Abstract
Crit Care Sci. 2023;35(2):117-146
DOI 10.5935/2965-2774.20230310-pt
Echocardiography in critically ill patients has become essential in the evaluation of patients in different settings, such as the hospital. However, unlike for other matters related to the care of these patients, there are still no recommendations from national medical societies on the subject. The objective of this document was to organize and make available expert consensus opinions that may help to better incorporate echocardiography in the evaluation of critically ill patients. Thus, the Associação de Medicina Intensiva Brasileira, the Associação Brasileira de Medicina de Emergência, and the Sociedade Brasileira de Medicina Hospitalar formed a group of 17 physicians to formulate questions relevant to the topic and discuss the possibility of consensus for each of them. All questions were prepared using a five-point Likert scale. Consensus was defined a priori as at least 80% of the responses between one and two or between four and five. The consideration of the issues involved two rounds of voting and debate among all participants. The 27 questions prepared make up the present document and are divided into 4 major assessment areas: left ventricular function, right ventricular function, diagnosis of shock, and hemodynamics. At the end of the process, there were 17 positive (agreement) and 3 negative (disagreement) consensuses; another 7 questions remained without consensus. Although areas of uncertainty persist, this document brings together consensus opinions on several issues related to echocardiography in critically ill patients and may enhance its development in the national scenario.
Abstract
Crit Care Sci. 2023;35(1):11-18
DOI 10.5935/2965-2774.20230336-pt
To explain the rationale and protocol of the methods and analyses to be used in the LIVER-PAM randomized clinical trial, which seeks to understand whether a higher mean arterial pressure is capable of reducing the incidence of renal dysfunction postoperatively after liver transplantation.
LIVER-PAM is an open-label, randomized, controlled, singlecenter clinical trial. Patients randomized to the intervention group will have a mean arterial pressure of 85 - 90mmHg in the initial 24 hours of postoperative management, while patients in the control group will have a mean arterial pressure of 65 - 70mmHg in the same period. A sample of 174 patients will be required to demonstrate a 20% reduction in the absolute incidence of renal dysfunction, with a power of 80% and an alpha of 0.05.
If a 20% reduction in the absolute incidence of renal dysfunction in the postoperative period of liver transplantation is achieved with higher target mean arterial pressure in the first 24 hours, this would represent an inexpensive and simple therapy for improving current outcomes in the management of liver transplant patients.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2021;33(2):206-218
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20210028
To describe fluid resuscitation practices in Brazilian intensive care units and to compare them with those of other countries participating in the Fluid-TRIPS.
This was a prospective, international, cross-sectional, observational study in a convenience sample of intensive care units in 27 countries (including Brazil) using the Fluid-TRIPS database compiled in 2014. We described the patterns of fluid resuscitation use in Brazil compared with those in other countries and identified the factors associated with fluid choice.
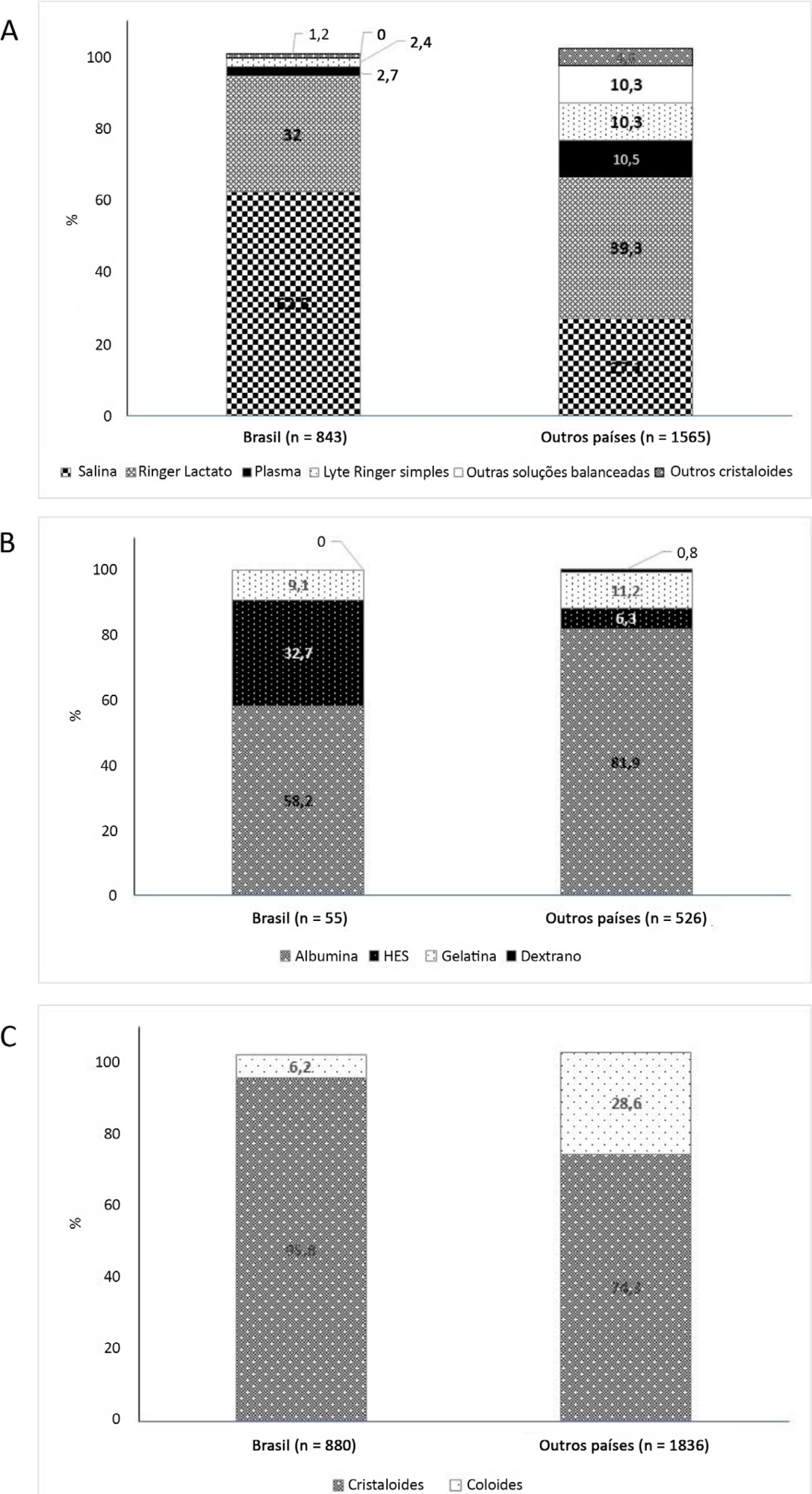
On the study day, 3,214 patients in Brazil and 3,493 patients in other countries were included, of whom 16.1% and 26.8% (p < 0.001) received fluids, respectively. The main indication for fluid resuscitation was impaired perfusion and/or low cardiac output (Brazil: 71.7% versus other countries: 56.4%, p < 0.001). In Brazil, the percentage of patients receiving crystalloid solutions was higher (97.7% versus 76.8%, p < 0.001), and 0.9% sodium chloride was the most commonly used crystalloid (62.5% versus 27.1%, p < 0.001). The multivariable analysis suggested that the albumin levels were associated with the use of both crystalloids and colloids, whereas the type of fluid prescriber was associated with crystalloid use only.
Our results suggest that crystalloids are more frequently used than colloids for fluid resuscitation in Brazil, and this discrepancy in frequencies is higher than that in other countries. Sodium chloride (0.9%) was the crystalloid most commonly prescribed. Serum albumin levels and the type of fluid prescriber were the factors associated with the choice of crystalloids or colloids for fluid resuscitation.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2020;32(4):606-610
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20200099
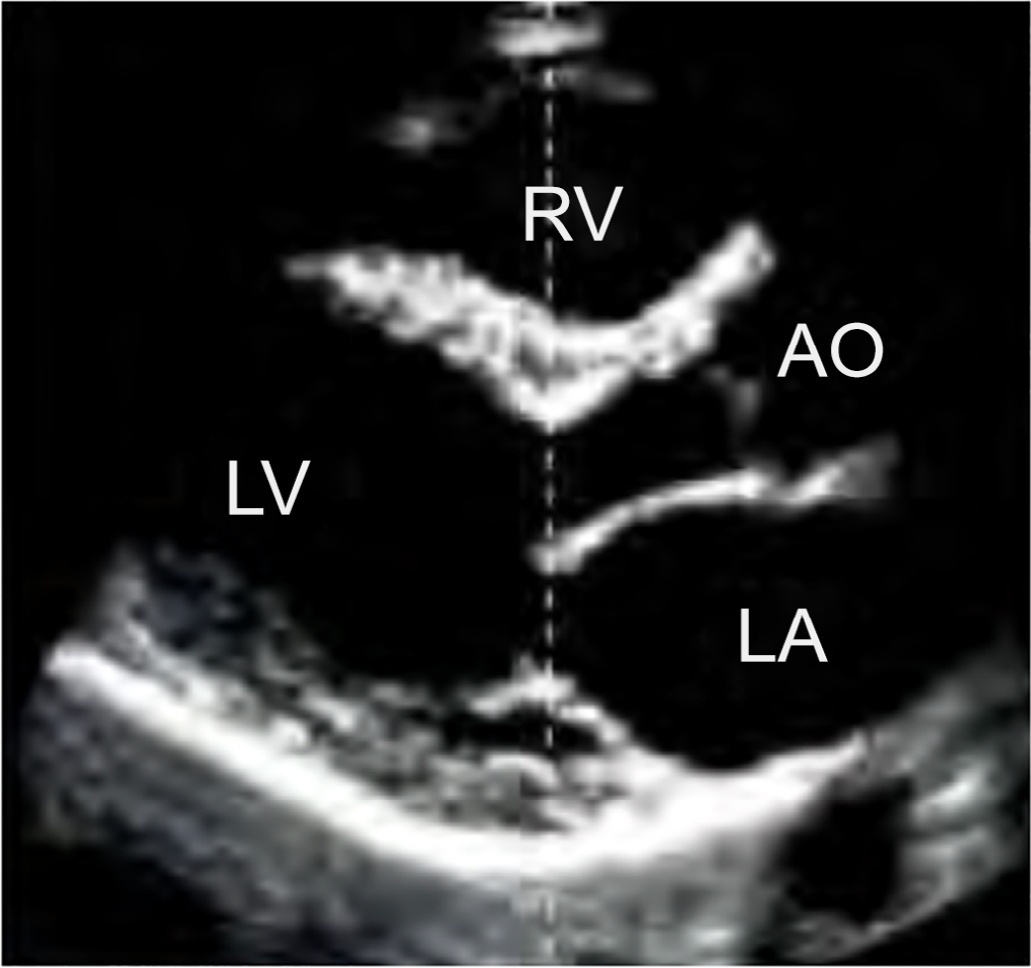
The authors report a rare case of successful Advanced Life Support in the context of cardiac arrest due to the presence of an anomalous aortic origin of the right coronary artery in a 49-year-old patient. The patient was admitted due to chest pain and dyspnea, with rapid evolution of pulseless ventricular tachycardia and cardiopulmonary arrest. Acute myocardial infarction was considered, and in the absence of a hemodynamic laboratory in the hospital, thrombolysis was performed. Subsequently, coronary angiography revealed no angiographic lesions in the coronary arteries and an anomalous right coronary artery originating from the opposite sinus of Valsalva. Coronary computed tomography angiography confirmed this finding and determined the course between the pulmonary artery and the aorta. The patient underwent cardiac surgery with a bypass graft to the right coronary artery, with no recurrent episodes of arrythmia.
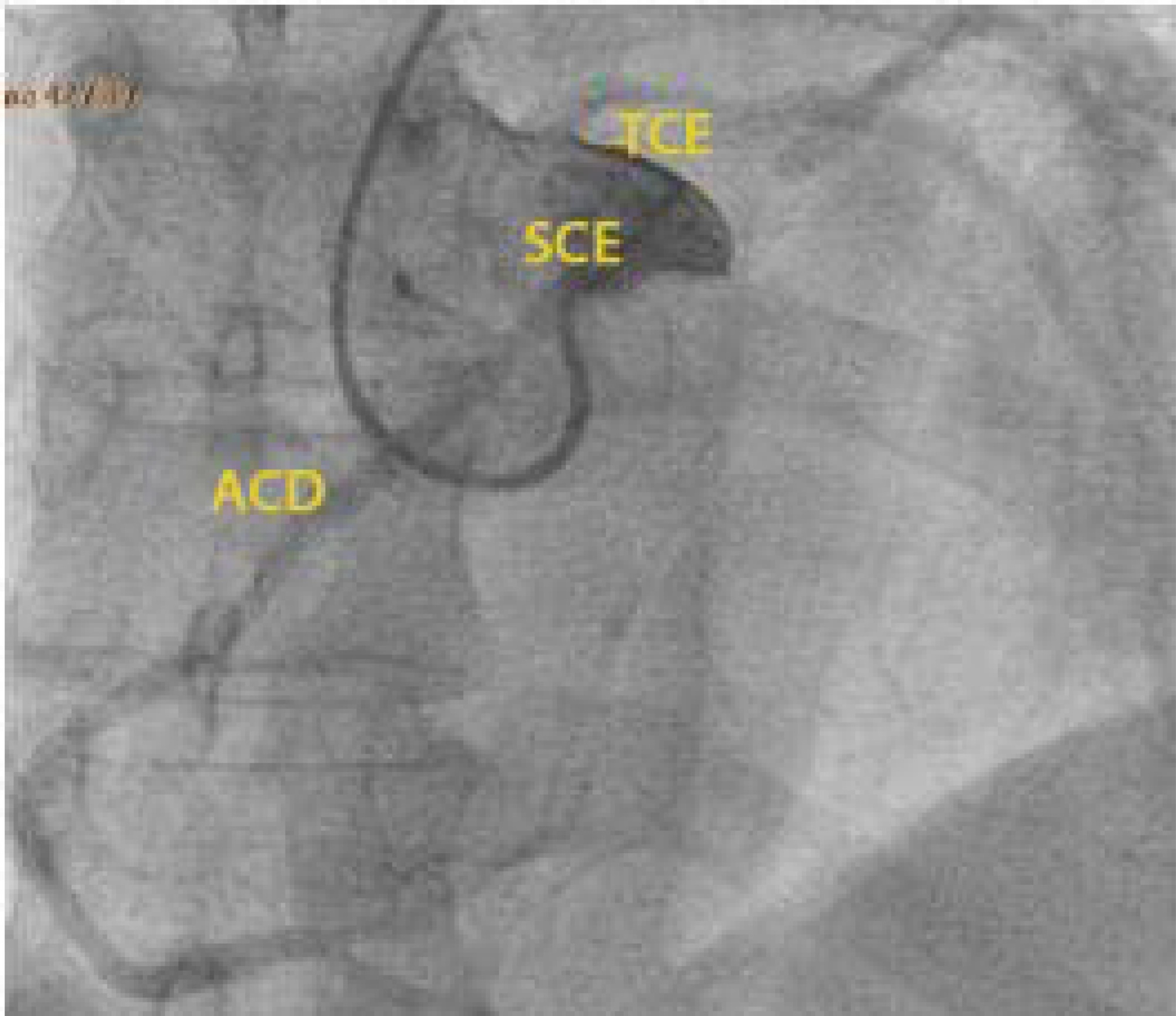
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2019;31(3):312-317
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20190056
To investigate the influence of respiratory distress syndrome management on clinical and echocardiographic parameters used for hemodynamic evaluation in ≤ 32- week newborns.
Thirty-three ≤ 32-week newborns were prospectively evaluated and subjected to invasive mechanical ventilation. The need for exogenous surfactant and clinical and echocardiographic parameters in the first 24 hours of life was detailed in this group of patients.
The mean airway pressure was significantly higher in newborn infants who required inotropes [10.8 (8.8 - 23) cmH2O versus 9 (6.2 - 12) cmH2O; p = 0.04]. A negative correlation was found between the mean airway pressure and velocity-time integral of the pulmonary artery (r = -0.39; p = 0.026), right ventricular output (r = -0.43; p = 0.017) and measurements of the tricuspid annular plane excursion (r = -0.37; p = 0.036). A negative correlation was found between the number of doses of exogenous surfactant and the right ventricular output (r = -0.39; p = 0.028) and pulmonary artery velocity-time integral (r = -0.35; p = 0.043).
In ≤ 32-week newborns under invasive mechanical ventilation, increases in the mean airway pressure and number of surfactant doses are correlated with the worsening of early cardiac function. Therefore, more aggressive management of respiratory distress syndrome may contribute to the hemodynamic instability of these patients.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2017;29(3):346-353
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20170045
Patients admitted to an intensive care unit are prone to cumulated fluid overload and receive intravenous volumes through the aggressive resuscitation recommended for septic shock treatment, as well as other fluid sources related to medications and nutritional support. The liberal liquid supply strategy has been associated with higher morbidity and mortality. Although there are few prospective pediatric studies, new strategies are being proposed. This non-systematic review discusses the pathophysiology of fluid overload, its consequences, and the available therapeutic strategies. During systemic inflammatory response syndrome, the endothelial glycocalyx is damaged, favoring fluid extravasation and resulting in interstitial edema. Extravasation to the third space results in longer mechanical ventilation, a greater need for renal replacement therapy, and longer intensive care unit and hospital stays, among other changes. Proper hemodynamic monitoring, as well as cautious infusion of fluids, can minimize these damages. Once cumulative fluid overload is established, treatment with long-term use of loop diuretics may lead to resistance to these medications. Strategies that can reduce intensive care unit morbidity and mortality include the early use of vasopressors (norepinephrine) to improve cardiac output and renal perfusion, the use of a combination of diuretics and aminophylline to induce diuresis, and the use of sedation and early mobilization protocols.
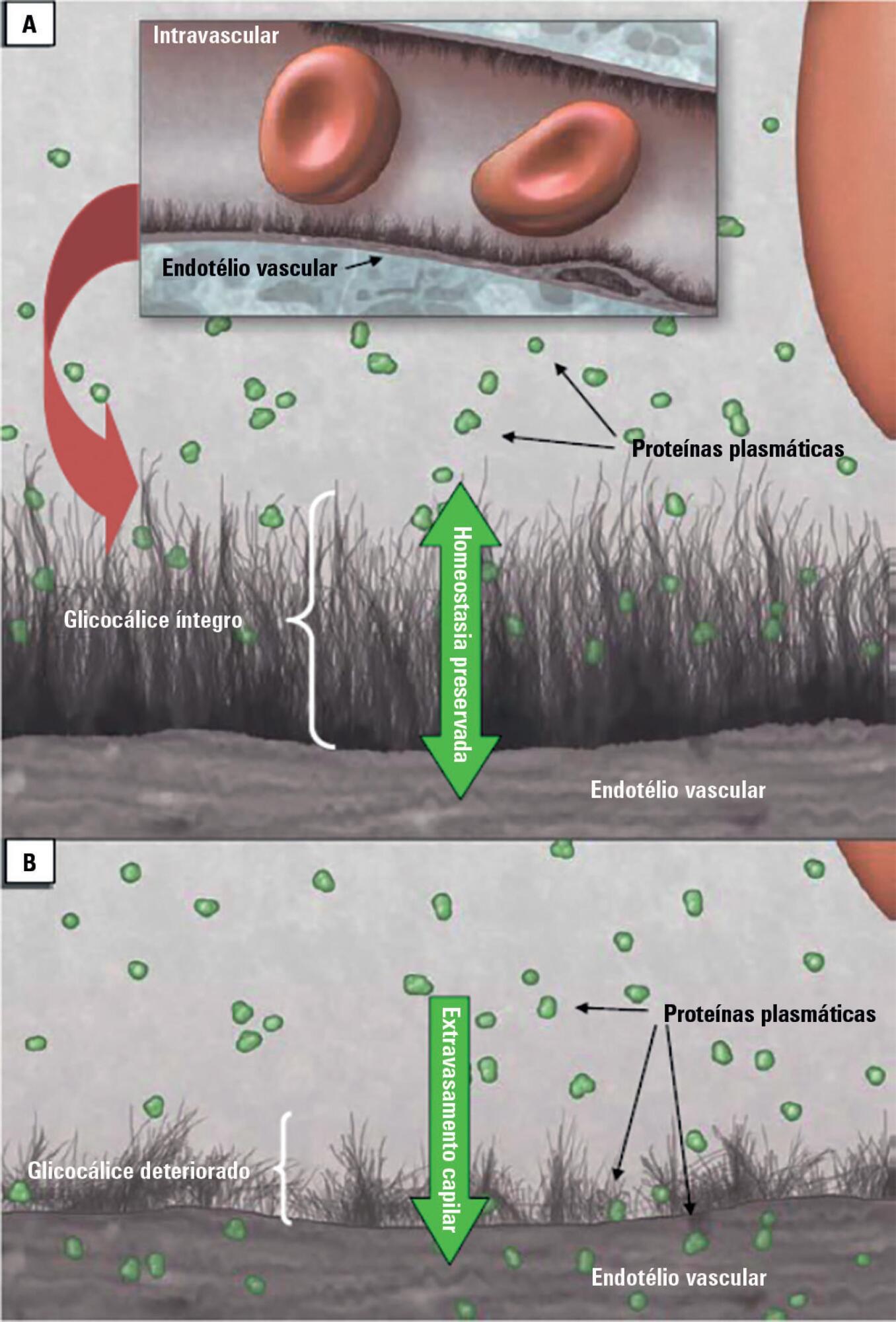
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2017;29(2):238-247
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20170033
Parameters related to macrocirculation, such as the mean arterial pressure, central venous pressure, cardiac output, mixed venous saturation and central oxygen saturation, are commonly used in the hemodynamic assessment of critically ill patients. However, several studies have shown that there is a dissociation between these parameters and the state of microcirculation in this group of patients. Techniques that allow direct viewing of the microcirculation are not completely disseminated, nor are they incorporated into the clinical management of patients in shock. The numerous techniques developed for microcirculation assessment include clinical assessment (e.g., peripheral perfusion index and temperature gradient), laser Doppler flowmetry, tissue oxygen assessment electrodes, videomicroscopy (orthogonal polarization spectral imaging, sidestream dark field imaging or incident dark field illumination) and near infrared spectroscopy. In the near future, the monitoring and optimization of tissue perfusion by direct viewing and microcirculation assessment may become a goal to be achieved in the hemodynamic resuscitation of critically ill patients.
Search
Search in:
Case reports (56) Child (53) Coronavirus infections (34) COVID-19 (46) Critical care (116) Critical illness (54) Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (26) Infant, newborn (27) Intensive care (72) Intensive care units (256) Intensive care units, pediatric (31) mechanical ventilation (38) Mortality (76) Physical therapy modalities (28) Prognosis (61) Respiration, artificial (119) Respiratory insufficiency (26) risk factors (34) SARS-CoV-2 (28) Sepsis (98)