Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2020;32(3):398-404
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20200068
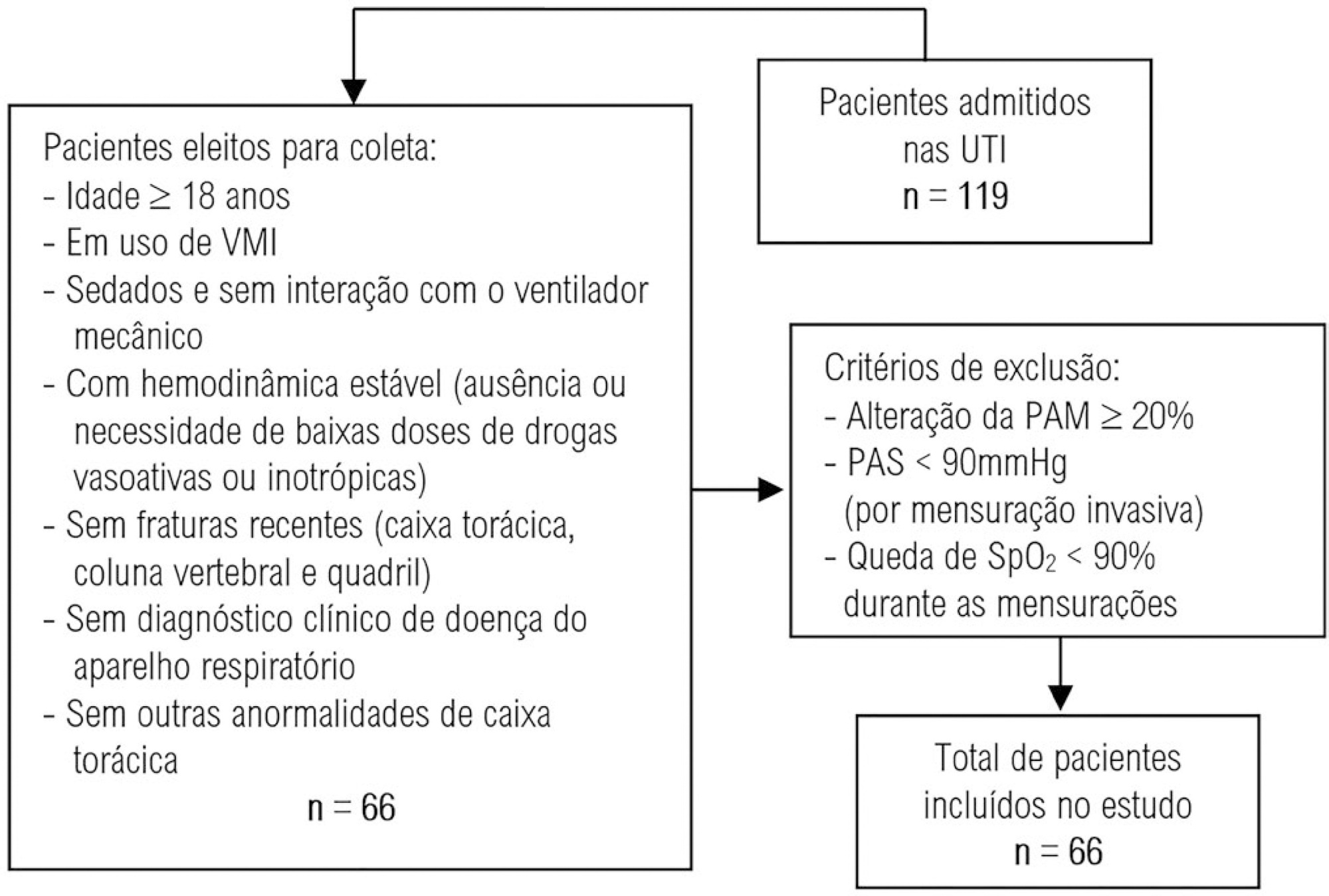
To evaluate the intra- and interexaminer reproducibility of measurements of the resistance and static and dynamic compliance of the respiratory system in patients on mechanical ventilation.
This was an analytical study conducted with individuals aged ≥ 18 years who were on invasive mechanical ventilation and had no clinical diagnosis of respiratory system disease and/or chest abnormality. Three measurements of respiratory mechanics were performed with a 1-minute interval between them. The first and third measurements were performed by examiner A, the second by examiner B. The values for the resistance and static and dynamic compliance of the respiratory system were compared using the intraclass correlation coefficient.
A total of 198 measurements of respiratory mechanics were performed for 66 patients on mechanical ventilation. The patients had a mean age of 52.6 ± 18.6 years and a mean body mass index of 21.6 ± 2.1kg/m2; a surgical profile (61.5%) and female sex (53.8%) were predominant. Mean values were obtained for the three measurements of respiratory system resistance (A1: 15.7 ± 6.8cmH2O/L/s; B1: 15.7 ± 6.4cmH2O/L/s and A2: 15.9 ± 6.2cmH2O/L/s), respiratory system static compliance (A1: 42.1 ± 13.7mL/cmH2O; B1: 42.4 ± 14.6mL/cmH2O and A2: 42.2 ± 14.5mL/cmH2O) and respiratory system dynamic compliance (A1: 21.3 ± 7.3mL/cmH2O; B1: 21.4 ± 7.5mL/cmH2O and A2: 21.3 ± 6.2mL/cmH2O). The intraclass correlation coefficient was also calculated for respiratory system resistance (R = 0.882 and p = 0.001; R = 0.949 and p = 0.001 - interexaminer A1 versus B and B versus A2, respectively; R = 0.932 and p = 0.001 - intraexaminer); respiratory system static compliance (R = 0.951 and p = 0.001; R = 0.958 and p = 0.001 - interexaminer A1 versus B and B versus A2, respectively; R = 0.965 and p = 0.001 - intraexaminer) and respiratory system dynamic compliance (R = 0.957 and p = 0.001; R = 0.946 and p = 0.001 - interexaminer A1 versus B and B versus A2, respectively; R = 0.926 and p = 0.001 - intraexaminer).
The measurements of resistance and static and dynamic compliance of the respiratory system show good intra- and interexaminer reproducibility for ventilated patients.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2020;32(1):66-71
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20200011
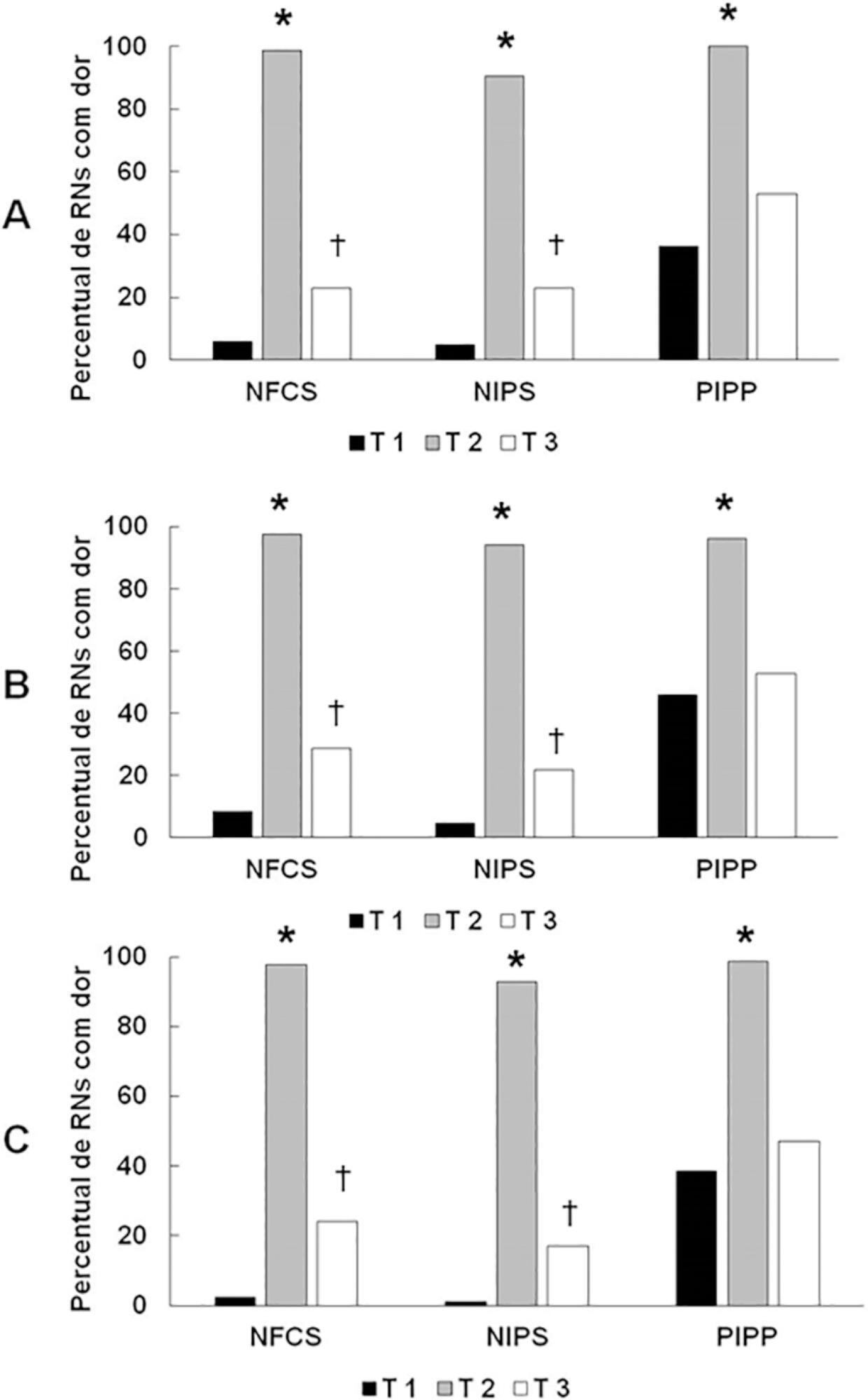
To temporally assess a painful stimulus in premature infants using 3 neonatal pain scales.
A total of 83 premature infants were observed during airway aspiration by 3 evaluators (E1, E2 and E3) using 3 pain assessment scales (Neonatal Facial Coding System - NFCS; Neonatal Infant Pain Scale - NIPS; and Premature Infant Pain Profile - PIPP) at 5 time points: T1 (before airway aspiration), T2 (during airway aspiration), T3 (1 minute after airway aspiration), T4 (3 minutes after airway aspiration), and T5 (5 minutes after airway aspiration). Light’s Kappa (agreement among examiners and among scales at each time point) and the McNemar test (comparison among time points) were used considering p < 0.05.
There was a significant difference between the 3 examiners for T1 and T2 using the 3 scales. In T3, pain was observed in 22.9%/E1, 28.9%/E2, and 24.1%/E3 according to the NFCS; 22.9%/E1, 21.7%/E2, and 16.9%/E3 according to the NIPS; and 49.4%/E1, 53.9%/E2, and 47%/E3 according to the PIPP. There was a difference between T1 and T3 using the 3 scales, except for 2 examiners for the PIPP (E2: p = 0.15/E3: p = 0.17). Comparing T4 and T5 to T1, there was no difference in the 3 scales.
Premature infants required at least 3 minutes to return to their initial state of rest (no pain).
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2019;31(3):354-360
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20190058
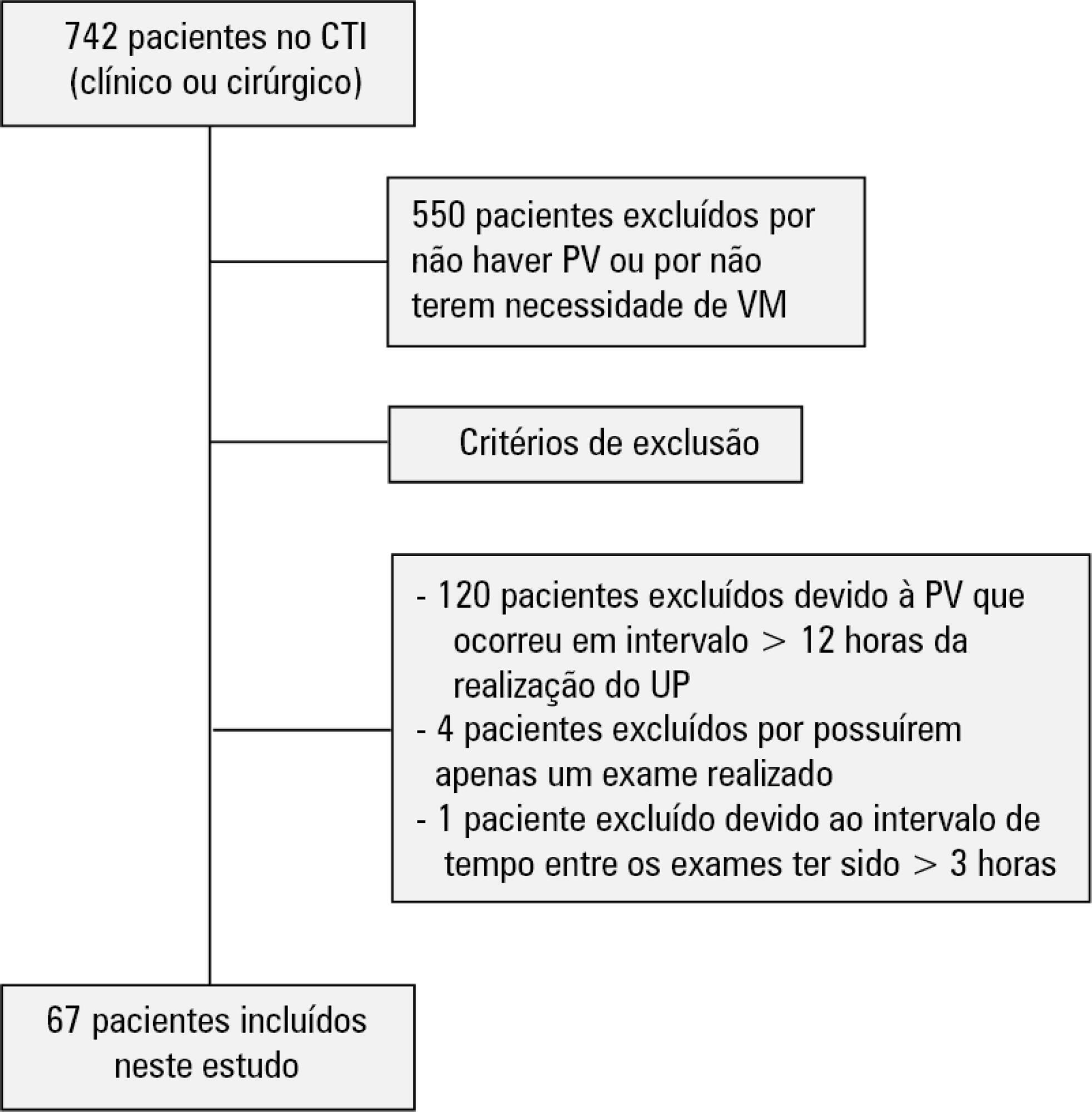
To evaluate the agreement between intensive care physicians with similar training in the use of bedside lung ultrasonography in identifying pulmonary B lines, visualized in real time, to verify the reproducibility of the method.
A total of 67 patients with some ventilatory deterioration identified within 12 hours after a pulmonary ultrasonography in the period from November 2016 to March 2017 were analyzed, and all were admitted to an intensive care unit of a private hospital in Belo Horizonte, Minas Gerais. The lung ultrasonographies were performed by three different professionals, termed A, B and C, and the time interval between each lung ultrasonography was less than 3 hours. The only visualized chest zones were the anterior and lateral, defined as right and left anterior (1) zones (Z1R and Z1L, respectively), which were delimited by the clavicle, the sternum and the horizontal line perpendicular to the xiphoid process and anterior axillary line. The right and left lateral (2) zones (Z2R and Z2L, respectively) covered the lateral area between the anterior and posterior axillary lines, with the lower limit being the same horizontal line corresponding to the height of the xiphoid process. A lung zone was considered positive for B lines upon visualization of three or more of these lines, suggesting the presence of alveolar-interstitial syndrome. Using the Kappa value, we evaluated the agreement among the four zones according to the execution of each pair of professionals (AB, AC and BC).
Approximately 80% of the areas that were visualized showed a moderate to substantial agreement, with the Kappa values ranging from 0.41 - 079 (p < 0.05; 95% CI). The highest levels of agreement occurred in the upper zones Z1R and Z1L between subgroups AC and BC, with a Kappa of approximately 0.65 (p < 0.001). In turn, Z2L showed one of the lowest agreements, with a Kappa of 0.36.
The possible limitation of an examiner-dependent effect on lung ultrasounds was not found in this study, suggesting the good reproducibility of this diagnostic modality at the bedside.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2015;27(3):228-234
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20150037
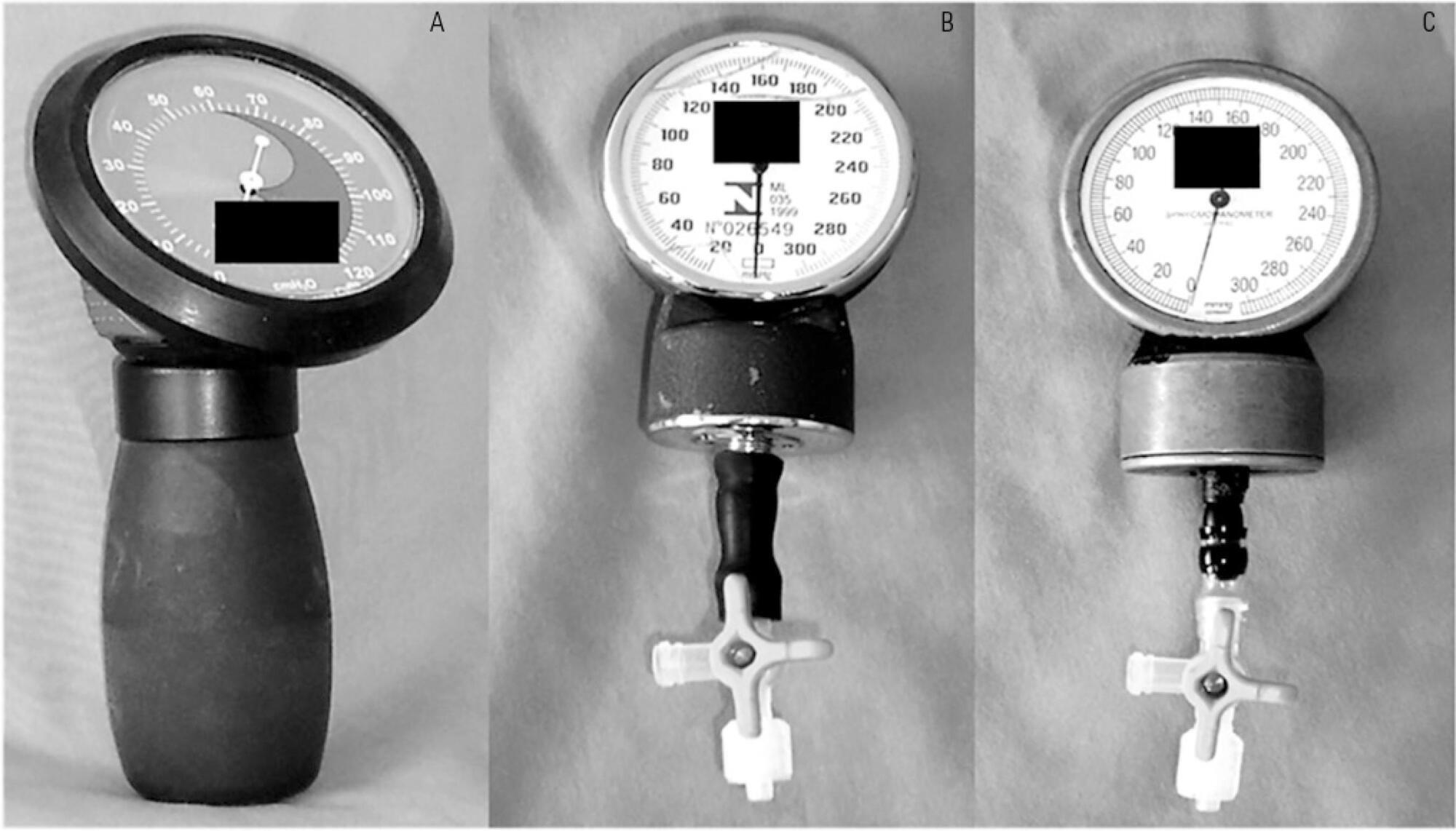
To test the agreement between two handcrafted devices and a cuff-specific manometer.
The agreement between two handcrafted devices adapted to measure tracheal tube cuff pressure and a cuff-specific manometer was tested on 79 subjects. The cuff pressure was measured with a commercial manometer and with two handcrafted devices (HD) assembled with aneroid sphygmomanometers (HD1 and HD2). The data were compared using Wilcoxon and Spearman tests, the intraclass correlation coefficient (ICC) and limit-of-agreement analysis.
Cuff pressures assessed with handcrafted devices were significantly different from commercial device measurements (pressures were higher when measured with HD1 and lower with HD2). The ICCs between the commercial device and HD1 and HD2 were excellent (ICC = 0.8 p < 0.001) and good (ICC = 0.66, p < 0.001), respectively. However, the Bland- Altman plots showed wide limits of agreement between HD1 and HD2 and the commercial device.
The handcrafted manometers do not provide accurate cuff pressure measurements when compared to a cuff-specific device and should not be used to replace the commercial cuff manometers in mechanically ventilated patients.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2015;27(2):105-112
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20150020
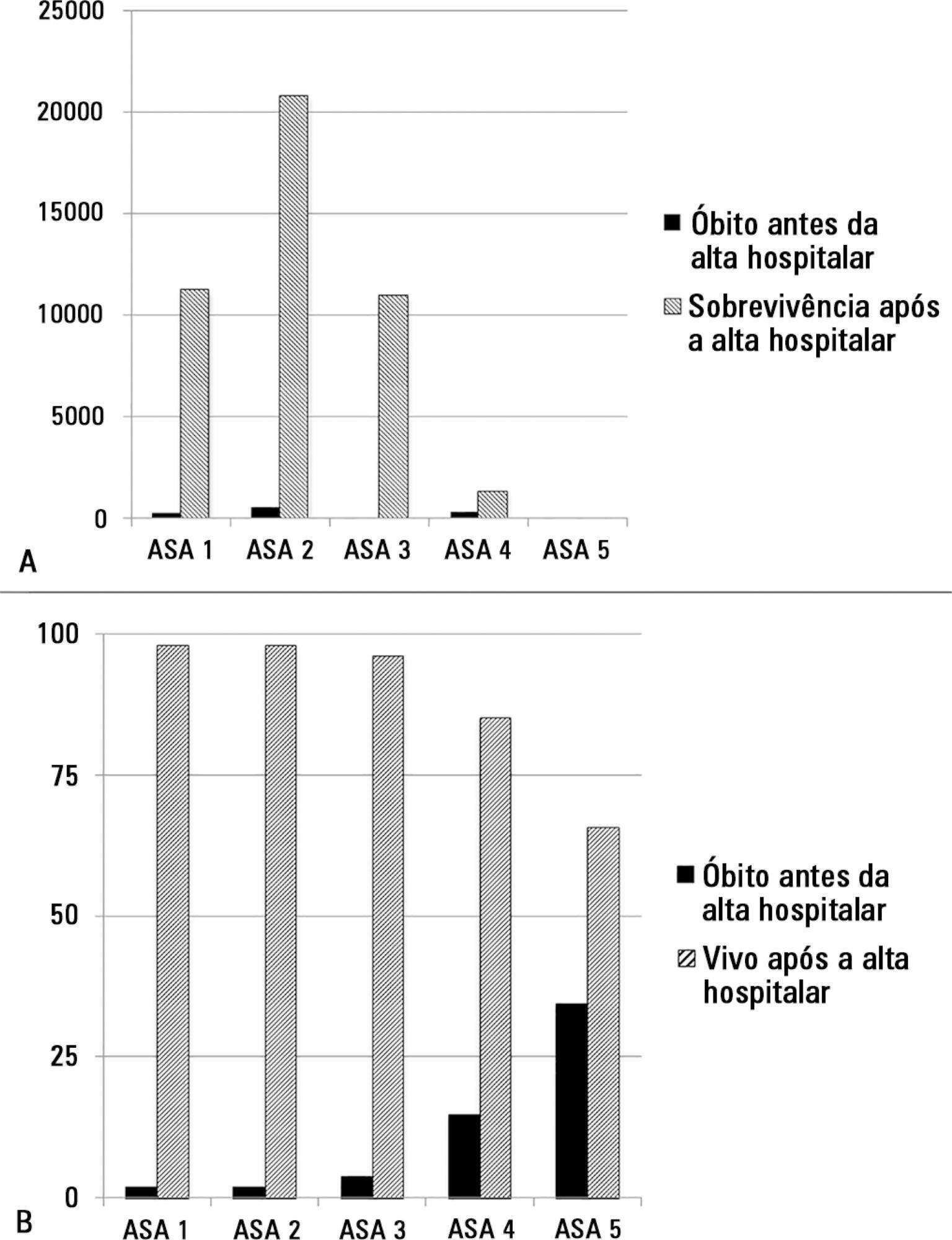
The European Surgical Outcomes Study described mortality following in-patient surgery. Several factors were identified that were able to predict poor outcomes in a multivariate analysis. These included age, procedure urgency, severity and type and the American Association of Anaesthesia score. This study describes in greater detail the relationship between the American Association of Anaesthesia score and postoperative mortality.
Patients in this 7-day cohort study were enrolled in April 2011. Consecutive patients aged 16 years and older undergoing inpatient non-cardiac surgery with a recorded American Association of Anaesthesia score in 498 hospitals across 28 European nations were included and followed up for a maximum of 60 days. The primary endpoint was in-hospital mortality. Decision tree analysis with the CHAID (SPSS) system was used to delineate nodes associated with mortality.
The study enrolled 46,539 patients. Due to missing values, 873 patients were excluded, resulting in the analysis of 45,666 patients. Increasing American Association of Anaesthesia scores were associated with increased admission rates to intensive care and higher mortality rates. Despite a progressive relationship with mortality, discrimination was poor, with an area under the ROC curve of 0.658 (95% CI 0.642 - 0.6775). Using regression trees (CHAID), we identified four discrete American Association of Anaesthesia nodes associated with mortality, with American Association of Anaesthesia 1 and American Association of Anaesthesia 2 compressed into the same node.
The American Association of Anaesthesia score can be used to determine higher risk groups of surgical patients, but clinicians cannot use the score to discriminate between grades 1 and 2. Overall, the discriminatory power of the model was less than acceptable for widespread use.
Search
Search in:
Case reports (56) Child (53) Coronavirus infections (34) COVID-19 (46) Critical care (116) Critical illness (54) Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (26) Infant, newborn (27) Intensive care (72) Intensive care units (256) Intensive care units, pediatric (31) mechanical ventilation (38) Mortality (76) Physical therapy modalities (28) Prognosis (61) Respiration, artificial (119) Respiratory insufficiency (26) risk factors (34) SARS-CoV-2 (28) Sepsis (98)