You searched for:"Javier Hernán Dorado"
We found (4) results for your search.-
Original Article
Impact of liberal versus conservative saturation targets on gas exchange indices in COVID-19 related acute respiratory distress syndrome: a physiological study
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2021;33(4):537-543
Abstract
Original ArticleImpact of liberal versus conservative saturation targets on gas exchange indices in COVID-19 related acute respiratory distress syndrome: a physiological study
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2021;33(4):537-543
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20210081
Views0ABSTRACT
Objective:
To compare gas exchange indices behavior by using liberal versus conservative oxygenation targets in patients with moderate to severe acute respiratory distress syndrome secondary to COVID-19 under invasive mechanical ventilation. We also assessed the influence of high FiO2 on respiratory system mechanics.
Methods:
We prospectively included consecutive patients aged over 18 years old with a diagnosis of COVID-19 and moderate-severe acute respiratory distress syndrome. For each patient, we randomly applied two FiO2 protocols to achieve SpO2 88% – 92% or 96%. We assessed oxygenation indices and respiratory system mechanics.
Results:
We enrolled 15 patients. All the oxygenation indices were significantly affected by the FiO2 strategy (p < 0.05) selected. The PaO2/FiO2 deteriorated, PA-aO2 increased and Pa/AO2 decreased significantly when using FiO2 to achieve SpO2 96%. Conversely, the functional shunt fraction was reduced. Respiratory mechanics were not affected by the FiO2 strategy.
Conclusion:
A strategy aimed at liberal oxygenation targets significantly deteriorated gas exchange indices, except for functional shunt, in COVID-19-related acute respiratory distress syndrome. The respiratory system mechanics were not altered by the FiO2 strategy.
Keywords:artificialCOVID-19OxygenationPulmonary gas exchangeRespirationRespiratory distress syndromeRespiratory mechanicsSee more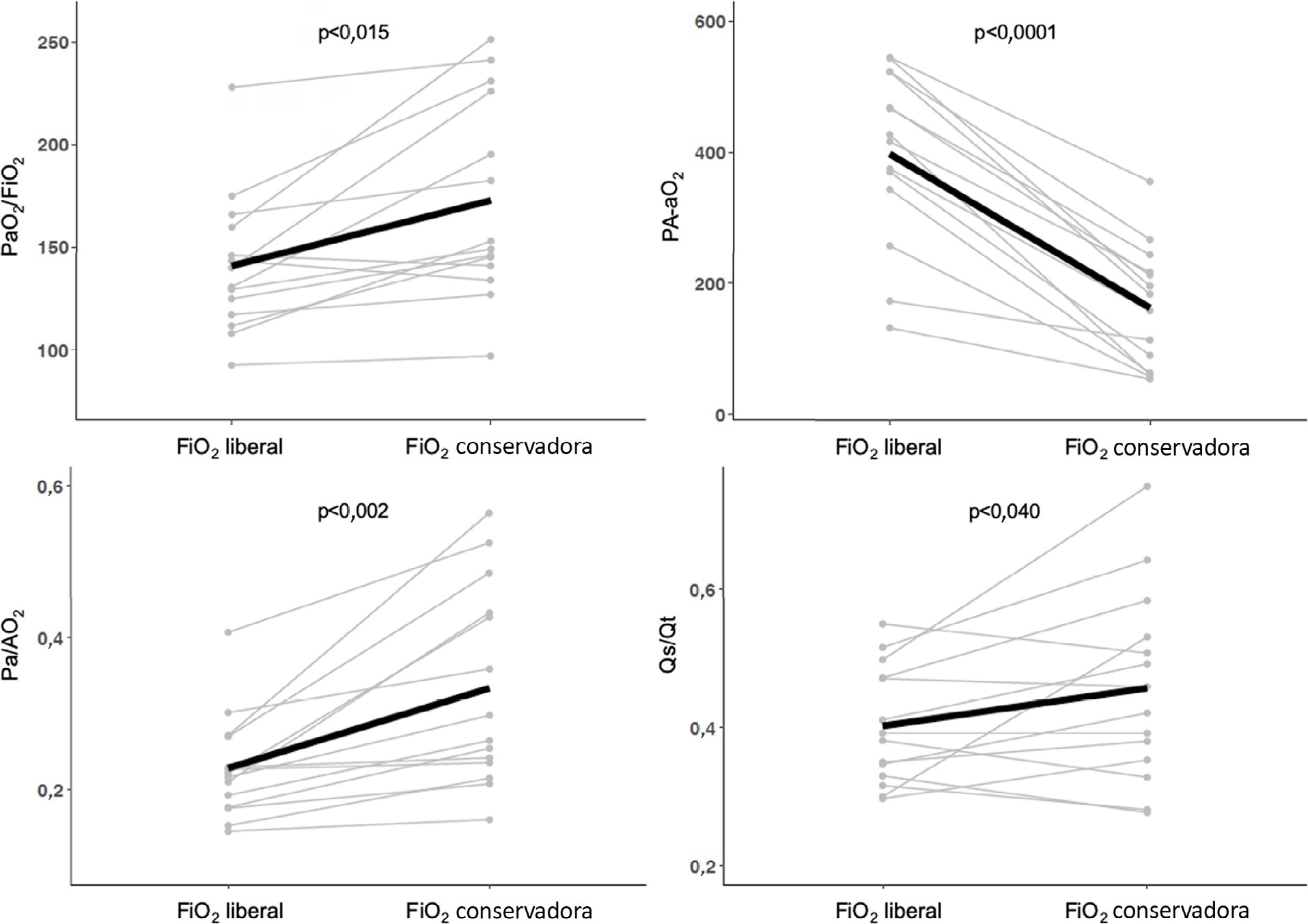
-
Case Report
Self-inflicted lung injury: is it possible to identify the risk? A case report
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2021;33(3):461-468
Abstract
Case ReportSelf-inflicted lung injury: is it possible to identify the risk? A case report
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2021;33(3):461-468
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20210061
Views0ABSTRACT
Spontaneous breathing can be deleterious in patients with previously injured lungs, especially in acute respiratory distress syndrome. Moreover, the failure to assume spontaneous breathing during mechanical ventilation and the need to switch back to controlled mechanical ventilation are associated with higher mortality. There is a gap of knowledge regarding which parameters might be useful to predict the risk of patient self-inflicted lung injury and to detect the inability to assume spontaneous breathing. We report a case of patient self-inflicted lung injury, the corresponding basic and advanced monitoring of the respiratory system mechanics and physiological and clinical results related to spontaneous breathing. The patient was a 33-year-old Caucasian man with a medical history of AIDS who developed acute respiratory distress syndrome and needed invasive mechanical ventilation after noninvasive ventilatory support failure. During the controlled ventilation periods, a protective ventilation strategy was adopted, and the patient showed clear clinical and radiographic improvement. However, during each spontaneous breathing period under pressure support ventilation, despite adequate initial parameters and a strictly adjusted ventilatory setting and monitoring, the patient developed progressive hypoxemia and worsening of respiratory system mechanics with a clearly correlated radiographic deterioration (patient self-inflicted lung injury). After failing three spontaneous breathing assumption trials, he died on day 29 due to refractory hypoxemia. Conventional basic and advanced monitoring variables in this case were not sufficient to identify the aptitude to breathe spontaneously or to predict the risk and development of patient self-inflicted lung injury during partial support ventilation.
Keywords:artificialInteractive ventilatory supportmonitoringRespirationRespiratory distress syndromeVentilator-induced lung injurySee more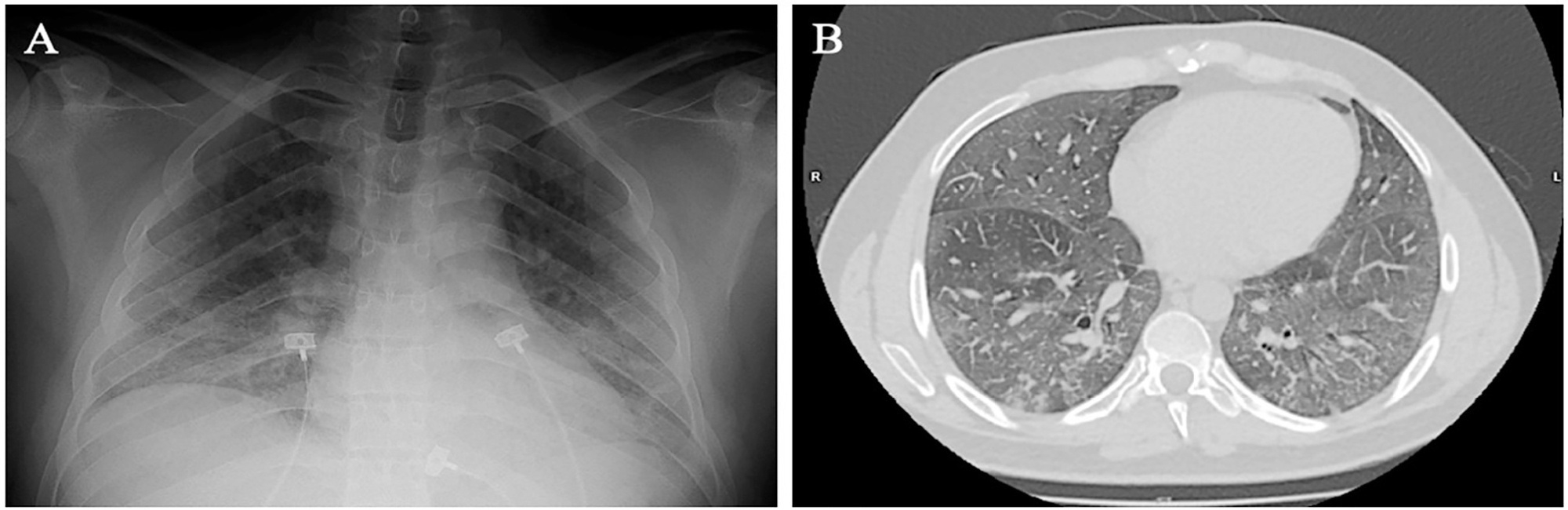
-
Original Article
Titration and characteristics of pressure-support ventilation use in Argentina: an online cross-sectional survey study
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2020;32(1):81-91
Abstract
Original ArticleTitration and characteristics of pressure-support ventilation use in Argentina: an online cross-sectional survey study
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2020;32(1):81-91
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20200013
Views1ABSTRACT
Objective:
To identify common practices related to the use and titration of pressure-support ventilation (PC-CSV – pressure control-continuous spontaneous ventilation) in patients under mechanical ventilation and to analyze diagnostic criteria for over-assistance and under-assistance. The secondary objective was to compare the responses provided by physician, physiotherapists and nurses related to diagnostic criteria for over-assistance and under-assistance.
Methods:
An online survey was conducted using the Survey Monkey tool. Physicians, nurses and physiotherapists from Argentina with access to PC-CSV in their usual clinical practice were included.
Results:
A total of 509 surveys were collected from October to December 2018. Of these, 74.1% were completed by physiotherapists. A total of 77.6% reported using PC-CSV to initiate the partial ventilatory support phase, and 43.8% of respondents select inspiratory pressure support level based on tidal volume. The main objective for selecting positive end-expiratory pressure (PEEP) level was to decrease the work of breathing. High tidal volume was the primary variable for detecting over-assistance, while the use of accessory respiratory muscles was the most commonly chosen for under-assistance. Discrepancies were observed between physicians and physiotherapists in relation to the diagnostic criteria for over-assistance.
Conclusion:
The most commonly used mode to initiate the partial ventilatory support phase was PC-CSV. The most frequently selected variable to guide the titration of inspiratory pressure support level was tidal volume, and the main objective of PEEP was to decrease the work of breathing. Over-assistance was detected primarily by high tidal volume, while under-assistance by accessory respiratory muscles activation. Discrepancies were observed among professions in relation to the diagnostic criteria for over-assistance, but not for under-assistance.
Keywords:Health care surveysIntensive care unitsInteractive ventilatory supportPositive-pressure ventilationRespiration, artificialSee more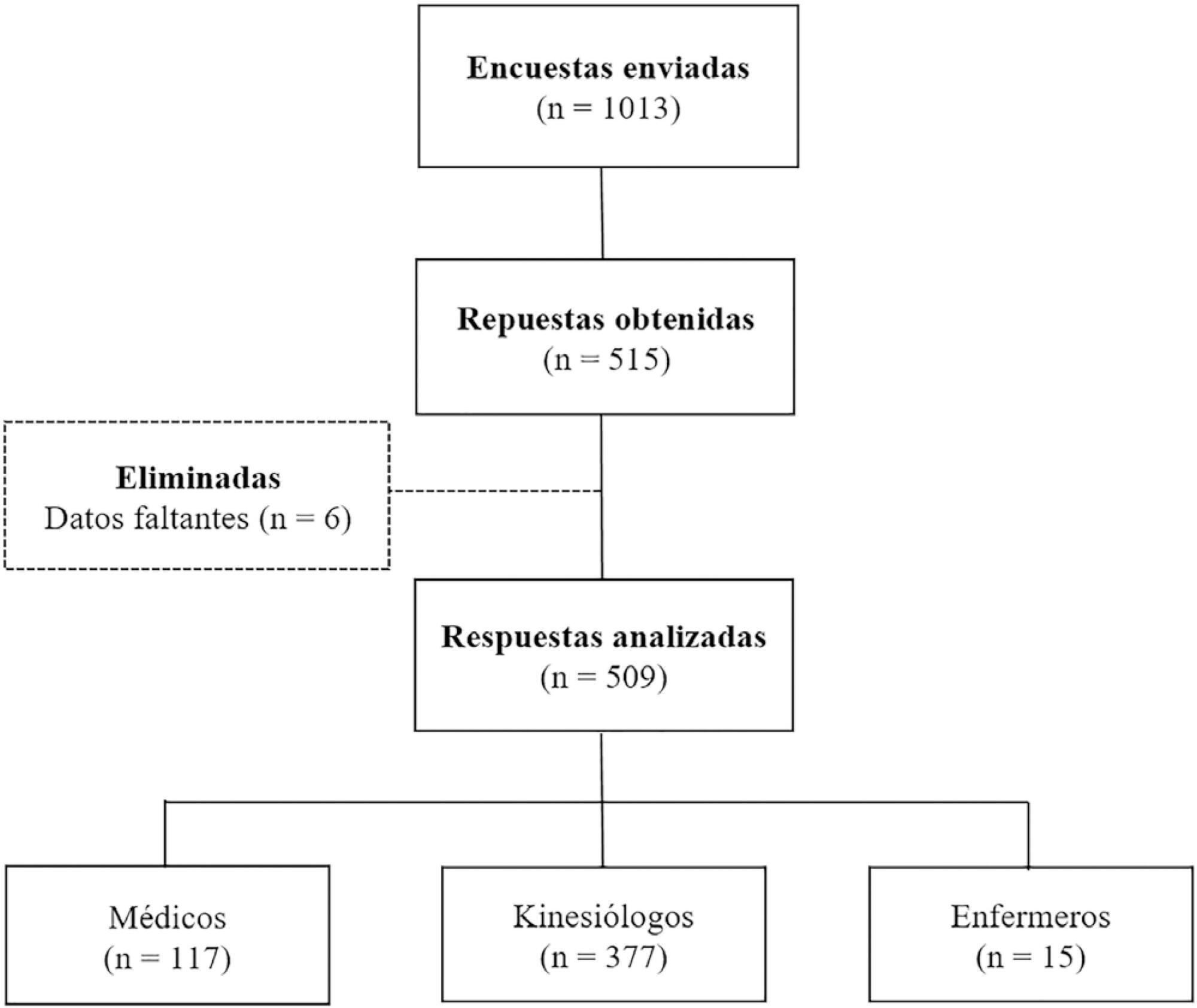
-
Review Articles
Chest wall effect on the monitoring of respiratory mechanics in acute respiratory distress syndrome
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2018;30(2):208-218
Abstract
Review ArticlesChest wall effect on the monitoring of respiratory mechanics in acute respiratory distress syndrome
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2018;30(2):208-218
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20180038
Views0ABSTRACT
The respiratory system mechanics depend on the characteristics of the lung and chest wall and their interaction. In patients with acute respiratory distress syndrome under mechanical ventilation, the monitoring of airway plateau pressure is fundamental given its prognostic value and its capacity to assess pulmonary stress. However, its validity can be affected by changes in mechanical characteristics of the chest wall, and it provides no data to correctly titrate positive end-expiratory pressure by restoring lung volume. The chest wall effect on respiratory mechanics in acute respiratory distress syndrome has not been completely described, and it has likely been overestimated, which may lead to erroneous decision making. The load imposed by the chest wall is negligible when the respiratory system is insufflated with positive end-expiratory pressure. Under dynamic conditions, moving this structure demands a pressure change whose magnitude is related to its mechanical characteristics, and this load remains constant regardless of the volume from which it is insufflated. Thus, changes in airway pressure reflect changes in the lung mechanical conditions. Advanced monitoring could be reserved for patients with increased intra-abdominal pressure in whom a protective mechanical ventilation strategy cannot be implemented. The estimates of alveolar recruitment based on respiratory system mechanics could reflect differences in chest wall response to insufflation and not actual alveolar recruitment.
Keywords:Respiration, artificialRespiratory distress syndrome, adultRespiratory mechanicsThoracic wallVentilator-induced lung injurySee more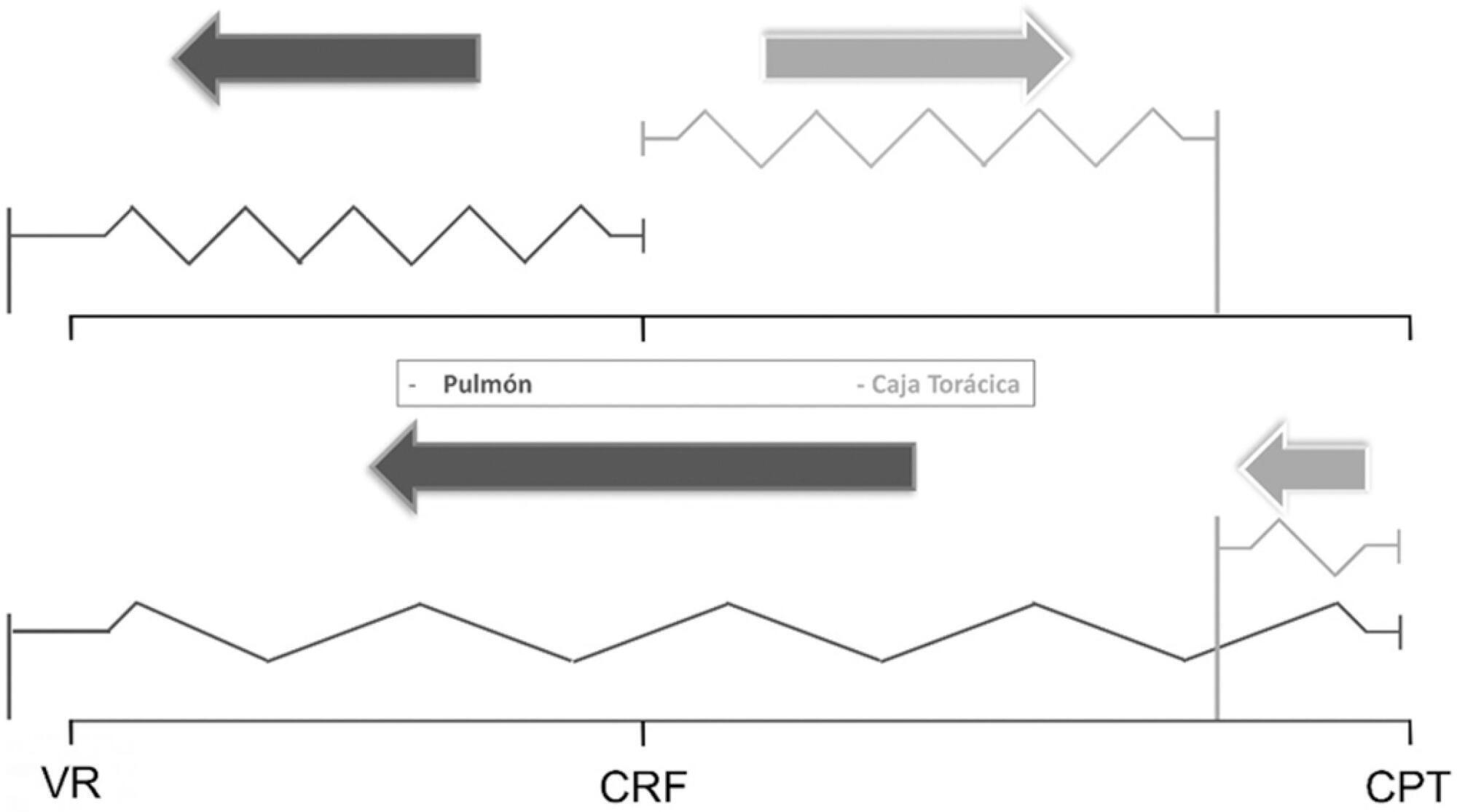
Search
Search in:
KEY WORDS
Case reports Child Coronavirus infections COVID-19 Critical care Critical illness Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation Infant, newborn Intensive care Intensive care units Intensive care units, pediatric mechanical ventilation Mortality Physical therapy modalities Prognosis Respiration, artificial Respiratory insufficiency risk factors SARS-CoV-2 Sepsis




