Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2022;34(3):360-366
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20220477-en
To investigate the applicability of the Respiratory Rate-Oxygenation Index to identify the risk of high-flow nasal cannula failure in post-extubation pneumonia patients.
This was a 2-year retrospective observational study conducted in a reference hospital in Bogotá, Colombia. All patients in whom post-extubation high-flow nasal cannula therapy was used as a bridge to extubation were included in the study. The Respiratory Rate-Oxygenation Index was calculated to assess the risk of post-extubation high-flow nasal cannula failure.
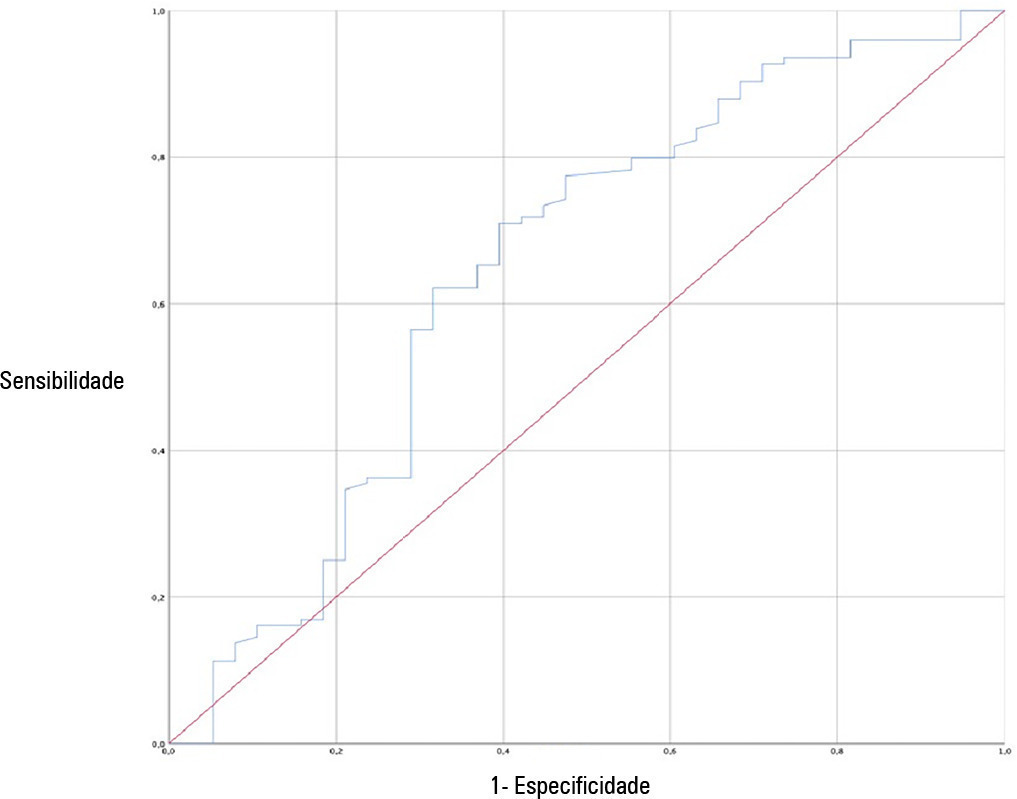
A total of 162 patients were included in the study. Of these, 23.5% developed high-flow nasal cannula failure. The Respiratory Rate-Oxygenation Index was significantly lower in patients who had high-flow nasal cannula failure [median (IQR): 10.0 (7.7 - 14.4) versus 12.6 (10.1 - 15.6); p = 0.006]. Respiratory Rate-Oxygenation Index > 4.88 showed a crude OR of 0.23 (95%CI 0.17 - 0.30) and an adjusted OR of 0.89 (95%CI 0.81 - 0.98) stratified by severity and comorbidity. After logistic regression analysis, the Respiratory Rate-Oxygenation Index had an adjusted OR of 0.90 (95%CI 0.82 - 0.98; p = 0.026). The area under the Receiver Operating Characteristic curve for extubation failure was 0.64 (95%CI 0.53 - 0.75; p = 0.06). The Respiratory Rate-Oxygenation Index did not show differences between patients who survived and those who died during the intensive care unit stay.
The Respiratory Rate-Oxygenation Index is an accessible tool to identify patients at risk of failing high-flow nasal cannula post-extubation treatment. Prospective studies are needed to broaden the utility in this scenario.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2021;33(3):384-393
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20210055
To describe current clinical practices related to the use of high-flow nasal cannula therapy by Brazilian pediatric intensivists and compare them with those in other countries.
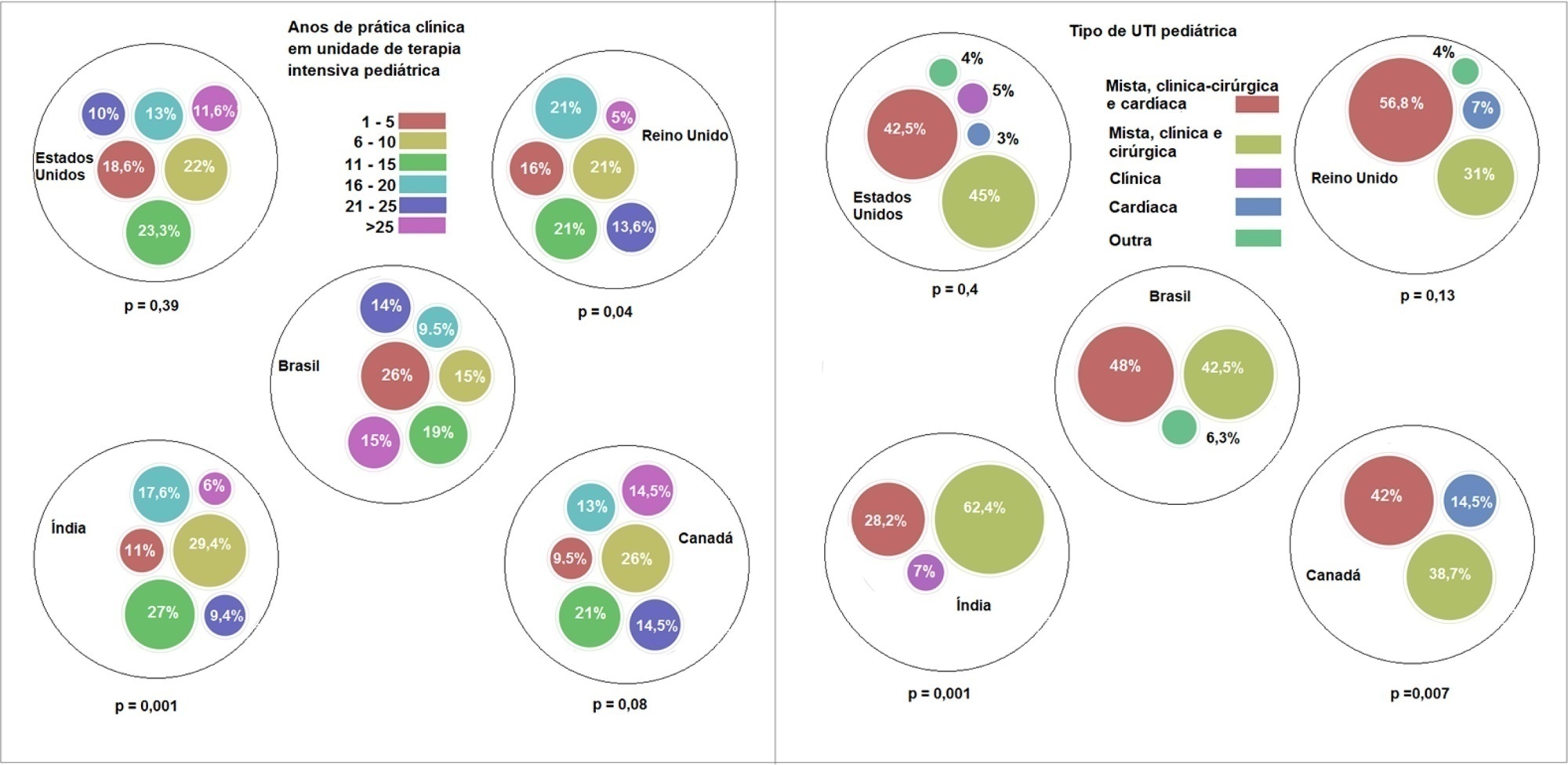
A questionnaire was administered to pediatric intensivists in North and South America, Asia, Europe, and Australia/New Zealand for the main study. We compared the Brazilian cohort with cohorts in the United States of America, Canada, the United Kingdom, and India
Overall, 501 physicians responded, 127 of which were in Brazil. Only 63.8% of respondents in Brazil had a high-flow nasal cannula available, in contrast to 100% of respondents in the United Kingdom, Canada, and the United States. The attending physician was responsible for the decision to start a high-flow nasal cannula according to 61.2% respondents in Brazil, 95.5% in the United Kingdom, 96.6% in the United States, 96.8% in Canada, and 84.7% in India. A total of 62% of respondents in Brazil, 96.3% in the United Kingdom, 96.6% in the United States, 96.8% in Canada, and 84.7% in India reported that the attending physician was responsible for the decision to wean or modify the high-flow nasal cannula settings. When high-flow nasal cannula therapy failed due to respiratory distress/failure, 82% of respondents in Brazil would consider a trial of noninvasive ventilation before endotracheal intubation, compared to 93% in the United Kingdom, 88% in the United States, 91.5% in Canada, and 76.8% in India. More Brazilian intensivists (6.5%) than intensivists in the United Kingdom, United States, and India (1.6% for all) affirmed using sedatives frequently with high-flow nasal cannulas.
The availability of high-flow nasal cannulas in Brazil is still not widespread. There are some divergences in clinical practices between Brazilian intensivists and their colleagues abroad, mainly in processes and decision-making about starting and weaning high-flow nasal cannula therapy.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2020;32(2):235-243
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20200038
To identify the neonatal, pediatric and mixed (neonatal and pediatric) intensive care units in Brazil that use cuffed tracheal tubes in clinical practice and to describe the characteristics related to the use of protocols and monitoring.
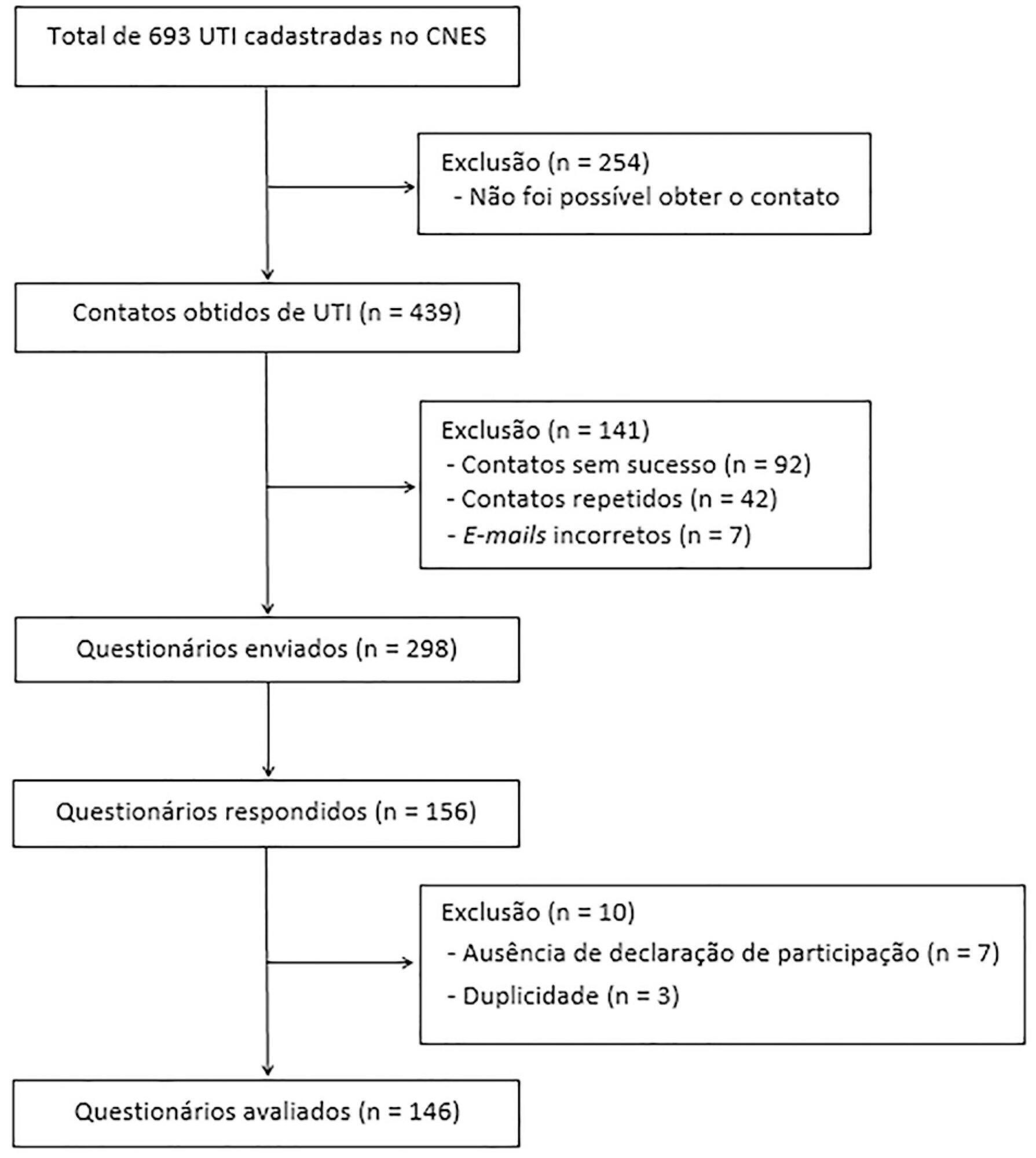
To identify the intensive care units in Brazil, the Ministry of Health’s National Registry of Health Facilities was accessed, and information was collected on 693 registered intensive care units. This was an analytical cross-sectional survey conducted through electronic questionnaires sent to 298 neonatal, pediatric and mixed intensive care units in Brazil.
This study analyzed 146 questionnaires (49.3% from neonatal intensive care units, 35.6% from pediatric intensive care units and 15.1% from mixed pediatric intensive care units). Most of the participating units (78/146) used cuffed tracheal tubes, with a predominance of use in pediatric intensive care units (52/78). Most of the units that used cuffed tracheal tubes applied a cuff pressure monitoring protocol (45/78). The use of cuff monitoring protocols was observed in intensive care units with a physical therapy service exclusive to the unit (38/61) and in those with a physical therapist present 24 hours/day (25/45). The most frequent cause of extubation failure related to the use of cuffed tracheal tubes in pediatric intensive care units was upper airway obstruction.
In this survey, the use of cuffed tracheal tubes and the application of a cuff pressure monitoring protocol was predominant in pediatric intensive care units. The use of a monitoring protocol was more common in intensive care units that had a physical therapist who was exclusive to the unit and was present 24 hours/day.
Search
Search in:
Case reports (56) Child (53) Coronavirus infections (34) COVID-19 (46) Critical care (116) Critical illness (54) Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (26) Infant, newborn (27) Intensive care (72) Intensive care units (256) Intensive care units, pediatric (31) mechanical ventilation (38) Mortality (76) Physical therapy modalities (28) Prognosis (61) Respiration, artificial (119) Respiratory insufficiency (26) risk factors (34) SARS-CoV-2 (28) Sepsis (98)