Abstract
Crit Care Sci. 2024;36:e20240158en
DOI 10.62675/2965-2774.20240158-pt
To evaluate the association of biomarkers with successful ventilatory weaning in COVID-19 patients.
An observational, retrospective, and single-center study was conducted between March 2020 and April 2021. C-reactive protein, total lymphocytes, and the neutrophil/lymphocyte ratio were evaluated during attrition and extubation, and the variation in these biomarker values was measured. The primary outcome was successful extubation. ROC curves were drawn to find the best cutoff points for the biomarkers based on sensitivity and specificity. Statistical analysis was performed using logistic regression.
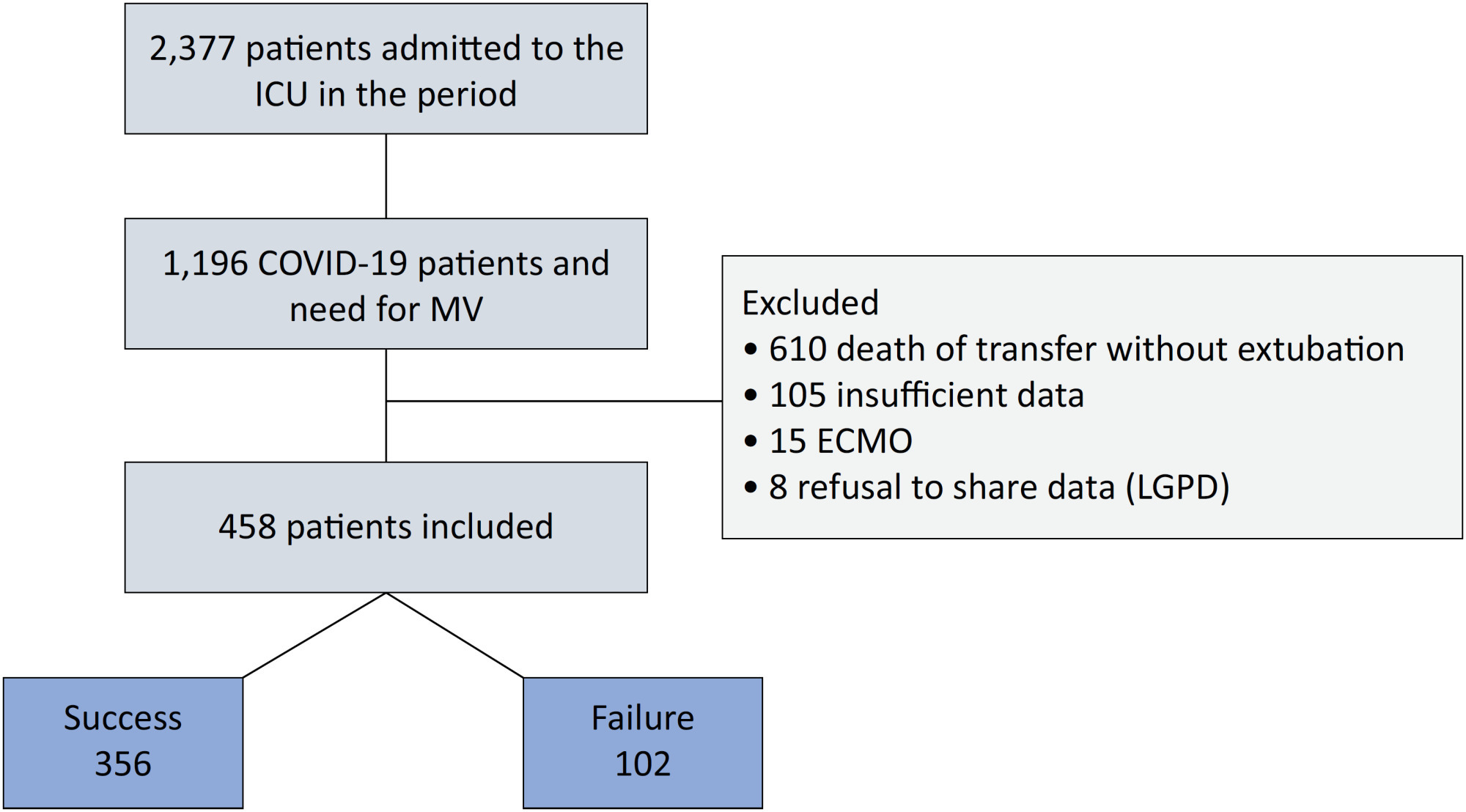
Of the 2,377 patients admitted to the intensive care unit, 458 were included in the analysis, 356 in the Successful Weaning Group and 102 in the Failure Group. The cutoff points found from the ROC curves were −62.4% for C-reactive protein, +45.7% for total lymphocytes, and −32.9% for neutrophil/lymphocyte ratio. These points were significantly associated with greater extubation success. In the multivariate analysis, only C-reactive protein variation remained statistically significant (OR 2.6; 95%CI 1.51 – 4.5; p < 0.001).
In this study, a decrease in C-reactive protein levels was associated with successful extubation in COVID-19 patients. Total lymphocytes and the neutrophil/lymphocyte ratio did not maintain the association after multivariate analysis. However, a decrease in C-reactive protein levels should not be used as a sole variable to identify COVID-19 patients suitable for weaning; as in our study, the area under the ROC curve demonstrated poor accuracy in discriminating extubation outcomes, with low sensitivity and specificity.
Abstract
Crit Care Sci. 2023;35(2):156-162
DOI 10.5935/2965-2774.20230343-pt
To identify risk factors for nonresponse to prone positioning in mechanically ventilated patients with COVID-19-associated severe acute respiratory distress syndrome and refractory hypoxemia in a tertiary care hospital in Colombia.
Observational study based on a retrospective cohort of mechanically ventilated patients with severe acute respiratory distress syndrome due to SARS-CoV-2 who underwent prone positioning due to refractory hypoxemia. The study considered an improvement ≥ 20% in the PaO2/FiO2 ratio after the first cycle of 16 hours in the prone position to be a ‘response’. Nonresponding patients were considered cases, and responding patients were controls. We controlled for clinical, laboratory, and radiological variables.
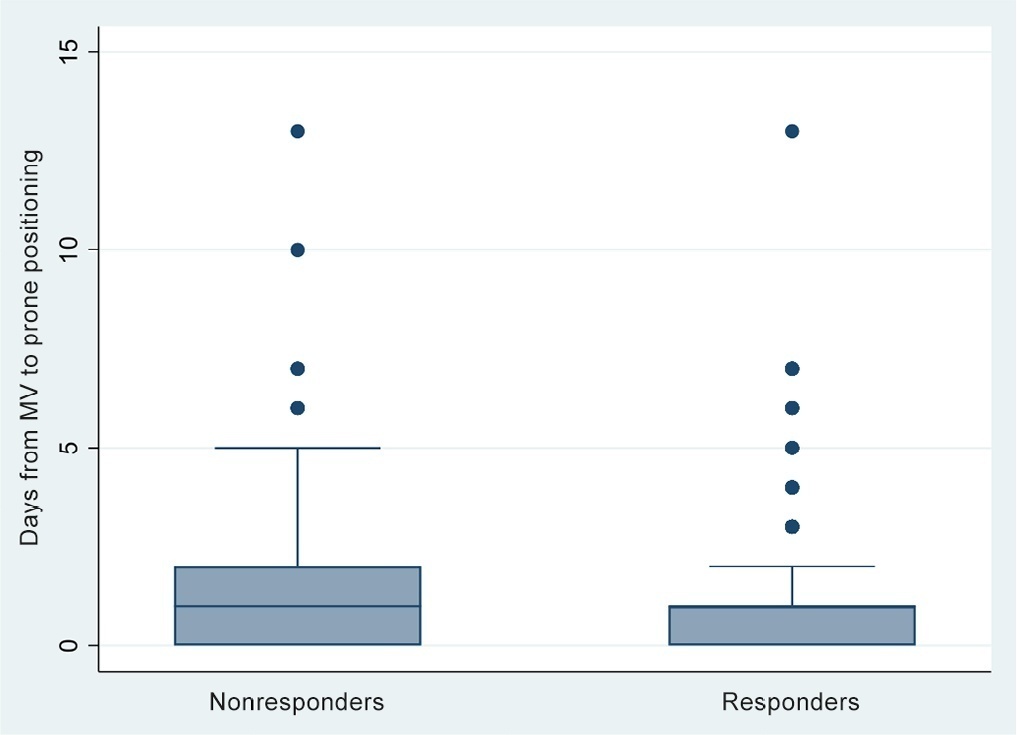
A total of 724 patients were included (58.67 ± 12.37 years, 67.7% males). Of those, 21.9% were nonresponders. Mortality was 54.1% for nonresponders and 31.3% for responders (p < 0.001). Variables associated with nonresponse were time from the start of mechanical ventilation to pronation (OR 1.23; 95%CI 1.10 - 1.41); preintubation PaO2/FiO2 ratio (OR 0.62; 95%CI 0.40 - 0.96); preprone PaO2/FiO2 ratio (OR 1.88. 95%CI 1.22 - 2.94); and radiologic multilobe consolidation (OR 2.12; 95%CI 1.33 - 3.33) or mixed pattern (OR 1.72; 95%CI 1.07 - 2.85) compared with a ground-glass pattern.
This study identified factors associated with nonresponse to prone positioning in patients with refractory hypoxemia and acute respiratory distress syndrome due to SARS-CoV-2 receiving mechanical ventilation. Recognizing such factors helps identify candidates for other rescue strategies, including more extensive prone positioning or extracorporeal membrane oxygenation. Further studies are needed to assess the consistency of these findings in populations with acute respiratory distress syndrome of other etiologies.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2022;34(1):131-140
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20220007-en
To evaluate the incidence of risk factors for postintubation hypotension in critically ill patients with COVID-19.
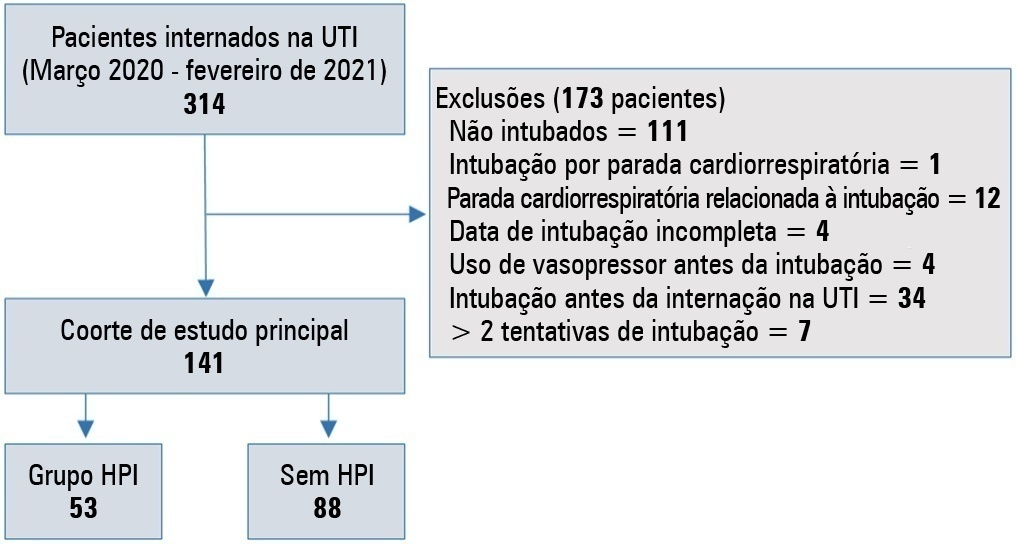
We conducted a retrospective study of 141 patients with COVID-19 who were intubated in the intensive care unit. Postintubation hypotension was defined as the need for any vasopressor dose at any time within the 60 minutes following intubation. Patients with intubation-related cardiac arrest and hypotension before intubation were excluded from the study.
Of the 141 included patients, 53 patients (37.5%) had postintubation hypotension, and 43.6% of the patients (n = 17) were female. The median age of the postintubation hypotension group was 75.0 (interquartile range: 67.0 - 84.0). In the multivariate analysis, shock index ≥ 0.90 (OR = 7.76; 95%CI 3.14 - 19.21; p < 0.001), albumin levels < 2.92g/dL (OR = 3.65; 95%CI 1.49 - 8.96; p = 0.005), and procalcitonin levels (OR = 1.07, 95%CI 1.01 - 1.15; p = 0.045) were independent risk factors for postintubation hypotension. Hospital mortality was similar in patients with postintubation hypotension and patients without postintubation hypotension (92.5% versus 85.2%; p = 0.29).
The incidence of postintubation hypotension was 37.5% in critically ill COVID-19 patients. A shock index ≥ 0.90 and albumin levels < 2.92g/dL were independently associated with postintubation hypotension. Furthermore, a shock index ≥ 0.90 may be a practical tool to predict the increased risk of postintubation hypotension in bedside scenarios before endotracheal intubation. In this study, postintubation hypotension was not associated with increased hospital mortality in COVID-19 patients.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2020;32(3):433-438
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20200073
To describe the use of neuromuscular blockade as well as other practices among Brazilian physicians in adult intensive care units.
An online national survey was designed and administered to Brazilian intensivists. Questions were selected using the Delphi method and assessed physicians’ demographic data, intensive care unit characteristics, practices regarding airway management, use of neuromuscular blockade and sedation during endotracheal intubation in the intensive care unit. As a secondary outcome, we applied a multivariate analysis to evaluate factors associated with the use of neuromuscular blockade.
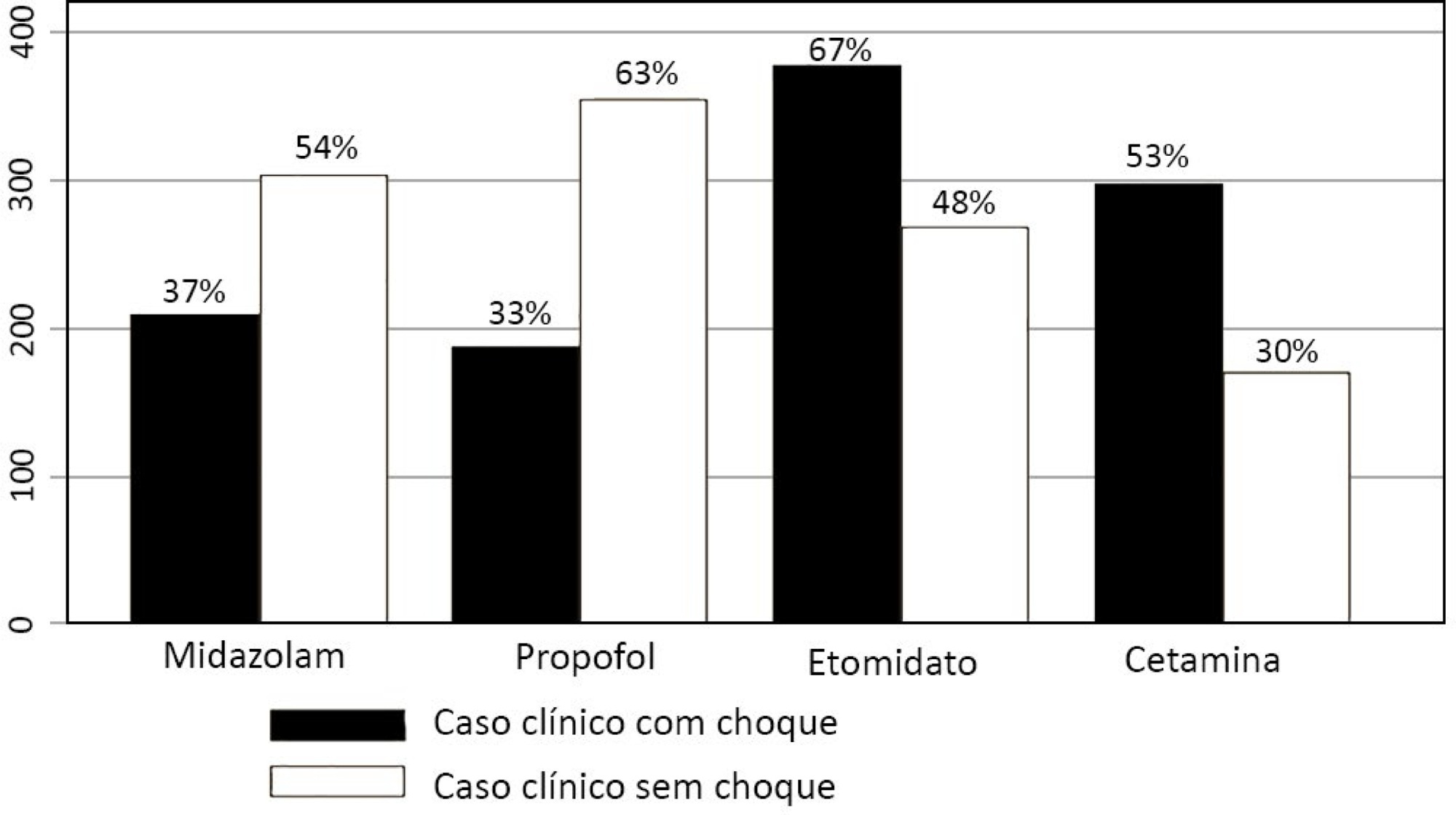
Five hundred sixty-five intensivists from all Brazilian regions responded to the questionnaire. The majority of respondents were male (65%), with a mean age of 38 ( 8.4 years, and 58.5% had a board certification in critical care. Only 40.7% of the intensivists reported the use of neuromuscular blockade during all or in more than 75% of endotracheal intubations. In the multivariate analysis, the number of intubations performed monthly and physician specialization in anesthesiology were directly associated with frequent use of neuromuscular blockade. Etomidate and ketamine were more commonly used in the clinical situation of hypotension and shock, while propofol and midazolam were more commonly prescribed in the situation of clinical stability.
The reported use of neuromuscular blockade was low among intensivists, and sedative drugs were chosen in accordance with patient hemodynamic stability. These results may help the design of future studies regarding airway management in Brazil.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2019;31(1):79-85
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20190012
We aimed to determine the incidence, risk factors, and outcomes of unplanned extubation among adult patients.
We conducted a prospective cohort study of adult intubated patients admitted to the charity wards of a government tertiary teaching hospital in the Philippines. Patients managed in both intensive care and nonintensive care settings were included. Patients were followed-up until discharge or until seven days postextubation.
The outcomes of the 191 included patients were planned extubation (35%), unplanned extubation (19%), death (39%), and discharge against advice (7%). Competing risk regression showed that male sex (Crude OR: 2.25, 95%CI: 1.10 - 4.63) and age (Crude OR 0.976, 95%CI: 0.957 - 0.996) were significant baseline factors. The night shift (Crude OR: 24.6, 95%CI: 2.87 - 211) was also consistently associated with more unplanned extubations. Among postextubation outcomes, reintubation (unplanned extubation: 61.1% versus planned extubation: 25.4%), acute respiratory failure (unplanned extubation: 38.9% versus planned extubation: 17.5%), and cardiovascular events (unplanned extubation: 8.33% versus planned extubation: 1.49%) occurred significantly more often among the unplanned extubation patients. Admission in an intensive care unit was not associated with a lower risk of unplanned extubation (Crude OR 1.15, 95%CI: 0.594 - 2.21).
Many intubated patients had unplanned extubation. Patients admitted in nonintensive care unit settings did not have significantly higher odds of unplanned extubation.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2017;29(2):180-187
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20170028
To analyze patients after cardiac surgery that needed endotracheal reintubation and identify factors associated with death and its relation with the severity scores.
Retrospective analysis of information of 1,640 patients in the postoperative period of cardiac surgery between 2007 and 2015.
The reintubation rate was 7.26%. Of those who were reintubated, 36 (30.3%) underwent coronary artery bypass surgery, 27 (22.7%) underwent valve replacement, 25 (21.0%) underwent correction of an aneurysm, and 8 (6.7%) underwent a heart transplant. Among those with comorbidities, 54 (51.9%) were hypertensive, 22 (21.2%) were diabetic, and 10 (9.6%) had lung diseases. Among those who had complications, 61 (52.6%) had pneumonia, 50 (42.4%) developed renal failure, and 49 (51.0%) had a moderate form of the transient disturbance of gas exchange. Noninvasive ventilation was performed in 53 (44.5%) patients. The death rate was 40.3%, and mortality was higher in the group that did not receive noninvasive ventilation before reintubation (53.5%). Within the reintubated patients who died, the SOFA and APACHE II values were 7.9 ± 3.0 and 16.9 ± 4.5, respectively. Most of the reintubated patients (47.5%) belonged to the high-risk group, EuroSCORE (> 6 points).
The reintubation rate was high, and it was related to worse SOFA, APACHE II and EuroSCORE scores. Mortality was higher in the group that did not receive noninvasive ventilation before reintubation.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2011;23(1):49-55
DOI 10.1590/S0103-507X2011000100009
OBJECTIVE: Appropriate nutritional support is important to the outcomes of critically ill patients. However, a significant portion of these patients experience intestinal motility problems. Administration of enteral nutrition by means of tubes placed in the post-pyloric position has been suggested to improve the nutrition tolerance. The aim of this study was to compare the rate of successful post-pyloric placement using a real-time electromagnetic positioning device to the success rate using the conventional placement method. METHODS: This was a prospective, randomized and controlled study, conducted in a tertiary hospital over a period of three months. The patients were randomized to one of two groups: electromagnetically guided system group, whose patients underwent real-time monitoring of post-pyloric tube placement; or the control group, whose patients underwent tube placment using to the conventional blinded technique. The rates of successful post-pyloric placement and the procedure times were assessed and compared between the groups. RESULTS: Thirty-seven patients were enrolled, 18 in the electromagnetic group and 19 in the control group. The final tube position was evaluated using radiography. The electromagnetic guided group showed better success rates and shorter procedure times when compared to the control group. Additionally, in the electromagnetic guided group, higher pH values were found in the fluids aspirated from the probe, suggesting successful postpyloric placement. CONCLUSION: The electromagnetically guided method provided better placement accuracy than did the conventional technique.
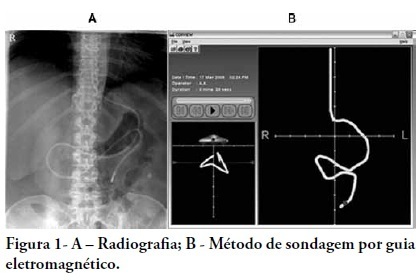
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2010;22(2):192-195
DOI 10.1590/S0103-507X2010000200014
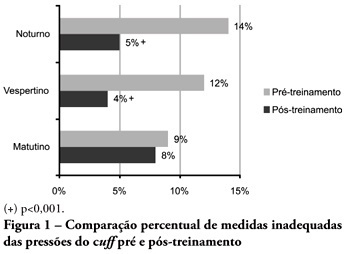
OBJECTIVES: Direct cuff pressure to the tracheal wall can cause damage. This paper aimed to verify the effectiveness of nursing team training on cuff pressure control. METHODS: A retrospective survey was initially made on the records of cuff pressure measurements from January 2007 to June 2008 and the inadequacy percent was verified. Next, a nursing team training program was provided involving all nursing shift teams during June 2008, and after the training the appropriate cuff pressures proportion was prospectively recorded between June and December 2008. The proportion of inappropriate cuff pressure was compared between the work shifts (morning, afternoon and evening-night) and between pre- and post-training, using the qualitative Chi-square test. The 5% limit (p<0.05) was considered for significant differences. RESULTS: For the pre-training period, inappropriate cuff pressure measures (over 30cmH2O) during morning, afternoon and evening-night shifts were 9.2%, 11.9% and 13.7%, respectively. For the post-training phase, 7.6%, 4.1% and 5.2% inappropriate cuff-pressures were identified for the morning, afternoon and evening-night shifts, respectively, with a significant reduction for the afternoon and evening-night shifts, respectively (p<0.001). CONCLUSION: Nursing team training was effective for inadequate cuff pressure harms awareness improvement, and resulted in safer pressure levels.
Search
Search in:
Case reports (56) Child (53) Coronavirus infections (33) COVID-19 (45) Critical care (115) Critical illness (54) Infant, newborn (27) Intensive care (72) Intensive care units (254) Intensive care units, pediatric (31) mechanical ventilation (38) Mortality (75) Physical therapy modalities (28) Prognosis (61) Respiration, artificial (117) Respiratory insufficiency (26) risk factors (34) SARS-CoV-2 (28) Sepsis (98) Septic shock (25)