You searched for:"Javier Hurtado"
We found (3) results for your search.-
Review Article
Central venous minus arterial carbon dioxide pressure to arterial minus central venous oxygen content ratio as an indicator of tissue oxygenation: a narrative review
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2020;32(1):115-122
Abstract
Review ArticleCentral venous minus arterial carbon dioxide pressure to arterial minus central venous oxygen content ratio as an indicator of tissue oxygenation: a narrative review
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2020;32(1):115-122
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20200017
Views0See moreABSTRACT
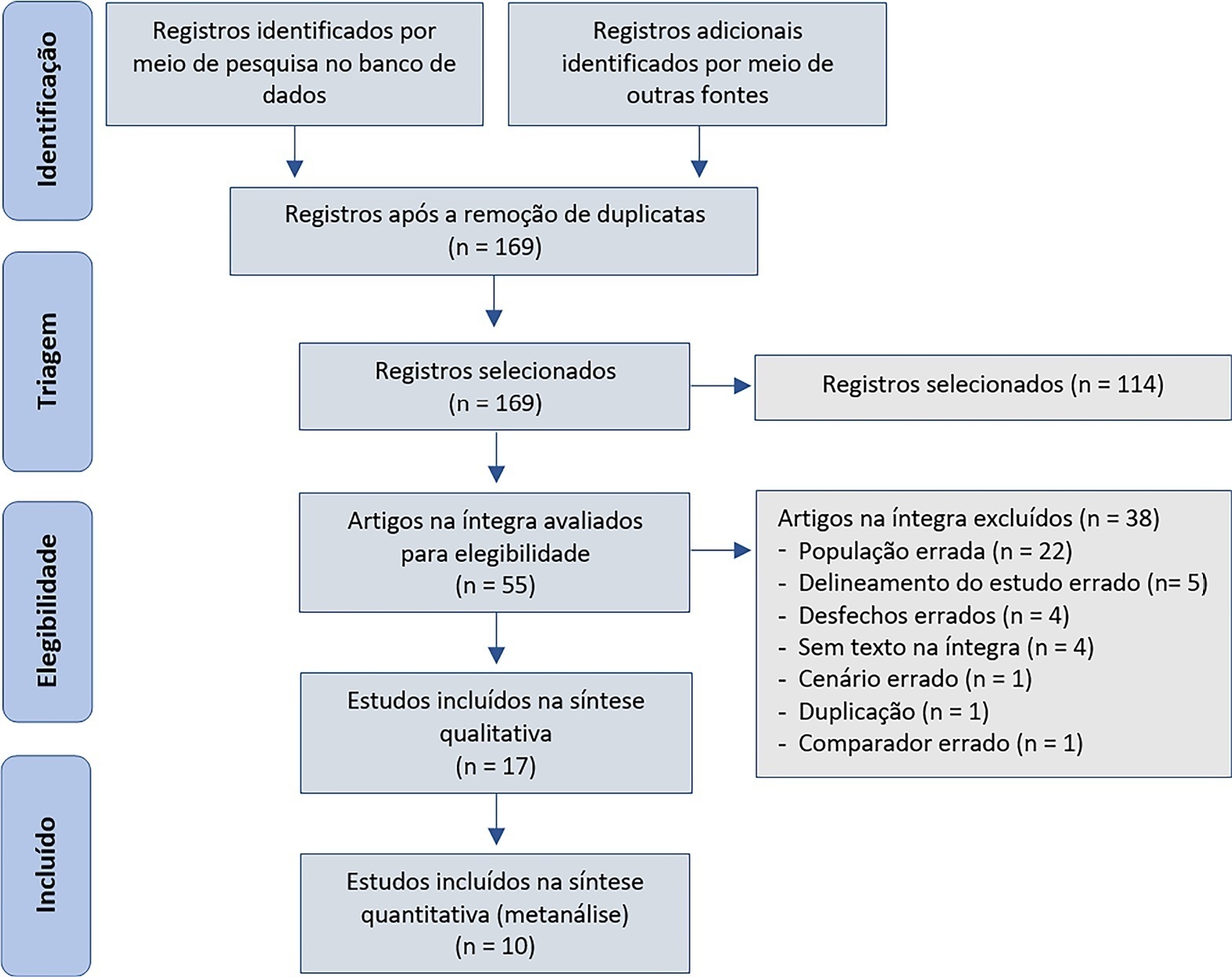
The central venous minus arterial carbon dioxide pressure to arterial minus central venous oxygen content ratio (Pcv-aCO2/Ca-cvO2) has been proposed as a surrogate for respiratory quotient and an indicator of tissue oxygenation. Some small observational studies have found that a Pcv-aCO2/Ca-cvO2 > 1.4 was associated with hyperlactatemia, oxygen supply dependency, and increased mortality. Moreover, Pcv-aCO2/Ca-cvO2 has been incorporated into algorithms for tissue oxygenation evaluation and resuscitation. However, the evidence for these recommendations is quite limited and of low quality. The goal of this narrative review was to analyze the methodological bases, the pathophysiologic foundations, and the experimental and clinical evidence supporting the use of Pcv-aCO2/Ca-cvO2 as a surrogate for respiratory quotient. Physiologically, the increase in respiratory quotient secondary to critical reductions in oxygen transport is a life-threatening and dramatic event. Nevertheless, this event is easily noticeable and probably does not require further monitoring. Since the beginning of anaerobic metabolism is indicated by the sudden increase in respiratory quotient and the normal range of respiratory quotient is wide, the use of a defined cutoff of 1.4 for Pcv-aCO2/Ca-cvO2 is meaningless. Experimental studies have shown that Pcv-aCO2/Ca-cvO2 is more dependent on factors that modify the dissociation of carbon dioxide from hemoglobin than on respiratory quotient and that respiratory quotient and Pcv-aCO2/Ca-cvO2 may have distinct behaviors. Studies performed in critically ill patients have shown controversial results regarding the ability of Pcv-aCO2/Ca-cvO2 to predict outcome, hyperlactatemia, microvascular abnormalities, and oxygen supply dependency. A randomized controlled trial also showed that Pcv-aCO2/Ca-cvO2 is useless as a goal of resuscitation. Pcv-aCO2/Ca-cvO2 should be carefully interpreted in critically ill patients.
-
Original Article
Statistical analysis plan for early goal-directed therapy using a physiological holistic view – the ANDROMEDA-SHOCK: a randomized controlled trial
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2018;30(3):253-263
Abstract
Original ArticleStatistical analysis plan for early goal-directed therapy using a physiological holistic view – the ANDROMEDA-SHOCK: a randomized controlled trial
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2018;30(3):253-263
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20180041
Views0See moreABSTRACT
Background:
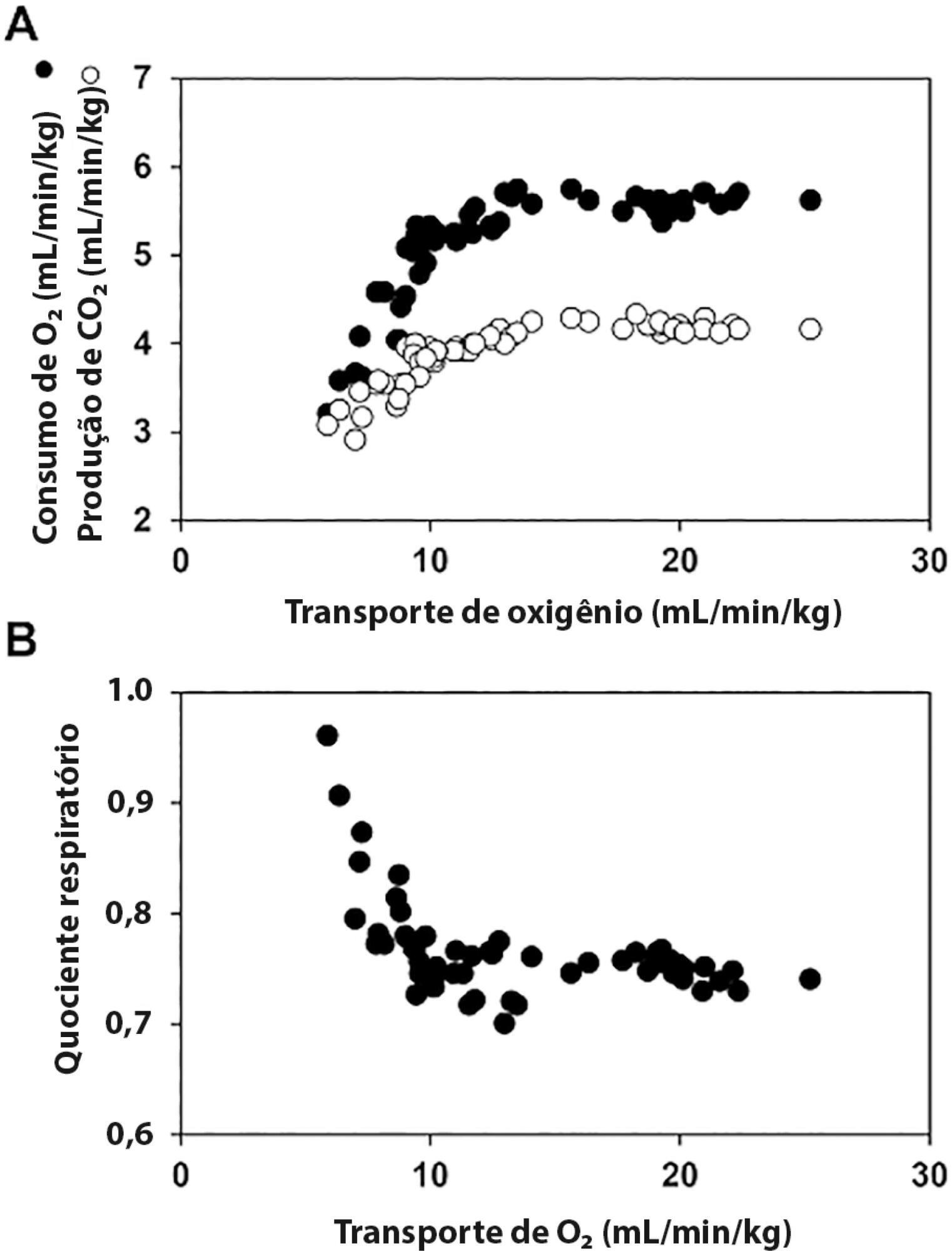
ANDROMEDA-SHOCK is an international, multicenter, randomized controlled trial comparing peripheral perfusion-targeted resuscitation to lactate-targeted resuscitation in patients with septic shock in order to test the hypothesis that resuscitation targeting peripheral perfusion will be associated with lower morbidity and mortality.
Objective:
To report the statistical analysis plan for the ANDROMEDA-SHOCK trial.
Methods:
We describe the trial design, primary and secondary objectives, patients, methods of randomization, interventions, outcomes, and sample size. We describe our planned statistical analysis for the primary, secondary and tertiary outcomes. We also describe the subgroup and sensitivity analyses. Finally, we provide details for presenting our results, including mock tables showing baseline characteristics, the evolution of hemodynamic and perfusion variables, and the effects of treatments on outcomes.
Conclusion:
According to the best trial practice, we report our statistical analysis plan and data management plan prior to locking the database and initiating the analyses. We anticipate that this procedure will prevent analysis bias and enhance the utility of the reported results.
Search
Search in:
KEY WORDS
Case reports Child Coronavirus infections COVID-19 Critical care Critical illness Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation Infant, newborn Intensive care Intensive care units Intensive care units, pediatric mechanical ventilation Mortality Physical therapy modalities Prognosis Respiration, artificial Respiratory insufficiency risk factors SARS-CoV-2 Sepsis