Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2022;34(4):492-498
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20220169-en
To describe the rate and factors related to nonreturn to work in the third month after discharge from the intensive care unit and the impact of unemployment, loss of income and health care expenses for survivors.
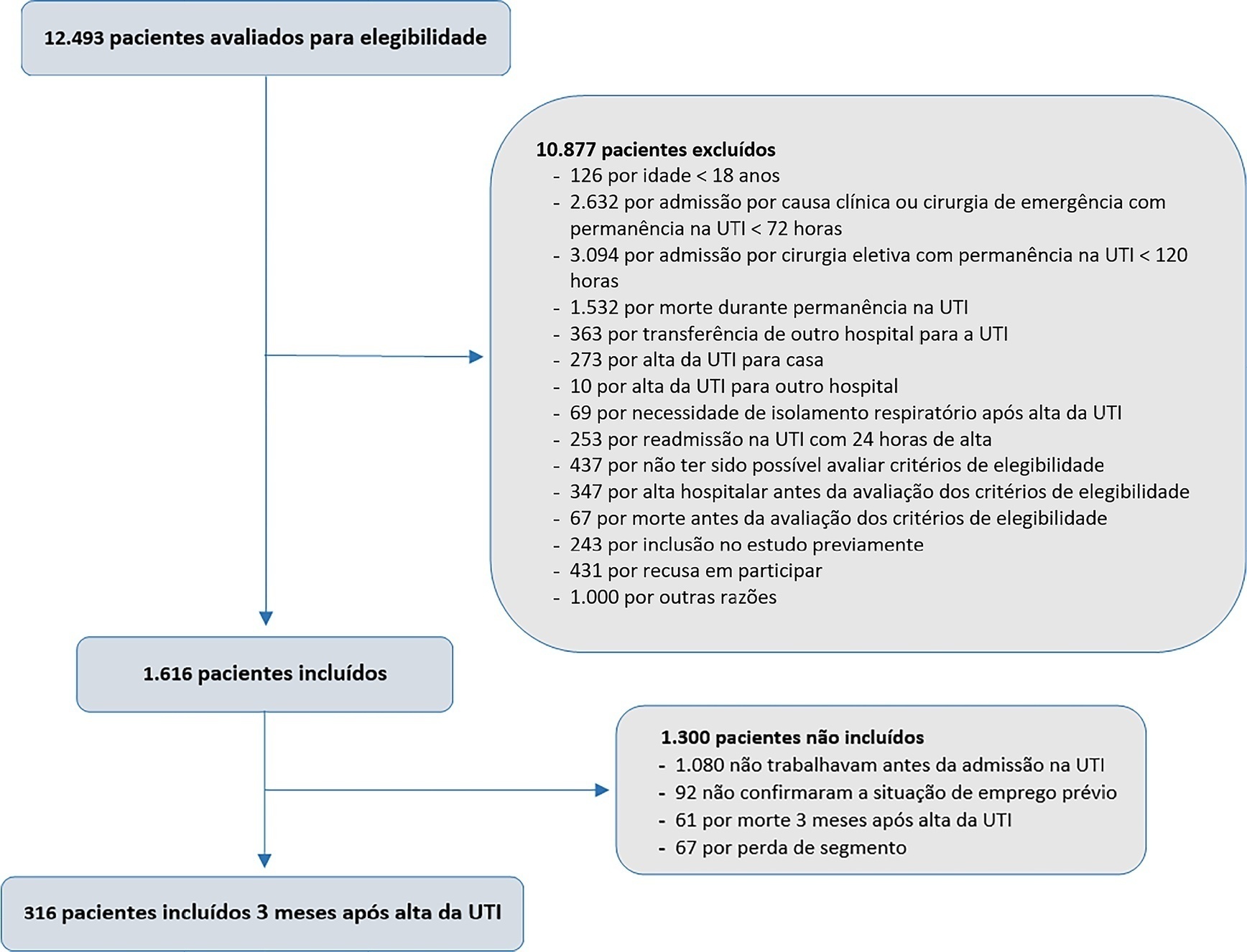
This was a prospective multicenter cohort study that included survivors of severe acute illness who were hospitalized between 2015 and 2018, previously employed, and who stayed more than 72 hours in the intensive care unit. Outcomes were assessed by telephone interview in the third month after discharge.
Of the 316 patients included in the study who had previously worked, 193 (61.1%) did not return to work within 3 months after discharge from the intensive care unit. The following factors were associated with nonreturn to work: low educational level (prevalence ratio 1.39; 95%CI 1.10 - 1.74; p = 0.006), previous employment relationship (prevalence ratio 1.32; 95%CI 1 10 - 1.58; p = 0.003), need for mechanical ventilation (prevalence ratio 1.20; 95%CI 1.01 - 1.42; p = 0.04) and physical dependence in the third month after discharge (prevalence ratio 1.27; 95%CI 1.08 - 1.48; p = 0.003). Survivors who were unable to return to work more often had reduced family income (49.7% versus 33.3%; p = 0.008) and increased health expenditures (66.9% versus 48.3%; p = 0.002). compared to those who returned to work in the third month after discharge from the intensive care unit.
Intensive care unit survivors often do not return to work until the third month after discharge from the intensive care unit. Low educational level, formal job, need for ventilatory support and physical dependence in the third month after discharge were related to nonreturn to work. Failure to return to work was also associated with reduced family income and increased health care costs after discharge.
Search
Search in:
Case reports (56) Child (53) Coronavirus infections (34) COVID-19 (46) Critical care (116) Critical illness (54) Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (26) Infant, newborn (27) Intensive care (72) Intensive care units (256) Intensive care units, pediatric (31) mechanical ventilation (38) Mortality (76) Physical therapy modalities (28) Prognosis (61) Respiration, artificial (119) Respiratory insufficiency (26) risk factors (34) SARS-CoV-2 (28) Sepsis (98)