You searched for:"Daniel Garros"
We found (6) results for your search.-
Original Article
Knowledge regarding extracorporeal membrane oxygenation management among Brazilian pediatric intensivists: a cross-sectional survey
Crit Care Sci. 2023;35(1):57-65
Abstract
Original ArticleKnowledge regarding extracorporeal membrane oxygenation management among Brazilian pediatric intensivists: a cross-sectional survey
Crit Care Sci. 2023;35(1):57-65
DOI 10.5935/2965-2774.20230350-pt
Views4ABSTRACT
Objective:
To assess Brazilian pediatric intensivists’ general knowledge of extracorporeal membrane oxygenation, including evidence for its use, the national funding model, indications, and complications.
Methods:
This was a multicenter cross-sectional survey including 45 Brazilian pediatric intensive care units. A convenience sample of 654 intensivists was surveyed regarding their knowledge on managing patients on extracorporeal membrane oxygenation, its indications, complications, funding, and literature evidence.
Results:
The survey addressed questions regarding the knowledge and experience of pediatric intensivists with extracorporeal membrane oxygenation, including two clinical cases and 6 optional questions about the management of patients on extracorporeal membrane oxygenation. Of the 45 invited centers, 42 (91%) participated in the study, and 412 of 654 (63%) pediatric intensivists responded to the survey. Most pediatric intensive care units were from the Southeast region of Brazil (59.5%), and private/for-profit hospitals represented 28.6% of the participating centers. The average age of respondents was 41.4 (standard deviation 9.1) years, and the majority (77%) were women. Only 12.4% of respondents had taken an extracorporeal membrane oxygenation course. Only 19% of surveyed hospitals have an extracorporeal membrane oxygenation program, and only 27% of intensivists reported having already managed patients on extracorporeal membrane oxygenation. Specific extracorporeal membrane oxygenation management questions were responded to by only 64 physicians (15.5%), who had a fair/good correct response rate (median 63.4%; range 32.8% to 91.9%).
Conclusion:
Most Brazilian pediatric intensivists demonstrated limited knowledge regarding extracorporeal membrane oxygenation, including its indications and complications. Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation is not yet widely available in Brazil, with few intensivists prepared to manage patients on extracorporeal membrane oxygenation and even fewer intensivists recognizing when to refer patients to extracorporeal membrane oxygenation centers.
Keywords:ChildExtracorporeal membrane oxygenationHealth knowledge, attitudes, practicePediatric intensive care unitsSurvey and questionnairesSee more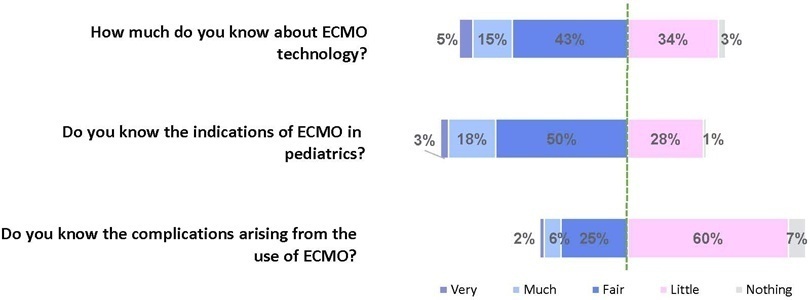
-
Original Article
Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation for respiratory failure in children: the years before and after the 2009 H1N1 pandemic
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2021;33(4):544-548
Abstract
Original ArticleExtracorporeal membrane oxygenation for respiratory failure in children: the years before and after the 2009 H1N1 pandemic
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2021;33(4):544-548
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20210082
Views0ABSTRACT
Objective:
To evaluate whether there was any impact on the number of pediatric extracorporeal membrane oxygenation runs and survival rates in the years subsequent to the 2009 pandemic.
Methods:
We studied two different periods of extracorporeal membrane oxygenation support for respiratory failure in children by analyzing datasets from the Extracorporeal Life Support Organization. Autoregressive integrated moving average models were constructed to estimate the effect of the pandemic. The year 2009 was the year of intervention (the H1N1 epidemic) in an interrupted time series model. Data collected from 2001 – 2010 were considered preintervention, and data collected from 2010 – 2017 were considered postintervention.
Results:
There was an increase in survival rates in the period 2010 – 2017 compared to 2001 – 2010 (p < 0.0001), with a significant improvement in survival when extracorporeal membrane oxygenation was performed for acute respiratory failure due to viral pneumonia. The autoregressive integrated moving average model shows an increase of 23 extracorporeal membrane oxygenation runs per year, prior to the point of the level effect (2009). In terms of survival, the preslope shows that there was no significant increase in survival rates before 2009 (p = 0.41), but the level effect was nearly significant after two years (p = 0.05), with a 6% increase in survival. In four years, there was an 8% (p = 0.03) increase in survival, and six years after 2009, there was up to a 10% (p = 0.026) increase in survival.
Conclusion:
In the years following 2009, there was a significant, global incremental increase in the extracorporeal membrane oxygenation survival rates for all runs, mainly due to improvements in the technology and treatment protocols for acute respiratory failure related to viral pneumonia and other respiratory conditions.
Keywords:ARDSChildExtracorporeal membrane oxygenationH1N1H1N1 SubtypeHumanInfluenzaInfluenza A virusPandemicsRespiratory distress syndromeRespiratory insufficiencySurvival rateSee more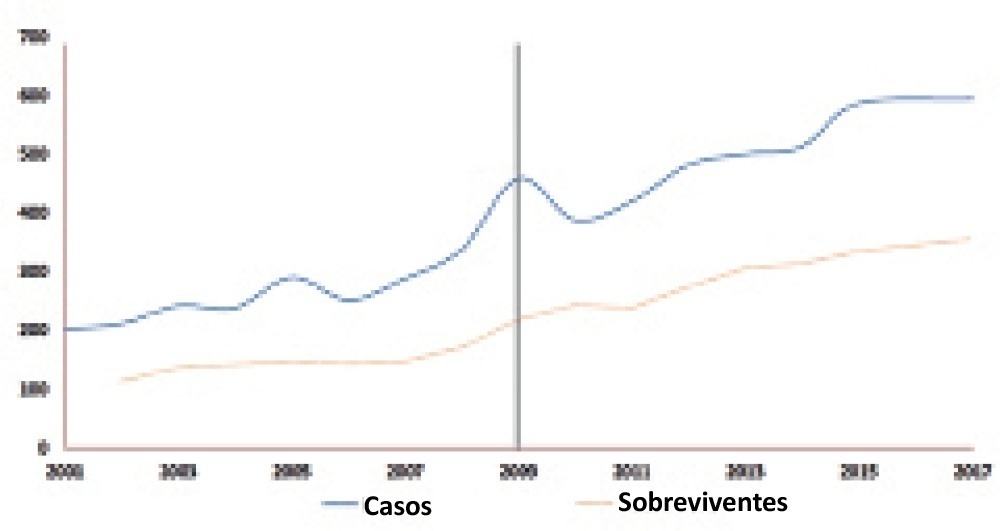
-
Original Article
Clinical practices related to high-flow nasal cannulas in pediatric critical care in Brazil compared to other countries: a Brazilian survey
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2021;33(3):384-393
Abstract
Original ArticleClinical practices related to high-flow nasal cannulas in pediatric critical care in Brazil compared to other countries: a Brazilian survey
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2021;33(3):384-393
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20210055
Views1ABSTRACT
Objective:
To describe current clinical practices related to the use of high-flow nasal cannula therapy by Brazilian pediatric intensivists and compare them with those in other countries.
Methods:
A questionnaire was administered to pediatric intensivists in North and South America, Asia, Europe, and Australia/New Zealand for the main study. We compared the Brazilian cohort with cohorts in the United States of America, Canada, the United Kingdom, and India
Results:
Overall, 501 physicians responded, 127 of which were in Brazil. Only 63.8% of respondents in Brazil had a high-flow nasal cannula available, in contrast to 100% of respondents in the United Kingdom, Canada, and the United States. The attending physician was responsible for the decision to start a high-flow nasal cannula according to 61.2% respondents in Brazil, 95.5% in the United Kingdom, 96.6% in the United States, 96.8% in Canada, and 84.7% in India. A total of 62% of respondents in Brazil, 96.3% in the United Kingdom, 96.6% in the United States, 96.8% in Canada, and 84.7% in India reported that the attending physician was responsible for the decision to wean or modify the high-flow nasal cannula settings. When high-flow nasal cannula therapy failed due to respiratory distress/failure, 82% of respondents in Brazil would consider a trial of noninvasive ventilation before endotracheal intubation, compared to 93% in the United Kingdom, 88% in the United States, 91.5% in Canada, and 76.8% in India. More Brazilian intensivists (6.5%) than intensivists in the United Kingdom, United States, and India (1.6% for all) affirmed using sedatives frequently with high-flow nasal cannulas.
Conclusion:
The availability of high-flow nasal cannulas in Brazil is still not widespread. There are some divergences in clinical practices between Brazilian intensivists and their colleagues abroad, mainly in processes and decision-making about starting and weaning high-flow nasal cannula therapy.
Keywords:BrazilCanadaCannulaIndiaIntensive careIntensive care units, pediatricNoninvasive ventilationOxygen inhalation therapyRespiratory insufficiencySurveys and questionnairesUnited KingdomUnited StatesSee more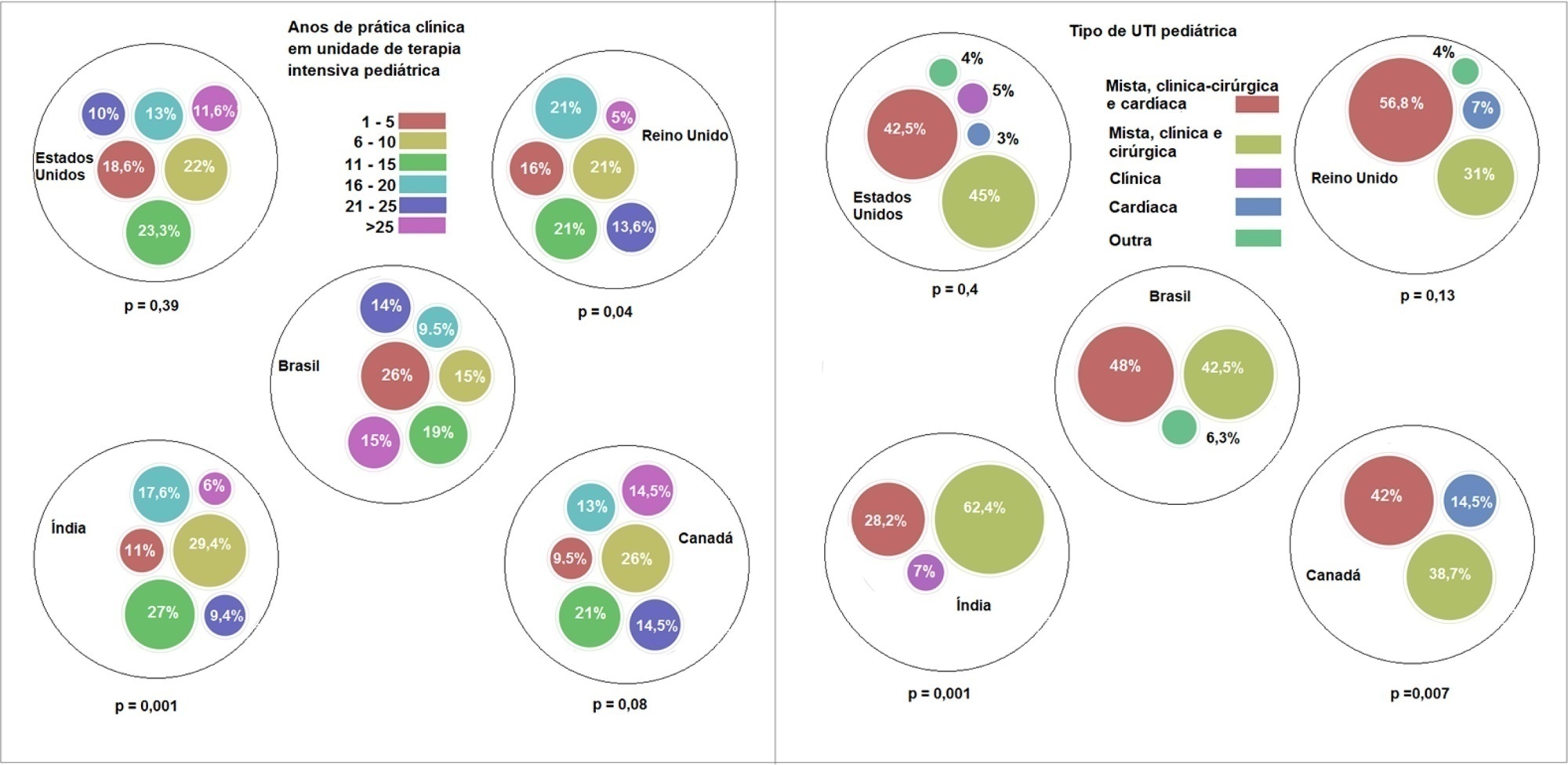
-
Review Articles
Difficult decisions in pediatric practice and moral distress in the intensive care unit
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2018;30(2):226-232
Abstract
Review ArticlesDifficult decisions in pediatric practice and moral distress in the intensive care unit
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2018;30(2):226-232
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20180039
Views0ABSTRACT
In an ethical dilemma, there is always an option that can be identified as the best one to be chosen. When it is impossible to adopt such option, the situation can lead professionals to experience moral distress. This review aims to define the issue of moral distress and propose coping strategies. Systematic searches in the MEDLINE/PubMed and SciELO databases were conducted using the keywords “moral distress” and “moral suffering” in articles published between 2000 and 2017. This review was non-exhaustive and contextual, with a focus on definitions, etiologies and methods of resolution for moral distress. In the daily practice of intensive care, moral distress was commonly related to the prolongation of patients’ suffering and feelings of helplessness, as well as difficulties in communication among team members. Coping strategies for moral distress included organizational, personal and administrative actions. Actions such as workload management, mutual support among professionals and the development of techniques to cultivate open communication, reflection and questioning within the multidisciplinary team were identified. In clinical practice, health professionals need to be recognized as moral agents, and the development of moral courage was considered helpful to overcome ethical dilemmas and interprofessional conflicts. Both in pediatric and adult intensive care, professionals are challenged by questions about their practice, and they may experience moral distress. This suffering can be minimized and solved by understanding that the focus is always on the patient and acting with moral courage and good communication in an environment of mutual respect.
Keywords:Attitudes of health personnelChildConflict (psychology)Decision making/ethicsEthics, clinicalInfantIntensive care units, pediatric/ethicsMoralsStress, psychologicalSee more -
Terminal ill children and dnd-of-life practices in the pediatric intensive care units
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2007;19(3):359-363
Abstract
Terminal ill children and dnd-of-life practices in the pediatric intensive care units
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2007;19(3):359-363
DOI 10.1590/S0103-507X2007000300017
Views0See moreBACKGROUND AND OBJECTIVES: To analyze and discuss the medical practices related to the end-of-life care provided to children admitted to pediatric intensive care unit (PICU) in Brazil and in some countries located in the northern hemisphere. CONTENTS: Selected articles on end-of-life care published during the last years searching the PubMed, MedLine and LILACS database, with special interest on studies of death conducted in pediatric intensive care units in Brazil, Latin America, Europe and North America, using the following key words: death, bioethics, PICU, cardiopulmonary resuscitation and life support limitation (LSL). CONCLUSIONS: In North America and North Europe, the incidence of LSL is greater (60%-80%) than in south Europe and Latin America (30%-40%). In Brazil the incidence of LSL depends on the region and in the last decade it is increasing from 6% to 40%; being the do-not-reanimated order the most frequent mode of LSL. The family participation in the decision making process is not stimulated and incipient. Based on the literature review and on their experience the authors present the measures that they consider most efficient and recommended for managing this situation in our region. Despite of LSL in children with terminal and irreversible disease be considered ethically, morally and legally; these measures are still adopted in a very few circumstances in our region. Urgent changes in this behavior are necessary, specially related to family participation in the decision-making process.
-
Family participation in the decision making process for life support limitation: paternalism, beneficence and omission
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2007;19(3):364-368
Abstract
Family participation in the decision making process for life support limitation: paternalism, beneficence and omission
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2007;19(3):364-368
DOI 10.1590/S0103-507X2007000300018
Views0BACKGROUND AND OBJECTIVES: To analyze and discuss the medical aspects related to the family involvement in the decision making process regarding end of life care to children admitted to the pediatric intensive care unit (PICU). CONTENTS: The authors selected articles on end-of-life care published during the last years searching the PubMed, MedLine and LILACS database, with special interest on studies of death conducted in pediatric intensive care units in Brazil, Latin America, Europe and North America, using the following keywords: death, bioethics, PICU, decision-making, terminal care, parents interview and life support limitation (LSL). CONCLUSIONS: Several studies have demonstrated the relevance of the family participation in the decision making process regarding LSL. In our region the family participation in this process is not stimulated and valued, ranging from 20%-55%. The authors present a practical sequence for discussing and defining LSL with the families. Despite of the family participation in the decision making process for LSL be legally, morally and ethically accepted in developed countries, this approach is adopted in a very few cases in our region. To explain this difficulty observed among the Brazilian pediatric intensivist, some studies should be conducted in our region.
Keywords:bioethicsDeathDecision Makingparents interview and life support limitationpediatric intensive care unitSee more
Search
Search in:
KEY WORDS
Case reports Child Coronavirus infections COVID-19 Critical care Critical illness Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation Infant, newborn Intensive care Intensive care units Intensive care units, pediatric mechanical ventilation Mortality Physical therapy modalities Prognosis Respiration, artificial Respiratory insufficiency risk factors SARS-CoV-2 Sepsis




