Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2009;21(3):255-261
DOI 10.1590/S0103-507X2009000300004
Currently, aging of the population is a widespread global phenomenon. Therefore, the assessment of prognosis in elderly patients is needed. This study aims to identify risk factors in a population of elderly patients admitted in the intensive care unit METHODS: A prospective study in the intensive care unit of a general tertiary hospital was carried out for five months. Patients with 65 years or more of age, who stayed in the intensive care unit for 24 hours or more were included and those at the-end-of-life, patients readmitted to intensive care unit during the same hospital stay were excluded. RESULTS: In this study 199 patients were involved, with a mean age of 75.4±6.8 years, and 58.8% were female. Mortality was 57.3%. The mean APACHE II, SOFA, MODS and Katz index (assessment of daily activities) were respectively 20.0±5.8, 6.8±3.9, 2.4±1.9 and 5.3±1.6. Most patients were postoperative 59.3% and 41.6% were under invasive mechanical ventilation. At regression analysis, the independent determinants of higher mortality were: older age (76.9±6.7 years death versus 73.3±6.5 years discharge, P<0.001, OR=1.08, CI 95% 1.01-1. 16), the Katz index (4.9±1.9 deaths versus 5.7±0.9 discharge, p=0.001, OR=0.66, CI 95% 0.45-0.98), hyperglycemia (158.1±69.0 death versus 139.6±48.5 discharge p=0.041; OR=1.02; CI 95% 1.01-1.03) and need for mechanical ventilation at admission to the intensive care unit (57.0% death versus 20.5% discharge p <0.001, OR=3.57, CI 95% 1.24-10.3). CONCLUSION: Elderly patients admitted to the intensive care unit that have difficulties in performing daily activities, hyperglycemia and who are under invasive mechanical ventilation had a worse hospital prognosis.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2006;18(3):263-267
DOI 10.1590/S0103-507X2006000300008
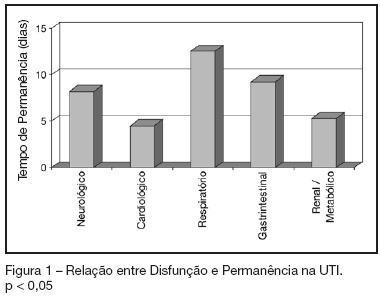
BACKGROUND AND OBJECTIVES: To identify the severity of elderly patients admitted to the intensive care unit (ICU) in a university hospital, relating it to the in-ICU mortality. METHODS: Retrospective study, with analysis of 130 patients admitted to ICU from March 2004 to July 2005. RESULTS: Of the 130 patients, there was a predominance of women, and mean 72.2 ± 7.3 years. There were more patients between 65 and 74 years old. More than 80% of the patients had come from the university hospital itself. The main dysfunctions were from the cardiocirculatory and respiratory systems. Sepsis caused 23.8% of the admissions. Length of stay in ICU was 8.2 ± 7.6 days. The mean of APACHE II was 18.2 ± 7.2. Lesser values of APACHE II, length of stay and mortality were observed in patients with cardiocirculatory dysfunction. The in-ICU mortality was 33.9%, 6.2% before 48 hours. The standardized mortality ratio (SMR) was 0.988. CONCLUSIONS: The age groups did not determine difference between values of APACHE II. They were related neither to higher mortality rate, nor to higher ICU length of stay. Patients with cardiocirculatory dysfunctions had lesser values of APACHE II, ICU length of stay and in-ICU mortality.
Search
Search in:
Case reports (56) Child (53) Coronavirus infections (34) COVID-19 (46) Critical care (115) Critical illness (54) Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (26) Infant, newborn (27) Intensive care (72) Intensive care units (256) Intensive care units, pediatric (31) mechanical ventilation (38) Mortality (76) Physical therapy modalities (28) Prognosis (61) Respiration, artificial (119) Respiratory insufficiency (26) risk factors (34) SARS-CoV-2 (28) Sepsis (98)