You searched for:"Emiliano Navarro"
We found (4) results for your search.-
Original Article
Impact of liberal versus conservative saturation targets on gas exchange indices in COVID-19 related acute respiratory distress syndrome: a physiological study
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2021;33(4):537-543
Abstract
Original ArticleImpact of liberal versus conservative saturation targets on gas exchange indices in COVID-19 related acute respiratory distress syndrome: a physiological study
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2021;33(4):537-543
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20210081
Views0ABSTRACT
Objective:
To compare gas exchange indices behavior by using liberal versus conservative oxygenation targets in patients with moderate to severe acute respiratory distress syndrome secondary to COVID-19 under invasive mechanical ventilation. We also assessed the influence of high FiO2 on respiratory system mechanics.
Methods:
We prospectively included consecutive patients aged over 18 years old with a diagnosis of COVID-19 and moderate-severe acute respiratory distress syndrome. For each patient, we randomly applied two FiO2 protocols to achieve SpO2 88% – 92% or 96%. We assessed oxygenation indices and respiratory system mechanics.
Results:
We enrolled 15 patients. All the oxygenation indices were significantly affected by the FiO2 strategy (p < 0.05) selected. The PaO2/FiO2 deteriorated, PA-aO2 increased and Pa/AO2 decreased significantly when using FiO2 to achieve SpO2 96%. Conversely, the functional shunt fraction was reduced. Respiratory mechanics were not affected by the FiO2 strategy.
Conclusion:
A strategy aimed at liberal oxygenation targets significantly deteriorated gas exchange indices, except for functional shunt, in COVID-19-related acute respiratory distress syndrome. The respiratory system mechanics were not altered by the FiO2 strategy.
Keywords:artificialCOVID-19OxygenationPulmonary gas exchangeRespirationRespiratory distress syndromeRespiratory mechanicsSee more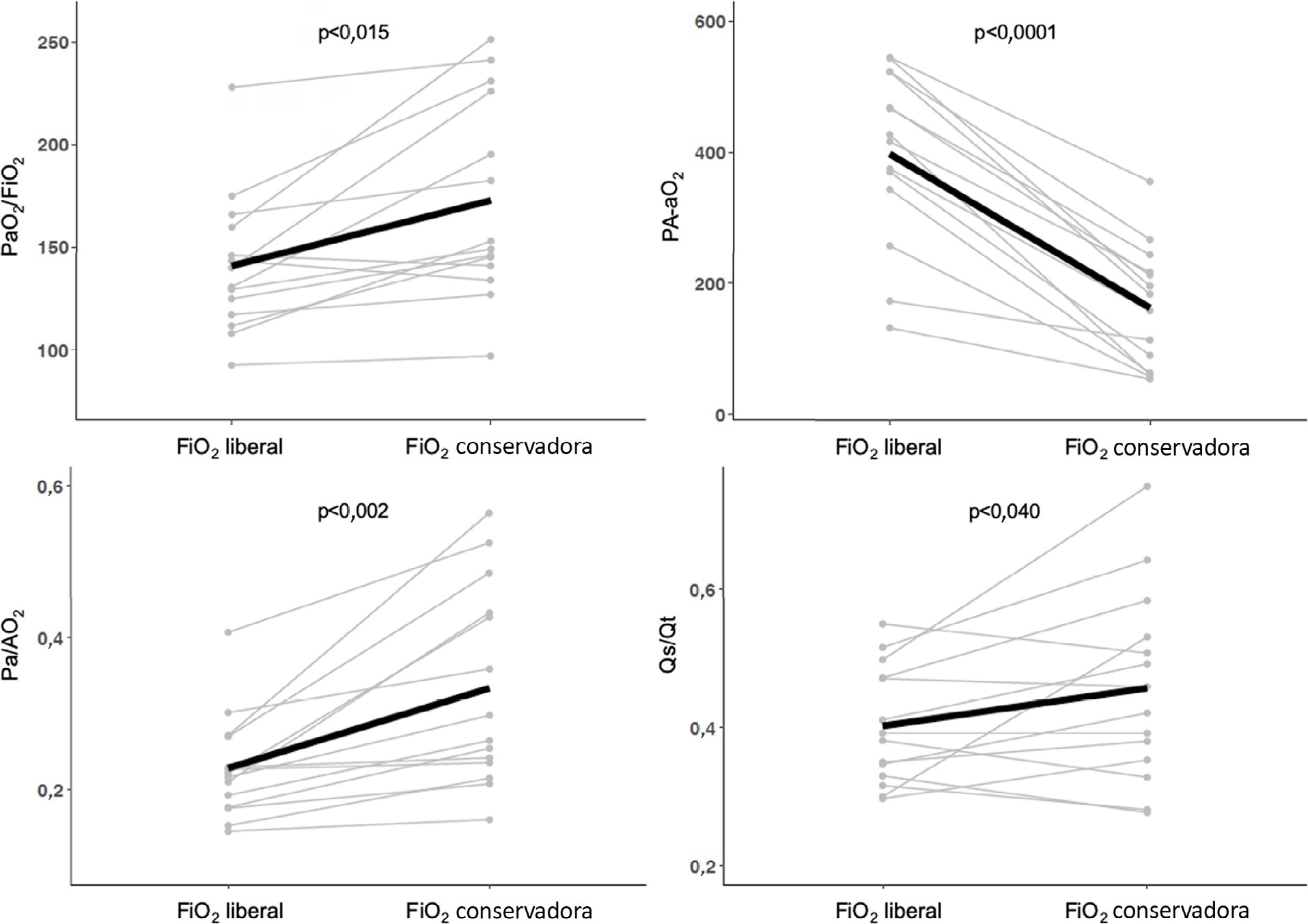
-
Case Report
Self-inflicted lung injury: is it possible to identify the risk? A case report
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2021;33(3):461-468
Abstract
Case ReportSelf-inflicted lung injury: is it possible to identify the risk? A case report
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2021;33(3):461-468
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20210061
Views0ABSTRACT
Spontaneous breathing can be deleterious in patients with previously injured lungs, especially in acute respiratory distress syndrome. Moreover, the failure to assume spontaneous breathing during mechanical ventilation and the need to switch back to controlled mechanical ventilation are associated with higher mortality. There is a gap of knowledge regarding which parameters might be useful to predict the risk of patient self-inflicted lung injury and to detect the inability to assume spontaneous breathing. We report a case of patient self-inflicted lung injury, the corresponding basic and advanced monitoring of the respiratory system mechanics and physiological and clinical results related to spontaneous breathing. The patient was a 33-year-old Caucasian man with a medical history of AIDS who developed acute respiratory distress syndrome and needed invasive mechanical ventilation after noninvasive ventilatory support failure. During the controlled ventilation periods, a protective ventilation strategy was adopted, and the patient showed clear clinical and radiographic improvement. However, during each spontaneous breathing period under pressure support ventilation, despite adequate initial parameters and a strictly adjusted ventilatory setting and monitoring, the patient developed progressive hypoxemia and worsening of respiratory system mechanics with a clearly correlated radiographic deterioration (patient self-inflicted lung injury). After failing three spontaneous breathing assumption trials, he died on day 29 due to refractory hypoxemia. Conventional basic and advanced monitoring variables in this case were not sufficient to identify the aptitude to breathe spontaneously or to predict the risk and development of patient self-inflicted lung injury during partial support ventilation.
Keywords:artificialInteractive ventilatory supportmonitoringRespirationRespiratory distress syndromeVentilator-induced lung injurySee more
-
Original Article
Description of physical rehabilitation in intensive care units in Argentina: usual practice and during the COVID-19 pandemic. Online survey
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2021;33(2):188-195
Abstract
Original ArticleDescription of physical rehabilitation in intensive care units in Argentina: usual practice and during the COVID-19 pandemic. Online survey
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2021;33(2):188-195
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20210026
Views0Abstract
Objective:
To describe the usual practice of mobility therapy in the adult intensive care unit for patients with and without COVID-19.
Methods:
Online survey in which physical therapists working in an adult intensive care unit in Argentina participated. Sixteen multiple-choice or single-response questions grouped into three sections were asked. The first section addressed personal, professional and work environment data. The second section presented questions regarding usual care, and the third focused on practices under COVID-19 pandemic conditions.
Results:
Of 351 physical therapists, 76.1% answer that they were exclusively responsible for patient mobility. The highest motor-based goal varied according to four patient scenarios: Mechanically ventilated patients, patients weaned from mechanical ventilation, patients who had never required mechanical ventilation, and patients with COVID-19 under mechanical ventilation. In the first and last scenarios, the highest goal was to optimize muscle strength, while for the other two, it was to perform activities of daily living. Finally, the greatest limitation in working with patients with COVID-19 was respiratory and/or contact isolation.
Conclusion:
Physical therapists in Argentina reported being responsible for the mobility of patients in the intensive care unit. The highest motor-based therapeutic goals for four classic scenarios in the closed area were limited by the need for mechanical ventilation. The greatest limitation when mobilizing patients with COVID-19 was respiratory and contact isolation.
Keywords:Critical careEarly mobilizationPhysical therapy modalitiesRehabilitationRespiration, artificialSurvey and questionnairesSee more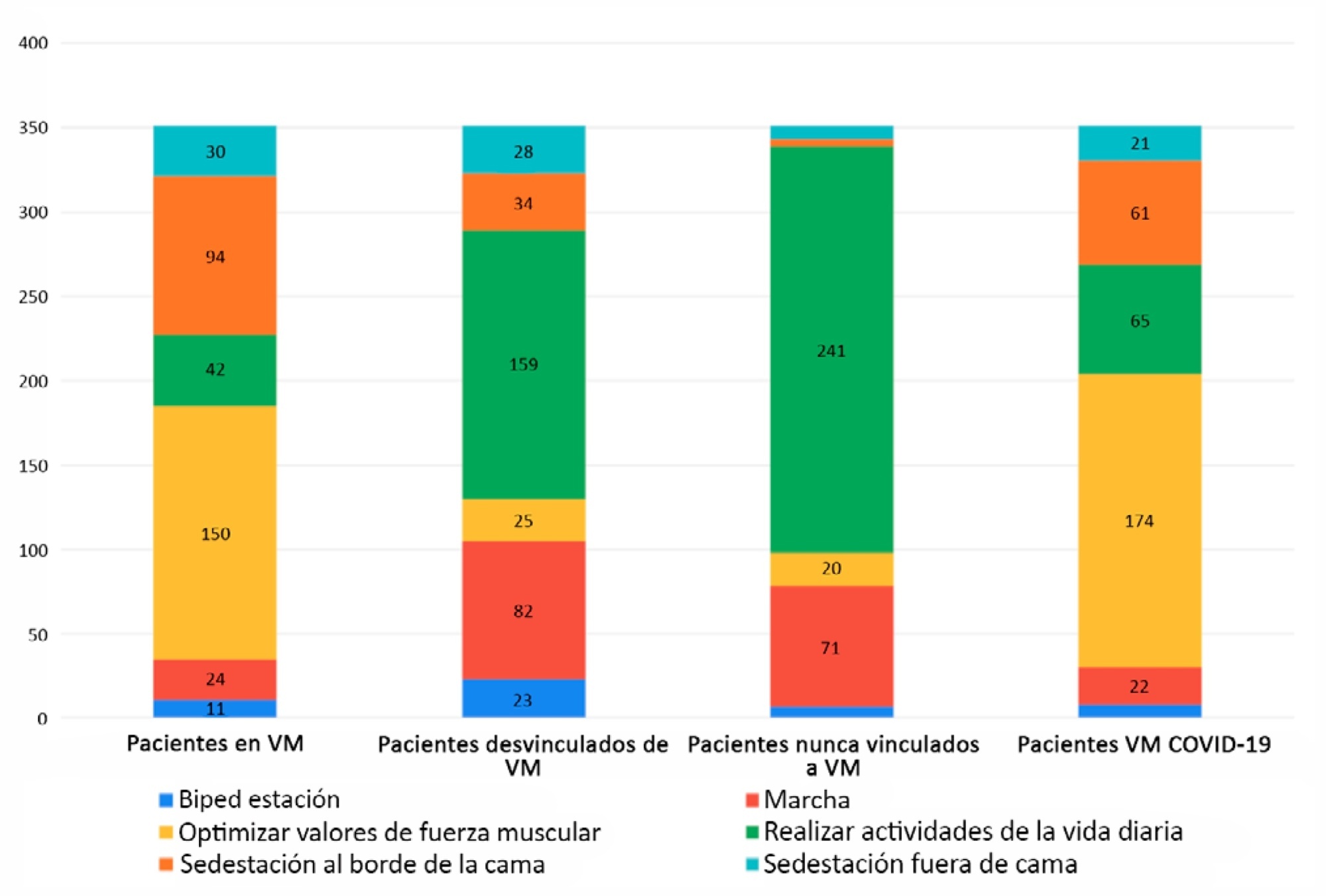
-
Review Articles
Humidification and heating of inhaled gas in patients with artificial airway. A narrative review
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2018;30(1):86-97
Abstract
Review ArticlesHumidification and heating of inhaled gas in patients with artificial airway. A narrative review
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2018;30(1):86-97
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20180015
Views2See moreABSTRACT
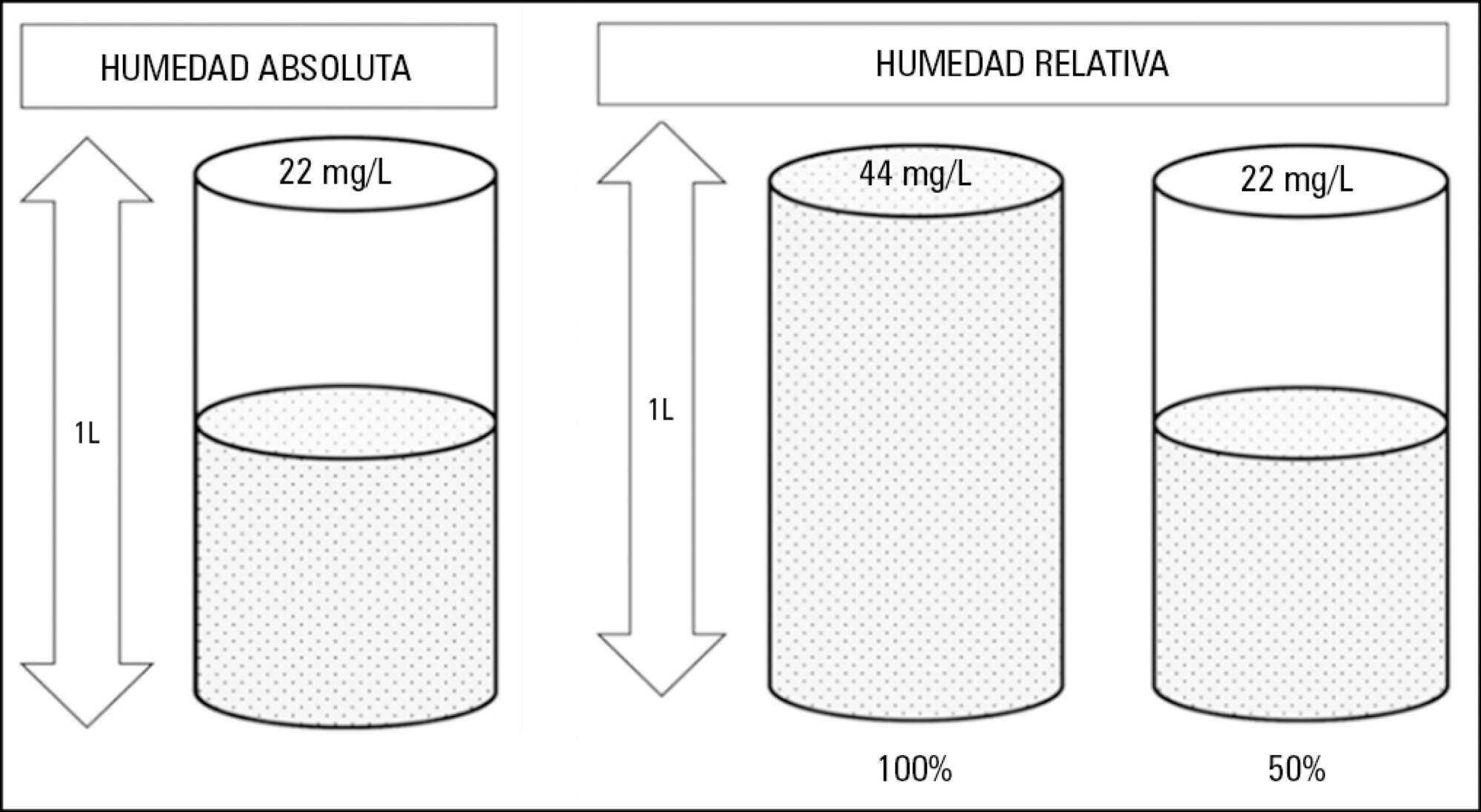
Instrumentation of the airways in critical patients (endotracheal tube or tracheostomy cannula) prevents them from performing their function of humidify and heating the inhaled gas. In addition, the administration of cold and dry medical gases and the high flows that patients experience during invasive and non-invasive mechanical ventilation generate an even worse condition. For this reason, a device for gas conditioning is needed, even in short-term treatments, to avoid potential damage to the structure and function of the respiratory epithelium. In the field of intensive therapy, the use of heat and moisture exchangers is common for this purpose, as is the use of active humidification systems. Acquiring knowledge about technical specifications and the advantages and disadvantages of each device is needed for proper use since the conditioning of inspired gases is a key intervention in patients with artificial airway and has become routine care. Incorrect selection or inappropriate configuration of a device can have a negative impact on clinical outcomes. The members of the Capítulo de Kinesiología Intensivista of the Sociedad Argentina de Terapia Intensiva conducted a narrative review aiming to show the available evidence regarding conditioning of inhaled gas in patients with artificial airways, going into detail on concepts related to the working principles of each one.
Search
Search in:
KEY WORDS
Case reports Child Coronavirus infections COVID-19 Critical care Critical illness Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation Infant, newborn Intensive care Intensive care units Intensive care units, pediatric mechanical ventilation Mortality Physical therapy modalities Prognosis Respiration, artificial Respiratory insufficiency risk factors SARS-CoV-2 Sepsis




