Abstract
Crit Care Sci. 2024;36:e20240158en
DOI 10.62675/2965-2774.20240158-pt
To evaluate the association of biomarkers with successful ventilatory weaning in COVID-19 patients.
An observational, retrospective, and single-center study was conducted between March 2020 and April 2021. C-reactive protein, total lymphocytes, and the neutrophil/lymphocyte ratio were evaluated during attrition and extubation, and the variation in these biomarker values was measured. The primary outcome was successful extubation. ROC curves were drawn to find the best cutoff points for the biomarkers based on sensitivity and specificity. Statistical analysis was performed using logistic regression.
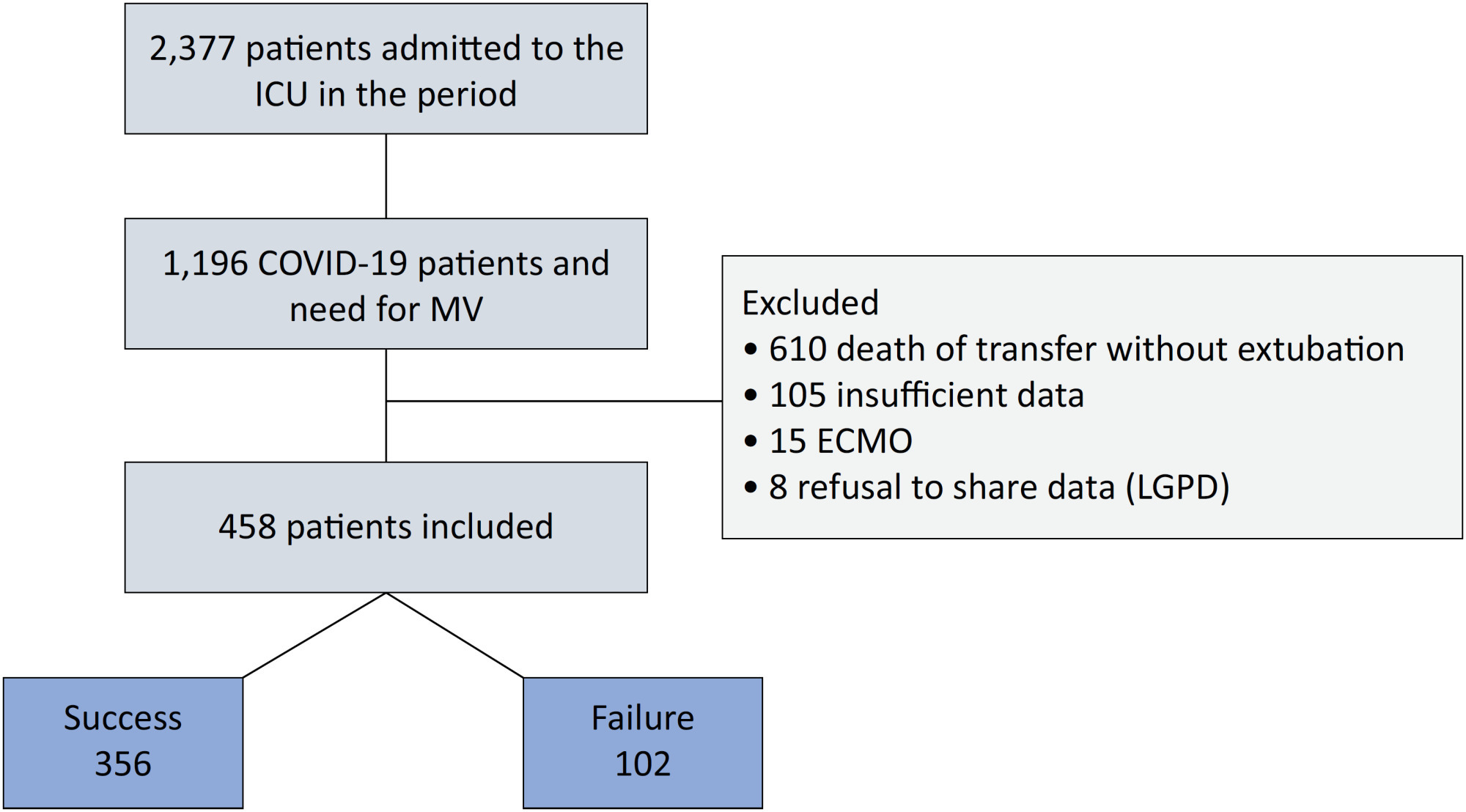
Of the 2,377 patients admitted to the intensive care unit, 458 were included in the analysis, 356 in the Successful Weaning Group and 102 in the Failure Group. The cutoff points found from the ROC curves were −62.4% for C-reactive protein, +45.7% for total lymphocytes, and −32.9% for neutrophil/lymphocyte ratio. These points were significantly associated with greater extubation success. In the multivariate analysis, only C-reactive protein variation remained statistically significant (OR 2.6; 95%CI 1.51 – 4.5; p < 0.001).
In this study, a decrease in C-reactive protein levels was associated with successful extubation in COVID-19 patients. Total lymphocytes and the neutrophil/lymphocyte ratio did not maintain the association after multivariate analysis. However, a decrease in C-reactive protein levels should not be used as a sole variable to identify COVID-19 patients suitable for weaning; as in our study, the area under the ROC curve demonstrated poor accuracy in discriminating extubation outcomes, with low sensitivity and specificity.
Abstract
Crit Care Sci. 2023;35(2):147-155
DOI 10.5935/2965-2774.20230422-pt
To assess factors associated with long-term neuropsychiatric outcomes, including biomarkers measured after discharge from the intensive care unit.
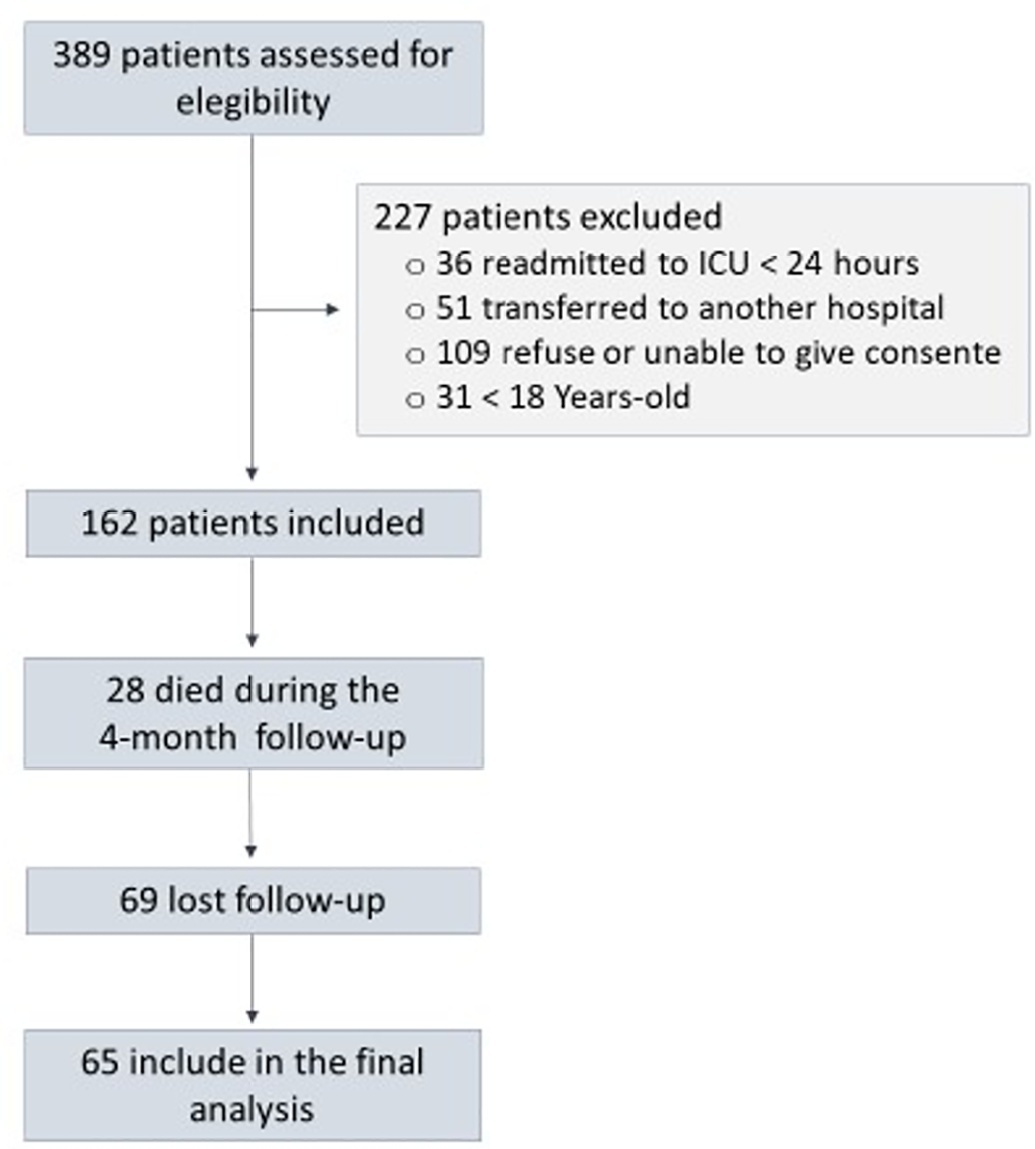
A prospective cohort study was performed with 65 intensive care unit survivors. The cognitive evaluation was performed through the Mini-Mental State Examination, the symptoms of anxiety and depression were evaluated using the Hospital Anxiety and Depression Scale, and posttraumatic stress disorder was evaluated using the Impact of Event Scale-6. Plasma levels of amyloid-beta (1-42) [Aβ (1-42)], Aβ (1-40), interleukin (IL)-10, IL-6, IL-33, IL-4, IL-5, tumor necrosis factor alpha, C-reactive protein, and brain-derived neurotrophic factor were measured at intensive care unit discharge.
Of the variables associated with intensive care, only delirium was independently related to the occurrence of long-term cognitive impairment. In addition, higher levels of IL-10 and IL-6 were associated with cognitive dysfunction. Only IL-6 was independently associated with depression. Mechanical ventilation, IL-33 levels, and C-reactive protein levels were independently associated with anxiety. No variables were independently associated with posttraumatic stress disorder.
Cognitive dysfunction, as well as symptoms of depression, anxiety, and posttraumatic stress disorder, are present in patients who survive a critical illness, and some of these outcomes are associated with the levels of inflammatory biomarkers measured at discharge from the intensive care unit.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2019;31(1):93-105
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20190001
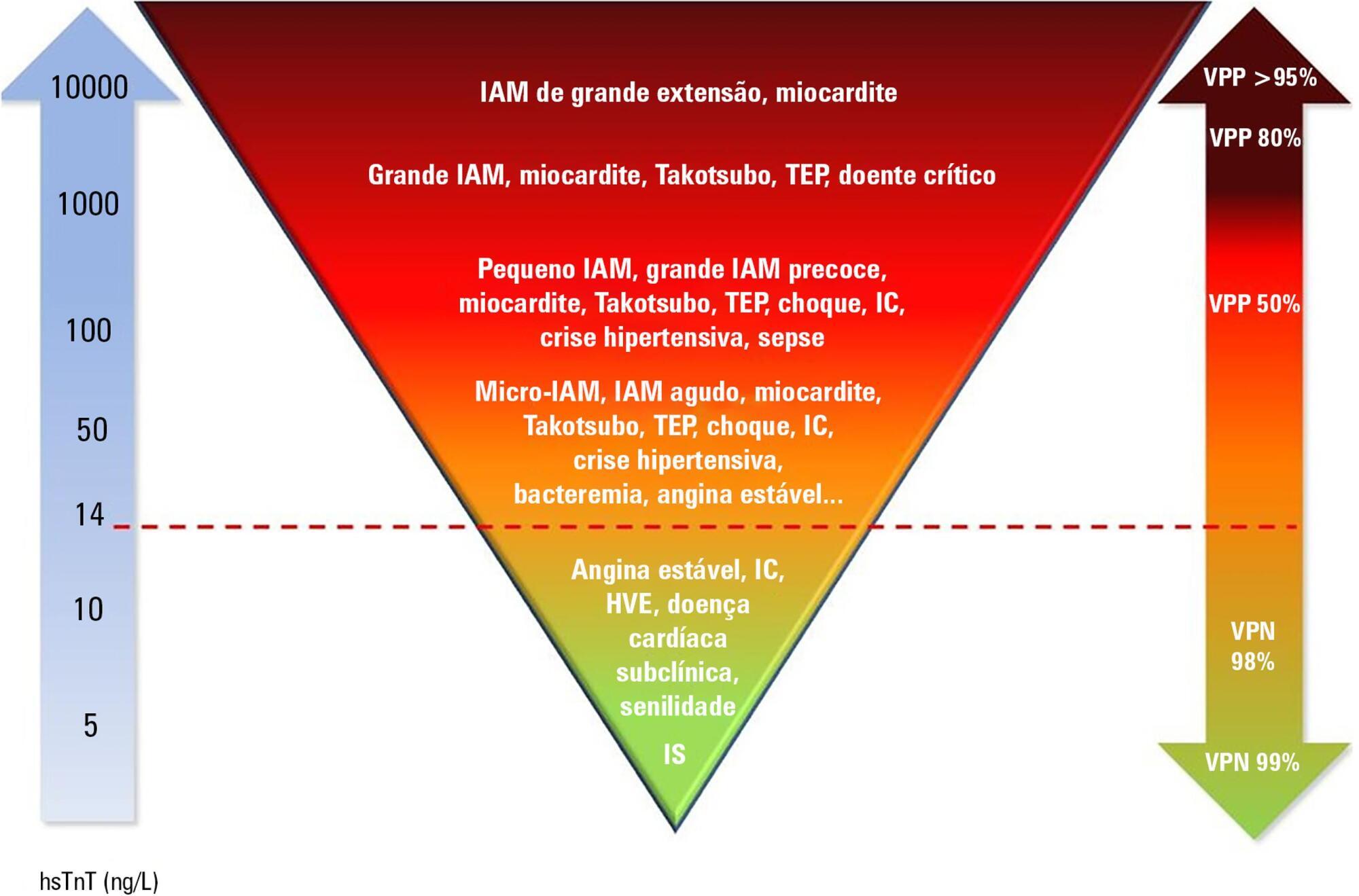
Cardiac troponins T and I are considered highly sensitive and specific markers for the diagnosis of acute myocardial infarction. Currently, a series of nonprimary cardiac abnormalities may manifest as an elevation in high-sensitive assays. The reduction in their detection limits has allowed earlier diagnosis and the use of evidence-based therapeutic measures; however, this characteristic has increased the spectrum of detectable noncoronary heart diseases, which poses challenges for characterizing acute coronary syndromes and creates a new role for these tests in known disorders in intensive care units, especially sepsis. Management of patients through a greater understanding of how these markers behave should be re-evaluated to ensure their correct interpretation.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2018;30(4):453-459
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20180062
To determine the performance of soluble urokinase-type plasminogen activator receptor upon intensive care unit discharge to predict post intensive care unit mortality.
A prospective observational cohort study was conducted during a 24-month period in an 8-bed polyvalent intensive care unit. APACHE II, SOFA, C-reactive protein, white cell count and soluble urokinase-type plasminogen activator receptor on the day of intensive care unit discharge were collected from patients who survived intensive care unit admission.
Two hundred and two patients were included in this study, 29 patients (18.6%) of whom died after intensive care unit discharge. Nonsurvivors were older and more seriously ill upon intensive care unit admission with higher severity scores, and nonsurvivors required extended use of vasopressors than did survivors. The area under the receiver operating characteristics curves of SOFA, APACHE II, C-reactive protein, white cell count, and soluble urokinase-type plasminogen activator receptor at intensive care unit discharge as prognostic markers of hospital death were 0.78 (95%CI 0.70 - 0.86); 0.70 (95%CI 0.61 - 0.79); 0.54 (95%CI 0.42 - 0.65); 0.48 (95%CI 0.36 - 0.58); and 0.68 (95%CI 0.58 - 0.78), respectively. SOFA was independently associated with a higher risk of in-hospital mortality (OR 1.673; 95%CI 1.252 - 2.234), 28-day mortality (OR 1.861; 95%CI 1.856 - 2.555) and 90-day mortality (OR 1.584; 95%CI 1.241 - 2.022).
At intensive care unit discharge, soluble urokinase-type plasminogen activator receptor is a poor predictor of post intensive care unit prognosis.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2018;30(4):443-452
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20180064
To evaluate the accuracy of IL-3 to predict the outcome of septic patients.
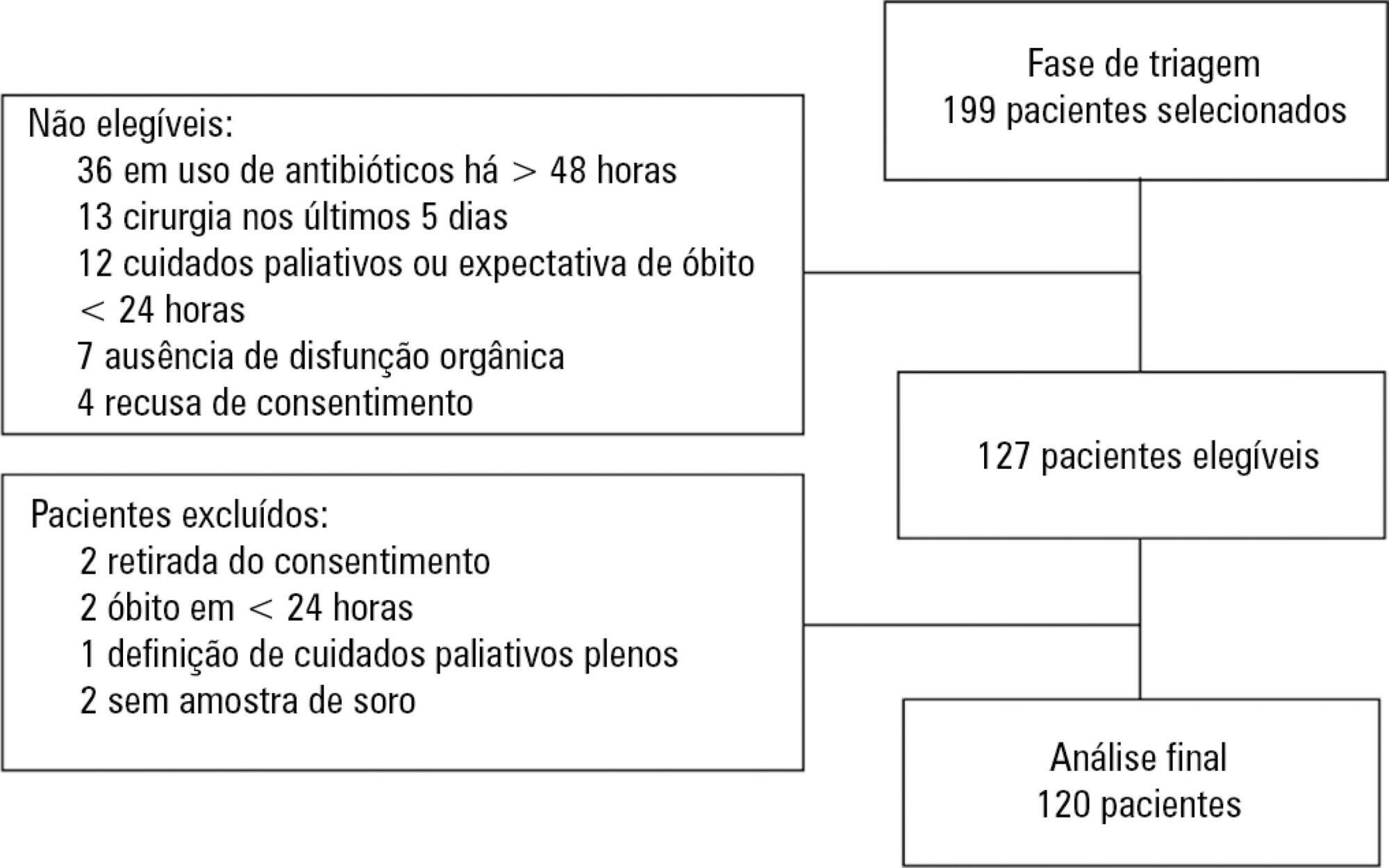
Prospective cohort study with adult patients in an intensive care unit with sepsis or septic shock diagnosed within the previous 48 hours. Circulating IL-3 levels were measured upon inclusion (day 1) and on days 3 and 7. The primary outcome was hospital mortality.
One hundred and twenty patients were included. Serum levels of IL-3 on day 1 were significantly higher among patients who died than among patients who survived the hospital stay (91.2pg/mL versus 36pg/mL, p = 0.024). In a Cox survival model considering the IL-3 levels at inclusion, age and sequential SOFA, IL-3 values remained independently associated with mortality (HR 1.032; 95%CI 1.010 - 1.055; p = 0.005). An receiver operating characteristic curve was built to further investigate the accuracy of IL-3, with an area under the curve of 0.62 (95%CI 0.51 - 0.73; p = 0.024) for hospital mortality. A cutoff initial IL-3 value above 127.5pg/mL was associated with hospital mortality (OR 2.97; 95%CI: 1.27 - 6.97; p = 0.0019) but with a low performance (82% for specificity, 39% for sensibility, 53% for the positive predictive value, 72% for the negative predictive value, 0.73 for the negative likelihood and 2.16 for the positive likelihood ratio).
Higher levels of IL-3 are shown to be independently associated with hospital mortality in septic patients but with poor clinical performance.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2017;29(3):373-381
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20170051
Novel biomarkers can be suitable for early acute kidney injury diagnosis and the prediction of the need for dialysis. It remains unclear whether such biomarkers may also play a role in the prediction of recovery after established acute kidney injury or in aiding the decision of when to stop renal support therapy. PubMed, Web of Science and Google Scholar were searched for studies that reported on the epidemiology of renal recovery after acute kidney injury, the risk factors of recovery versus non-recovery after acute kidney injury, and potential biomarkers of acute kidney injury recovery. The reference lists of these articles and relevant review articles were also reviewed. Final references were selected for inclusion in the review based on their relevance. New biomarkers exhibited a potential role in the early diagnosis of acute kidney injury recovery. Urine HGF, IGFBP-7, TIMP-2 and NGAL may improve our ability to predict the odds and timing of recovery and eventually renal support withdrawal. Acute kidney injury recovery requires more study, and its definition needs to be standardized to allow for better and more powerful research on biomarkers because some of them show potential for the prediction of acute kidney injury recovery.
Search
Search in:
Case reports (56) Child (53) Coronavirus infections (33) COVID-19 (45) Critical care (115) Critical illness (54) Infant, newborn (27) Intensive care (72) Intensive care units (254) Intensive care units, pediatric (31) mechanical ventilation (38) Mortality (75) Physical therapy modalities (28) Prognosis (61) Respiration, artificial (117) Respiratory insufficiency (26) risk factors (34) SARS-CoV-2 (28) Sepsis (98) Septic shock (25)