Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2010;22(4):351-357
DOI 10.1590/S0103-507X2010000400007
OBJECTIVE: To identify the relevant differences between portable blood glucose meter readings in different sampling accesses blood and laboratory analysis. METHODS: Quantitative validity study. Daily samples were collected from capillary blood, central venous access catheter and arterial catheter and the blood glucose values checked using portable blood glucose meter and laboratory analysis. The findings were analyzed with the Statistical Package for the Social Sciences - SPSS software. RESULTS: Central venous catheter samples blood glucose meter readings were found to have the best correlation with the laboratory analysis results, considered as the gold-standard. CONCLUSION: Hemodynamically unstable patients' capillary blood samples may provide false blood glucose results, and lead to inappropriate insulin solution management. Therefore, ideal blood glucose sampling is relevant to prevent insulin solution management errors.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2010;22(1):5-10
DOI 10.1590/S0103-507X2010000100003
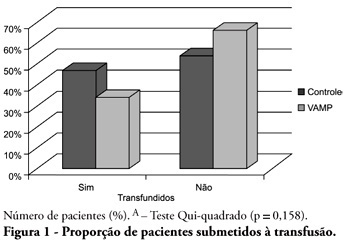
OBJECTIVE: Anemia is common in severely ill patients, and blood sampling plays a relevant causative role. Consequently, blood transfusions are frequent an related to several complications. Trying to reduce the transfusion-related risk, minimizing blood loss is mandatory. Thus, this work aimed to evaluate a closed blood sampling system as a strategy to spare unnecessary blood losses and transfusions. METHODS: This was a prospective, randomized, controlled, multicenter, 6 months, clinical trial. The patients were assigned to either VAMP (Venous Arterial Blood Management Protection) group, using a closed blood sampling system, or control group. The groups' transfusion rate, as well as hemoglobin (Hb) and Hematocrit (Ht) changes were compared for 14 days. RESULTS: Were included 127 patients, 65 assigned to the control group, and 62 to VAMP. During the intensive care unit stay, both groups experienced both hemoglobin and hematocrit drops. However, when the final Ht and Hb were compared between the groups, a difference was identified with higher values in the VAMP group (p=0.03; p=0.006, respectively). No statistical difference was found for both groups transfusion rates, although the VAMP group had an absolute 12% blood transfusion reduction. CONCLUSION: The use of a closed blood sampling system was able to minimize blood count values changes, however failed to reduce transfusions rate.
Search
Search in:
Case reports (56) Child (53) Coronavirus infections (34) COVID-19 (46) Critical care (116) Critical illness (54) Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (26) Infant, newborn (27) Intensive care (72) Intensive care units (256) Intensive care units, pediatric (31) mechanical ventilation (38) Mortality (76) Physical therapy modalities (28) Prognosis (61) Respiration, artificial (119) Respiratory insufficiency (26) risk factors (34) SARS-CoV-2 (28) Sepsis (98)