You searched for:"Iara Serra Azul Machado Bezerra"
We found (2) results for your search.-
Morbidity and mortality of elderly patients admitted to an Intensive Care Unit of a University Hospital in Fortaleza
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2006;18(3):263-267
Abstract
Morbidity and mortality of elderly patients admitted to an Intensive Care Unit of a University Hospital in Fortaleza
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2006;18(3):263-267
DOI 10.1590/S0103-507X2006000300008
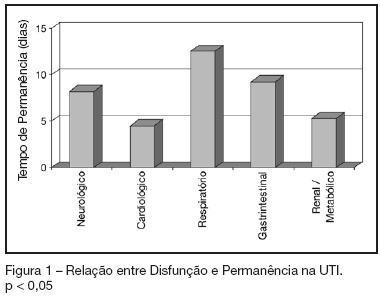
Views0See moreBACKGROUND AND OBJECTIVES: To identify the severity of elderly patients admitted to the intensive care unit (ICU) in a university hospital, relating it to the in-ICU mortality. METHODS: Retrospective study, with analysis of 130 patients admitted to ICU from March 2004 to July 2005. RESULTS: Of the 130 patients, there was a predominance of women, and mean 72.2 ± 7.3 years. There were more patients between 65 and 74 years old. More than 80% of the patients had come from the university hospital itself. The main dysfunctions were from the cardiocirculatory and respiratory systems. Sepsis caused 23.8% of the admissions. Length of stay in ICU was 8.2 ± 7.6 days. The mean of APACHE II was 18.2 ± 7.2. Lesser values of APACHE II, length of stay and mortality were observed in patients with cardiocirculatory dysfunction. The in-ICU mortality was 33.9%, 6.2% before 48 hours. The standardized mortality ratio (SMR) was 0.988. CONCLUSIONS: The age groups did not determine difference between values of APACHE II. They were related neither to higher mortality rate, nor to higher ICU length of stay. Patients with cardiocirculatory dysfunctions had lesser values of APACHE II, ICU length of stay and in-ICU mortality.
-
Base deficit at intensive care unit admission: an early mortality indicator
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2007;19(4):434-436
Abstract
Base deficit at intensive care unit admission: an early mortality indicator
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2007;19(4):434-436
DOI 10.1590/S0103-507X2007000400005
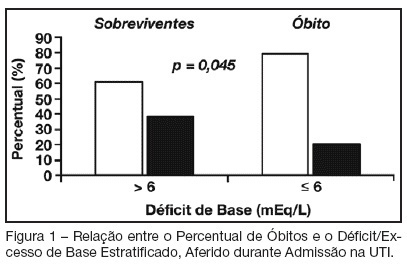
Views0See moreBACKGROUND AND OBJECTIVES: Base deficit is considered an indicator of tissue injury, shock and resuscitation. The objective of this study was to establish an association between base deficit obtained on the admission of patients in intensive care unit (ICU) and their prognosis. METHODS: A retrospective study with analysis of 110 patients admitted consecutively in the ICU, during the period of June to December 2006. RESULTS: There was a predominance of women, with age mean 54.2 ± 18.7 years old. Length of stay in ICU was 6.5 ± 7.4 days and the mean APACHE II score was 21 ± 8.1 points. The standardized mortality ratio was 0.715. Mortality was higher in patients with base deficit > 6 mEq/L (38.9%) than in those with base deficit < 6 mEq/L (20.6%); p < 0.05. Patients with early mortality had lower base deficit (7.75 ± 8.33 mEq/L) than survivors (3.17 ± 5.43 mEq/L); p < 0.05. Patients with permanence in ICU until 7 days and patients that stayed in this unit for more than 7 days had similar base deficit. CONCLUSIONS: Base deficit had been associated with early mortality during ICU internment. Base deficit > 6 mEq/L is a marker of significant mortality.
Search
Search in:
KEY WORDS
Case reports Child Coronavirus infections COVID-19 Critical care Critical illness Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation Infant, newborn Intensive care Intensive care units Intensive care units, pediatric mechanical ventilation Mortality Physical therapy modalities Prognosis Respiration, artificial Respiratory insufficiency risk factors SARS-CoV-2 Sepsis




