients
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2015;27(4):347-352
Abstract
Original ArticleInfluence of different degrees of head elevation on respiratory mechanics in mechanically ventilated patients
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2015;27(4):347-352
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20150059
Views0See moreRESUMO
Objective:
The positioning of a patient in bed may directly affect their respiratory mechanics. The objective of this study was to evaluate the respiratory mechanics of mechanically ventilated patients positioned with different head angles hospitalized in an intensive care unit.
Methods:
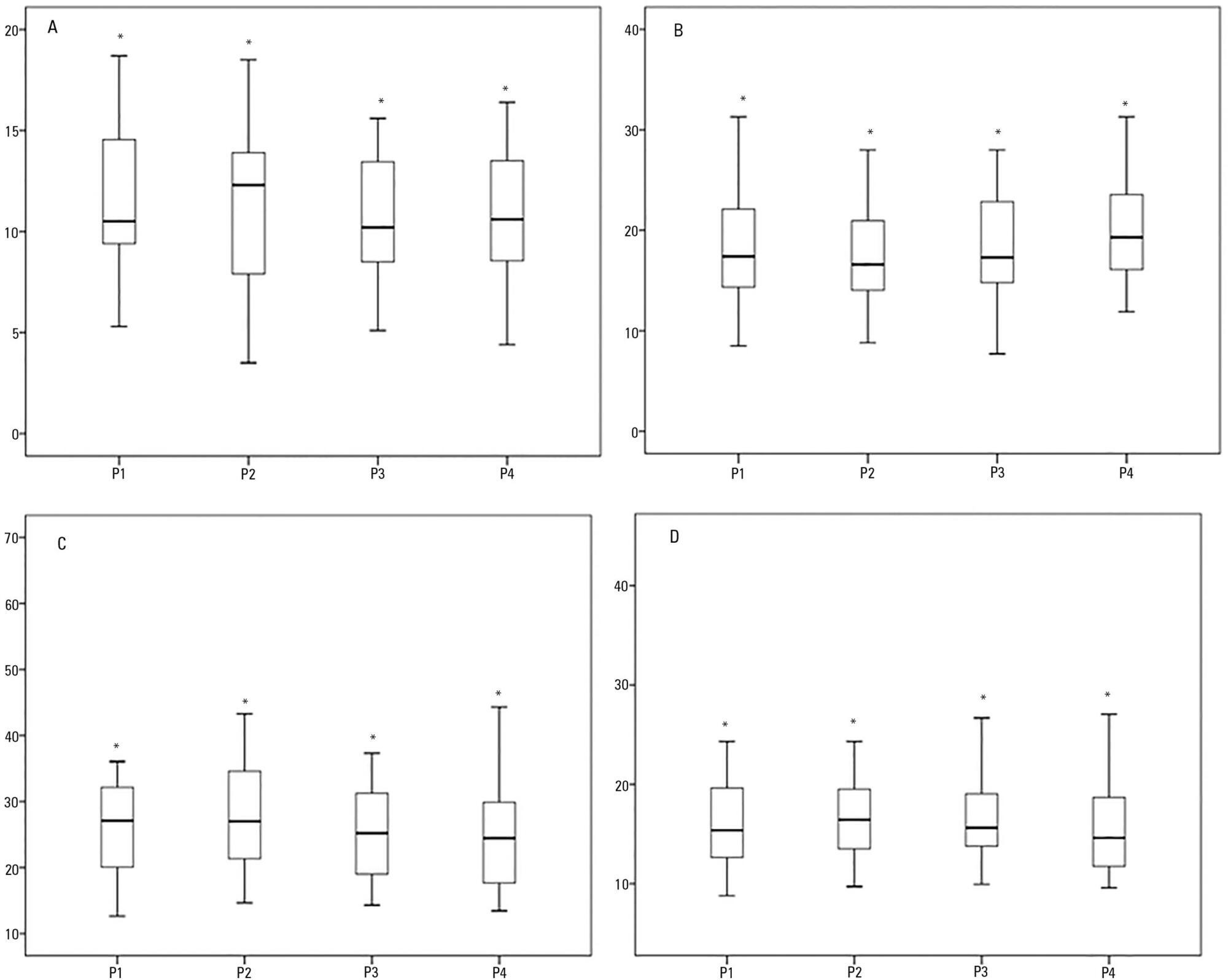
This was a prospective physiological study in which static and dynamic compliance, resistive airway pressure, and peripheral oxygen saturation were measured with the head at four different positions (0° = P1, 30° = P2, 45° = P3, and 60° = P4). Repeated-measures analysis of variance (ANOVA) with a Bonferroni post-test and Friedman analysis were used to compare the values obtained at the different positions.
Results:
A comparison of the 35 evaluated patients revealed that the resistive airway pressure values in the 0° position were higher than those obtained when patients were positioned at greater angles. The elastic pressure analysis revealed that the 60° position produced the highest value relative to the other positions. Regarding static compliance, a reduction in values was observed from the 0° position to the 60° position. The dynamic compliance analysis revealed that the 30° angle produced the greatest value compared to the other positions. The peripheral oxygen saturation showed little variation, with the highest value obtained at the 0° position.
Conclusion:
The highest dynamic compliance value was observed at the 30° position, and the highest oxygenation value was observed at the 0° position.
-
Original Articles
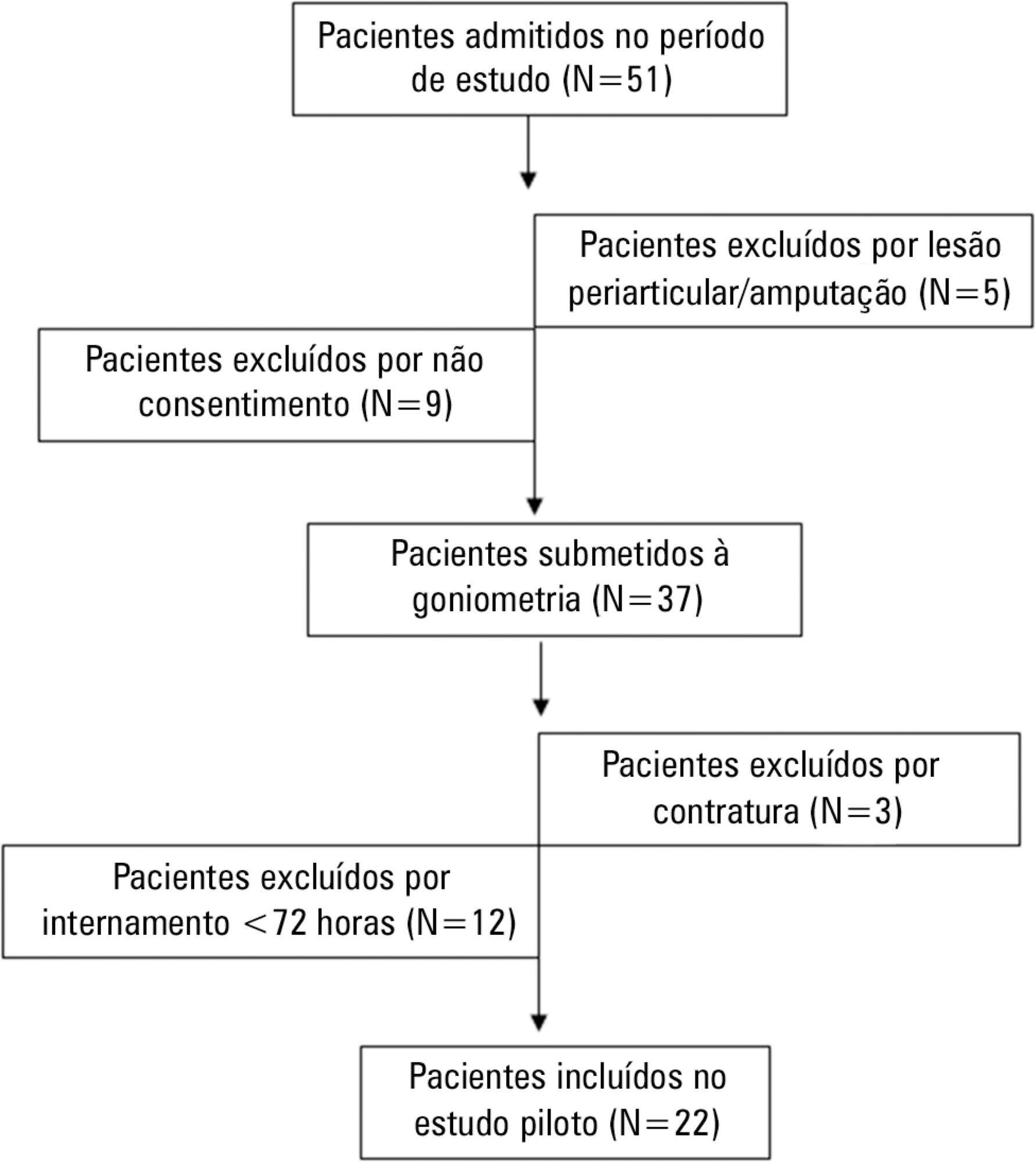
Impact of hospitalization in an intensive care unit on range of motion of critically ill patients: a pilot study
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2014;26(1):65-70
Abstract
Original ArticlesImpact of hospitalization in an intensive care unit on range of motion of critically ill patients: a pilot study
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2014;26(1):65-70
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20140010
Views0See moreObjective:
To evaluate the joint range of motion of critically ill patients during hospitalization in the intensive care unit.
Methods:
This work was a prospective longitudinal study conducted in a critical care unit of a public hospital in the city of Salvador (BA) from September to November 2010. The main variable evaluated was the passive joint range of motion. A goniometer was used to measure the elbows, knees and ankles at the time of admission and at discharge. All patients admitted in the period were included other than patients with length of stay <72 hours and patients with reduced joint range of motion on admission.
Results:
The sample consisted of 22 subjects with a mean age of 53.5±17.6 years, duration of stay in the intensive care unit of 13.0±6.0 days and time on mechanical ventilation of 12.0±6.3 days. The APACHE II score was 28.5±7.3, and the majority of patients had functional independence at admission with a prior Barthel index of 88.8±19. The losses of joint range of motion were 11.1±2.1°, 11.0±2.2°, 8.4±1.7°, 9.2±1.6°, 5.8±0.9° and 5.1±1.0°, for the right and left elbows, knees and ankles, respectively (p<0.001).
Conclusion:
There was a tendency towards decreased range of motion of large joints such as the ankle, knee and elbow during hospitalization in the intensive care unit.
-
Special Articles
Physical therapy in critically ill adult patients: recommendations from the Brazilian Association of Intensive Care Medicine Department of Physical Therapy
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2012;24(1):6-22
Abstract
Special ArticlesPhysical therapy in critically ill adult patients: recommendations from the Brazilian Association of Intensive Care Medicine Department of Physical Therapy
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2012;24(1):6-22
DOI 10.1590/S0103-507X2012000100003
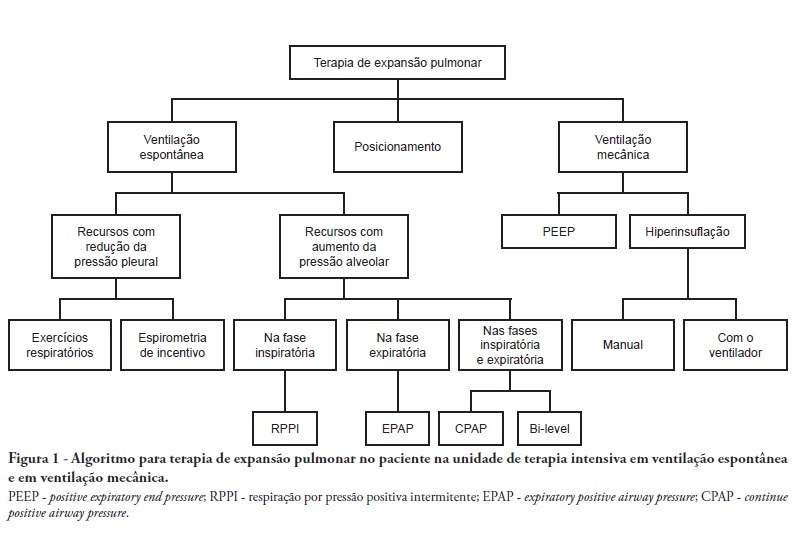
Views5See moreComplications from immobility in intensive care unit patients contribute to functional decline, increased healthcare costs, reduced quality of life and higher post-discharge mortality. Physical therapy focuses on promoting recovery and preserving function, and it may minimize the impact of these complications. A group of Brazilian Association of Intensive Care Medicine physical therapy experts developed this document that contains minimal physical therapy recommendations appropriate to the Brazilian real-world clinical situation. Prevention and treatment of atelectasis, procedures related to the removal of secretions and treatment of conditions related to physical deconditioning and functional decline are discussed. Equally important is the consideration that prescribing and executing activities, mobilizations and exercises are roles of the physical therapist, whose diagnosis should precede any intervention.
Search
Search in:
KEY WORDS
Case reports Child Coronavirus infections COVID-19 Critical care Critical illness ICU Infant, newborn Intensive care Intensive care units Intensive care units, pediatric mechanical ventilation Mortality Physical therapy modalities Prognosis Respiration, artificial Respiratory insufficiency risk factors SARS-CoV-2 Sepsis




