You searched for:"João Paulo Arruda de Oliveira"
We found (1) results for your search.-
Original Article
Factors associated with mortality in mechanically ventilated patients with severe acute respiratory syndrome due to COVID-19 evolution
Crit Care Sci. 2023;35(1):19-30
Abstract
Original ArticleFactors associated with mortality in mechanically ventilated patients with severe acute respiratory syndrome due to COVID-19 evolution
Crit Care Sci. 2023;35(1):19-30
DOI 10.5935/2965-2774.20230203-pt
Views16ABSTRACT
Objectives:
To evaluate the factors associated with mortality in mechanically ventilated patients with acute respiratory distress syndrome due to COVID-19.
Methods:
This was a retrospective, multicenter cohort study that included 425 mechanically ventilated adult patients with COVID-19 admitted to 4 intensive care units. Clinical data comprising the SOFA score, laboratory data and mechanical characteristics of the respiratory system were collected in a standardized way immediately after the start of invasive mechanical ventilation. The risk factors for death were analyzed using Cox regression to estimate the risk ratios and their respective 95%CIs.
Results:
Body mass index (RR 1.17; 95%CI 1.11 – 1.20; p < 0.001), SOFA score (RR 1.39; 95%CI 1.31 - 1.49; p < 0.001) and driving pressure (RR 1.24; 95%CI 1.21 - 1.29; p < 0.001) were considered independent factors associated with mortality in mechanically ventilated patients with acute respiratory distress syndrome due to COVID-19. Respiratory system compliance (RR 0.92; 95%CI 0.90 - 0.93; p < 0.001) was associated with lower mortality. The comparative analysis of the survival curves indicated that patients with respiratory system compliance (< 30mL/cmH2O), a higher SOFA score (> 5 points) and higher driving pressure (> 14cmH2O) were more significantly associated with the outcome of death at 28 days and 60 days.
Conclusion:
Patients with a body mass index > 32kg/m2, respiratory system compliance < 30mL/cmH2O, driving pressure > 14cmH2O and SOFA score > 5.8 immediately after the initiation of invasive ventilatory support had worse outcomes, and independent risk factors were associated with higher mortality in this population.
Keywords:artificialCoronavirus infectionsCOVID-19MortalityRespirationRespiratory distress syndromeRespiratory mechanicsSARS-CoV-2See more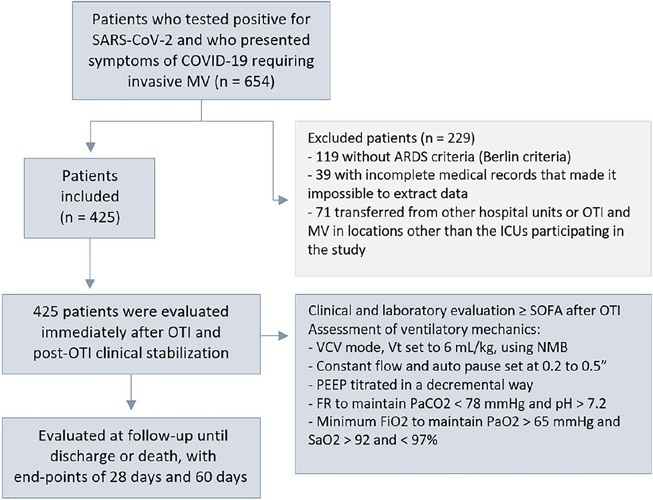
Search
Search in:
KEY WORDS
Case reports Child Coronavirus infections COVID-19 Critical care Critical illness Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation Infant, newborn Intensive care Intensive care units Intensive care units, pediatric mechanical ventilation Mortality Physical therapy modalities Prognosis Respiration, artificial Respiratory insufficiency risk factors SARS-CoV-2 Sepsis




