Home » Drug-related side effects and adverse reactions
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2020;32(4):557-563
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20200093
To evaluate the association between the use of nephrotoxic drugs and acute kidney injury in critically ill pediatric patients.
This was a retrospective cohort study involving all children admitted to the intensive care unit of a pediatric hospital during a 1-year period. Acute kidney injury was defined according to the KDIGO classification. Patients with a length of hospital stay longer than 48 hours and an age between 1 month and 14 years were included. Patients with acute or chronic nephropathy, uropathy, congenital or acquired heart disease, chronic use of nephrotoxic drugs, rhabdomyolysis and tumor lysis syndrome were excluded. Patients were classified according to the use of nephrotoxic drugs during their stay at the pediatric intensive care unit.
The sample consisted of 226 children, of whom 37.1% used nephrotoxic drugs, 42.4% developed acute kidney injury, and 7.5% died. The following drugs, when used alone, were associated with acute kidney injury: acyclovir (p < 0.001), vancomycin (p < 0.001), furosemide (p < 0.001) and ganciclovir (p = 0.008). The concomitant use of two or more nephrotoxic drugs was characterized as an independent marker of renal dysfunction (p < 0.001). After discharge from the pediatric intensive care unit, renal function monitoring in the ward was inadequate in 19.8% of cases.
It is necessary for intensivist physicians to have knowledge of the main nephrotoxic drugs to predict, reduce or avoid damage to their patients.


Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2020;32(4):557-563
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20200093
To evaluate the association between the use of nephrotoxic drugs and acute kidney injury in critically ill pediatric patients.
This was a retrospective cohort study involving all children admitted to the intensive care unit of a pediatric hospital during a 1-year period. Acute kidney injury was defined according to the KDIGO classification. Patients with a length of hospital stay longer than 48 hours and an age between 1 month and 14 years were included. Patients with acute or chronic nephropathy, uropathy, congenital or acquired heart disease, chronic use of nephrotoxic drugs, rhabdomyolysis and tumor lysis syndrome were excluded. Patients were classified according to the use of nephrotoxic drugs during their stay at the pediatric intensive care unit.
The sample consisted of 226 children, of whom 37.1% used nephrotoxic drugs, 42.4% developed acute kidney injury, and 7.5% died. The following drugs, when used alone, were associated with acute kidney injury: acyclovir (p < 0.001), vancomycin (p < 0.001), furosemide (p < 0.001) and ganciclovir (p = 0.008). The concomitant use of two or more nephrotoxic drugs was characterized as an independent marker of renal dysfunction (p < 0.001). After discharge from the pediatric intensive care unit, renal function monitoring in the ward was inadequate in 19.8% of cases.
It is necessary for intensivist physicians to have knowledge of the main nephrotoxic drugs to predict, reduce or avoid damage to their patients.


Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2019;31(4):536-540
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20190064
To describe the occurrence of delirium in cancer patients admitted to the intensive care unit according to clinical and demographic characteristics.
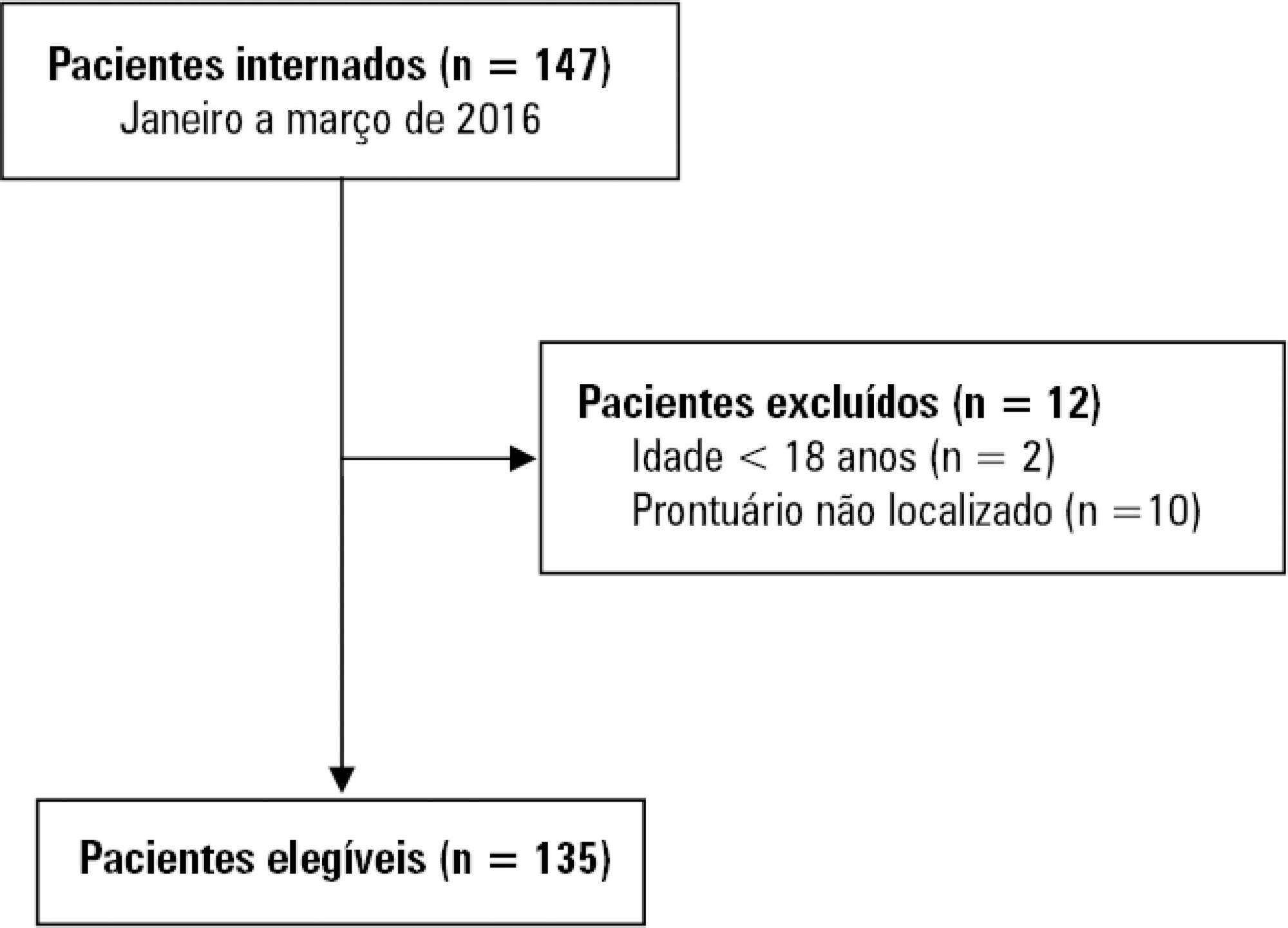
A retrospective study was conducted with 135 adults admitted to the intensive care unit of a public cancer hospital in the city of Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, between January and March 2016. Fisher's exact test and the linear association test were used to identify statistically significant associations between the occurrence of delirium and categorical and ordinal variables, respectively, considering a p-value < 0.05.
The overall occurrence of delirium was 39.3%. Delirium was more frequent among individuals aged 60 years or older and those who required extensive assistance or were bedbound, were admitted to the intensive care unit for clinical reasons, were using sedative drugs, were undergoing chemotherapy, and those who remained 8 or more days in the intensive care unit. Considering only patients on mechanical ventilation, the overall occurrence of delirium was 64.6%, and only a length of stay in the intensive care unit ≥ 8 days showed a statistically significant association with delirium.
The occurrence of delirium in critically ill cancer patients is high. When only those on mechanical ventilation are considered, the occurrence of delirium is even greater.


Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2019;31(4):536-540
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20190064
To describe the occurrence of delirium in cancer patients admitted to the intensive care unit according to clinical and demographic characteristics.
A retrospective study was conducted with 135 adults admitted to the intensive care unit of a public cancer hospital in the city of Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, between January and March 2016. Fisher's exact test and the linear association test were used to identify statistically significant associations between the occurrence of delirium and categorical and ordinal variables, respectively, considering a p-value < 0.05.
The overall occurrence of delirium was 39.3%. Delirium was more frequent among individuals aged 60 years or older and those who required extensive assistance or were bedbound, were admitted to the intensive care unit for clinical reasons, were using sedative drugs, were undergoing chemotherapy, and those who remained 8 or more days in the intensive care unit. Considering only patients on mechanical ventilation, the overall occurrence of delirium was 64.6%, and only a length of stay in the intensive care unit ≥ 8 days showed a statistically significant association with delirium.
The occurrence of delirium in critically ill cancer patients is high. When only those on mechanical ventilation are considered, the occurrence of delirium is even greater.


Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2018;30(2):219-225
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20180036
To review the evidence on the safety of neuromuscular electrical stimulation when used in the intensive care unit.
A systematic review was conducted; a literature search was performed of the MEDLINE (via PubMed), PEDro, Cochrane CENTRAL and EMBASE databases, and a further manual search was performed among the references cited in randomized studies. Randomized clinical trials that compared neuromuscular electrical stimulation to a control or placebo group in the intensive care unit and reporting on the technique safety in the outcomes were included. Hemodynamic variables and information on adverse effects were considered safety parameters. Articles were independently analyzed by two reviewers, and the data analysis was descriptive.
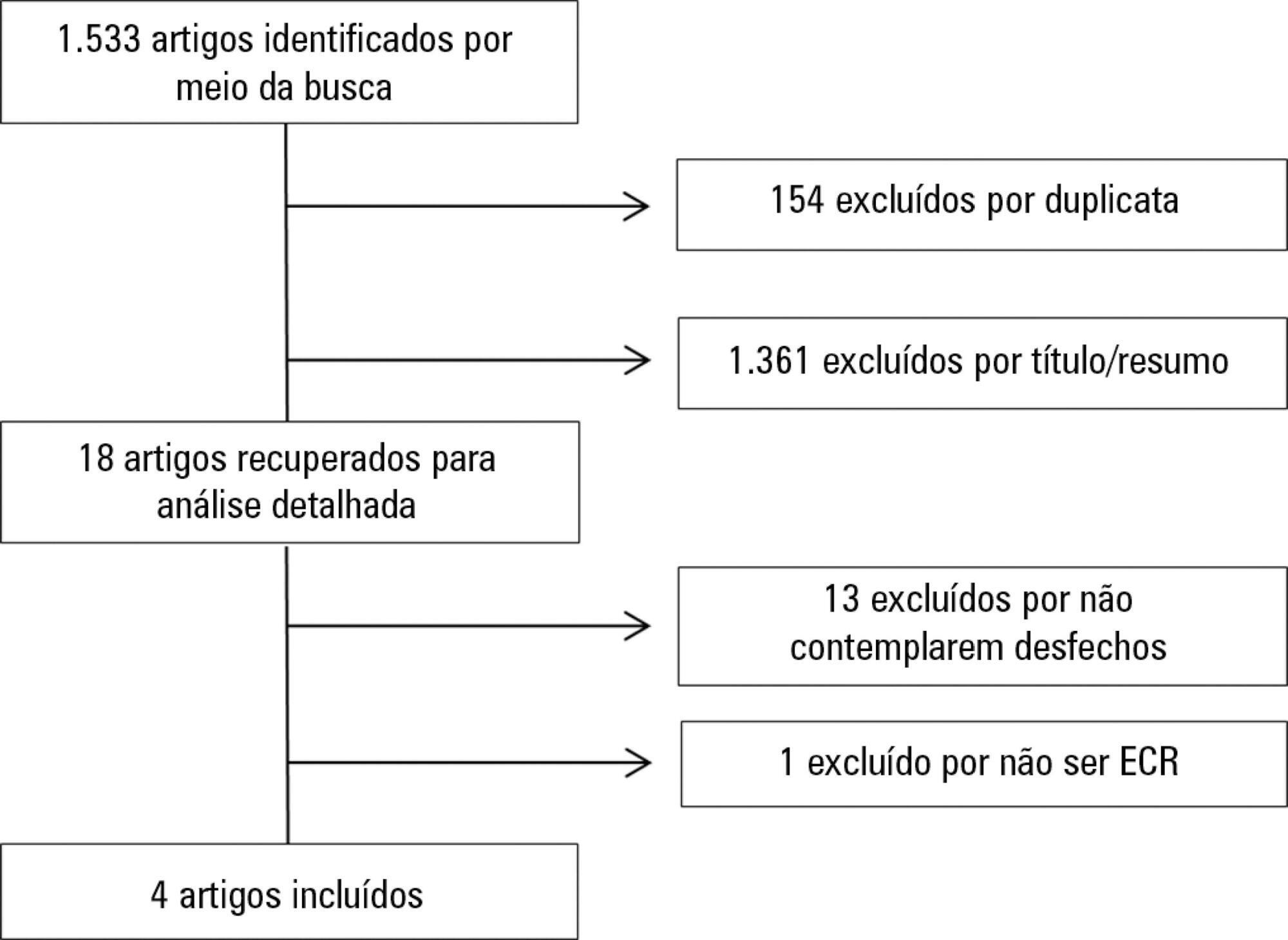
The initial search located 1,533 articles, from which only four randomized clinical trials were included. Two studies assessed safety based on hemodynamic variables, and only one study reported an increase in heart rate, respiratory rate and blood lactate, without clinical relevance. The other two studies assessed safety based on reported adverse effects. In one, 15% of patients described a prickling sensation, without any clinically relevant abnormalities. In the other, one patient suffered a superficial burn due to improper parameter configuration.
Neuromuscular electrical stimulation is safe for critically ill patients; however, it should be applied by duly trained professionals and with proper evidence-based parameters.


Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2018;30(2):219-225
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20180036
To review the evidence on the safety of neuromuscular electrical stimulation when used in the intensive care unit.
A systematic review was conducted; a literature search was performed of the MEDLINE (via PubMed), PEDro, Cochrane CENTRAL and EMBASE databases, and a further manual search was performed among the references cited in randomized studies. Randomized clinical trials that compared neuromuscular electrical stimulation to a control or placebo group in the intensive care unit and reporting on the technique safety in the outcomes were included. Hemodynamic variables and information on adverse effects were considered safety parameters. Articles were independently analyzed by two reviewers, and the data analysis was descriptive.
The initial search located 1,533 articles, from which only four randomized clinical trials were included. Two studies assessed safety based on hemodynamic variables, and only one study reported an increase in heart rate, respiratory rate and blood lactate, without clinical relevance. The other two studies assessed safety based on reported adverse effects. In one, 15% of patients described a prickling sensation, without any clinically relevant abnormalities. In the other, one patient suffered a superficial burn due to improper parameter configuration.
Neuromuscular electrical stimulation is safe for critically ill patients; however, it should be applied by duly trained professionals and with proper evidence-based parameters.


Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2015;27(4):353-359
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20150060
To evaluate the incidence of potential drug-drug interactions in an intensive care unit of a hospital, focusing on antimicrobial drugs.
This cross-sectional study analyzed electronic prescriptions of patients admitted to the intensive care unit of a teaching hospital between January 1 and March 31, 2014 and assessed potential drug-drug interactions associated with antimicrobial drugs. Antimicrobial drug consumption levels were expressed in daily doses per 100 patient-days. The search and classification of the interactions were based on the Micromedex® system.
The daily prescriptions of 82 patients were analyzed, totaling 656 prescriptions. Antimicrobial drugs represented 25% of all prescription drugs, with meropenem, vancomycin and ceftriaxone being the most prescribed medications. According to the approach of daily dose per 100 patient-days, the most commonly used antimicrobial drugs were cefepime, meropenem, sulfamethoxazole + trimethoprim and ciprofloxacin. The mean number of interactions per patient was 2.6. Among the interactions, 51% were classified as contraindicated or significantly severe. Highly significant interactions (clinical value 1 and 2) were observed with a prevalence of 98%.
The current study demonstrated that antimicrobial drugs are frequently prescribed in intensive care units and present a very high number of potential drug-drug interactions, with most of them being considered highly significant.


Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2015;27(4):353-359
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20150060
To evaluate the incidence of potential drug-drug interactions in an intensive care unit of a hospital, focusing on antimicrobial drugs.
This cross-sectional study analyzed electronic prescriptions of patients admitted to the intensive care unit of a teaching hospital between January 1 and March 31, 2014 and assessed potential drug-drug interactions associated with antimicrobial drugs. Antimicrobial drug consumption levels were expressed in daily doses per 100 patient-days. The search and classification of the interactions were based on the Micromedex® system.
The daily prescriptions of 82 patients were analyzed, totaling 656 prescriptions. Antimicrobial drugs represented 25% of all prescription drugs, with meropenem, vancomycin and ceftriaxone being the most prescribed medications. According to the approach of daily dose per 100 patient-days, the most commonly used antimicrobial drugs were cefepime, meropenem, sulfamethoxazole + trimethoprim and ciprofloxacin. The mean number of interactions per patient was 2.6. Among the interactions, 51% were classified as contraindicated or significantly severe. Highly significant interactions (clinical value 1 and 2) were observed with a prevalence of 98%.
The current study demonstrated that antimicrobial drugs are frequently prescribed in intensive care units and present a very high number of potential drug-drug interactions, with most of them being considered highly significant.


Search
Search in:
Case reports (56) Child (53) Coronavirus infections (34) COVID-19 (46) Critical care (116) Critical illness (54) Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (26) Infant, newborn (27) Intensive care (72) Intensive care units (256) Intensive care units, pediatric (31) mechanical ventilation (38) Mortality (76) Physical therapy modalities (28) Prognosis (61) Respiration, artificial (119) Respiratory insufficiency (26) risk factors (34) SARS-CoV-2 (28) Sepsis (98)


