Abstract
Crit Care Sci. 2024;36:e20240158en
DOI 10.62675/2965-2774.20240158-pt
To evaluate the association of biomarkers with successful ventilatory weaning in COVID-19 patients.
An observational, retrospective, and single-center study was conducted between March 2020 and April 2021. C-reactive protein, total lymphocytes, and the neutrophil/lymphocyte ratio were evaluated during attrition and extubation, and the variation in these biomarker values was measured. The primary outcome was successful extubation. ROC curves were drawn to find the best cutoff points for the biomarkers based on sensitivity and specificity. Statistical analysis was performed using logistic regression.
Of the 2,377 patients admitted to the intensive care unit, 458 were included in the analysis, 356 in the Successful Weaning Group and 102 in the Failure Group. The cutoff points found from the ROC curves were −62.4% for C-reactive protein, +45.7% for total lymphocytes, and −32.9% for neutrophil/lymphocyte ratio. These points were significantly associated with greater extubation success. In the multivariate analysis, only C-reactive protein variation remained statistically significant (OR 2.6; 95%CI 1.51 – 4.5; p < 0.001).
In this study, a decrease in C-reactive protein levels was associated with successful extubation in COVID-19 patients. Total lymphocytes and the neutrophil/lymphocyte ratio did not maintain the association after multivariate analysis. However, a decrease in C-reactive protein levels should not be used as a sole variable to identify COVID-19 patients suitable for weaning; as in our study, the area under the ROC curve demonstrated poor accuracy in discriminating extubation outcomes, with low sensitivity and specificity.
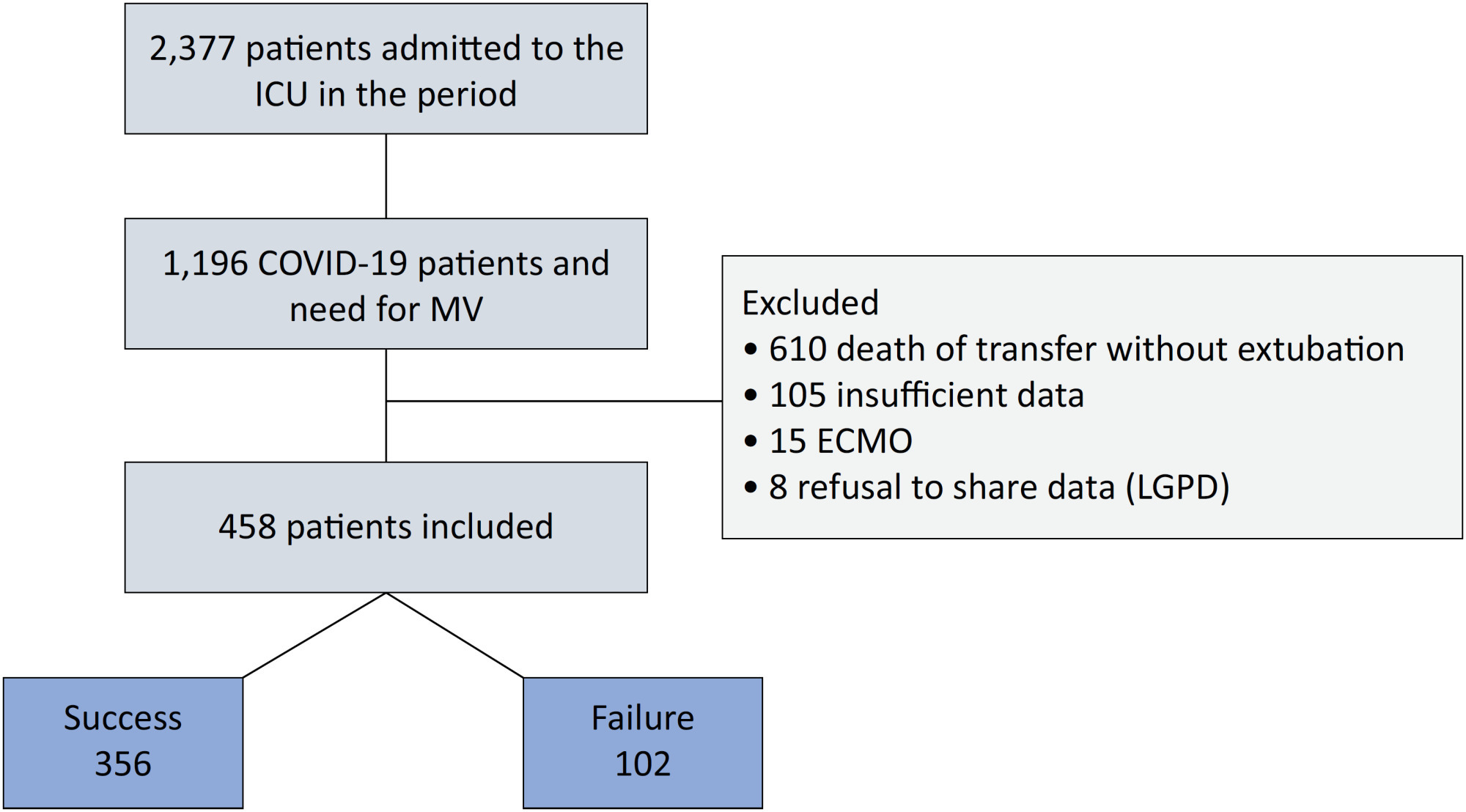
Abstract
Crit Care Sci. 2023;35(2):156-162
DOI 10.5935/2965-2774.20230343-pt
To identify risk factors for nonresponse to prone positioning in mechanically ventilated patients with COVID-19-associated severe acute respiratory distress syndrome and refractory hypoxemia in a tertiary care hospital in Colombia.
Observational study based on a retrospective cohort of mechanically ventilated patients with severe acute respiratory distress syndrome due to SARS-CoV-2 who underwent prone positioning due to refractory hypoxemia. The study considered an improvement ≥ 20% in the PaO2/FiO2 ratio after the first cycle of 16 hours in the prone position to be a ‘response’. Nonresponding patients were considered cases, and responding patients were controls. We controlled for clinical, laboratory, and radiological variables.
A total of 724 patients were included (58.67 ± 12.37 years, 67.7% males). Of those, 21.9% were nonresponders. Mortality was 54.1% for nonresponders and 31.3% for responders (p < 0.001). Variables associated with nonresponse were time from the start of mechanical ventilation to pronation (OR 1.23; 95%CI 1.10 - 1.41); preintubation PaO2/FiO2 ratio (OR 0.62; 95%CI 0.40 - 0.96); preprone PaO2/FiO2 ratio (OR 1.88. 95%CI 1.22 - 2.94); and radiologic multilobe consolidation (OR 2.12; 95%CI 1.33 - 3.33) or mixed pattern (OR 1.72; 95%CI 1.07 - 2.85) compared with a ground-glass pattern.
This study identified factors associated with nonresponse to prone positioning in patients with refractory hypoxemia and acute respiratory distress syndrome due to SARS-CoV-2 receiving mechanical ventilation. Recognizing such factors helps identify candidates for other rescue strategies, including more extensive prone positioning or extracorporeal membrane oxygenation. Further studies are needed to assess the consistency of these findings in populations with acute respiratory distress syndrome of other etiologies.
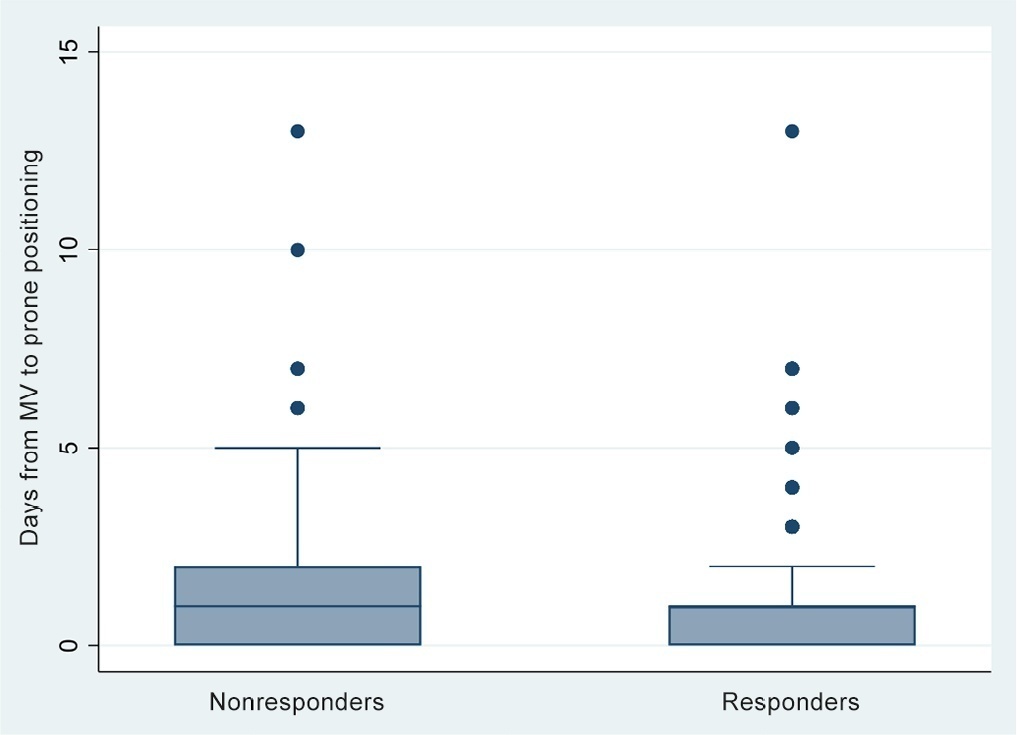
Abstract
Crit Care Sci. 2023;35(2):163-167
DOI 10.5935/2965-2774.20230009-pt
To assess the outcome of extubation in COVID-19 patients and the use of noninvasive ventilation in the weaning process.
This retrospective, observational, single-center study was conducted in COVID-19 patients aged 18 years or older who were admitted to an intensive care unit between April 2020 and December 2021, placed under mechanical ventilation for more than 48 hours and progressed to weaning. Early extubation was defined as extubation without a spontaneous breathing trial and immediate use of noninvasive ventilation after extubation. In patients who underwent a spontaneous breathing trial, noninvasive ventilation could be used as prophylactic ventilatory assistance when started immediately after extubation (prophylactic noninvasive ventilation) or as rescue therapy in cases of postextubation respiratory failure (therapeutic noninvasive ventilation). The primary outcome was extubation failure during the intensive care unit stay.
Three hundred eighty-four extubated patients were included. Extubation failure was observed in 107 (27.9%) patients. Forty-seven (12.2%) patients received prophylactic noninvasive ventilation. In 26 (6.8%) patients, early extubation was performed with immediate use of noninvasive ventilation. Noninvasive ventilation for the management of postextubation respiratory failure was administered to 64 (16.7%) patients.
We found that COVID-19 patients had a high rate of extubation failure. Despite the high risk of extubation failure, we observed low use of prophylactic noninvasive ventilation in these patients.
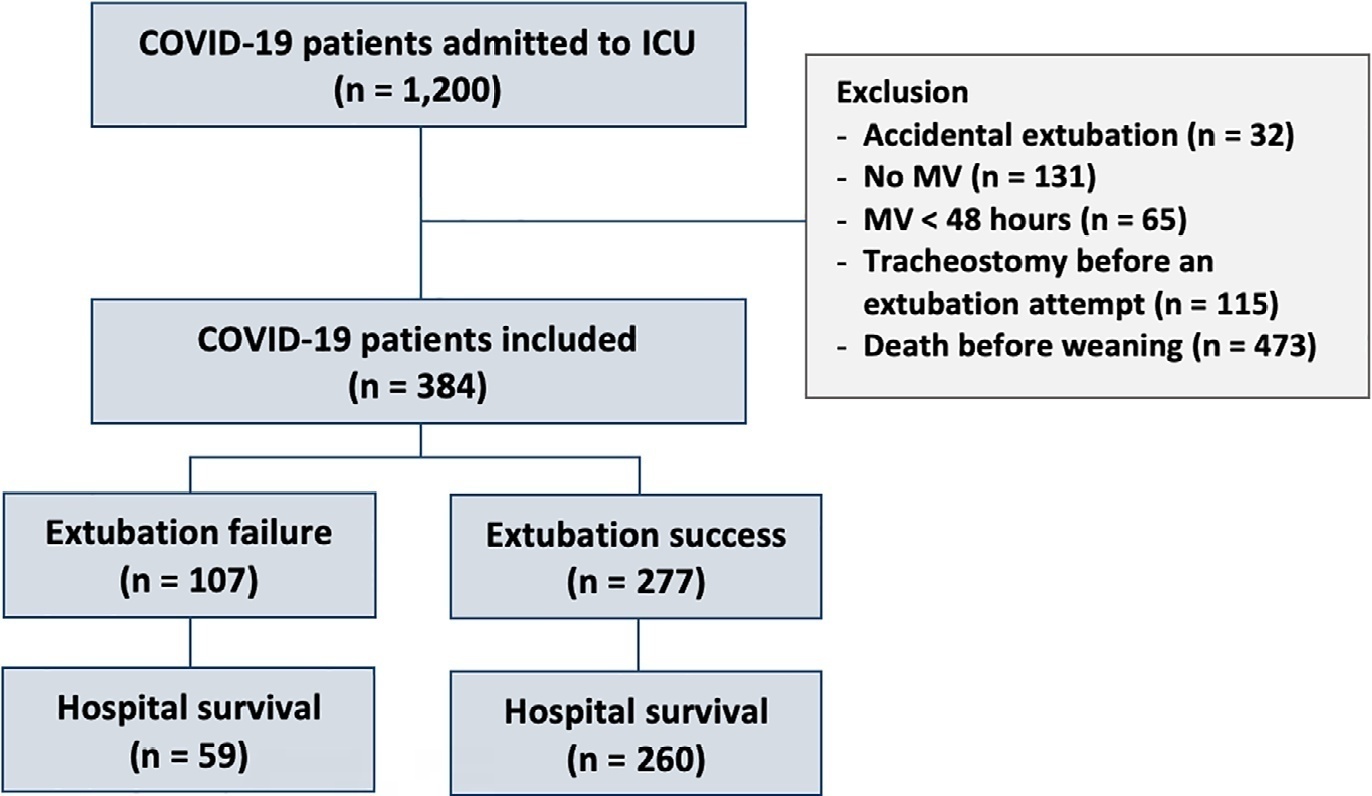
Abstract
Crit Care Sci. 2023;35(1):19-30
DOI 10.5935/2965-2774.20230203-pt
To evaluate the factors associated with mortality in mechanically ventilated patients with acute respiratory distress syndrome due to COVID-19.
This was a retrospective, multicenter cohort study that included 425 mechanically ventilated adult patients with COVID-19 admitted to 4 intensive care units. Clinical data comprising the SOFA score, laboratory data and mechanical characteristics of the respiratory system were collected in a standardized way immediately after the start of invasive mechanical ventilation. The risk factors for death were analyzed using Cox regression to estimate the risk ratios and their respective 95%CIs.
Body mass index (RR 1.17; 95%CI 1.11 - 1.20; p < 0.001), SOFA score (RR 1.39; 95%CI 1.31 - 1.49; p < 0.001) and driving pressure (RR 1.24; 95%CI 1.21 - 1.29; p < 0.001) were considered independent factors associated with mortality in mechanically ventilated patients with acute respiratory distress syndrome due to COVID-19. Respiratory system compliance (RR 0.92; 95%CI 0.90 - 0.93; p < 0.001) was associated with lower mortality. The comparative analysis of the survival curves indicated that patients with respiratory system compliance (< 30mL/cmH2O), a higher SOFA score (> 5 points) and higher driving pressure (> 14cmH2O) were more significantly associated with the outcome of death at 28 days and 60 days.
Patients with a body mass index > 32kg/m2, respiratory system compliance < 30mL/cmH2O, driving pressure > 14cmH2O and SOFA score > 5.8 immediately after the initiation of invasive ventilatory support had worse outcomes, and independent risk factors were associated with higher mortality in this population.
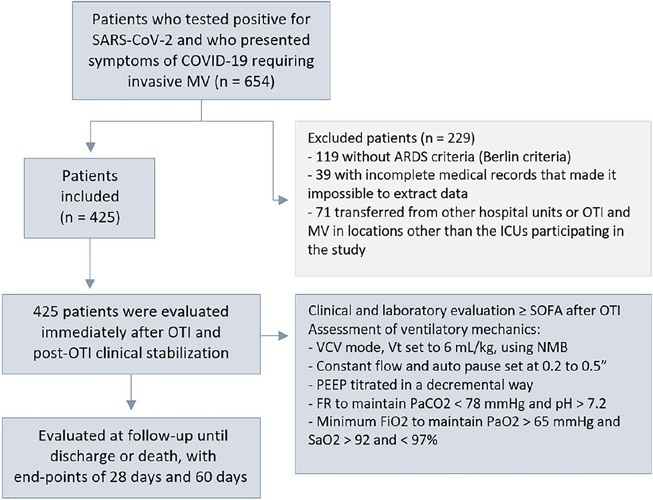
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2022;34(4):426-432
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20220278-en
To characterize the knowledge and perceived attitudes toward pharmacologic interventions for light sedation in mechanically ventilated patients and to understand the current gaps comparing current practice with the recommendations of the Clinical Practice Guidelines for the Prevention and Management of Pain, Agitation/Sedation, Delirium, Immobility, and Sleep Disruption in Adult Patients in the Intensive Care Unit.
This was a cross-sectional cohort study based on the application of an electronic questionnaire focused on sedation practices.
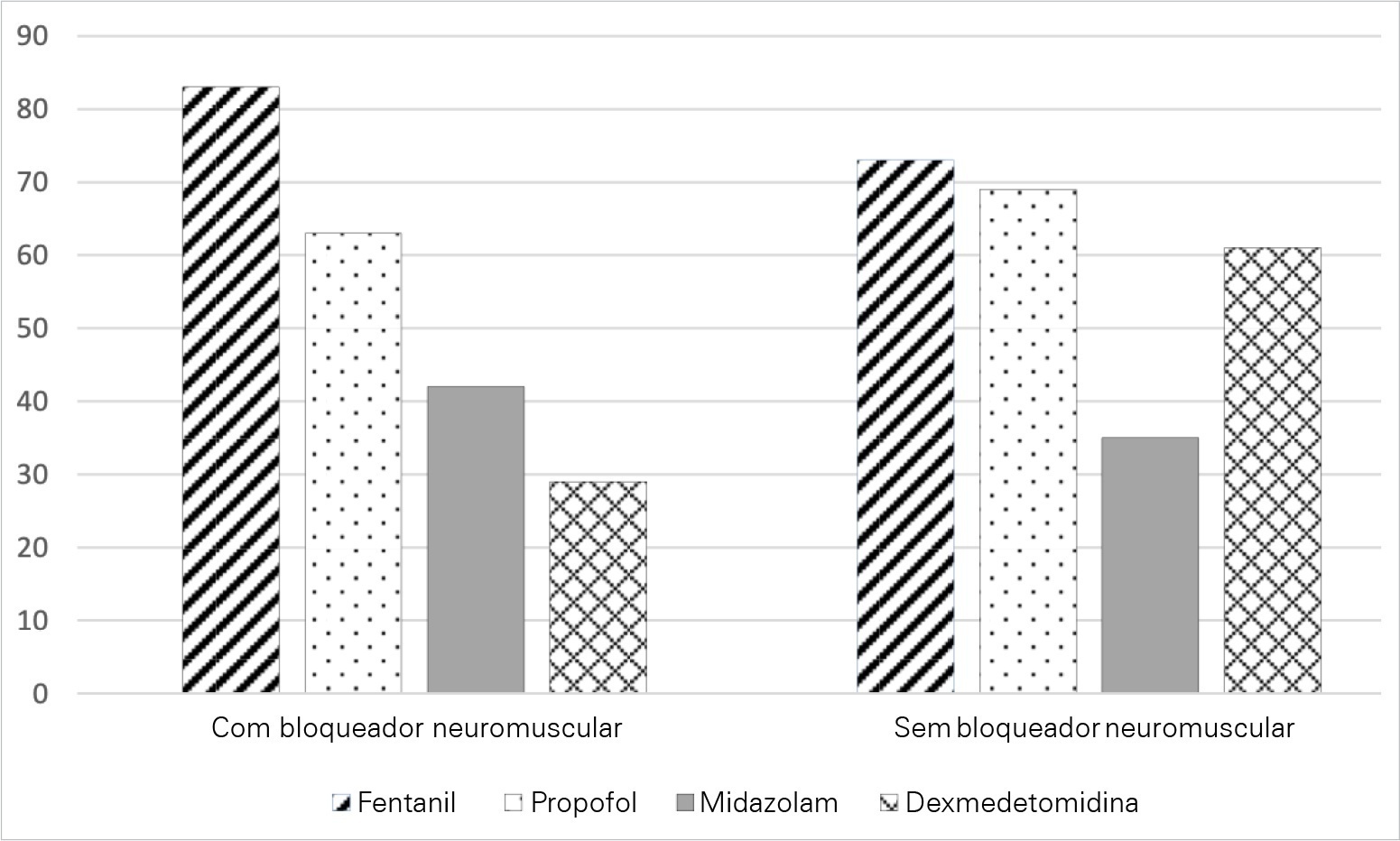
A total of 303 critical care physicians provided responses to the survey. Most respondents reported routine use of a structured sedation scale (281; 92.6%). Almost half of the respondents reported performing daily interruptions of sedation (147; 48.4%), and the same percentage of participants (48.0%) agreed that patients are often over sedated. During the COVID-19 pandemic, participants reported that patients had a higher chance of receiving midazolam compared to before the pandemic (178; 58.8% versus 106; 34.0%; p = 0.05), and heavy sedation was more common during the COVID-19 pandemic (241; 79.4% versus 148; 49.0%; p = 0.01).
This survey provides valuable data on the perceived attitudes of Brazilian intensive care physicians regarding sedation. Although daily interruption of sedation was a well-known concept and sedation scales were often used by the respondents, insufficient effort was put into frequent monitoring, use of protocols and systematic implementation of sedation strategies. Despite the perception of the benefits linked with light sedation, there is a need to identify improvement targets to propose educational strategies to improve current practices.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2022;34(2):212-219
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20220018-en
To analyze the influence of mechanical power and its components on mechanical ventilation for patients infected with SARS-CoV-2; identify the values of the mechanical ventilation components and verify their correlations with each other and with the mechanical power and effects on the result of the Gattinoni-S and Giosa formulas.
This was an observational, longitudinal, analytical and quantitative study of respirator and mechanical power parameters in patients with SARS-CoV-2.
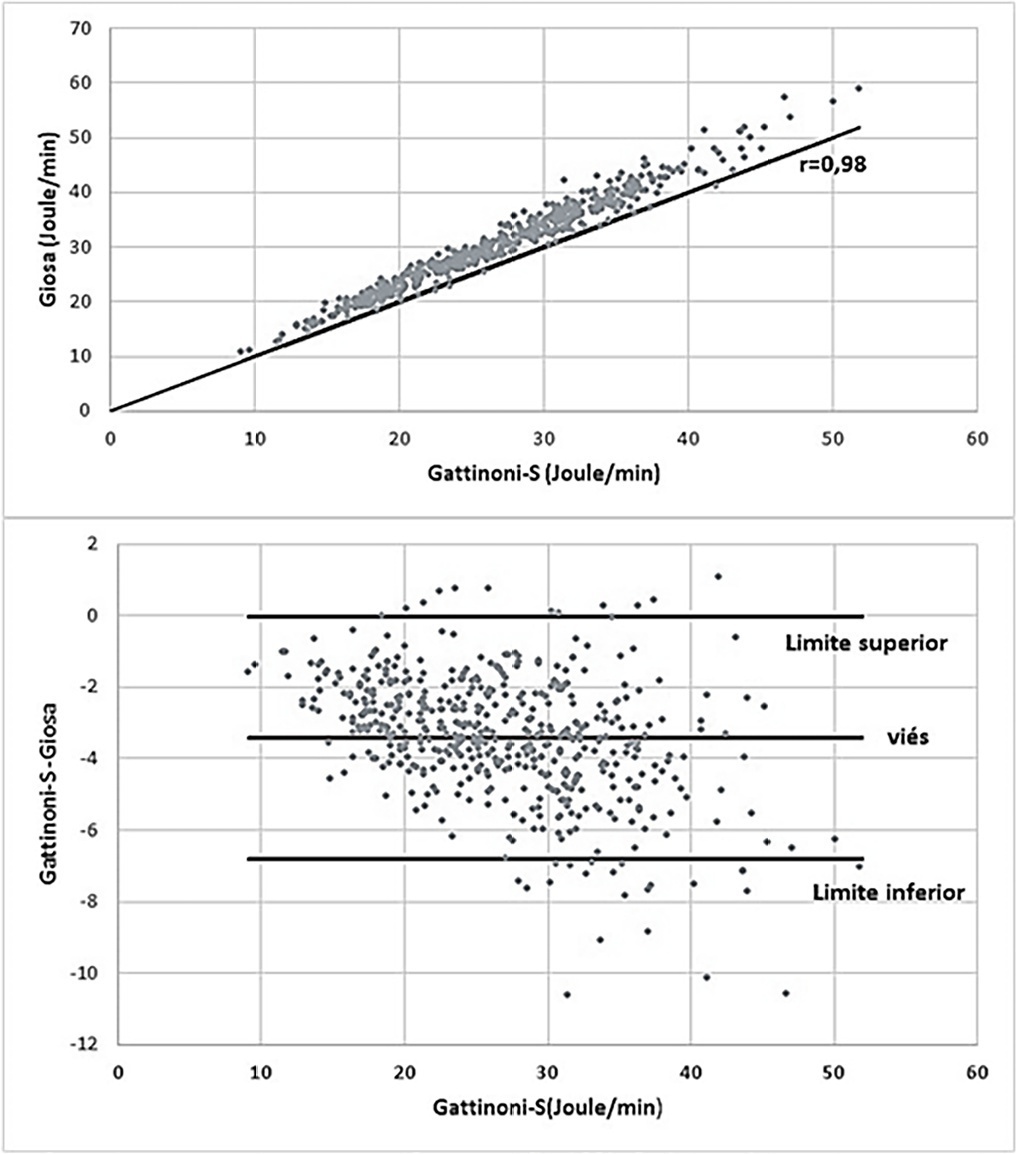
The mean mechanical power was 26.9J/minute (Gattinoni-S) and 30.3 J/minute (Giosa). The driving pressure was 14.4cmH2O, the plateau pressure was 26.5cmH2O, the positive end-expiratory pressure was 12.1cmH2O, the elastance was 40.6cmH2O/L, the tidal volume was 0.36L, and the respiratory rate was 32 breaths/minute. The correlation between the Gattinoni and Giosa formulas was 0.98, with a bias of -3.4J/minute and a difference in the correlation of the resistance pressure of 0.39 (Gattinoni) and 0.24 (Giosa). Among the components, the correlations between elastance and driving pressure (0.88), positive end-expiratory pressure (-0.54) and tidal volume (-0.44) stood out.
In the analysis of mechanical ventilation for patients with SARS-CoV-2, it was found that the correlations of its components with mechanical power influenced its high momentary values and and that the correlations of its components with each other influenced their behavior throughout the study period. Because they have specific effects on the Gatinnoni-S and Giosa formulas, the mechanical ventilation components influenced their calculations and caused divergence in the mechanical power values.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2022;34(1):176-184
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20220012-en
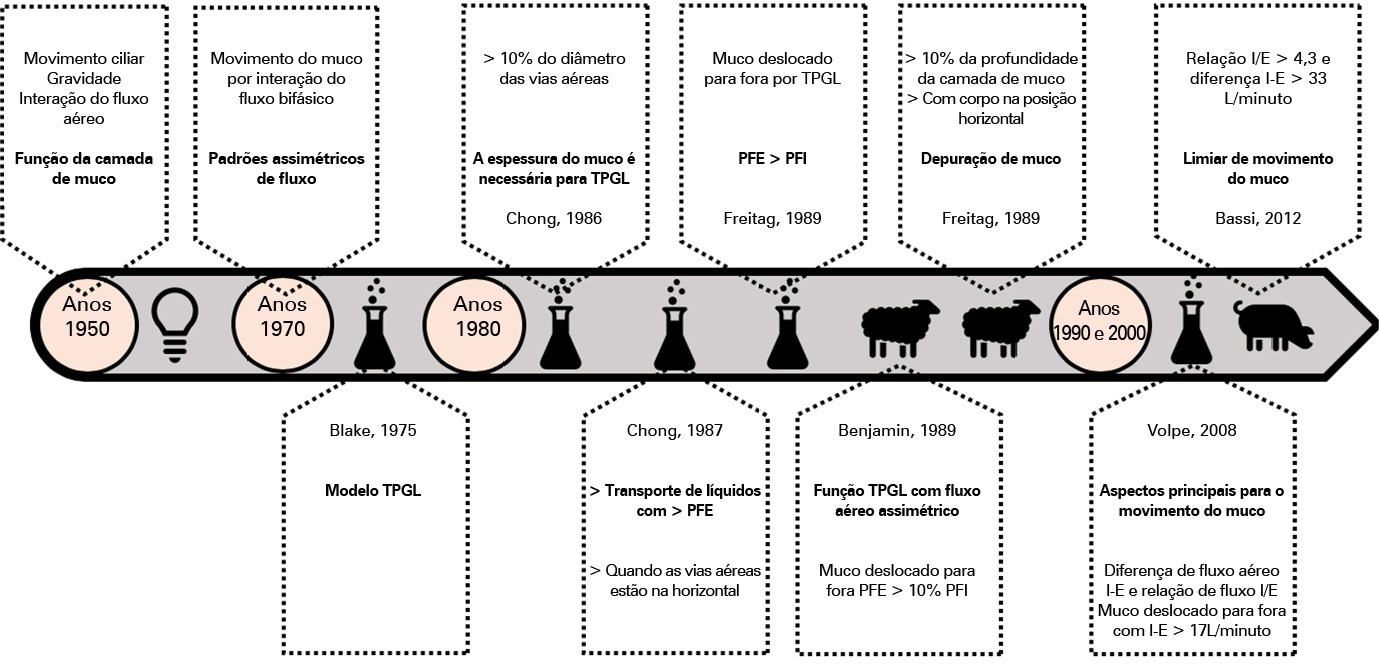
Defective management of secretions is one of the most frequent complications in invasive mechanically ventilated patients. Clearance of secretions through chest physiotherapy is a critical aspect of the treatment of these patients. Manual rib cage compression is one of the most practiced chest physiotherapy techniques in ventilated patients; however, its impact on clinical outcomes remains controversial due to methodological issues and poor understanding of its action. In this review, we present a detailed analysis of the physical principles involved in rib cage compression technique performance, as well as the physiological effects observed in experimental and clinical studies, which show that the use of brief and vigorous rib cage compression, based on increased expiratory flows (expiratory-inspiratory airflow difference of > 33L/minute), can improve mucus movement toward the glottis. On the other hand, the use of soft and gradual rib cage compression throughout the whole expiratory phase does not impact the expiratory flows, resulting in ineffective or undesired effects in some cases. More physiological studies are needed to understand the principles of the rib cage compression technique in ventilated humans. However, according to the evidence, rib cage compression has more potential benefits than risks, so its implementation should be promoted.
Search
Search in:
Case reports (56) Child (53) Coronavirus infections (33) COVID-19 (45) Critical care (115) Critical illness (54) Infant, newborn (27) Intensive care (72) Intensive care units (254) Intensive care units, pediatric (31) mechanical ventilation (38) Mortality (75) Physical therapy modalities (28) Prognosis (61) Respiration, artificial (117) Respiratory insufficiency (26) risk factors (34) SARS-CoV-2 (28) Sepsis (98) Septic shock (25)