Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2013;25(2):162-167
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20130028
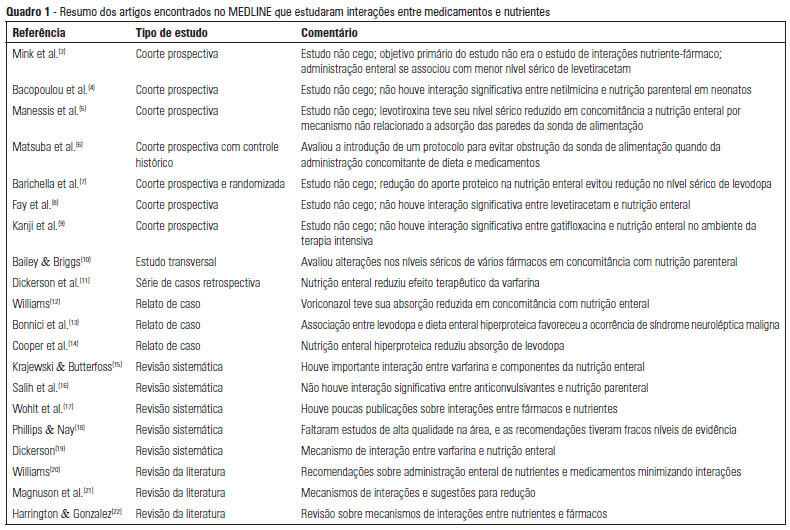
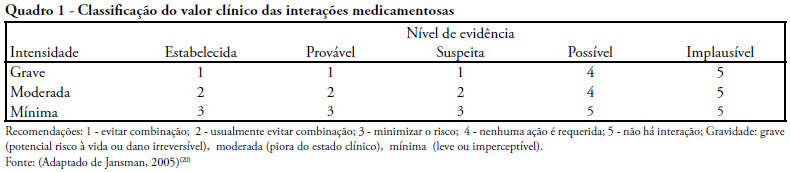
OBJECTIVE: To describe the interactions between drugs and nutrients and their frequency in the intensive care unit and to assess the professional team's awareness regarding this subject. METHODS: The keywords "drug interactions" and "nutrition therapy" were searched in the PubMed (specifically MeSH) electronic database. The studies were systematically reviewed for descriptions of the types of interactions between drugs and nutrients, including their frequency and consequences. RESULTS: Sixty-seven articles were found. Among these, 20 articles were appropriate for the methodology adopted and accomplished the objectives of the study. Of these 20 articles, 14 articles described interactions between drugs and enteral nutrition, three described interactions between drugs and parenteral nutrition, and three described the importance and care required to avoid such interactions. CONCLUSIONS: The literature about drug and nutrient interactions is limited and suggests the inability of health care teams to recognize the potential for these interactions. Possibly, the elaboration of a protocol to evaluate drug-nutrient interactions will increase the safety and efficacy of therapeutics.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2008;20(4):349-354
DOI 10.1590/S0103-507X2008000400006
OBJECTIVES: Drug interactions occur when effects and/or toxicity of a drug are affected by presence of another drug. They are usually unpredictable and undesirable. A study was conducted to verify the prevalence and clinical value of potential drug interactions in intensive care units METHODS: All patients, of three intensive care units were included in a cross-sectional study, over a period of two months. Patients with less than a 2 days length of stay were excluded. Data were collected from twenty-four hour prescriptions and all possible paired combinations drug-drug were recorded. Prevalence and clinical value (significance) were checked at the end of follow-up. RESULTS: One hundred and forty patients were analyzed, 67.1% presented with some significant potential drug interactions and of the 1069 prescriptions, 39.2% disclosed the same potential. Of 188 different potential drug interactions, 29 were considered highly significant. Univariate analysis showed that in the group with significant potential drug interactions a higher number of different drugs, drugs/day had been used, there were more prescribing physicians and extended stay in intensive care units. Adjusted to the multivariate logistic regression model, only the number of drugs/day correlated with increased risk of significant potential drug interaction (p = 0.0011) and, furthermore that use of more than 6 drugs/day increased relative risk by 9.8 times. CONCLUSIONS: Critically ill patients are submitted to high risk of potential drug interactions and the number of drugs/day has a high positive predictive value for these interactions. Therefore, it is imperative that critical care physicians be constantly alert to recognize this problem and provide appropriate mechanisms for management, thereby reducing adverse outcomes.
Search
Search in:
Case reports (56) Child (53) Coronavirus infections (34) COVID-19 (46) Critical care (116) Critical illness (54) Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (26) Infant, newborn (27) Intensive care (72) Intensive care units (256) Intensive care units, pediatric (31) mechanical ventilation (38) Mortality (76) Physical therapy modalities (28) Prognosis (61) Respiration, artificial (119) Respiratory insufficiency (26) risk factors (34) SARS-CoV-2 (28) Sepsis (98)