Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2010;22(1):5-10
DOI 10.1590/S0103-507X2010000100003
OBJECTIVE: Anemia is common in severely ill patients, and blood sampling plays a relevant causative role. Consequently, blood transfusions are frequent an related to several complications. Trying to reduce the transfusion-related risk, minimizing blood loss is mandatory. Thus, this work aimed to evaluate a closed blood sampling system as a strategy to spare unnecessary blood losses and transfusions. METHODS: This was a prospective, randomized, controlled, multicenter, 6 months, clinical trial. The patients were assigned to either VAMP (Venous Arterial Blood Management Protection) group, using a closed blood sampling system, or control group. The groups' transfusion rate, as well as hemoglobin (Hb) and Hematocrit (Ht) changes were compared for 14 days. RESULTS: Were included 127 patients, 65 assigned to the control group, and 62 to VAMP. During the intensive care unit stay, both groups experienced both hemoglobin and hematocrit drops. However, when the final Ht and Hb were compared between the groups, a difference was identified with higher values in the VAMP group (p=0.03; p=0.006, respectively). No statistical difference was found for both groups transfusion rates, although the VAMP group had an absolute 12% blood transfusion reduction. CONCLUSION: The use of a closed blood sampling system was able to minimize blood count values changes, however failed to reduce transfusions rate.
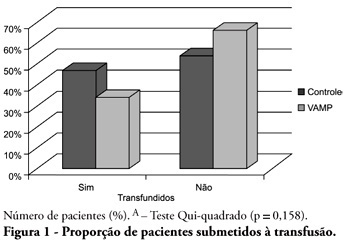
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2009;21(3):315-323
DOI 10.1590/S0103-507X2009000300013
Anemia is a prevalent issue in intensive care units. It appears in the first days, and may continue or worsen during hospital stay. Its etiology is generally multifactorial. Red blood cell transfusion is the most common intervention for treating anemia. Approximately 12 million blood units are used for transfusions in the United States, 25% to 30% in the intensive care units. Due to reduction of transfusion infections the increased safety has allowed an expansion of clinical indications. However, transfusion therapy is associated with other adverse effects such as nosocomial infections, immunological impairment, lung injury, hemolytic reactions and higher cancer incidence. Various papers have tried to show an association between correction of anemia and mortality-morbidity, but no consensus has been reached in literature. One of the current World Health Organization's proposals is to reduce potentially unnecessary transfusions, promoting a rational transfusion attitude. The primary objective of this narrative review is to approach controversies regarding the transfusion threshold according to recent studies, and as a secondary objective, it aims to discuss iatrogenic anemia aspects and the different behaviors among intensivists on the best practices for implementation of transfusion practices. It is not within our objectives to discuss transfusion complications, although they are mentioned. A search was conducted on electronic literature databases (PubMed - Clinical Queries), and UpToDate 16.2, and additional consultation to textbooks. It became clear that transfusion practices are widely variable among intensive care units. Evidence is scarce that routine transfusion in non-hemorrhagic patients should be used in those with > 7 g/dL hemoglobin. There is no consensus on the transfusion threshold in critically ill patients. Cardiovascular disease patients seem to present a higher risk of death than non-cardiovascular patients, for any level of hemoglobin. Transfusion guided by hemoglobin levels and individual oxy-hemodynamic physiologic parameters and clinical context is apparently, the current best accepted strategy, rather than arbitrary and isolated hemoglobin correction.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2006;18(3):234-241
DOI 10.1590/S0103-507X2006000300004
BACKGROUND AND OBJECTIVES: Anemia of critical illness is a multifactorial condition caused by blood loss, frequent phlebotomies and inadequate production of red blood cells (RBC). Controversy surrounds the most appropriate hemoglobin concentration "trigger" for transfusion of RBC. We aimed to evaluate transfusion practices in Brazilian ICUs. METHODS: A prospective study throughout a 2-week period in 19 Brazilian ICUs. Hemoglobin (Hb) level, transfusion rate, organ dysfunction assessment and 28-day mortality were evaluated. Primary indication for transfusion and pretransfusion hemoglobin level were collected for each transfusion. RESULTS: Two hundred thirty-one patients with an ICU length of stay longer than 48h were included. An Hb level lower than 10 g/dL was found in 33% on admission in the ICU. A total of 348 RBC units were transfused in 86 patients (36.5%). The mean pretransfusion hemoglobin level was 7.7 ± 1.1 g/dL. Transfused-patients had significantly higher SOFA score (7.9 ± 4.6 vs 5.6 ± 3.8, p < 0.05, respectively), days on mechanical ventilation (10.7 ± 8.2 vs 7.2 ± 6.4, p < 0.05) and days on vasoactive drugs (6.7 ± 6.4 vs 4.2 ± 4.0, p < 0.05) than non-transfused patients despite similar APACHE II scores (15.2 ± 8.1 vs 14.2 ± 8.1, NS). Transfused patients had higher mortality rate (43.5%) than non-transfused patients (36.3%) (RR 0.60-1.15, NS). Only one patient (0.28%) had febrile non-hemolytic transfusion and urticarial reactions. CONCLUSIONS: Anemia is common in critically ill patients.It seems from the present study that transfusion practices in Brazil have had a more restrictive approach with a lower limit "transfusion trigger".
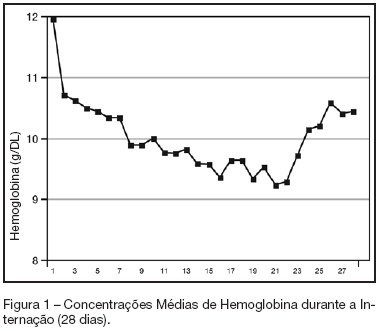
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2006;18(3):242-250
DOI 10.1590/S0103-507X2006000300005
BACKGROUND AND OBJECTIVES: Packed red blood cell (PRBC) transfusion is frequent in intensive care unit (ICU). However, the consequences of anemia in ICU patients are poorly understood. Our aim was to evaluate the prevalence, indications, pre-transfusion hematocrit and hemoglobin levels, and outcomes of ICU patients transfused with PRBC. METHODS: Prospective cohort study conducted at a medical-surgical ICU of a teaching hospital during a 16-month period. Patients' demographic, clinical, laboratory and transfusion-related data were collected. Logistic regression was used after univariate analyses. RESULTS: A total of 698 patients were evaluated and 244 (35%) received PRBC, mainly within the first four days of ICU (82.4%). Transfusion was more frequent in medical and emergency surgical patients. The mean pre-transfusion hematocrit and hemoglobin were 22.8% ± 4.5% and 7.9 ± 1.4 g/dL, respectively. Transfused patients received 4.4 ± 3.7 PRBC during ICU stay and 2.2 ± 1 PRBC at each transfusion. The ICU (39.8% versus 13.2%; p < 0.0001) and hospital (48.8% versus 20.3%; p < 0.0001) mortality rates were higher in transfused patients. Mortality increased as the number of transfused PRBC increased (R² = 0.91). In logistic regression, predictive factors for PRBC transfusion were hepatic cirrhosis, mechanical ventilation (MV), type and duration of ICU admission, and hematocrit. The independent factors associated to hospital mortality were MV, transfusions of more than five PRBC and SAPS II score. CONCLUSIONS: PRBC transfusions are frequent in ICU patients, especially in those with medical and emergency surgical complications, longer ICU stay, and hepatic cirrhosis and in need of MV. Pre-transfusion hemoglobin levels were lower than those previously reported. In our study, PRBC transfusion was associated with increased mortality.
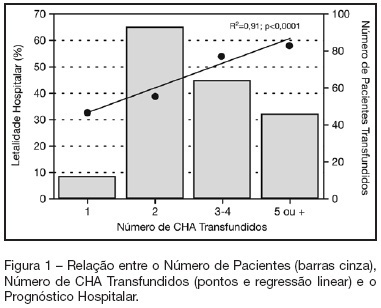
Search
Search in:
Case reports (56) Child (53) Coronavirus infections (34) COVID-19 (46) Critical care (116) Critical illness (54) Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (26) Infant, newborn (27) Intensive care (72) Intensive care units (256) Intensive care units, pediatric (31) mechanical ventilation (38) Mortality (76) Physical therapy modalities (28) Prognosis (61) Respiration, artificial (119) Respiratory insufficiency (26) risk factors (34) SARS-CoV-2 (28) Sepsis (98)