Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2015;27(3):228-234
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20150037
To test the agreement between two handcrafted devices and a cuff-specific manometer.
The agreement between two handcrafted devices adapted to measure tracheal tube cuff pressure and a cuff-specific manometer was tested on 79 subjects. The cuff pressure was measured with a commercial manometer and with two handcrafted devices (HD) assembled with aneroid sphygmomanometers (HD1 and HD2). The data were compared using Wilcoxon and Spearman tests, the intraclass correlation coefficient (ICC) and limit-of-agreement analysis.
Cuff pressures assessed with handcrafted devices were significantly different from commercial device measurements (pressures were higher when measured with HD1 and lower with HD2). The ICCs between the commercial device and HD1 and HD2 were excellent (ICC = 0.8 p < 0.001) and good (ICC = 0.66, p < 0.001), respectively. However, the Bland- Altman plots showed wide limits of agreement between HD1 and HD2 and the commercial device.
The handcrafted manometers do not provide accurate cuff pressure measurements when compared to a cuff-specific device and should not be used to replace the commercial cuff manometers in mechanically ventilated patients.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2014;26(4):367-372
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20140056
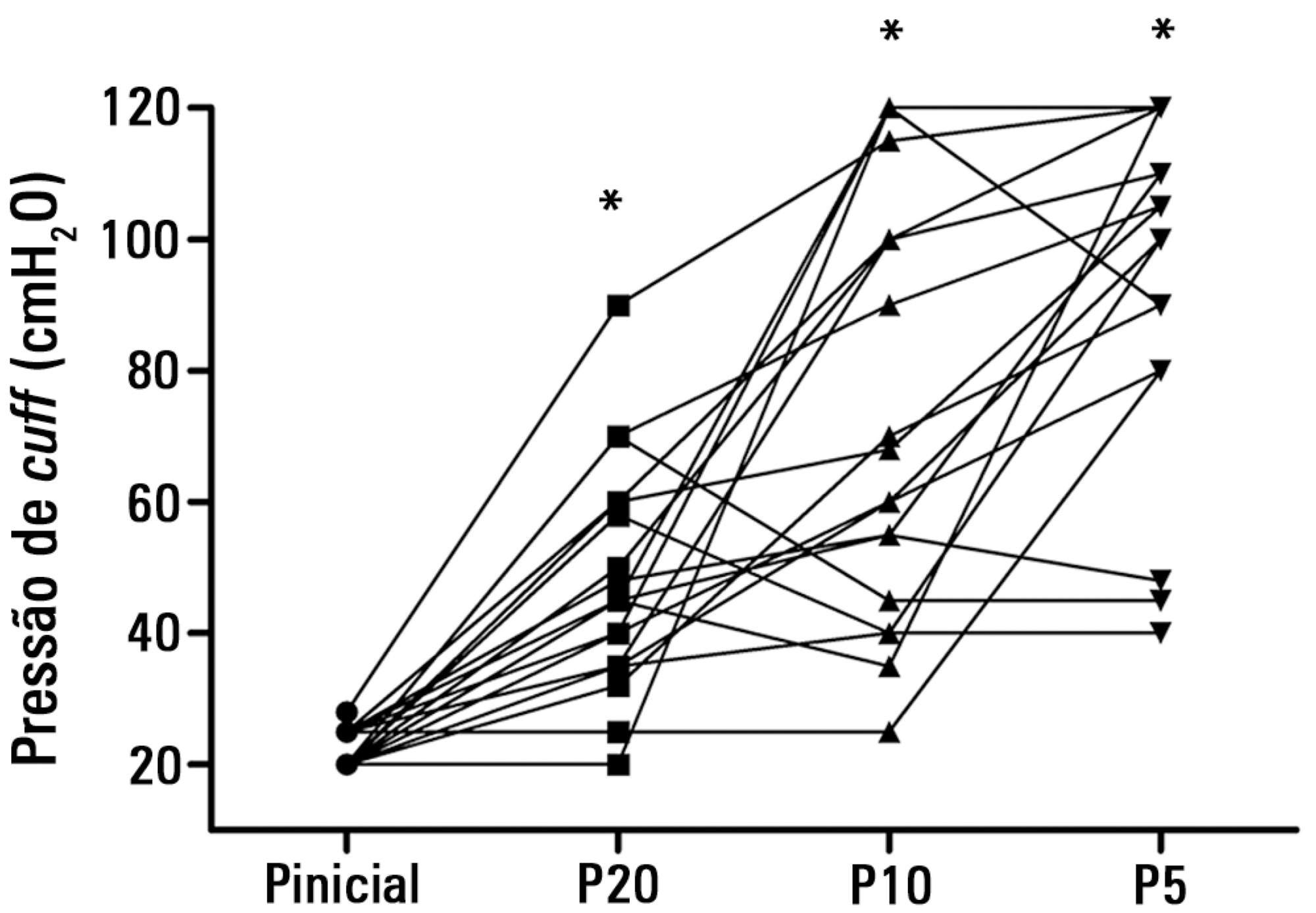
To test the effectiveness of using a cuff pressure relief valve technique to maintain cuff pressure levels within the normal in vitro range (Phase 1) in patients admitted to the intensive care unit (Phase 2) and to test the reproducibility of the technique using different syringes.
In Phase 1, a tracheal tube was inserted into a trachea model. Ten- and 20mL syringes were used to inflate the cuff through the tracheal tube. The cuff was slowly and steadily inflated until the syringe plunger would move in the opposite direction of the application. After the plunger stopped, the cuff pressures were recorded. In Phase 2, the same maneuvers for inflating the cuff were performed on 20 patients using 5, 10, and 20mL syringes and were compared with manometer measurements. The intraclass correlation coefficient and Bland-Altman analysis were employed to determine the reproducibility and agreement between syringes. Data were expressed as medians (interquartile range).
There was no reproducibility between syringes with an intraclass correlation coefficient ranging between -0.33 and 0.8 (p>0.05). The pressures generated with the syringes were higher than the pressures generated using a standard manometer: the 5mL syringe pressure was 105cmH2O (82.5-120cmH2O), the 10mL syringe pressure was 69cmH2O (47.5-111.3cmH2O), and the 20mL syringe pressure was 45cmH2O (35-59.5cmH2O). The Bland-Altman analysis confirmed the large bias and variability between the syringes used, compared with the manometer.
The use of syringes is not an effective technique for determining the cuff pressure in patients admitted to the intensive care unit.