You searched for:"José da Natividade Menezes Júnior"
We found (1) results for your search.-
Original Article
Reproducibility of respiratory mechanics measurements in patients on invasive mechanical ventilation
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2020;32(3):398-404
Abstract
Original ArticleReproducibility of respiratory mechanics measurements in patients on invasive mechanical ventilation
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2020;32(3):398-404
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20200068
Views0See moreABSTRACT
Objective:
To evaluate the intra- and interexaminer reproducibility of measurements of the resistance and static and dynamic compliance of the respiratory system in patients on mechanical ventilation.
Methods:
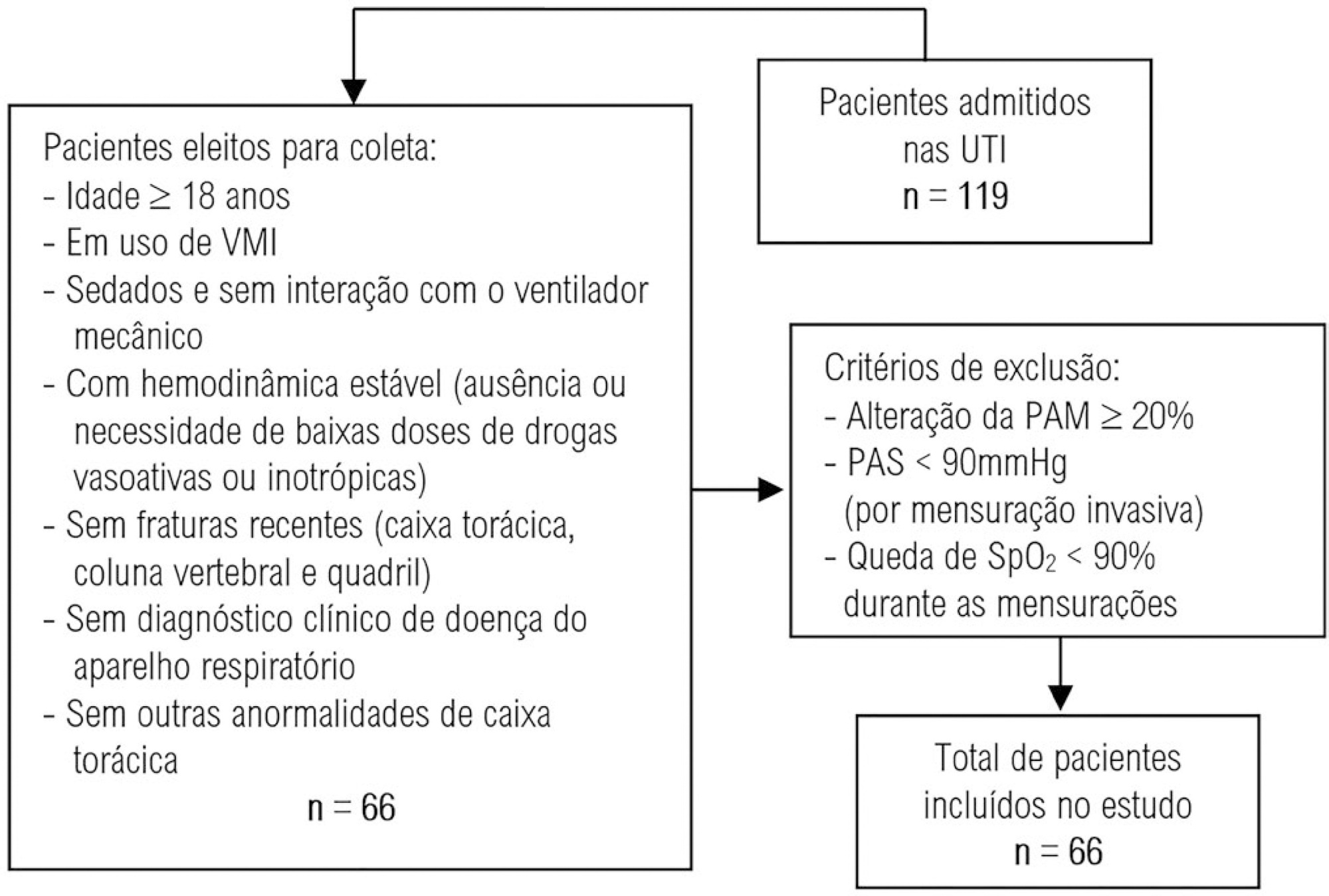
This was an analytical study conducted with individuals aged ≥ 18 years who were on invasive mechanical ventilation and had no clinical diagnosis of respiratory system disease and/or chest abnormality. Three measurements of respiratory mechanics were performed with a 1-minute interval between them. The first and third measurements were performed by examiner A, the second by examiner B. The values for the resistance and static and dynamic compliance of the respiratory system were compared using the intraclass correlation coefficient.
Results:
A total of 198 measurements of respiratory mechanics were performed for 66 patients on mechanical ventilation. The patients had a mean age of 52.6 ± 18.6 years and a mean body mass index of 21.6 ± 2.1kg/m2; a surgical profile (61.5%) and female sex (53.8%) were predominant. Mean values were obtained for the three measurements of respiratory system resistance (A1: 15.7 ± 6.8cmH2O/L/s; B1: 15.7 ± 6.4cmH2O/L/s and A2: 15.9 ± 6.2cmH2O/L/s), respiratory system static compliance (A1: 42.1 ± 13.7mL/cmH2O; B1: 42.4 ± 14.6mL/cmH2O and A2: 42.2 ± 14.5mL/cmH2O) and respiratory system dynamic compliance (A1: 21.3 ± 7.3mL/cmH2O; B1: 21.4 ± 7.5mL/cmH2O and A2: 21.3 ± 6.2mL/cmH2O). The intraclass correlation coefficient was also calculated for respiratory system resistance (R = 0.882 and p = 0.001; R = 0.949 and p = 0.001 – interexaminer A1 versus B and B versus A2, respectively; R = 0.932 and p = 0.001 – intraexaminer); respiratory system static compliance (R = 0.951 and p = 0.001; R = 0.958 and p = 0.001 – interexaminer A1 versus B and B versus A2, respectively; R = 0.965 and p = 0.001 – intraexaminer) and respiratory system dynamic compliance (R = 0.957 and p = 0.001; R = 0.946 and p = 0.001 – interexaminer A1 versus B and B versus A2, respectively; R = 0.926 and p = 0.001 – intraexaminer).
Conclusion:
The measurements of resistance and static and dynamic compliance of the respiratory system show good intra- and interexaminer reproducibility for ventilated patients.
Search
Search in:
KEY WORDS
Case reports Child Coronavirus infections COVID-19 Critical care Critical illness Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation Infant, newborn Intensive care Intensive care units Intensive care units, pediatric mechanical ventilation Mortality Physical therapy modalities Prognosis Respiration, artificial Respiratory insufficiency risk factors SARS-CoV-2 Sepsis




