Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2022;34(3):360-366
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20220477-en
To investigate the applicability of the Respiratory Rate-Oxygenation Index to identify the risk of high-flow nasal cannula failure in post-extubation pneumonia patients.
This was a 2-year retrospective observational study conducted in a reference hospital in Bogotá, Colombia. All patients in whom post-extubation high-flow nasal cannula therapy was used as a bridge to extubation were included in the study. The Respiratory Rate-Oxygenation Index was calculated to assess the risk of post-extubation high-flow nasal cannula failure.
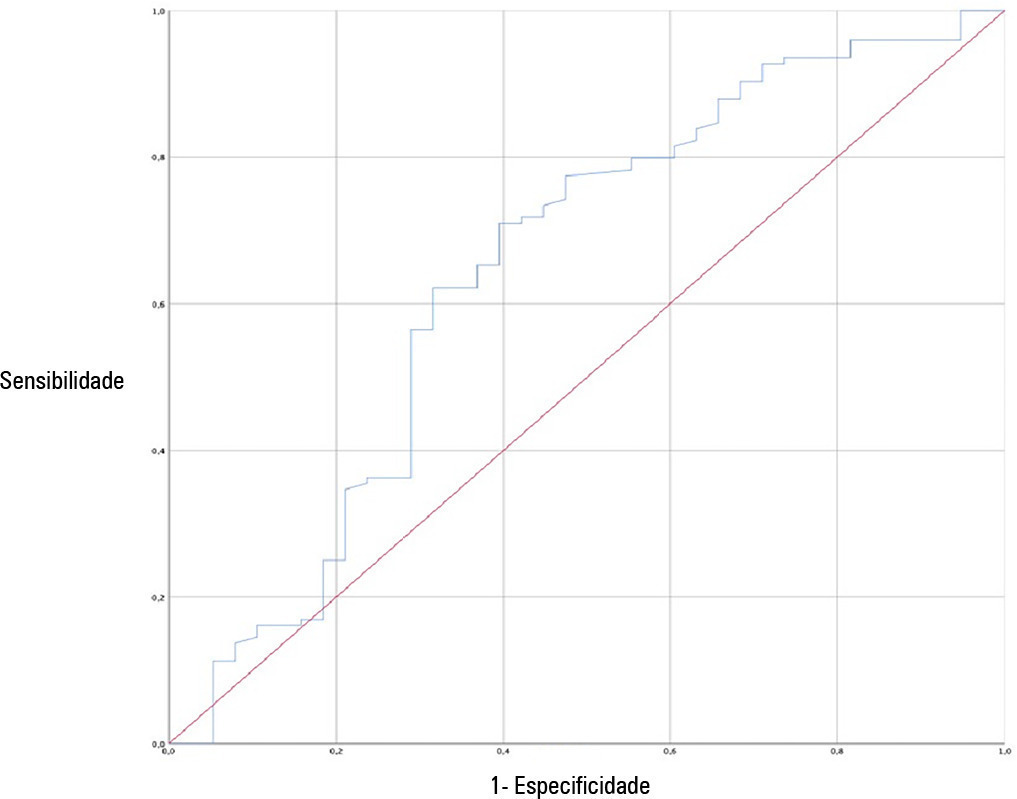
A total of 162 patients were included in the study. Of these, 23.5% developed high-flow nasal cannula failure. The Respiratory Rate-Oxygenation Index was significantly lower in patients who had high-flow nasal cannula failure [median (IQR): 10.0 (7.7 - 14.4) versus 12.6 (10.1 - 15.6); p = 0.006]. Respiratory Rate-Oxygenation Index > 4.88 showed a crude OR of 0.23 (95%CI 0.17 - 0.30) and an adjusted OR of 0.89 (95%CI 0.81 - 0.98) stratified by severity and comorbidity. After logistic regression analysis, the Respiratory Rate-Oxygenation Index had an adjusted OR of 0.90 (95%CI 0.82 - 0.98; p = 0.026). The area under the Receiver Operating Characteristic curve for extubation failure was 0.64 (95%CI 0.53 - 0.75; p = 0.06). The Respiratory Rate-Oxygenation Index did not show differences between patients who survived and those who died during the intensive care unit stay.
The Respiratory Rate-Oxygenation Index is an accessible tool to identify patients at risk of failing high-flow nasal cannula post-extubation treatment. Prospective studies are needed to broaden the utility in this scenario.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2021;33(4):537-543
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20210081
To compare gas exchange indices behavior by using liberal versus conservative oxygenation targets in patients with moderate to severe acute respiratory distress syndrome secondary to COVID-19 under invasive mechanical ventilation. We also assessed the influence of high FiO2 on respiratory system mechanics.
We prospectively included consecutive patients aged over 18 years old with a diagnosis of COVID-19 and moderate-severe acute respiratory distress syndrome. For each patient, we randomly applied two FiO2 protocols to achieve SpO2 88% - 92% or 96%. We assessed oxygenation indices and respiratory system mechanics.
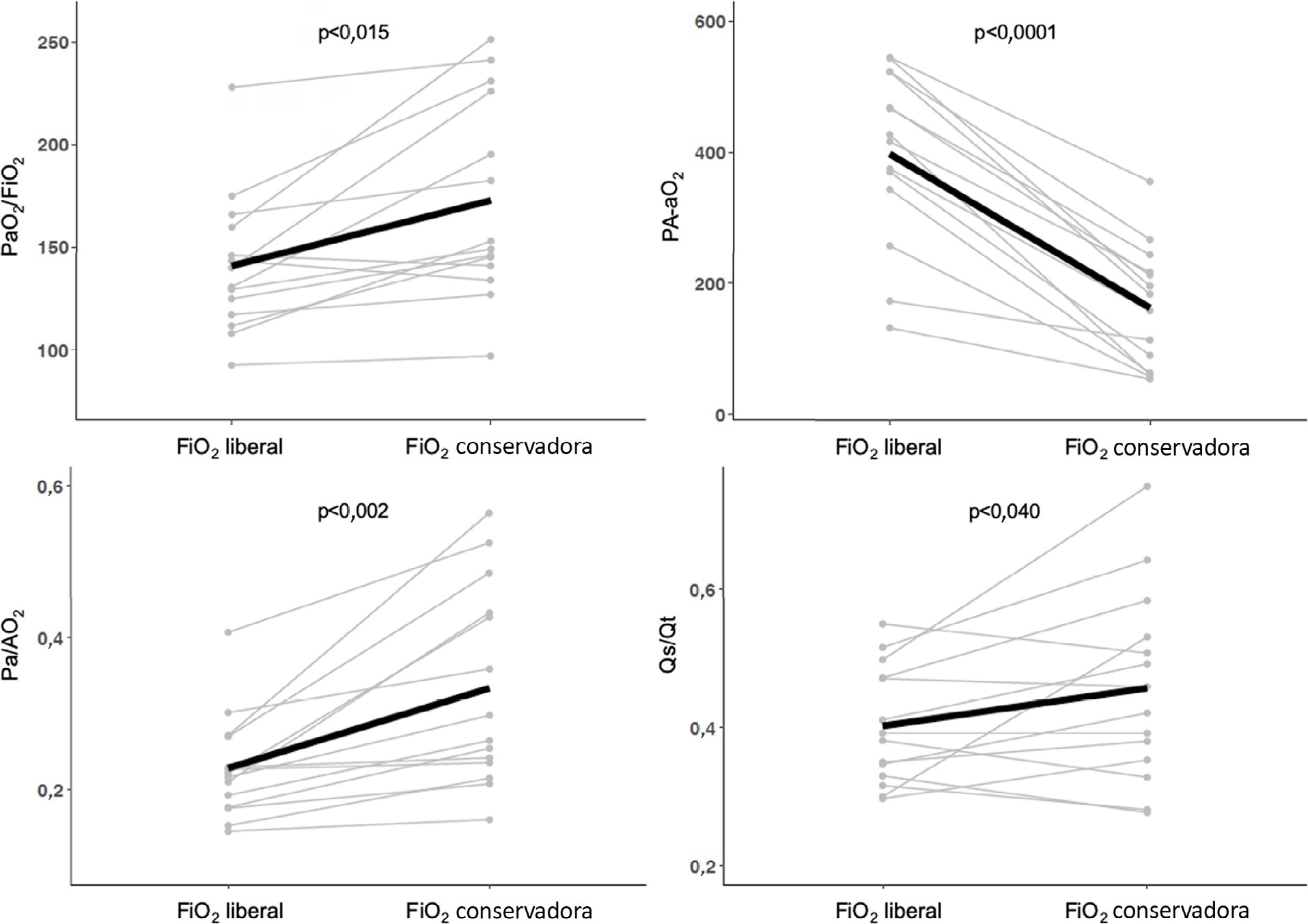
We enrolled 15 patients. All the oxygenation indices were significantly affected by the FiO2 strategy (p < 0.05) selected. The PaO2/FiO2 deteriorated, PA-aO2 increased and Pa/AO2 decreased significantly when using FiO2 to achieve SpO2 96%. Conversely, the functional shunt fraction was reduced. Respiratory mechanics were not affected by the FiO2 strategy.
A strategy aimed at liberal oxygenation targets significantly deteriorated gas exchange indices, except for functional shunt, in COVID-19-related acute respiratory distress syndrome. The respiratory system mechanics were not altered by the FiO2 strategy.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2021;33(1):154-166
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20210017
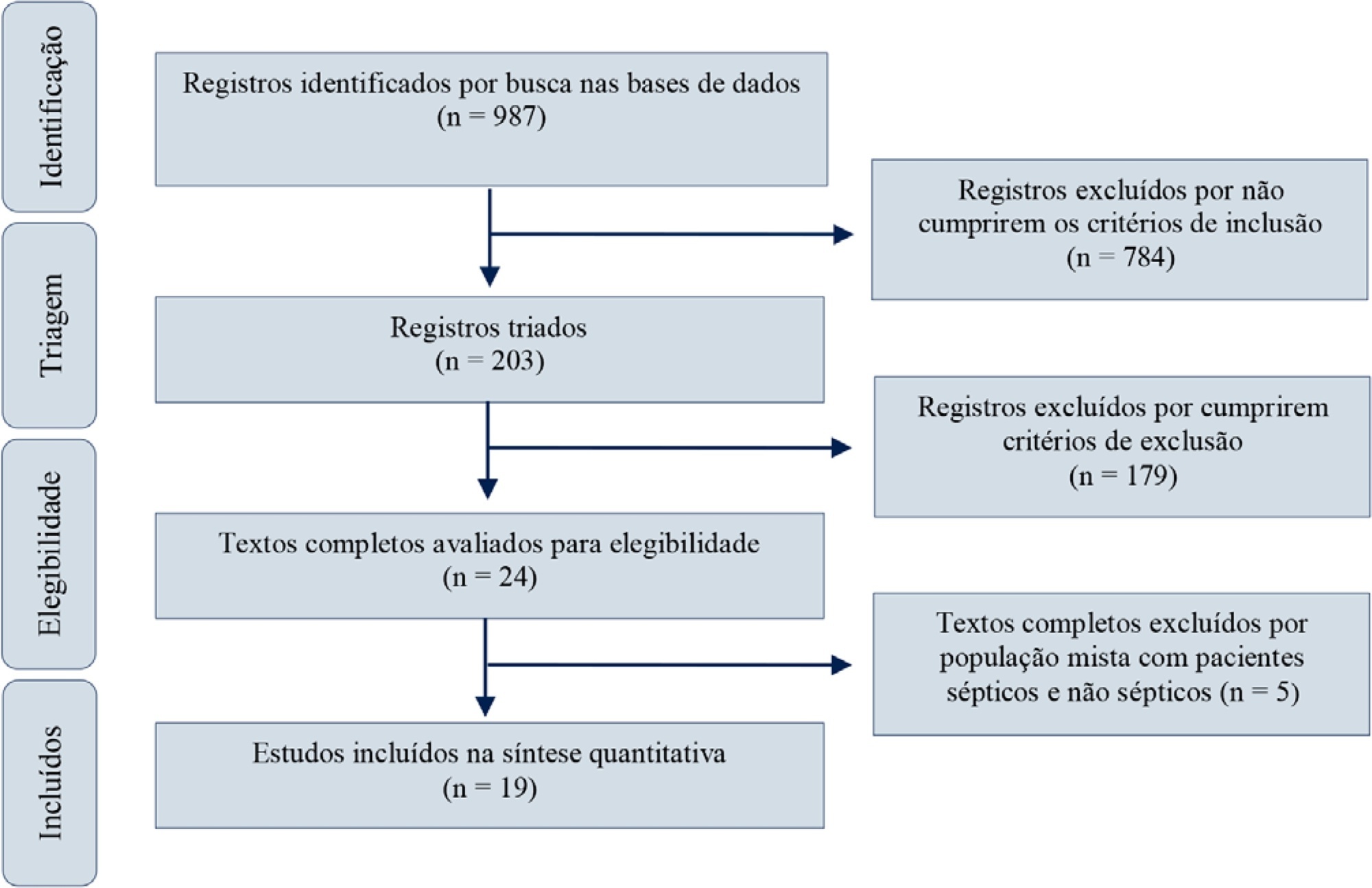
Red blood cell transfusion is thought to improve cell respiration during septic shock. Nevertheless, its acute impact on oxygen transport and metabolism in this condition remains highly debatable. The objective of this study was to evaluate the impact of red blood cell transfusion on microcirculation and oxygen metabolism in patients with sepsis and septic shock. We conducted a search in the MEDLINE®, Elsevier and Scopus databases. We included studies conducted in adult humans with sepsis and septic shock. A systematic review and meta-analysis were performed using the DerSimonian and Laird random-effects model. A p value < 0.05 was considered significant. Nineteen manuscripts with 428 patients were included in the analysis. Red blood cell transfusions were associated with an increase in the pooled mean venous oxygen saturation of 3.7% (p < 0.001), a decrease in oxygen extraction ratio of -6.98 (p < 0.001) and had no significant effect on the cardiac index (0.02L/minute; p = 0,96). Similar results were obtained in studies including simultaneous measurements of venous oxygen saturation, oxygen extraction ratio, and cardiac index. Red blood cell transfusions led to a significant increase in the proportion of perfused small vessels (2.85%; p = 0.553), while tissue oxygenation parameters revealed a significant increase in the tissue hemoglobin index (1.66; p = 0.018). Individual studies reported significant improvements in tissue oxygenation and sublingual microcirculatory parameters in patients with deranged microcirculation at baseline. Red blood cell transfusions seemed to improve systemic oxygen metabolism with apparent independence from cardiac index variations. Some beneficial effects have been observed for tissue oxygenation and microcirculation parameters, particularly in patients with more severe alterations at baseline. More studies are necessary to evaluate their clinical impact and to individualize transfusion decisions.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2020;32(1):115-122
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20200017
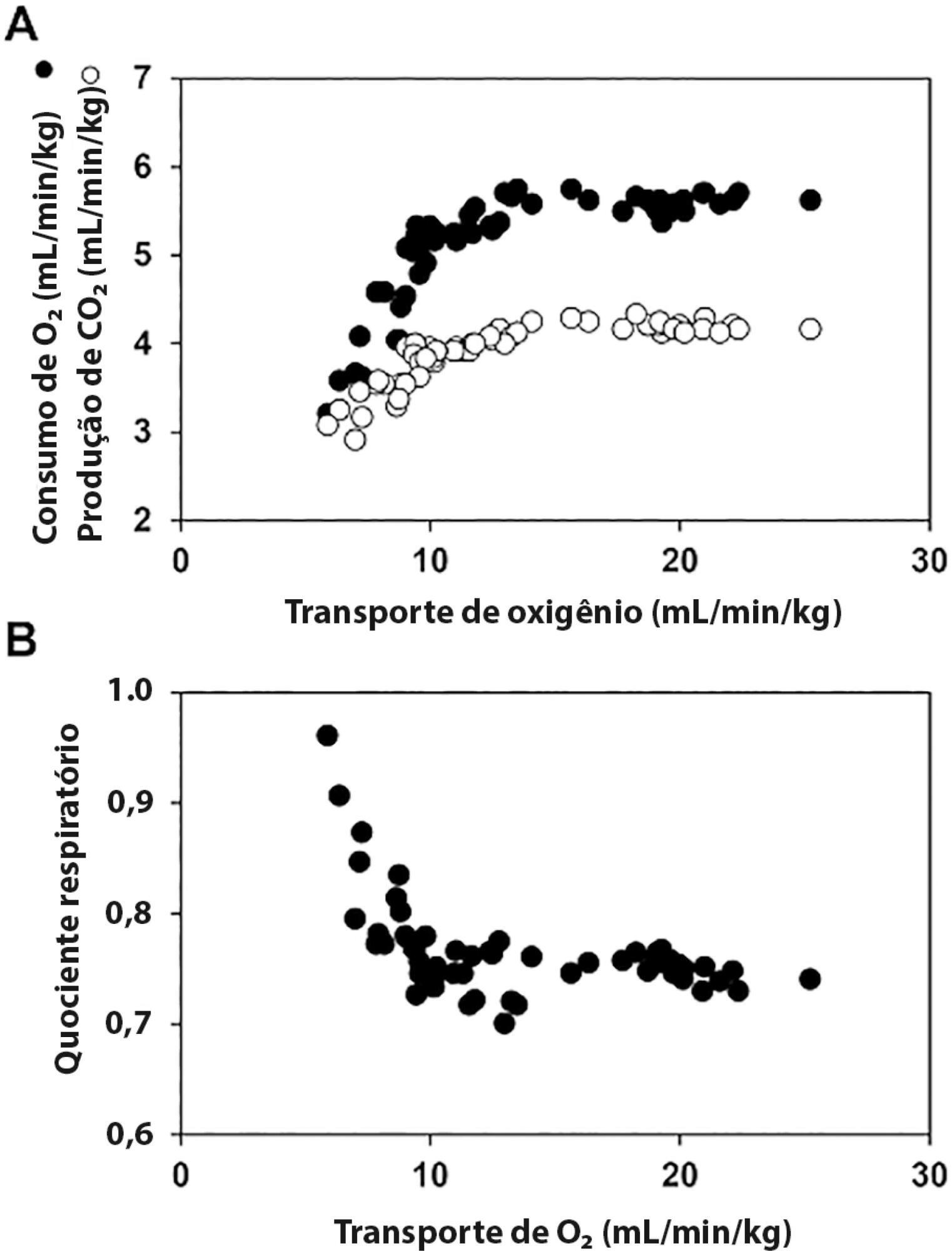
The central venous minus arterial carbon dioxide pressure to arterial minus central venous oxygen content ratio (Pcv-aCO2/Ca-cvO2) has been proposed as a surrogate for respiratory quotient and an indicator of tissue oxygenation. Some small observational studies have found that a Pcv-aCO2/Ca-cvO2 > 1.4 was associated with hyperlactatemia, oxygen supply dependency, and increased mortality. Moreover, Pcv-aCO2/Ca-cvO2 has been incorporated into algorithms for tissue oxygenation evaluation and resuscitation. However, the evidence for these recommendations is quite limited and of low quality. The goal of this narrative review was to analyze the methodological bases, the pathophysiologic foundations, and the experimental and clinical evidence supporting the use of Pcv-aCO2/Ca-cvO2 as a surrogate for respiratory quotient. Physiologically, the increase in respiratory quotient secondary to critical reductions in oxygen transport is a life-threatening and dramatic event. Nevertheless, this event is easily noticeable and probably does not require further monitoring. Since the beginning of anaerobic metabolism is indicated by the sudden increase in respiratory quotient and the normal range of respiratory quotient is wide, the use of a defined cutoff of 1.4 for Pcv-aCO2/Ca-cvO2 is meaningless. Experimental studies have shown that Pcv-aCO2/Ca-cvO2 is more dependent on factors that modify the dissociation of carbon dioxide from hemoglobin than on respiratory quotient and that respiratory quotient and Pcv-aCO2/Ca-cvO2 may have distinct behaviors. Studies performed in critically ill patients have shown controversial results regarding the ability of Pcv-aCO2/Ca-cvO2 to predict outcome, hyperlactatemia, microvascular abnormalities, and oxygen supply dependency. A randomized controlled trial also showed that Pcv-aCO2/Ca-cvO2 is useless as a goal of resuscitation. Pcv-aCO2/Ca-cvO2 should be carefully interpreted in critically ill patients.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2015;27(1):36-43
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20150007
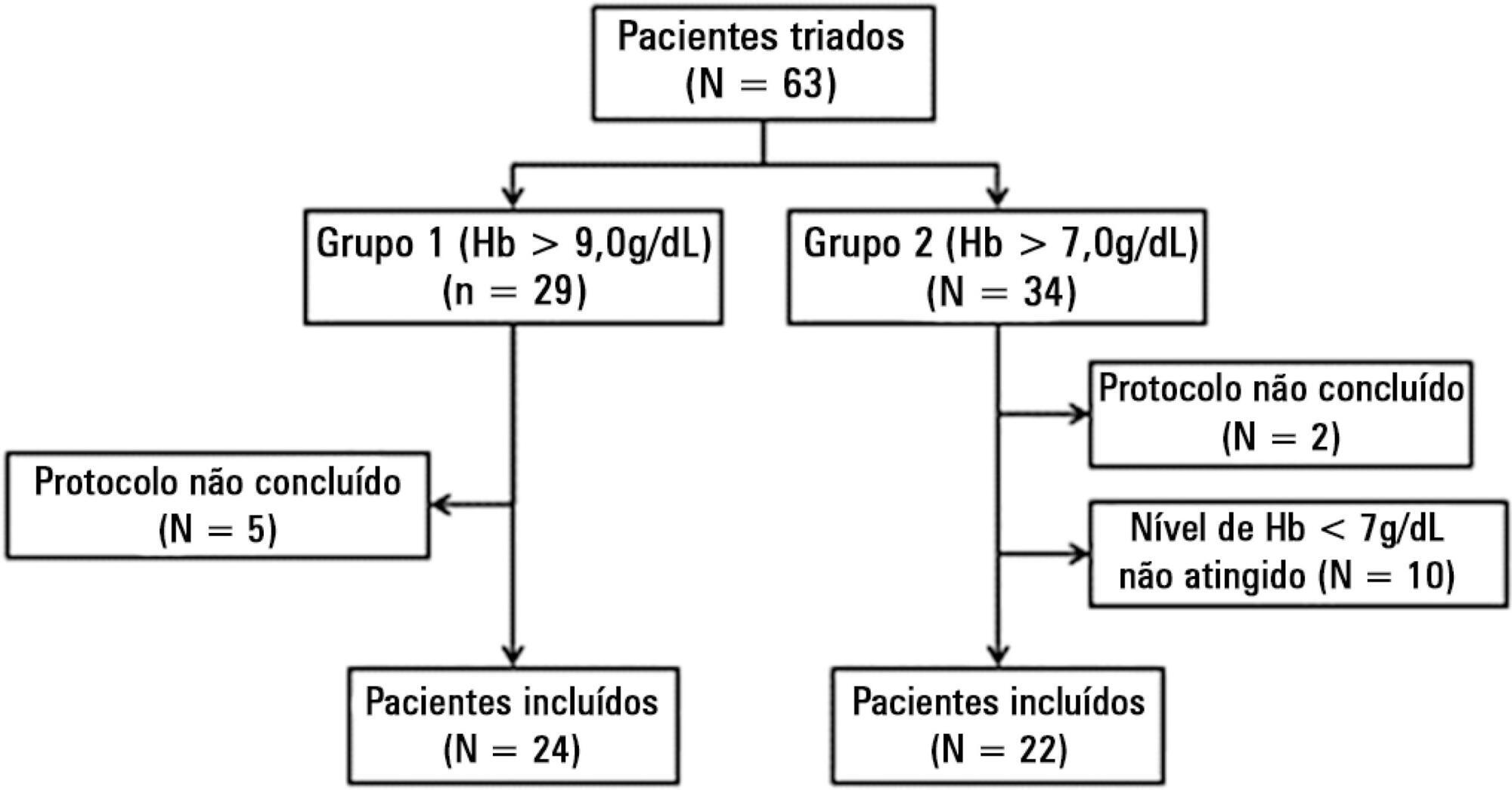
To evaluate the immediate effects of red blood cell transfusion on central venous oxygen saturation and lactate levels in septic shock patients with different transfusion triggers.
We included patients with a diagnosis of septic shock within the last 48 hours and hemoglobin levels below 9.0g/dL Patients were randomized for immediate transfusion with hemoglobin concentrations maintained above 9.0g/dL (Group Hb9) or to withhold transfusion unless hemoglobin felt bellow 7.0g/dL (Group Hb7). Hemoglobin, lactate, central venous oxygen saturation levels were determined before and one hour after each transfusion.
We included 46 patients and 74 transfusions. Patients in Group Hb7 had a significant reduction in median lactate from 2.44 (2.00 - 3.22) mMol/L to 2.21 (1.80 - 2.79) mMol/L, p = 0.005, which was not observed in Group Hb9 [1.90 (1.80 - 2.65) mMol/L to 2.00 (1.70 - 2.41) mMol/L, p = 0.23]. Central venous oxygen saturation levels increased in Group Hb7 [68.0 (64.0 - 72.0)% to 72.0 (69.0 - 75.0)%, p < 0.0001] but not in Group Hb9 [72.0 (69.0 - 74.0)% to 72.0 (71.0 - 73.0)%, p = 0.98]. Patients with elevated lactate or central venous oxygen saturation < 70% at baseline had a significant increase in these variables, regardless of baseline hemoglobin levels. Patients with normal values did not show a decrease in either group.
Red blood cell transfusion increased central venous oxygen saturation and decreased lactate levels in patients with hypoperfusion regardless of their baseline hemoglobin levels. Transfusion did not appear to impair these variables in patients without hypoperfusion.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2011;23(3):374-379
DOI 10.1590/S0103-507X2011000300017
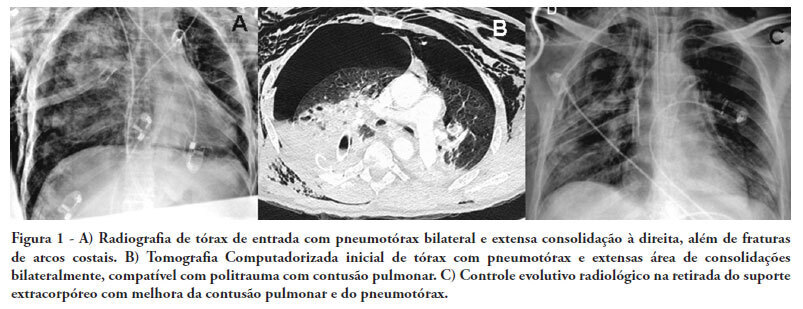
There are few reports in the literature regarding the use of venoarterial extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO) for double-dysfunction from both heart and lung contusions in polytrauma patients. This article reports a 48-year-old patient admitted after a traffic accident. He rapidly progressed to shock with low cardiac output due to myocardial contusion and refractory hypoxemia due to pulmonary contusion, an unstable chest wall and bilateral pneumothorax. ECMO was an effective rescue procedure in this dramatic situation and was successfully discontinued on the fourth day after the trauma. The patient also developed an extensive brain infarction and eventually died on the seventh day after admission
Search
Search in:
Case reports (56) Child (53) Coronavirus infections (34) COVID-19 (46) Critical care (115) Critical illness (54) Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (26) Infant, newborn (27) Intensive care (72) Intensive care units (256) Intensive care units, pediatric (31) mechanical ventilation (38) Mortality (76) Physical therapy modalities (28) Prognosis (61) Respiration, artificial (119) Respiratory insufficiency (26) risk factors (34) SARS-CoV-2 (28) Sepsis (98)