Abstract
Crit Care Sci. 2023;35(3):302-310
DOI 10.5935/2965-2774.20230141-pt
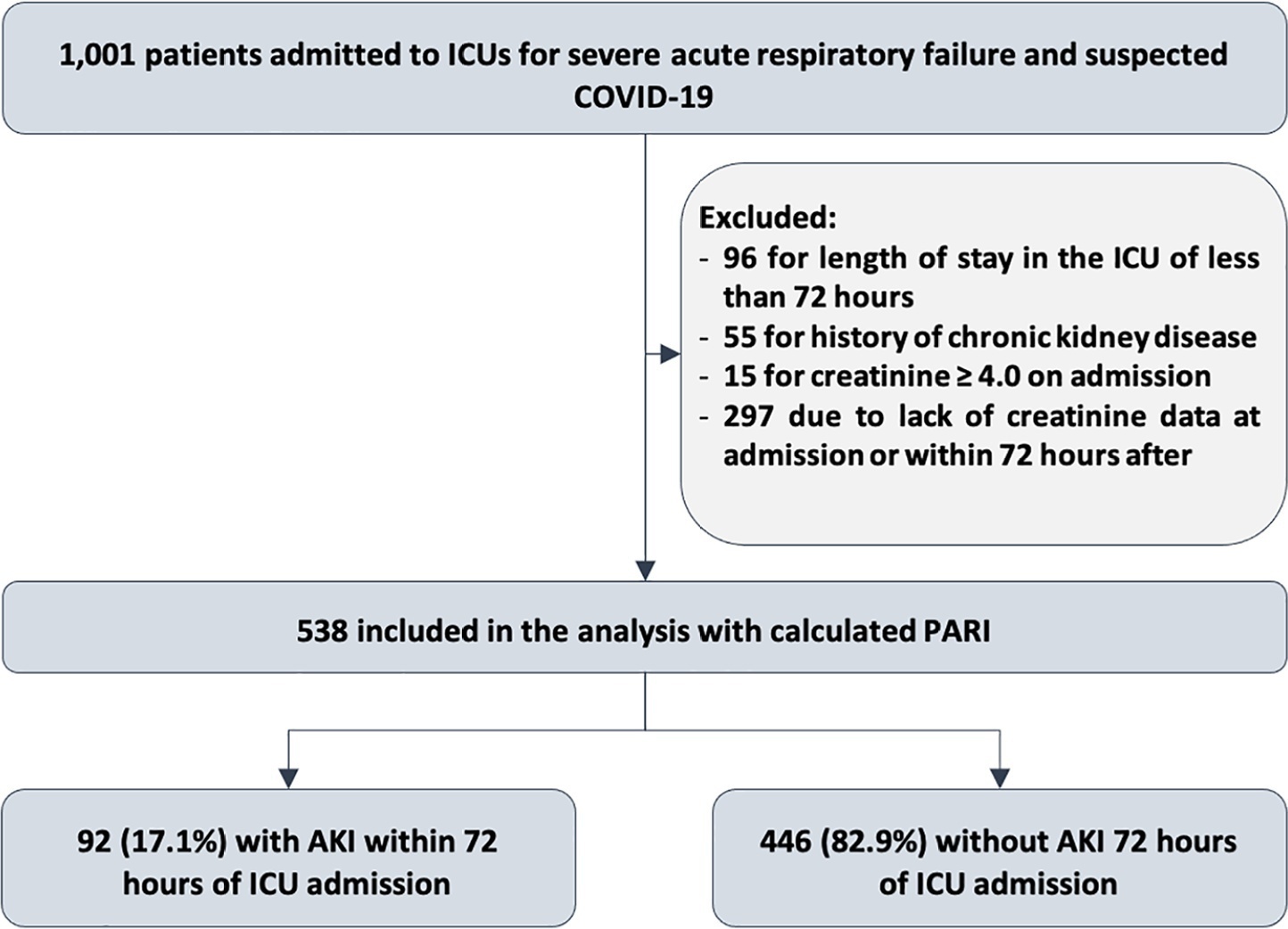
To evaluate the accuracy of the persistent AKI risk index (PARI) in predicting acute kidney injury within 72 hours after admission to the intensive care unit, persistent acute kidney injury, renal replacement therapy, and death within 7 days in patients hospitalized due to acute respiratory failure.
This study was done in a cohort of diagnoses of consecutive adult patients admitted to the intensive care unit of eight hospitals in Curitiba, Brazil, between March and September 2020 due to acute respiratory failure secondary to suspected COVID-19. The COVID-19 diagnosis was confirmed or refuted by RT-PCR for the detection of SARS-CoV-2. The ability of PARI to predict acute kidney injury at 72 hours, persistent acute kidney injury, renal replacement therapy, and death within 7 days was analyzed by ROC curves in comparison to delta creatinine, SOFA, and APACHE II.
Of the 1,001 patients in the cohort, 538 were included in the analysis. The mean age was 62 ± 17 years, 54.8% were men, and the median APACHE II score was 12. At admission, the median SOFA score was 3, and 83.3% had no renal dysfunction. After admission to the intensive care unit, 17.1% had acute kidney injury within 72 hours, and through 7 days, 19.5% had persistent acute kidney injury, 5% underwent renal replacement therapy, and 17.1% died. The PARI had an area under the ROC curve of 0.75 (0.696 - 0.807) for the prediction of acute kidney injury at 72 hours, 0.71 (0.613 - 0.807) for renal replacement therapy, and 0.64 (0.565 - 0.710) for death.
The PARI has acceptable accuracy in predicting acute kidney injury within 72 hours and renal replacement therapy within 7 days of admission to the intensive care unit, but it is not significantly better than the other scores.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2020;32(4):564-570
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20200094
To evaluate renal responsiveness in oliguric critically ill patients after a fluid challenge.
We conducted a prospective observational study in one university intensive care unit. Patients with urine output < 0.5mL/kg/h for 3 hours with a mean arterial pressure > 60mmHg received a fluid challenge. We examined renal fluid responsiveness (defined as urine output > 0.5mL/kg/h for 3 hours) after fluid challenge.
Forty-two patients (age 67 ± 13 years; APACHE II score 16 ± 6) were evaluated. Patient characteristics were similar between renal responders and renal nonresponders. Thirteen patients (31%) were renal responders. Hemodynamic or perfusion parameters were not different between those who did and those who did not increase urine output before the fluid challenge. The areas under the receiver operating characteristic curves were calculated for mean arterial pressure, heart rate, creatinine, urea, creatinine clearance, urea/creatinine ratio and lactate before the fluid challenge. None of these parameters were sensitive or specific enough to predict reversal of oliguria.
After achieving hemodynamic stability, oliguric patients did not increase urine output after a fluid challenge. Systemic hemodynamic, perfusion or renal parameters were weak predictors of urine responsiveness. Our results suggest that volume replacement to correct oliguria in patients without obvious hypovolemia should be done with caution.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2020;32(4):493-505
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20200081
To report the statistical analysis plan (first version) for the Balanced Solutions versus Saline in Intensive Care Study (BaSICS).
BaSICS is a multicenter factorial randomized controlled trial that will assess the effects of Plasma-Lyte 148 versus 0.9% saline as the fluid of choice in critically ill patients, as well as the effects of a slow (333mL/h) versus rapid (999mL/h) infusion speed during fluid challenges, on important patient outcomes. The fluid type will be blinded for investigators, patients and the analyses. No blinding will be possible for the infusion speed for the investigators, but all analyses will be kept blinded during the analysis procedure.
BaSICS will have 90-day mortality as its primary endpoint, which will be tested using mixed-effects Cox proportional hazard models, considering sites as a random variable (frailty models) adjusted for age, organ dysfunction and admission type. Important secondary endpoints include renal replacement therapy up to 90 days, acute renal failure, organ dysfunction at days 3 and 7, and mechanical ventilation-free days within 28 days.
This manuscript provides details on the first version of the statistical analysis plan for the BaSICS trial and will guide the study’s analysis when follow-up is finished.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2020;32(1):123-132
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20200018
To report on the currently available prediction models for the development of acute kidney injury in heterogeneous adult intensive care units.
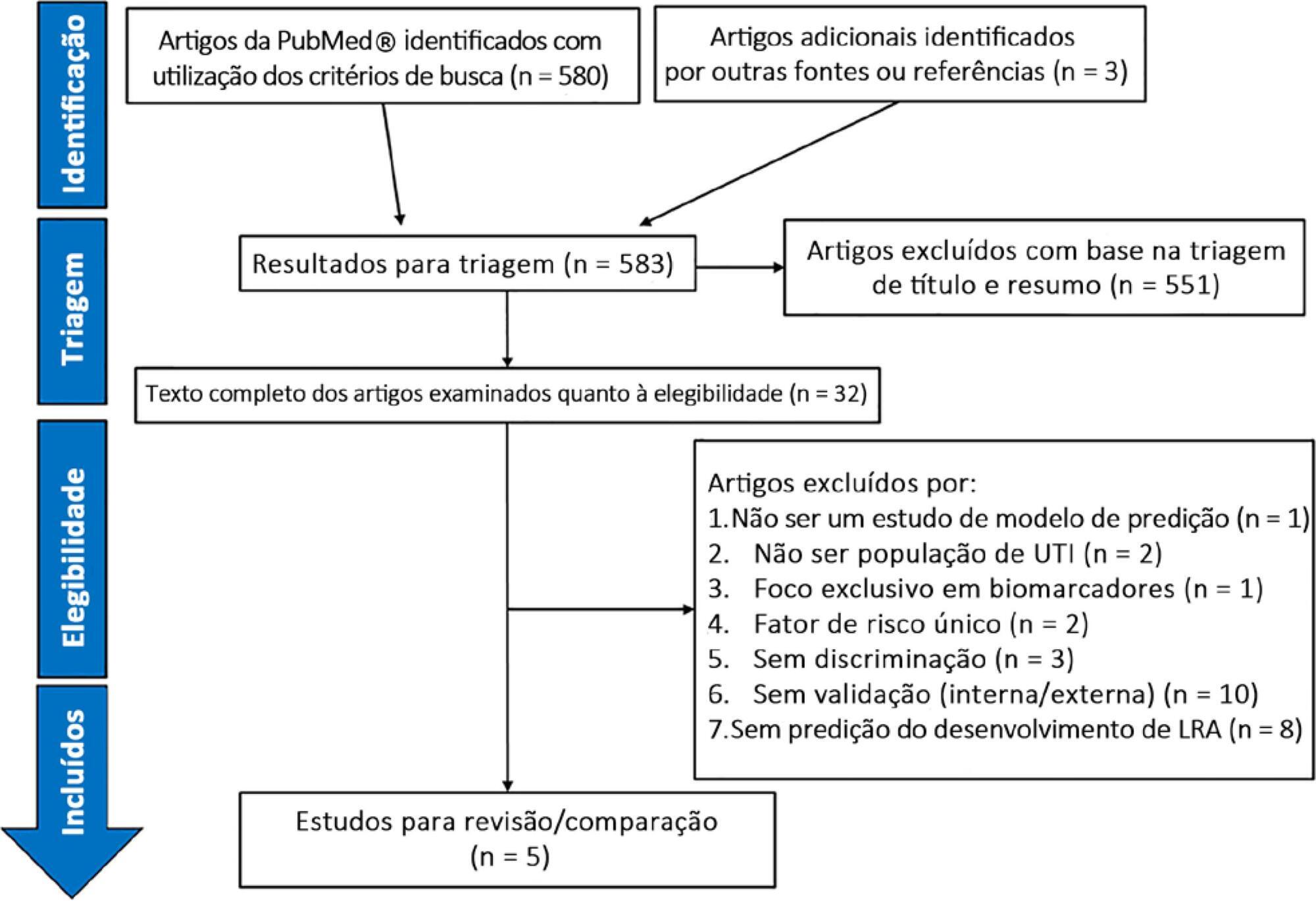
A systematic review of clinical prediction models for acute kidney injury in adult intensive care unit populations was carried out. PubMed® was searched for publications reporting on the development of a novel prediction model, validation of an established model, or impact of an existing prediction model for early acute kidney injury diagnosis in intensive care units.
We screened 583 potentially relevant articles. Among the 32 remaining articles in the first selection, only 5 met the inclusion criteria. The nonstandardized adaptations that were made to define baseline serum creatinine when the preadmission value was missing led to heterogeneous definitions of the outcome. Commonly included predictors were sepsis, age, and serum creatinine level. The final models included between 5 and 19 risk factors. The areas under the Receiver Operating Characteristic curves to predict acute kidney injury development in the internal validation cohorts ranged from 0.78 to 0.88. Only two studies were externally validated.
Clinical prediction models for acute kidney injury can help in applying more timely preventive interventions to the right patients. However, in intensive care unit populations, few models have been externally validated. In addition, heterogeneous definitions for acute kidney injury and evaluation criteria and the lack of impact analysis hamper a thorough comparison of existing models. Future research is needed to validate the established models and to analyze their clinical impact before they can be applied in clinical practice.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2018;30(4):429-435
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20180065
To evaluate the association between acute kidney injury through the pediatric Risk, Injury, Failure, Loss and End Stage Renal Disease score and mortality in a pediatric intensive care unit.
This retrospective cohort study assessed all children admitted to the pediatric intensive care unit of a reference hospital in Brazil from January to December 2016. Patients were screened for the presence of acute kidney injury through the pediatric Risk, Injury, Failure, Loss and End Stage Renal Disease score. Patients were subdivided into the stages of Risk, Injury and Kidney Failure.
The sample comprised 192 children, of whom 45.8% developed acute kidney injury, with 79.5% of the cases identified up to 72 hours after admission. Patients with acute kidney injury showed a 3.74 increase risk of death (p = 0.01) than the control group. Patients with kidney failure had a mortality rate that was 8.56 times greater than that of the remaining sample (p < 0.001). The variables that were associated with the stages of acute kidney injury were nephrotoxic drugs (p = 0.025), renal replacement therapy (p < 0.001), vasoactive drugs (p < 0.001), pediatric risk of mortality 2 score (p = 0.023), fluid overload (p = 0.005), pediatric intensive care unit length of stay (p = 0.001) and death (p < 0.001).
In this study, the pediatric Risk, Injury, Failure, Loss and End Stage Renal Disease score proved to be a useful tool for the early identification of severely ill children with acute kidney injury, showing an association with mortality. We thus suggest its use for pediatric intensive care unit patient admission.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2018;30(2):153-159
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20180030
To investigate prognostic factors among critically ill patients with community-acquired bacterial meningitis and acute kidney injury.
A retrospective study including patients admitted to a tertiary infectious disease hospital in Fortaleza, Brazil diagnosed with community-acquired bacterial meningitis complicated with acute kidney injury. Factors associated with death, mechanical ventilation and use of vasopressors were investigated.
Forty-one patients were included, with a mean age of 41.6 ± 15.5 years; 56% were males. Mean time between intensive care unit admission and acute kidney injury diagnosis was 5.8 ± 10.6 days. Overall mortality was 53.7%. According to KDIGO criteria, 10 patients were classified as stage 1 (24.4%), 18 as stage 2 (43.9%) and 13 as stage 3 (31.7%). KDIGO 3 significantly increased mortality (OR = 6.67; 95%CI = 1.23 - 36.23; p = 0.028). Thrombocytopenia was not associated with higher mortality, but it was a risk factor for KDIGO 3 (OR = 5.67; 95%CI = 1.25 - 25.61; p = 0.024) and for mechanical ventilation (OR = 6.25; 95%CI = 1.33 - 29.37; p = 0.02). Patients who needed mechanical ventilation by 48 hours from acute kidney injury diagnosis had higher urea (44.6 versus 74mg/dL, p = 0.039) and sodium (138.6 versus 144.1mEq/L; p = 0.036).
Mortality among critically ill patients with community-acquired bacterial meningitis and acute kidney injury is high. Acute kidney injury severity was associated with even higher mortality. Thrombocytopenia was associated with severer acute kidney injury. Higher urea was an earlier predictor of severer acute kidney injury than was creatinine.
Search
Search in:
Case reports (56) Child (53) Coronavirus infections (33) COVID-19 (45) Critical care (115) Critical illness (54) Infant, newborn (27) Intensive care (72) Intensive care units (254) Intensive care units, pediatric (31) mechanical ventilation (38) Mortality (75) Physical therapy modalities (28) Prognosis (61) Respiration, artificial (117) Respiratory insufficiency (26) risk factors (34) SARS-CoV-2 (28) Sepsis (98) Septic shock (25)