Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2008;20(2):115-123
DOI 10.1590/S0103-507X2008000200001
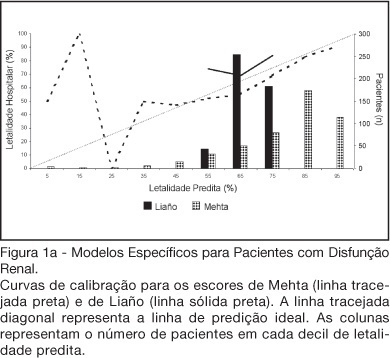
BACKGROUND AND OBJECTIVES: There is no consensus about prognostic scores for use in patients with acute kidney injury (AKI). The aim of this study was to evaluate the performance of six prognostic scores in predicting hospital mortality in patients with AKI and need for renal replacement therapy (RRT). METHODS: Prospective cohort of patients admitted to the intensive care units (ICU) of three tertiary care hospitals that required RRT for AKI over a 32-month period. Patients with end-stage renal disease and those with ICU stay < 24h were excluded. Data from the first 24h of ICU admission were used to calculate SAPS II and APACHE II scores, and data from the first 24h of RRT were used in the calculation of LOD, ODIN, Liaño and Mehta scores. Discrimination was evaluated using the area under ROC curve (AUROC) and calibration using the Hosmer-Lemeshow goodness-of-fit test. The hospital mortality was the end-point of interest. RESULTS: 467 patients were evaluated. Hospital mortality rate was 75%. Mean SAPS II and APACHE II scores were 48.5 ±11.2 and 27.4 ± 6.3 points, and median LOD score was 7 (5-8) points. Except for Mehta score (p = 0.001), calibration was appropriate in all models. However, discrimination was uniformly unsatisfactory; AUROC ranged from 0.60 for ODIN to 0.72 for SAPS II and Mehta scores. In addition, except for Mehta, all models tended to underestimate hospital mortality. CONCLUSIONS: Organ dysfunction, general and renal-specific severity-of-illness scores were inaccurate in predicting outcome in ICU patients in need for RRT.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2006;18(1):22-26
DOI 10.1590/S0103-507X2006000100005
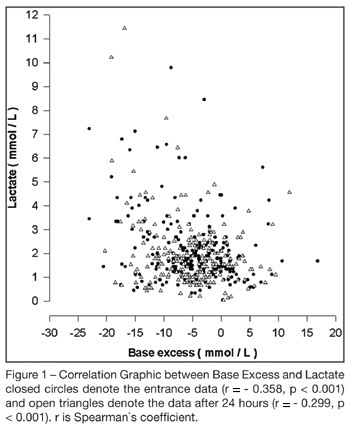
BACKGROUND AND OBJECTIVES: To correlate standard base excess (SBE) with serum lactate level and demonstrate the independent prognostic significance of each one. METHODS: In a retrospective study, we retrieved data from 333 patients of our prospectively collected database of 7-bed medical intensive care unit of a 1800-bed university hospital. RESULTS: The results have shown a poor correlation between SBE and lactate, r = - 0.358, p < 0.001, and an independent prognostic significance of each one when analyzed concomitantly, odds ratio (95% Confidence interval) = 0.996 (0.992 - 0.999) to standard base excess and 1.000 (1.000 - 1.002) to lactate at entrance; and odds ratio (95% Confidence interval ) = 0.990 (0.985 - 0.994) to standard base excess and 1.003 (1.001 - 1.005) to lactate after 24 hours. The accuracy of standard base excess was close to lactate to determine in-intensive care unit death. CONCLUSIONS: The lactic component of the metabolic acidosis is not the major determinant of standard base excess. Serum lactate and SBE are independent outcome predictors in critically ill patients.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2006;18(3):242-250
DOI 10.1590/S0103-507X2006000300005
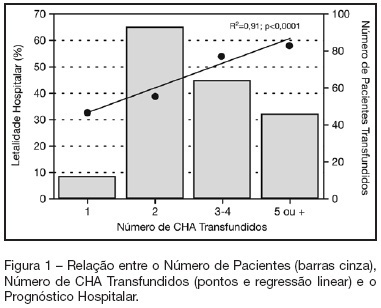
BACKGROUND AND OBJECTIVES: Packed red blood cell (PRBC) transfusion is frequent in intensive care unit (ICU). However, the consequences of anemia in ICU patients are poorly understood. Our aim was to evaluate the prevalence, indications, pre-transfusion hematocrit and hemoglobin levels, and outcomes of ICU patients transfused with PRBC. METHODS: Prospective cohort study conducted at a medical-surgical ICU of a teaching hospital during a 16-month period. Patients' demographic, clinical, laboratory and transfusion-related data were collected. Logistic regression was used after univariate analyses. RESULTS: A total of 698 patients were evaluated and 244 (35%) received PRBC, mainly within the first four days of ICU (82.4%). Transfusion was more frequent in medical and emergency surgical patients. The mean pre-transfusion hematocrit and hemoglobin were 22.8% ± 4.5% and 7.9 ± 1.4 g/dL, respectively. Transfused patients received 4.4 ± 3.7 PRBC during ICU stay and 2.2 ± 1 PRBC at each transfusion. The ICU (39.8% versus 13.2%; p < 0.0001) and hospital (48.8% versus 20.3%; p < 0.0001) mortality rates were higher in transfused patients. Mortality increased as the number of transfused PRBC increased (R² = 0.91). In logistic regression, predictive factors for PRBC transfusion were hepatic cirrhosis, mechanical ventilation (MV), type and duration of ICU admission, and hematocrit. The independent factors associated to hospital mortality were MV, transfusions of more than five PRBC and SAPS II score. CONCLUSIONS: PRBC transfusions are frequent in ICU patients, especially in those with medical and emergency surgical complications, longer ICU stay, and hepatic cirrhosis and in need of MV. Pre-transfusion hemoglobin levels were lower than those previously reported. In our study, PRBC transfusion was associated with increased mortality.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2006;18(3):263-267
DOI 10.1590/S0103-507X2006000300008
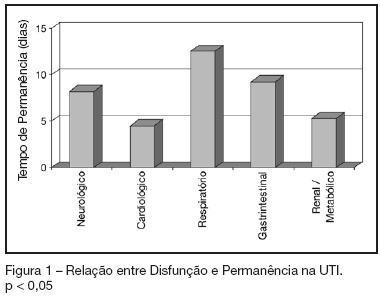
BACKGROUND AND OBJECTIVES: To identify the severity of elderly patients admitted to the intensive care unit (ICU) in a university hospital, relating it to the in-ICU mortality. METHODS: Retrospective study, with analysis of 130 patients admitted to ICU from March 2004 to July 2005. RESULTS: Of the 130 patients, there was a predominance of women, and mean 72.2 ± 7.3 years. There were more patients between 65 and 74 years old. More than 80% of the patients had come from the university hospital itself. The main dysfunctions were from the cardiocirculatory and respiratory systems. Sepsis caused 23.8% of the admissions. Length of stay in ICU was 8.2 ± 7.6 days. The mean of APACHE II was 18.2 ± 7.2. Lesser values of APACHE II, length of stay and mortality were observed in patients with cardiocirculatory dysfunction. The in-ICU mortality was 33.9%, 6.2% before 48 hours. The standardized mortality ratio (SMR) was 0.988. CONCLUSIONS: The age groups did not determine difference between values of APACHE II. They were related neither to higher mortality rate, nor to higher ICU length of stay. Patients with cardiocirculatory dysfunctions had lesser values of APACHE II, ICU length of stay and in-ICU mortality.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2007;19(1):23-30
DOI 10.1590/S0103-507X2007000100003
BACKGROUND AND OBJECTIVES: Verify the association between clinical, epidemiological and laboratorial characteristics with mortality of septic patient in an Intensive Care Unit (ICU) from Pernambuco, northeast of Brazil, to improve the attention for patients with sepse which are in risk of developing organ dysfunction. METHODS: Case-control study, without intervention, that included adults' patients admitted in ICU with sepsis or that developed it during ICU stay. RESULTS: It was included 199 patients. After logistic regression, the length of hospital stay more than 72 hours before admission in ICU, evidence of associated co-morbidities, more than three organ failures, and lactate more than 4 mmol/L were associated with mortality. The SOFA score with more than 12 points was associated with precocity mortality (< 72hours). CONCLUSIONS: The septic patients admitted ICU with less than 72h of hospital stay have a better prognosis, and those with a great number of organ failure, and co-morbidities have a superior mortality rate. Between laboratory results, only the high concentration of lactate is associated with mortality.
Search
Search in:
Case reports (56) Child (53) Coronavirus infections (34) COVID-19 (46) Critical care (116) Critical illness (54) Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (26) Infant, newborn (27) Intensive care (72) Intensive care units (256) Intensive care units, pediatric (31) mechanical ventilation (38) Mortality (76) Physical therapy modalities (28) Prognosis (61) Respiration, artificial (119) Respiratory insufficiency (26) risk factors (34) SARS-CoV-2 (28) Sepsis (98)