Abstract
Crit Care Sci. 2023;35(4):345-354
DOI 10.5935/2965-2774.20230162-pt
The optimal target for blood glucose concentration in critically ill patients is unclear. We will perform a systematic review and meta-analysis with aggregated and individual patient data from randomized controlled trials, comparing intensive glucose control with liberal glucose control in critically ill adults.
MEDLINE®, Embase, the Cochrane Central Register of Clinical Trials, and clinical trials registries (World Health Organization, clinical trials.gov). The authors of eligible trials will be invited to provide individual patient data. Published trial-level data from eligible trials that are not at high risk of bias will be included in an aggregated data meta-analysis if individual patient data are not available.
Inclusion criteria: randomized controlled trials that recruited adult patients, targeting a blood glucose of ≤ 120mg/dL (≤ 6.6mmol/L) compared to a higher blood glucose concentration target using intravenous insulin in both groups. Excluded studies: those with an upper limit blood glucose target in the intervention group of > 120mg/dL (> 6.6mmol/L), or where intensive glucose control was only performed in the intraoperative period, and those where loss to follow-up exceeded 10% by hospital discharge.
In-hospital mortality during index hospital admission. Secondary endpoints: mortality and survival at other timepoints, duration of invasive mechanical ventilation, vasoactive agents, and renal replacement therapy. A random effect Bayesian meta-analysis and hierarchical Bayesian models for individual patient data will be used.
This systematic review with aggregate and individual patient data will address the clinical question, ‘what is the best blood glucose target for critically ill patients overall?’
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2017;29(3):364-372
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20170054
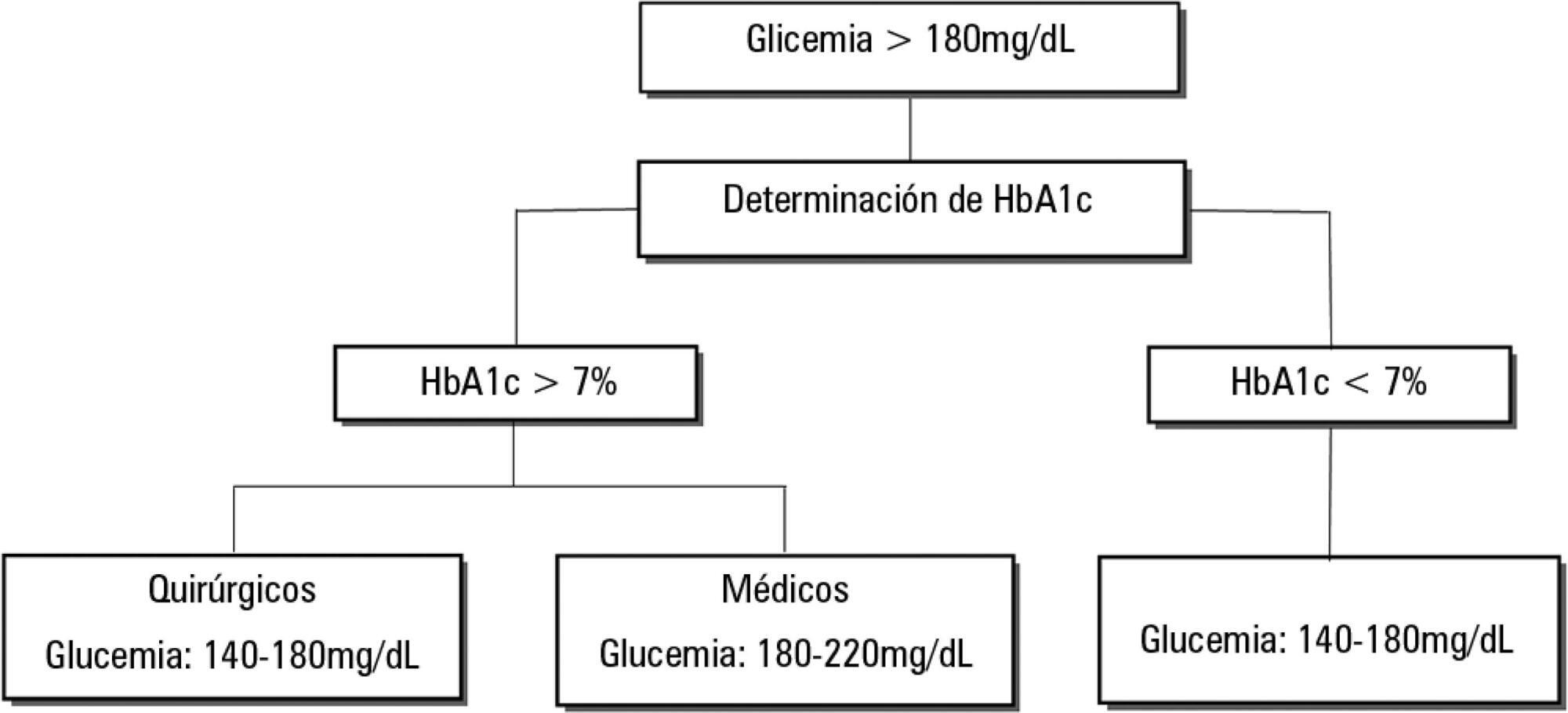
Dysglycemia in critically ill patients (hyperglycemia, hypoglycemia, glycemic variability and time in range) is a biomarker of disease severity and is associated with higher mortality. However, this impact appears to be weakened in patients with previous diabetes mellitus, particularly in those with poor premorbid glycemic control; this phenomenon has been called "diabetes paradox". This phenomenon determines that glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c) values should be considered in choosing glycemic control protocols on admission to an intensive care unit and that patients' target blood glucose ranges should be adjusted according to their HbA1c values. Therefore, HbA1c emerges as a simple tool that allows information that has therapeutic utility and prognostic value to be obtained in the intensive care unit.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2010;22(4):351-357
DOI 10.1590/S0103-507X2010000400007
OBJECTIVE: To identify the relevant differences between portable blood glucose meter readings in different sampling accesses blood and laboratory analysis. METHODS: Quantitative validity study. Daily samples were collected from capillary blood, central venous access catheter and arterial catheter and the blood glucose values checked using portable blood glucose meter and laboratory analysis. The findings were analyzed with the Statistical Package for the Social Sciences - SPSS software. RESULTS: Central venous catheter samples blood glucose meter readings were found to have the best correlation with the laboratory analysis results, considered as the gold-standard. CONCLUSION: Hemodynamically unstable patients' capillary blood samples may provide false blood glucose results, and lead to inappropriate insulin solution management. Therefore, ideal blood glucose sampling is relevant to prevent insulin solution management errors.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2009;21(4):398-403
DOI 10.1590/S0103-507X2009000400010
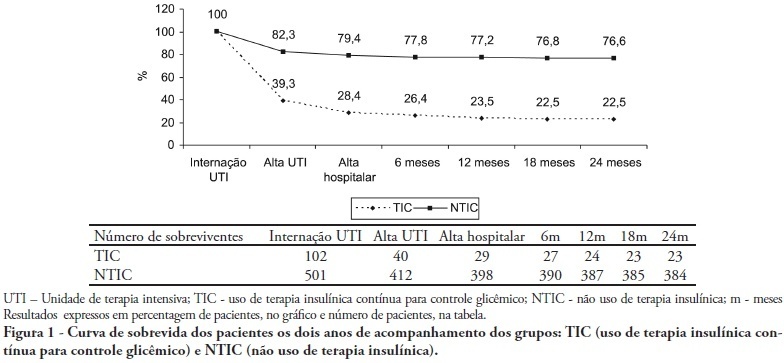
OBJECTIVES: Stress-induced hyperglycemia is frequent in critically ill patients and has been associated with increased mortality and morbidity (both in diabetic and non-diabetic patients). This study objective was to evaluate the profile and long-term prognosis of critically ill patients undergoing tight glucose-control. METHODS: Prospective cohort. All patients admitted to the intensive care unit over 1-year were enrolled. We analyzed demographic data, therapeutic intervention, and short- (during the stay) and long-term (2 years after discharge) mortality. The patients were categorized in 2 groups: tight glucose control and non-tight glucose-control, based on the unit staff decision. RESULTS: From the 603 enrolled patients, 102 (16.9%) underwent tight control (glucose <150 mg/dL) while 501 patients (83.1%) non-tight control. Patients in the TGC-group were more severely ill than those in the non-tight control group [APACHE II score (14 ± 3 versus 11 ± 4, P=0.04), SOFA (4.9 ± 3.2 versus 3.5 ± 3.4, P<0.001) and TISS-24h (25.7 ± 6.9 versus 21.1 ± 7.2, P< 0.001)]. The tight control group patients also had worse prognosis: [acute renal failure (51% versus 18.5%, P<0.001), critical illness neuropathy (16.7% versus 5.6%, P<0.001)] and increased mortality (during the ICU-stay [60.7% versus 17.7%, P<0.001] and within 2-years of the discharge [77.5% versus 23.4%; P<0.001]). CONCLUSION: Critically ill patients needing tight glucose control during the unit stay have more severe disease and have worse short and long-term prognosis.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2009;21(3):310-314
DOI 10.1590/S0103-507X2009000300012
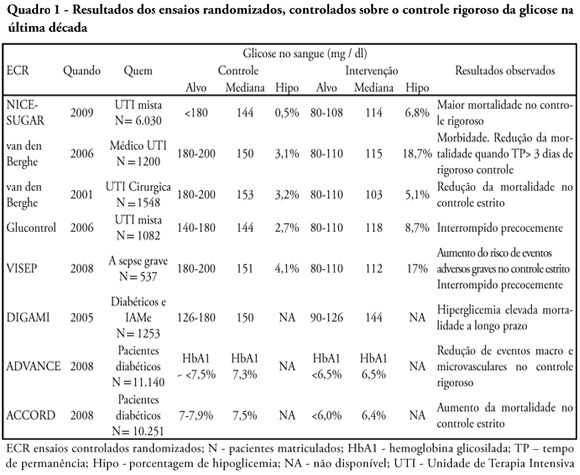
Glucose control is a major issue in critical care since landmark publications from the last decade leading to widespread use of strict glucose control in the clinical practice. Subsequent trials showed discordant results that lead to several questions and concerns about benefits and risks of implementing an intensive glucose control protocol. In the midst of all recent controversy, we propose that a new glycemic target -150mg/dl) should be aimed. This target glucose level could offer protection against the deleterious effects of hyperglycemia and at the same time keep patient's safety avoiding hypoglicemia. The article presents a critical review of the current literature on intensive insulin therapy in critically ill patients.
Search
Search in:
Case reports (56) Child (53) Coronavirus infections (34) COVID-19 (46) Critical care (116) Critical illness (54) Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (26) Infant, newborn (27) Intensive care (72) Intensive care units (256) Intensive care units, pediatric (31) mechanical ventilation (38) Mortality (76) Physical therapy modalities (28) Prognosis (61) Respiration, artificial (119) Respiratory insufficiency (26) risk factors (34) SARS-CoV-2 (28) Sepsis (98)