You searched for:"Catherine Bouman"
We found (1) results for your search.-
Review Article
Early versus delayed initiation of renal replacement therapy for acute kidney injury: an updated systematic review, meta-analysis, meta-regression and trial sequential analysis of randomized controlled trials
- Fabio Tanzillo Moreira,
- Henrique Palomba,
- Renato Carneiro de Freitas Chaves,
- Catherine Bouman,
- Marcus Josephus Schultz, [ … ],
- Ary Serpa Neto
Abstract
Review ArticleEarly versus delayed initiation of renal replacement therapy for acute kidney injury: an updated systematic review, meta-analysis, meta-regression and trial sequential analysis of randomized controlled trials
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2018;30(3):376-384
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20180054
- Fabio Tanzillo Moreira,
- Henrique Palomba,
- Renato Carneiro de Freitas Chaves,
- Catherine Bouman,
- Marcus Josephus Schultz,
- Ary Serpa Neto
Views0ABSTRACT
Objective:
To evaluate whether early initiation of renal replacement therapy is associated with lower mortality in patients with acute kidney injury compared to delayed initiation.
Methods:
We performed a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials comparing early versus delayed initiation of renal replacement therapy in patients with acute kidney injury without the life-threatening acute kidney injury-related symptoms of fluid overload or metabolic disorders. Two investigators extracted the data from the selected studies. The Cochrane Risk of Bias Tool was used to assess the quality of the studies, and the Grading of Recommendations Assessment, Development and Evaluation (GRADE) approach was used to test the overall quality of the evidence.
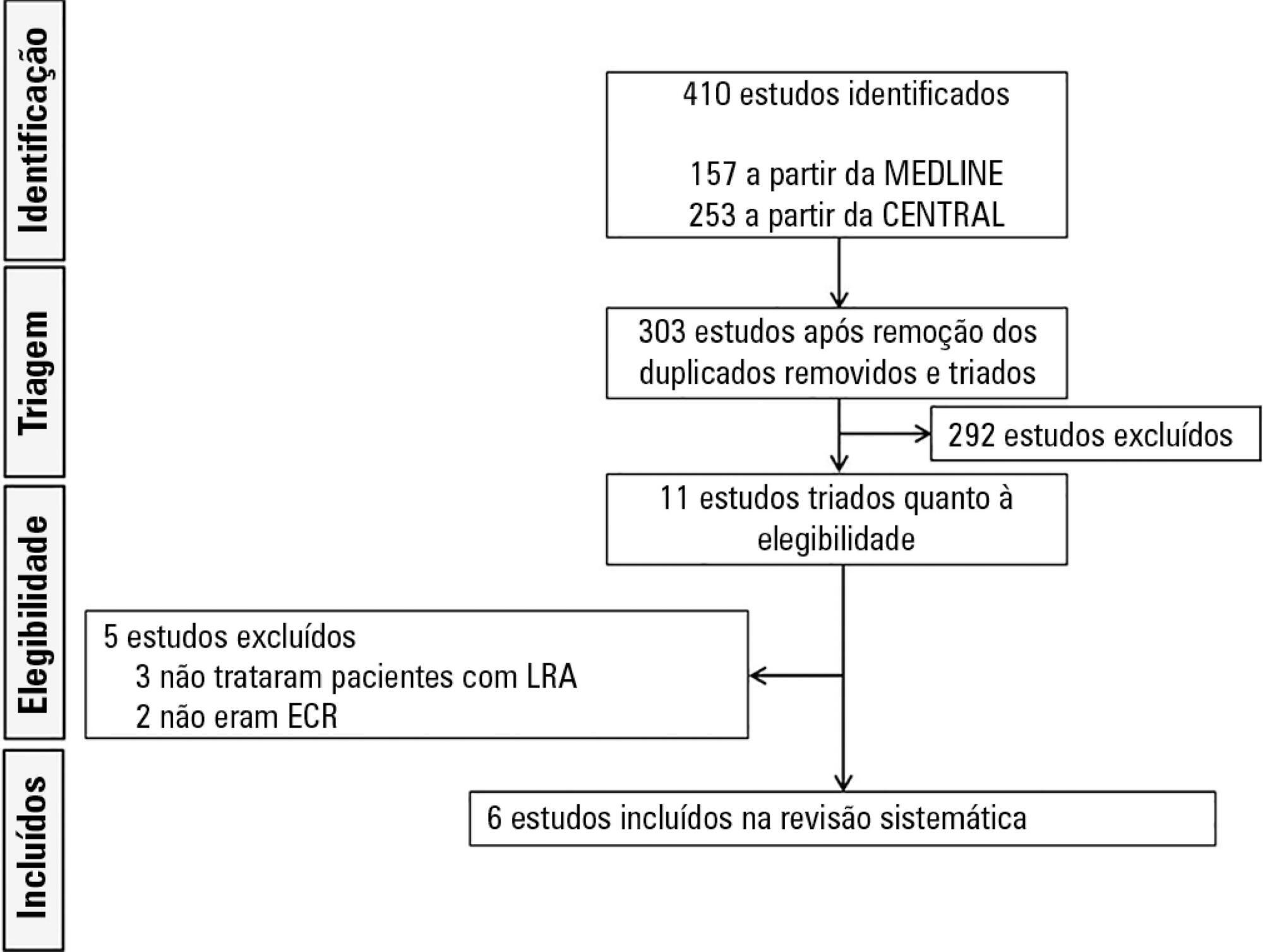
Results:
Six randomized controlled trials (1,292 patients) were included. There was no statistically significant difference between early and delayed initiation of renal replacement therapy regarding the primary outcome (OR 0.82; 95%CI, 0.48 – 1.42; p = 0.488), but there was an increased risk of catheter-related bloodstream infection when renal replacement therapy was initiated early (OR 1.77; 95%CI, 1.01 – 3.11; p = 0.047). The quality of evidence generated by our meta-analysis for the primary outcome was considered low due to the risk of bias of the included studies and the heterogeneity among them.
Conclusion:
Early initiation of renal replacement therapy is not associated with improved survival. However, the quality of the current evidence is low, and the criteria used for -early- and -delayed- initiation of renal replacement therapy are too heterogeneous among studies.
Keywords:Acute kidney injuryCritically illMeta-analysisRandomized controlled trialRenal replacement therapysystematic reviewSee moreViews0

Abstract
Review ArticleEarly versus delayed initiation of renal replacement therapy for acute kidney injury: an updated systematic review, meta-analysis, meta-regression and trial sequential analysis of randomized controlled trials
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2018;30(3):376-384
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20180054
- Fabio Tanzillo Moreira,
- Henrique Palomba,
- Renato Carneiro de Freitas Chaves,
- Catherine Bouman,
- Marcus Josephus Schultz,
- Ary Serpa Neto
Views0ABSTRACT
Objective:
To evaluate whether early initiation of renal replacement therapy is associated with lower mortality in patients with acute kidney injury compared to delayed initiation.
Methods:
We performed a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials comparing early versus delayed initiation of renal replacement therapy in patients with acute kidney injury without the life-threatening acute kidney injury-related symptoms of fluid overload or metabolic disorders. Two investigators extracted the data from the selected studies. The Cochrane Risk of Bias Tool was used to assess the quality of the studies, and the Grading of Recommendations Assessment, Development and Evaluation (GRADE) approach was used to test the overall quality of the evidence.
Results:
Six randomized controlled trials (1,292 patients) were included. There was no statistically significant difference between early and delayed initiation of renal replacement therapy regarding the primary outcome (OR 0.82; 95%CI, 0.48 – 1.42; p = 0.488), but there was an increased risk of catheter-related bloodstream infection when renal replacement therapy was initiated early (OR 1.77; 95%CI, 1.01 – 3.11; p = 0.047). The quality of evidence generated by our meta-analysis for the primary outcome was considered low due to the risk of bias of the included studies and the heterogeneity among them.
Conclusion:
Early initiation of renal replacement therapy is not associated with improved survival. However, the quality of the current evidence is low, and the criteria used for -early- and -delayed- initiation of renal replacement therapy are too heterogeneous among studies.
Keywords:Acute kidney injuryCritically illMeta-analysisRandomized controlled trialRenal replacement therapysystematic reviewSee more

Search
Search in:
KEY WORDS
Case reports Child Coronavirus infections COVID-19 Critical care Critical illness Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation Infant, newborn Intensive care Intensive care units Intensive care units, pediatric mechanical ventilation Mortality Physical therapy modalities Prognosis Respiration, artificial Respiratory insufficiency risk factors SARS-CoV-2 Sepsis


