Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2015;27(4):322-332
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20150056
The determination of coma patient prognosis after cardiac arrest has clinical, ethical and social implications. Neurological examination, imaging and biochemical markers are helpful tools accepted as reliable in predicting recovery. With the advent of therapeutic hypothermia, these data need to be reconfirmed. In this study, we attempted to determine the validity of different markers, which can be used in the detection of patients with poor prognosis under hypothermia.
Data from adult patients admitted to our intensive care unit for a hypothermia protocol after cardiac arrest were recorded prospectively to generate a descriptive and analytical study analyzing the relationship between clinical, neurophysiological, imaging and biochemical parameters with 6-month outcomes defined according to the Cerebral Performance Categories scale (good 1-2, poor 3-5). Neuron-specific enolase was collected at 72 hours. Imaging and neurophysiologic exams were carried out in the 24 hours after the rewarming period.
Sixty-seven patients were included in the study, of which 12 had good neurological outcomes. Ventricular fibrillation and electroencephalographic theta activity were associated with increased likelihood of survival and improved neurological outcomes. Patients who had more rapid cooling (mean time of 163 versus 312 minutes), hypoxic-ischemic brain injury on magnetic resonance imaging or neuron-specific enolase > 58ng/mL had poor neurological outcomes (p < 0.05).
Hypoxic-ischemic brain injury on magnetic resonance imaging and neuron-specific enolase were strong predictors of poor neurological outcomes. Although there is the belief that early achievement of target temperature improves neurological prognoses, in our study, there were increased mortality and worse neurological outcomes with earlier target-temperature achievement.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2011;23(4):455-461
DOI 10.1590/S0103-507X2011000400010
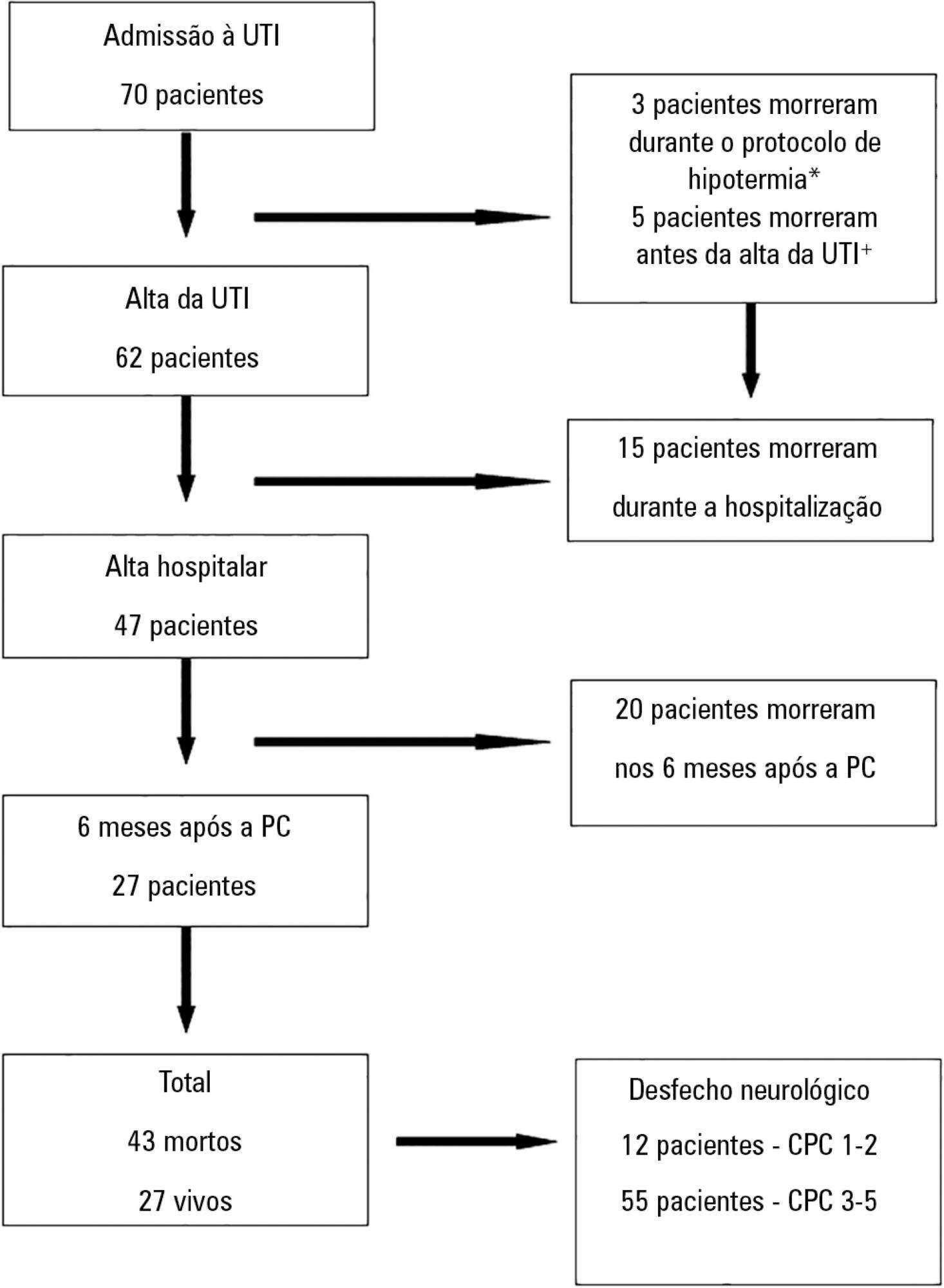
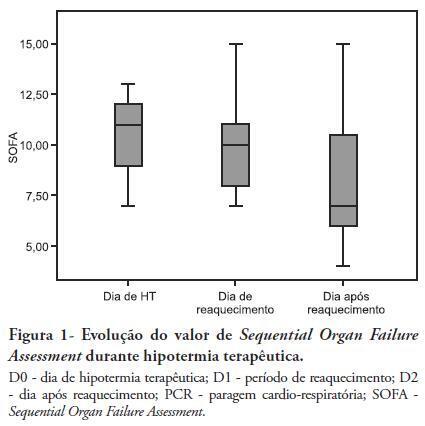
OBJECTIVES: Therapeutic hypothermia following cardiorespiratory arrest has been demonstrated to have cardio- and neuroprotective effects, resulting in improved survival and better neurological outcomes. The objective of this study was to assess the outcomes of patients undergoing therapeutic hypothermia following cardiorespiratory arrest. METHODS: A prospective, 10-month observational study of patients admitted to an intensive care unit and undergoing therapeutic hypothermia after cardiorespiratory arrest was undertaken. Therapeutic hypothermia was induced by cold fluid administration and body surface cooling in patients admitted no more than 12 hours after resuscitation from cardiorespiratory arrest. A target temperature of 33ºC was maintained for 24 hours. RESULTS: Overall, 12 patients were included (median age 64 years, 58% male). Half of the cardiorespiratory arrests were in-hospital. The median first-day Charlson Index, Sequential Organ Failure Assessment (SOFA) and Acute Physiology and Chronic Health Evaluation II scores were of 2.9, 11 and 24.5, respectively. The intensive care unit mortality rate was 42% (N=5). Five of the 7 surviving patients recovered their pre-cardiorespiratory arrest neurological status. Hypothermia was initiated 120 min (median) after recovery of spontaneous circulation. Most patients (75%) required vasopressor support. During the first 3 days after cardiorespiratory arrest and therapeutic hypothermia, a progressive SOFA score decrease (median 11 on day 0, 10 on day 1 and 7 on day 2) was observed. DISCUSSION: In this study, therapeutic hypothermia was applied to all post-cardiorespiratory arrest patients and demonstrated good neurological outcome in surviving patients.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2010;22(2):196-205
DOI 10.1590/S0103-507X2010000200015
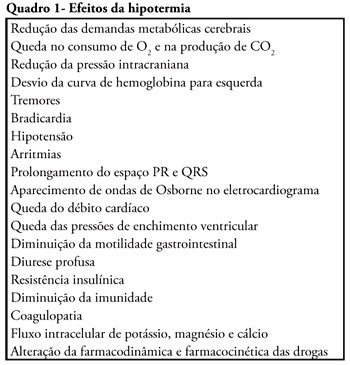
Cardiac arrest is a high mortality event and the associated brain ischemia frequently causes severe neurological damage and persistent vegetative state. Therapeutic hypothermia is an important tool for the treatment of post-anoxic coma after cardiopulmonary resuscitation. It has been shown to reduce mortality and to improve neurological outcomes after cardiac arrest. Nevertheless, hypothermia is underused in critical care units. This manuscript aims to review the hypothermia mechanism of action in cardiac arrest survivors and to propose a simple protocol, feasible to be implemented in any critical care unit.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2009;21(1):65-71
DOI 10.1590/S0103-507X2009000100010
Cardiac arrest survivors frequently suffer from ischemic brain injury associated with poor neurological outcome and death. Therapeutic hypothermia improves outcomes in comatose survivors after resuscitation from out-of-hospital cardiac arrest. Considering its formal recommendation as a therapy, post-return of spontaneous circulation after cardiac arrest, the objective of this study was to review the clinical aspects of therapeutic hypothermia. Non-systematic review of articles using the keywords "cardiac arrest, cardiopulmonary resuscitation, cooling, hypothermia, post resuscitation syndrome" in the Med-Line database was performed. References of these articles were also reviewed. Unconscious adult patients with spontaneous circulation after out-of-hospital ventricular fibrillation or pulseless ventricular tachycardia should be cooled. Moreover, for any other rhythm or in the intra-hospital scenario, such cooling may also be beneficial. There are different ways of promoting hypothermia. The cooling system should be adjusted as soon as possible to the target temperature. Mild therapeutic hypothermia should be administered under close control, using neuromuscular blocking drugs to avoid shivering. The rewarming process should be slow, and reach 36º C, usually in no less then 8 hours. When temperature increases to more than 35º C, sedation, analgesia, and paralysis could be discontinued. The expected complications of hypothermia may be pneumonia, sepsis, cardiac arrhythmias, and coagulopathy. In spite of potential complications which require rigorous control, only six patients need to be treated to save one life.
