You searched for:"João Gonçalves-Pereira"
We found (3) results for your search.-
Original Article
Prognostic value of hyperlactatemia in infected patients admitted to intensive care units: a multicenter study
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2022;34(1):154-162
Abstract
Original ArticlePrognostic value of hyperlactatemia in infected patients admitted to intensive care units: a multicenter study
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2022;34(1):154-162
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20220010-en
Views1See moreABSTRACT
Objective:
To evaluate the influence of patient characteristics on hyperlactatemia in an infected population admitted to intensive care units and the influence of hyperlactatemia severity on hospital mortality.
Methods:
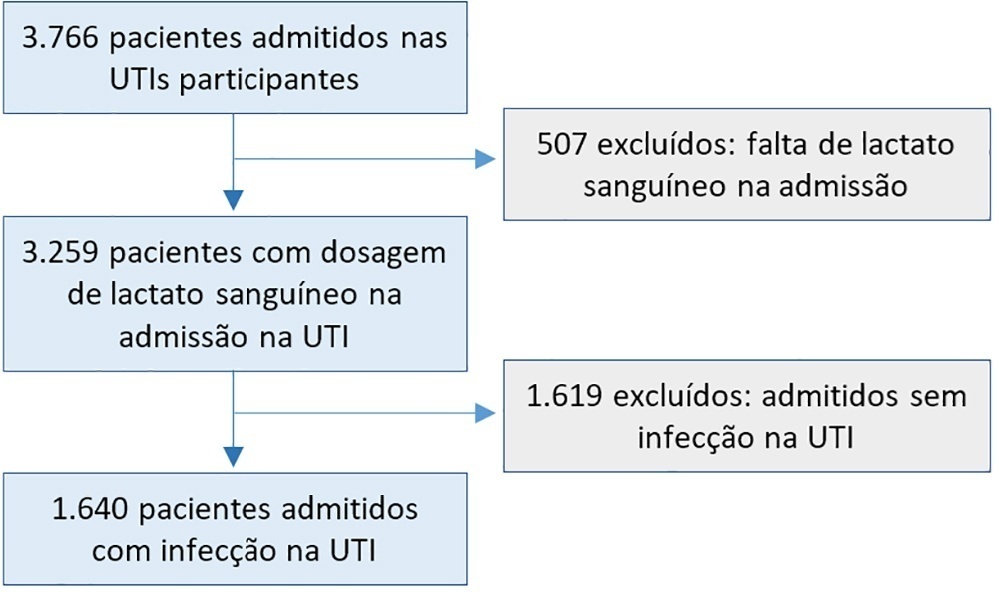
A post hoc analysis of hyperlactatemia in the INFAUCI study, a national prospective, observational, multicenter study, was conducted in 14 Portuguese intensive care units. Infected patients admitted to intensive care units with a lactate measurement in the first 12 hours of admission were selected. Sepsis was identified according to the Sepsis-2 definition accepted at the time of data collection. The severity of hyperlactatemia was classified as mild (2 – 3.9mmol/L), moderate (4.0 – 9.9mmol/L) or severe (> 10mmol/L).
Results:
In a total of 1,640 patients infected on admission, hyperlactatemia occurred in 934 patients (57%), classified as mild, moderate and severe in 57.0%, 34.4% and 8.7% of patients, respectively. The presence of hyperlactatemia and a higher degree of hyperlactatemia were both associated with a higher Simplified Acute Physiology Score II, a higher Charlson Comorbidity Index and the presence of septic shock. The lactate Receiver Operating Characteristic curve for hospital mortality had an area under the curve of 0.64 (95%CI 0.61 – 0.72), which increased to 0.71 (95%CI 0.68 – 0.74) when combined with Sequential Organ Failure Assessment score. In-hospital mortality with other covariates adjusted by Simplified Acute Physiology Score II was associated with moderate and severe hyperlactatemia, with odds ratio of 1.95 (95%CI 1.4 – 2.7; p < 0.001) and 4.54 (95%CI 2.4 - 8.5; p < 0.001), respectively.
Conclusion:
Blood lactate levels correlate independently with in-hospital mortality for moderate and severe degrees of hyperlactatemia.
-
Original Article
Hidden hospital mortality in patients with sepsis discharged from the intensive care unit
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2019;31(2):122-128
Abstract
Original ArticleHidden hospital mortality in patients with sepsis discharged from the intensive care unit
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2019;31(2):122-128
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20190037
Views1See moreABSTRACT
Objective:
To evaluate the impact of the presence of sepsis on in-hospital mortality after intensive care unit discharge.
Methods:
Retrospective, observational, single-center study. All consecutive patients discharged alive from the intensive care unit of Hospital Vila Franca de Xira (Portugal) from January 1 to December 31, 2015 (N = 473) were included and followed until death or hospital discharge. In-hospital mortality after intensive care unit discharge was calculated for septic and non-septic patients.
Results:
A total of 61 patients (12.9%) died in the hospital after being discharged alive from the intensive care unit. This rate was higher among the patients with sepsis on admission, 21.4%, whereas the in-hospital, post-intensive care unit mortality rate for the remaining patients was nearly half that, 9.3% (p < 0.001). Other patient characteristics associated with mortality were advanced age (p = 0.02), male sex (p < 0.001), lower body mass index (p = 0.02), end-stage renal disease (p = 0.04) and high Simplified Acute Physiology Score II (SAPS II) at intensive care unit admission (p < 0.001), the presence of shock (p < 0.001) and medical admission (p < 0.001). We developed a logistic regression model and identified the independent predictors of in-hospital mortality after intensive care unit discharge.
Conclusion:
Admission to the intensive care unit with a sepsis diagnosis is associated with an increased risk of dying in the hospital, not only in the intensive care unit but also after resolution of the acute process and discharge from the intensive care unit.
-
Original Articles – Clinical Research
The neuroprotective role of therapeutic hypothermia after cardiac arrest
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2011;23(4):455-461
Abstract
Original Articles – Clinical ResearchThe neuroprotective role of therapeutic hypothermia after cardiac arrest
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2011;23(4):455-461
DOI 10.1590/S0103-507X2011000400010
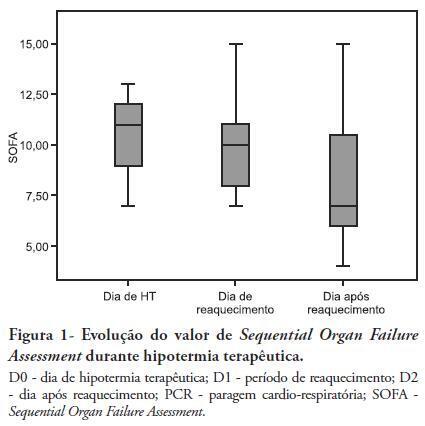
Views0See moreOBJECTIVES: Therapeutic hypothermia following cardiorespiratory arrest has been demonstrated to have cardio- and neuroprotective effects, resulting in improved survival and better neurological outcomes. The objective of this study was to assess the outcomes of patients undergoing therapeutic hypothermia following cardiorespiratory arrest. METHODS: A prospective, 10-month observational study of patients admitted to an intensive care unit and undergoing therapeutic hypothermia after cardiorespiratory arrest was undertaken. Therapeutic hypothermia was induced by cold fluid administration and body surface cooling in patients admitted no more than 12 hours after resuscitation from cardiorespiratory arrest. A target temperature of 33ºC was maintained for 24 hours. RESULTS: Overall, 12 patients were included (median age 64 years, 58% male). Half of the cardiorespiratory arrests were in-hospital. The median first-day Charlson Index, Sequential Organ Failure Assessment (SOFA) and Acute Physiology and Chronic Health Evaluation II scores were of 2.9, 11 and 24.5, respectively. The intensive care unit mortality rate was 42% (N=5). Five of the 7 surviving patients recovered their pre-cardiorespiratory arrest neurological status. Hypothermia was initiated 120 min (median) after recovery of spontaneous circulation. Most patients (75%) required vasopressor support. During the first 3 days after cardiorespiratory arrest and therapeutic hypothermia, a progressive SOFA score decrease (median 11 on day 0, 10 on day 1 and 7 on day 2) was observed. DISCUSSION: In this study, therapeutic hypothermia was applied to all post-cardiorespiratory arrest patients and demonstrated good neurological outcome in surviving patients.
Search
Search in:
KEY WORDS
Case reports Child Coronavirus infections COVID-19 Critical care Critical illness Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation Infant, newborn Intensive care Intensive care units Intensive care units, pediatric mechanical ventilation Mortality Physical therapy modalities Prognosis Respiration, artificial Respiratory insufficiency risk factors SARS-CoV-2 Sepsis




