Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2009;21(4):398-403
DOI 10.1590/S0103-507X2009000400010
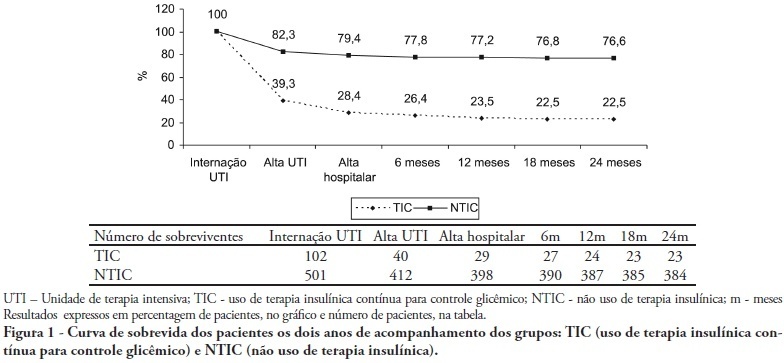
OBJECTIVES: Stress-induced hyperglycemia is frequent in critically ill patients and has been associated with increased mortality and morbidity (both in diabetic and non-diabetic patients). This study objective was to evaluate the profile and long-term prognosis of critically ill patients undergoing tight glucose-control. METHODS: Prospective cohort. All patients admitted to the intensive care unit over 1-year were enrolled. We analyzed demographic data, therapeutic intervention, and short- (during the stay) and long-term (2 years after discharge) mortality. The patients were categorized in 2 groups: tight glucose control and non-tight glucose-control, based on the unit staff decision. RESULTS: From the 603 enrolled patients, 102 (16.9%) underwent tight control (glucose <150 mg/dL) while 501 patients (83.1%) non-tight control. Patients in the TGC-group were more severely ill than those in the non-tight control group [APACHE II score (14 ± 3 versus 11 ± 4, P=0.04), SOFA (4.9 ± 3.2 versus 3.5 ± 3.4, P<0.001) and TISS-24h (25.7 ± 6.9 versus 21.1 ± 7.2, P< 0.001)]. The tight control group patients also had worse prognosis: [acute renal failure (51% versus 18.5%, P<0.001), critical illness neuropathy (16.7% versus 5.6%, P<0.001)] and increased mortality (during the ICU-stay [60.7% versus 17.7%, P<0.001] and within 2-years of the discharge [77.5% versus 23.4%; P<0.001]). CONCLUSION: Critically ill patients needing tight glucose control during the unit stay have more severe disease and have worse short and long-term prognosis.
Search
Search in:
Case reports (56) Child (53) Coronavirus infections (34) COVID-19 (46) Critical care (116) Critical illness (54) Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (26) Infant, newborn (27) Intensive care (72) Intensive care units (256) Intensive care units, pediatric (31) mechanical ventilation (38) Mortality (76) Physical therapy modalities (28) Prognosis (61) Respiration, artificial (119) Respiratory insufficiency (26) risk factors (34) SARS-CoV-2 (28) Sepsis (98)