Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2020;32(4):564-570
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20200094
To evaluate renal responsiveness in oliguric critically ill patients after a fluid challenge.
We conducted a prospective observational study in one university intensive care unit. Patients with urine output < 0.5mL/kg/h for 3 hours with a mean arterial pressure > 60mmHg received a fluid challenge. We examined renal fluid responsiveness (defined as urine output > 0.5mL/kg/h for 3 hours) after fluid challenge.
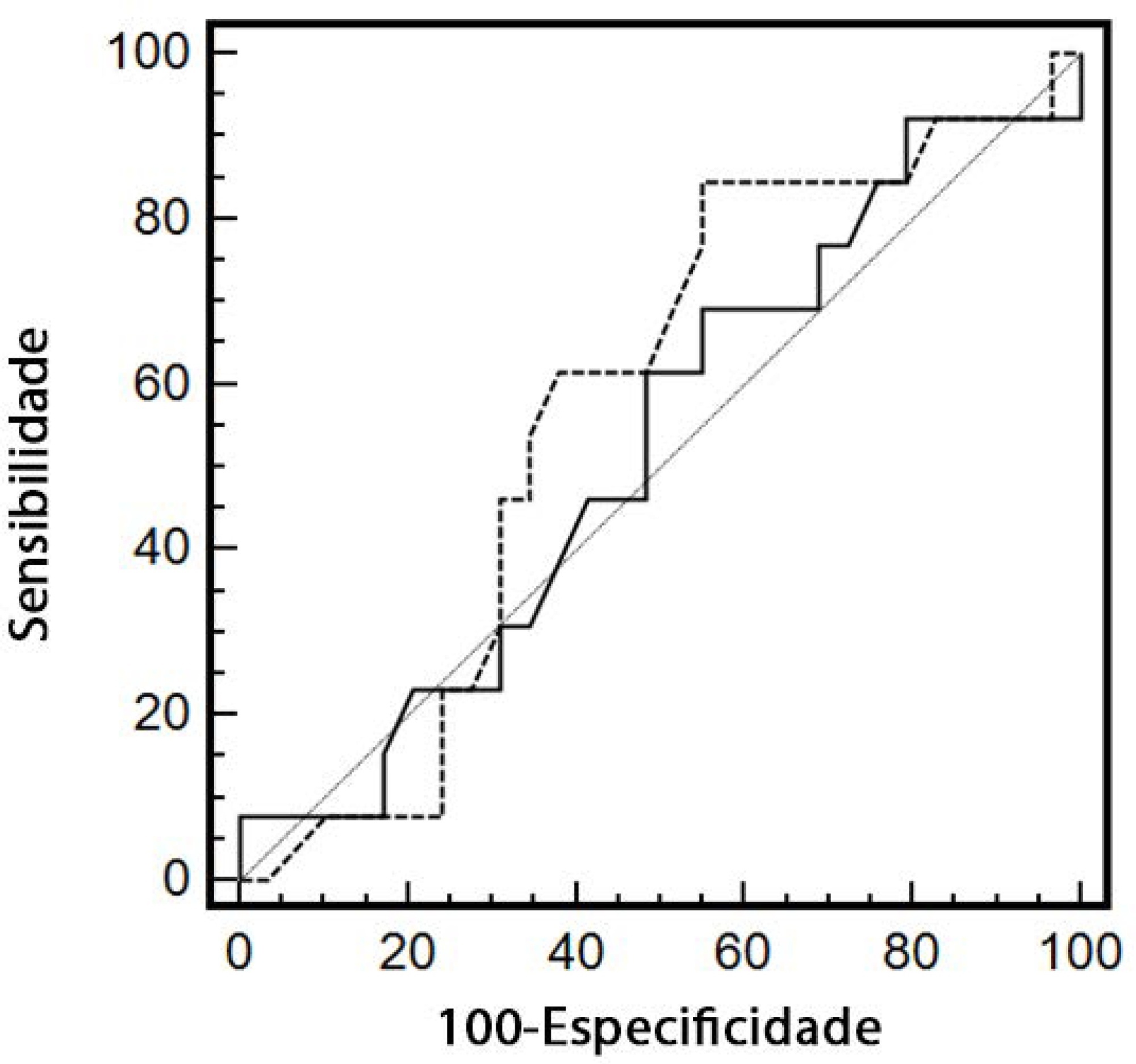
Forty-two patients (age 67 ± 13 years; APACHE II score 16 ± 6) were evaluated. Patient characteristics were similar between renal responders and renal nonresponders. Thirteen patients (31%) were renal responders. Hemodynamic or perfusion parameters were not different between those who did and those who did not increase urine output before the fluid challenge. The areas under the receiver operating characteristic curves were calculated for mean arterial pressure, heart rate, creatinine, urea, creatinine clearance, urea/creatinine ratio and lactate before the fluid challenge. None of these parameters were sensitive or specific enough to predict reversal of oliguria.
After achieving hemodynamic stability, oliguric patients did not increase urine output after a fluid challenge. Systemic hemodynamic, perfusion or renal parameters were weak predictors of urine responsiveness. Our results suggest that volume replacement to correct oliguria in patients without obvious hypovolemia should be done with caution.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2016;28(4):463-471
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20160079
Timely fluid administration is crucial to maintain tissue perfusion in septic shock patients. However, the question concerning which fluid should be used for septic shock resuscitation remains a matter of debate. A growing body of evidence suggests that the type, amount and timing of fluid administration during the course of sepsis may affect patient outcomes. Crystalloids have been recommended as the first-line fluids for septic shock resuscitation. Nevertheless, given the inconclusive nature of the available literature, no definitive recommendations about the most appropriate crystalloid solution can be made. Resuscitation of septic and non-septic critically ill patients with unbalanced crystalloids, mainly 0.9% saline, has been associated with a higher incidence of acid-base balance and electrolyte disorders and might be associated with a higher incidence of acute kidney injury. This can result in greater demand for renal replacement therapy and increased mortality. Balanced crystalloids have been proposed as an alternative to unbalanced solutions in order to mitigate their detrimental effects. Nevertheless, the safety and effectiveness of balanced crystalloids for septic shock resuscitation need to be further addressed in a well-designed, multicenter, pragmatic, randomized controlled trial.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2014;26(4):397-406
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20140061
Severe trauma can be associated with significant hemorrhagic shock and impaired organ perfusion. We hypothesized that goal-directed therapy would confer morbidity and mortality benefits in major trauma.
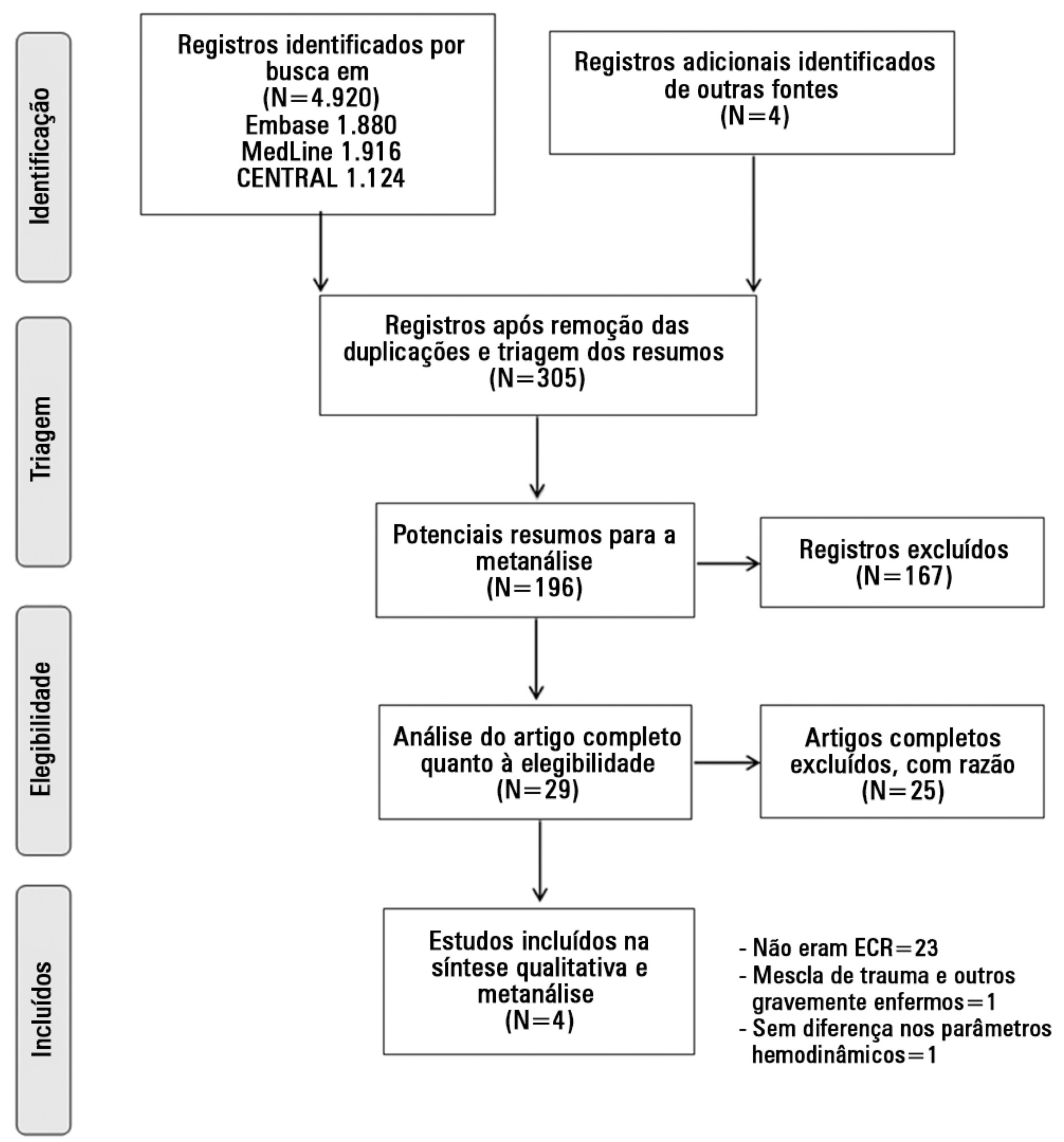
The MedLine, Embase and Cochrane Controlled Clinical Trials Register databases were systematically searched for randomized, controlled trials of goal-directed therapy in severe trauma patients. Mortality was the primary outcome of this review. Secondary outcomes included complication rates, length of hospital and intensive care unit stay, and the volume of fluid and blood administered. Meta-analysis was performed using RevMan software, and the data presented are as odds ratios for dichotomous outcomes and as mean differences (MDs) and standard MDs for continuous outcomes.
Four randomized, controlled trials including 419 patients were analyzed. Mortality risk was significantly reduced in goal-directed therapy-treated patients, compared to the control group (OR=0.56, 95%CI: 0.34-0.92). Intensive care (MD: 3.7 days 95%CI: 1.06-6.5) and hospital length of stay (MD: 3.5 days, 95%CI: 2.75-4.25) were significantly shorter in the protocol group patients. There were no differences in reported total fluid volume or blood transfusions administered. Heterogeneity in reporting among the studies prevented quantitative analysis of complications.
Following severe trauma, early goal-directed therapy was associated with lower mortality and shorter durations of intensive care unit and hospital stays. The findings of this analysis should be interpreted with caution due to the presence of significant heterogeneity and the small number of the randomized, controlled trials included.
Search
Search in:
Case reports (56) Child (53) Coronavirus infections (34) COVID-19 (46) Critical care (116) Critical illness (54) Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (26) Infant, newborn (27) Intensive care (72) Intensive care units (256) Intensive care units, pediatric (31) mechanical ventilation (38) Mortality (76) Physical therapy modalities (28) Prognosis (61) Respiration, artificial (119) Respiratory insufficiency (26) risk factors (34) SARS-CoV-2 (28) Sepsis (98)