Abstract
Crit Care Sci. 2023;35(2):177-186
DOI 10.5935/2965-2774.20230348-pt
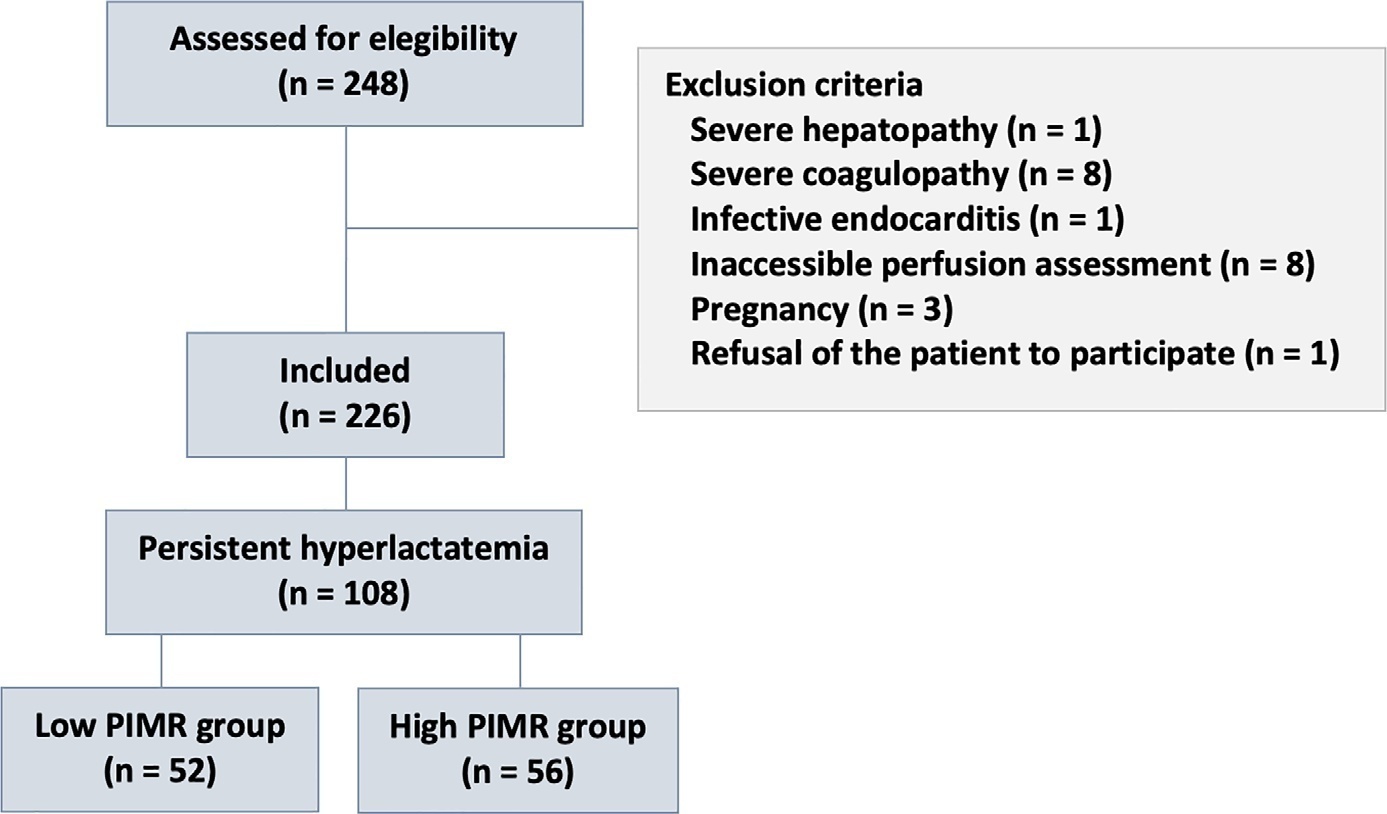
To measure the prognostic value of peripheral ischemic microvascular reserve in the context of persistent sepsis-induced hyperlactatemia and measure its influence on the temporal dynamics of lactate and the strength of association between these variables.
This post hoc analysis of the peripheral perfusion index/postocclusive reactive hyperemia trial, an observational cohort study that enrolled patients with sepsis who persisted with lactate levels ≥ 2mmol/L after fluid resuscitation (with or without shock). Peripheral ischemic microvascular reserve was evaluated using the association of the peripheral perfusion index and postocclusive reactive hyperemia techniques. The cutoff point of ∆ peripheral perfusion index peak values (%) defined the groups with low (≤ 62%) and high peripheral ischemic microvascular reserve (> 62%).
A total of 108 consecutive patients with persistent sepsis-induced hyperlactatemia were studied. The high peripheral ischemic microvascular reserve group showed higher 28-day mortality than the low peripheral ischemic microvascular reserve group (p < 0.01). The temporal dynamics of lactate within the first 48 hours showed a rapid decrease in lactate levels in the low peripheral ischemic microvascular reserve group (p < 0.01). However, this result was not reproduced in the linear mixed effects model. A weak correlation between peripheral ischemic microvascular reserve (%) and lactate level (mmol/L) was observed within the first 24 hours (r = 0.23; p < 0.05).
The prognostic value of high peripheral ischemic microvascular reserve was confirmed in the context of persistent sepsis-induced hyperlactatemia. Although there was a weak positive correlation between peripheral ischemic microvascular reserve value and lactate level within the first 24 hours of sepsis diagnosis, the low peripheral ischemic microvascular reserve group appeared to have a faster decrease in lactate over the 48 hours of follow-up.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2022;34(3):367-373
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20220102-en
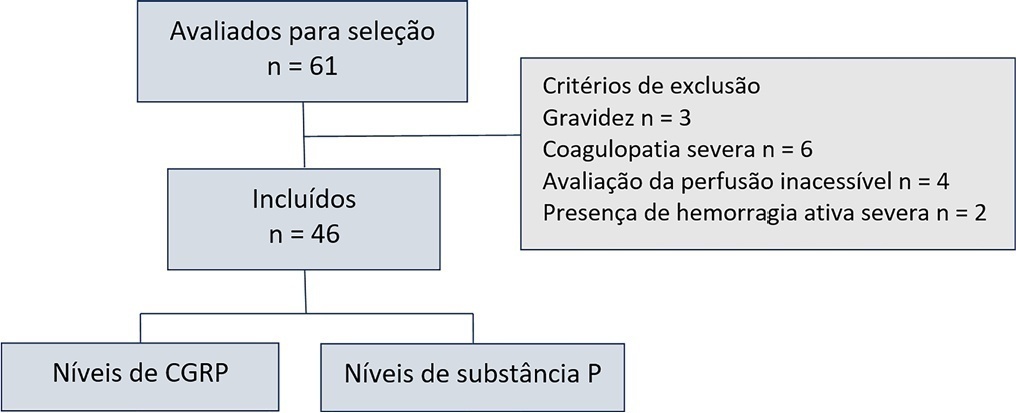
To evaluate the mechanisms attributed to the prognostic value of peripheral ischemic microvascular reserve in patients with sepsis.
This observational cohort study enrolled 46 consecutive septic patients in the intensive care unit between November 2020 and October 2021. After fluid resuscitation, the peripheral ischemic microvascular reserve was evaluated using the association of postocclusion reactive hyperemia with the peripheral perfusion index. Additionally, peripheral venous blood samples were used to evaluate the neuropeptide calcitonin gene-related peptide and substance P levels in the upper limb before and immediately after postocclusion reactive hyperemia
There was no statistically significant correlation (p > 0.05) between basal values (pg/mL) or variations from neuropeptide levels (%) and the peripheral ischemic microvascular reserve (%).
Although calcitonin gene-related peptide and substance P may have a prognostic role in sepsis, these neuropeptides do not appear to contribute to peripheral ischemic microvascular reserve.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2021;33(1):154-166
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20210017
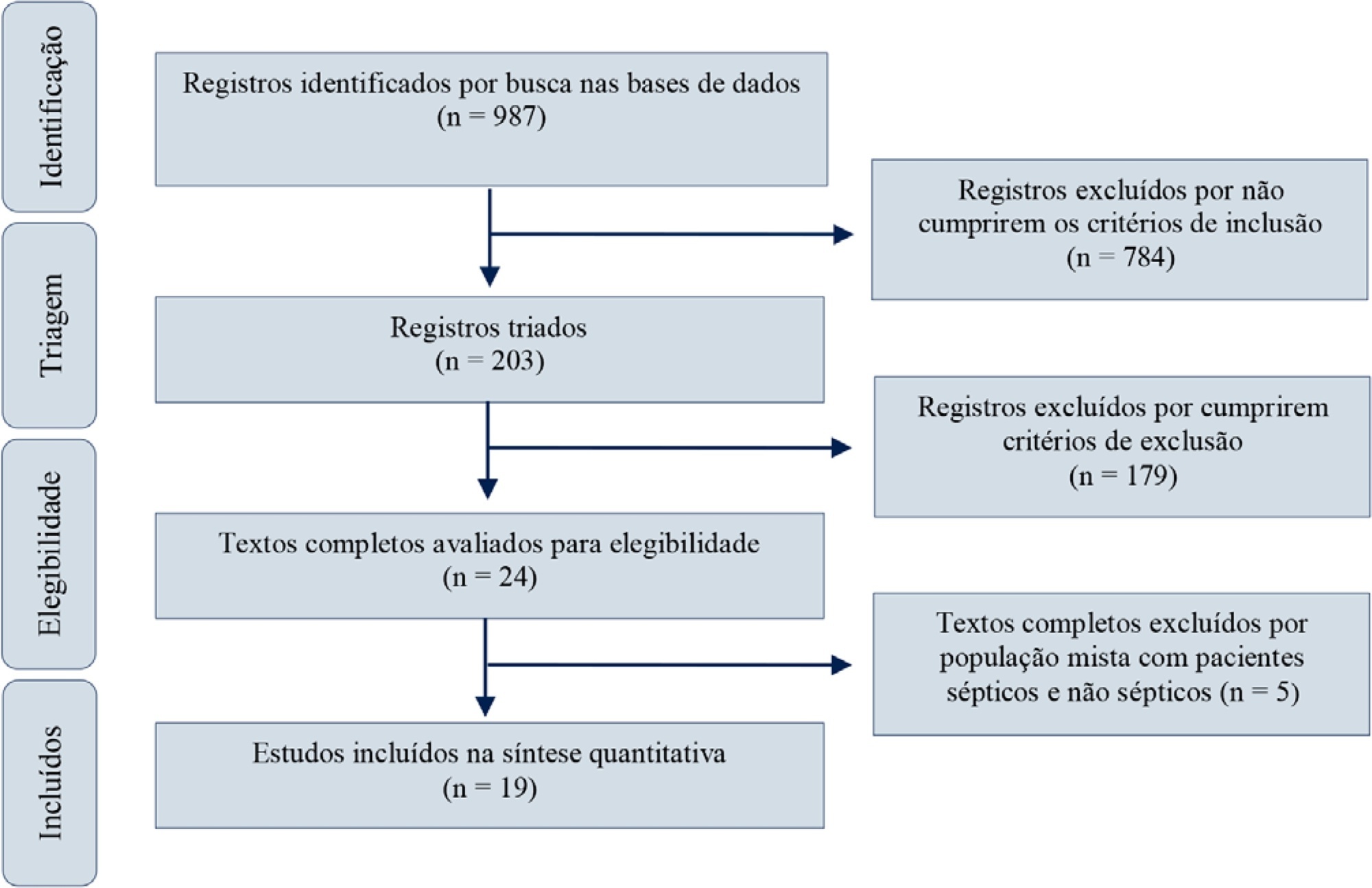
Red blood cell transfusion is thought to improve cell respiration during septic shock. Nevertheless, its acute impact on oxygen transport and metabolism in this condition remains highly debatable. The objective of this study was to evaluate the impact of red blood cell transfusion on microcirculation and oxygen metabolism in patients with sepsis and septic shock. We conducted a search in the MEDLINE®, Elsevier and Scopus databases. We included studies conducted in adult humans with sepsis and septic shock. A systematic review and meta-analysis were performed using the DerSimonian and Laird random-effects model. A p value < 0.05 was considered significant. Nineteen manuscripts with 428 patients were included in the analysis. Red blood cell transfusions were associated with an increase in the pooled mean venous oxygen saturation of 3.7% (p < 0.001), a decrease in oxygen extraction ratio of -6.98 (p < 0.001) and had no significant effect on the cardiac index (0.02L/minute; p = 0,96). Similar results were obtained in studies including simultaneous measurements of venous oxygen saturation, oxygen extraction ratio, and cardiac index. Red blood cell transfusions led to a significant increase in the proportion of perfused small vessels (2.85%; p = 0.553), while tissue oxygenation parameters revealed a significant increase in the tissue hemoglobin index (1.66; p = 0.018). Individual studies reported significant improvements in tissue oxygenation and sublingual microcirculatory parameters in patients with deranged microcirculation at baseline. Red blood cell transfusions seemed to improve systemic oxygen metabolism with apparent independence from cardiac index variations. Some beneficial effects have been observed for tissue oxygenation and microcirculation parameters, particularly in patients with more severe alterations at baseline. More studies are necessary to evaluate their clinical impact and to individualize transfusion decisions.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2018;30(2):135-143
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20180027
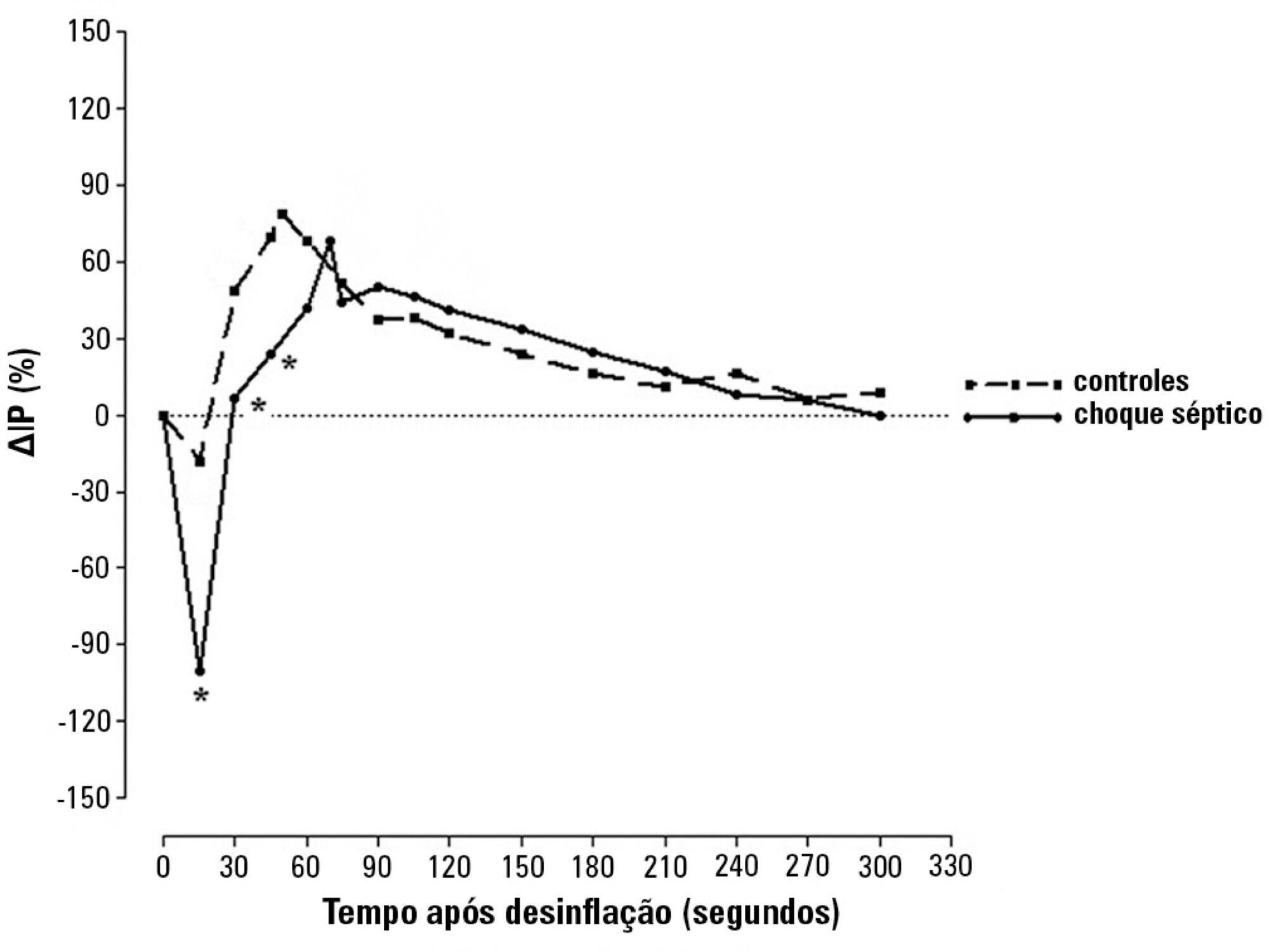
Microcirculation disturbances are implicated in the prognosis of septic shock. Microvascular hyporesponsiveness can be assessed by an oximetry-derived perfusion index and reactive hyperemia. Using this perfusion index, we investigated reactive hyperemia and its relationship with peripheral perfusion and clinical-hemodynamic parameters in septic shock.
Eighty-two patients were evaluated: 47 with septic shock and 35 controls. Tests were performed within 24 hours after admission. The perfusion index was evaluated before and after a 3-min blood flow occlusion using a time-response analysis for 5 min. The perfusion index was also evaluated in the hyperemic phases and was mainly derived by mechanosensitive (ΔPI0-60) and metabolic mechanisms (ΔPI60-120). Correlation tests were performed between reactive hyperemia and clinical-hemodynamic data.
Reactive hyperemia measured by the perfusion index was significantly lower in patients with septic shock, but this was only observed for the first 45 seconds after cuff-deflation. In the remaining period, there were no statistical differences between the groups. The peaks in the perfusion index were similar between groups, although the peak was reached more slowly in the septic group. Values of ΔPI0-60 were lower in shock [01% (-19% - -40%) versus 39% (6% - 75%); p = 0.001]. However, ΔPI60-120 was similar between the groups [43% (18% - 93%) versus 48% (18% - 98%); p = 0.58]. The time-to-peak of the perfusion index was correlated positively with the SOFA scores and negatively with C-reactive protein; the peak of the perfusion index was positively correlated with vasopressor doses; and the ΔPI60-120 values were positively correlated with C-reactive protein and vasopressor doses. No other significant correlations occurred.
This perfusion index-based study suggests that septic shock promotes initial peripheral vascular hyporesponsiveness and preserves posterior vascular reactivity to a considerable degree. These results demonstrate a time-dependent peripheral hyperemic response and a significant ischemic reserve in septic shock.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2017;29(2):238-247
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20170033
Parameters related to macrocirculation, such as the mean arterial pressure, central venous pressure, cardiac output, mixed venous saturation and central oxygen saturation, are commonly used in the hemodynamic assessment of critically ill patients. However, several studies have shown that there is a dissociation between these parameters and the state of microcirculation in this group of patients. Techniques that allow direct viewing of the microcirculation are not completely disseminated, nor are they incorporated into the clinical management of patients in shock. The numerous techniques developed for microcirculation assessment include clinical assessment (e.g., peripheral perfusion index and temperature gradient), laser Doppler flowmetry, tissue oxygen assessment electrodes, videomicroscopy (orthogonal polarization spectral imaging, sidestream dark field imaging or incident dark field illumination) and near infrared spectroscopy. In the near future, the monitoring and optimization of tissue perfusion by direct viewing and microcirculation assessment may become a goal to be achieved in the hemodynamic resuscitation of critically ill patients.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2017;29(4):490-498
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20170068
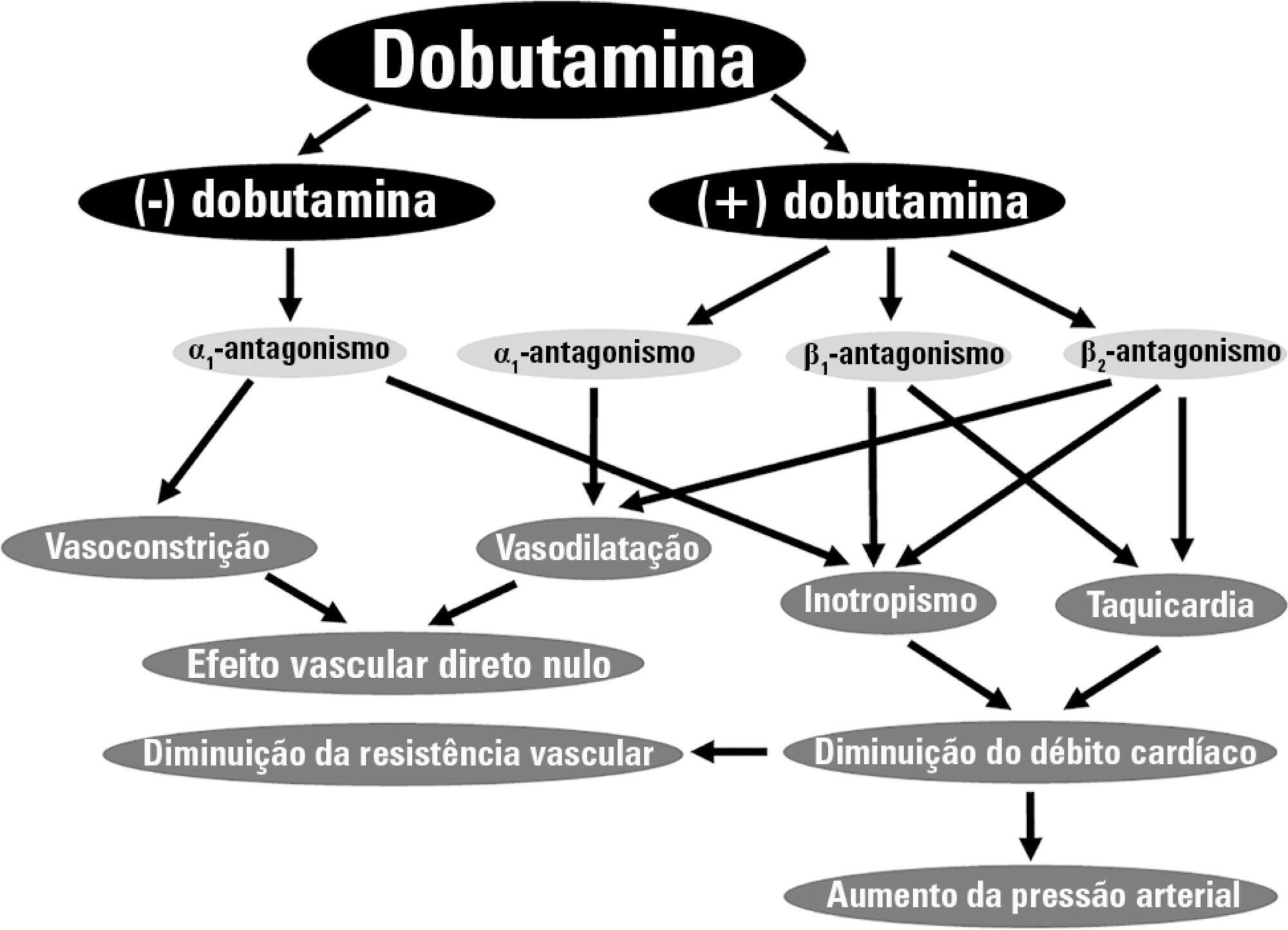
Dobutamine is the inotrope most commonly used in septic shock patients to increase cardiac output and correct hypoperfusion. Although some experimental and clinical studies have shown that dobutamine can improve systemic and regional hemodynamics, other research has found that its effects are heterogenous and unpredictable. In this review, we analyze the pharmacodynamic properties of dobutamine and its physiologic effects. Our goal is to show that the effects of dobutamine might differ between healthy subjects, in experimental and clinical cardiac failure, in animal models and in patients with septic shock. We discuss evidence supporting the claim that dobutamine, in septic shock, frequently behaves as a chronotropic and vasodilatory drug, without evidence of inotropic action. Since the side effects are very common, and the therapeutic benefits are unclear, we suggest that dobutamine should be used cautiously in septic shock. Before a definitive therapeutic decision, the efficacy and tolerance of dobutamine should be assessed during a brief time with close monitoring of its positive and negative side effects.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2011;23(3):352-357
DOI 10.1590/S0103-507X2011000300014
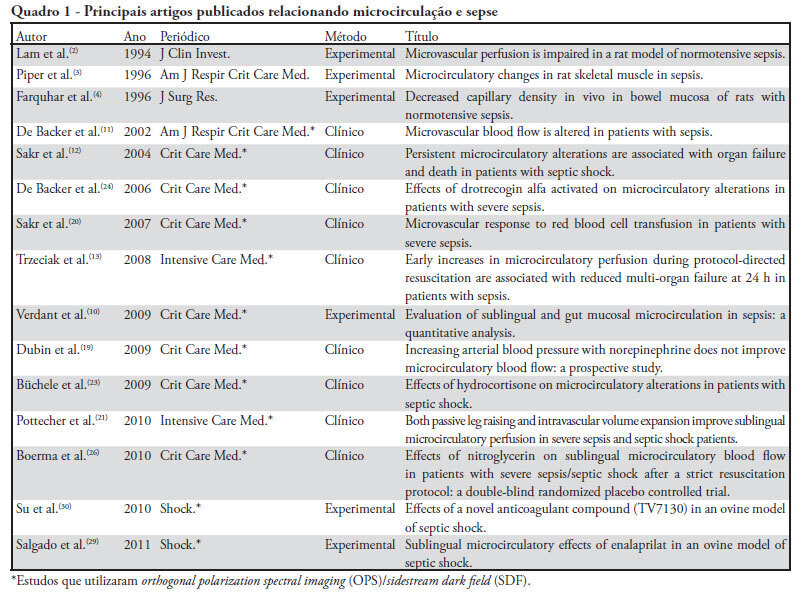
The progression into multi-organ failure continues to be a common feature of sepsis and is directly related to microcirculatory dysfunction. Based on a PubMed database search using the key words microcirculation and sepsis, twenty-six articles were selected for this review. The relevant references from these articles were also selected and included in this analysis. Orthogonal polarization spectral imaging allows for the bedside assessment of the microcirculation of critically ill patients. Such imaging has established a correlation between microvascular dysfunction and patient outcomes, which allows practitioners to directly assess the effects of therapeutic interventions. However, the causal relationships between microcirculatory dysfunction, adverse outcomes, and the effects of therapies aimed at these microcirculatory changes in sepsis, are not clear.
Search
Search in:
Case reports (56) Child (53) Coronavirus infections (34) COVID-19 (46) Critical care (116) Critical illness (54) Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (26) Infant, newborn (27) Intensive care (72) Intensive care units (256) Intensive care units, pediatric (31) mechanical ventilation (38) Mortality (76) Physical therapy modalities (28) Prognosis (61) Respiration, artificial (119) Respiratory insufficiency (26) risk factors (34) SARS-CoV-2 (28) Sepsis (98)