Abstract
Crit Care Sci. 2024;36:e20240196en
DOI 10.62675/2965-2774.20240196-en
To provide insights into the potential benefits of goal-directed therapy guided by FloTrac in reducing postoperative complications and improving outcomes.
We performed a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials to evaluate goal-directed therapy guided by FloTrac in major surgery, comparing goal-directed therapy with usual care or invasive monitoring in cardiac and noncardiac surgery subgroups. The quality of the articles and evidence were evaluated with a risk of bias tool and GRADE.
We included 29 randomized controlled trials with 3,468 patients. Goal-directed therapy significantly reduced the duration of hospital stay (mean difference -1.43 days; 95%CI 2.07 to -0.79; I2 81%), intensive care unit stay (mean difference -0.77 days; 95%CI -1.18 to -0.36; I2 93%), and mechanical ventilation (mean difference -2.48 hours, 95%CI -4.10 to -0.86, I2 63%). There was no statistically significant difference in mortality, myocardial infarction, acute kidney injury or hypotension, but goal-directed therapy significantly reduced the risk of heart failure or pulmonary edema (RR 0.46; 95%CI 0.23 - 0.92; I2 0%).
Goal-directed therapy guided by the FloTrac sensor improved clinical outcomes and shortened the length of stay in the hospital and intensive care unit in patients undergoing major surgery. Further research can validate these results using specific protocols and better understand the potential benefits of FloTrac beyond these outcomes.
Abstract
Crit Care Sci. 2024;36:e20240208en
DOI 10.62675/2965-2774.20240208-en
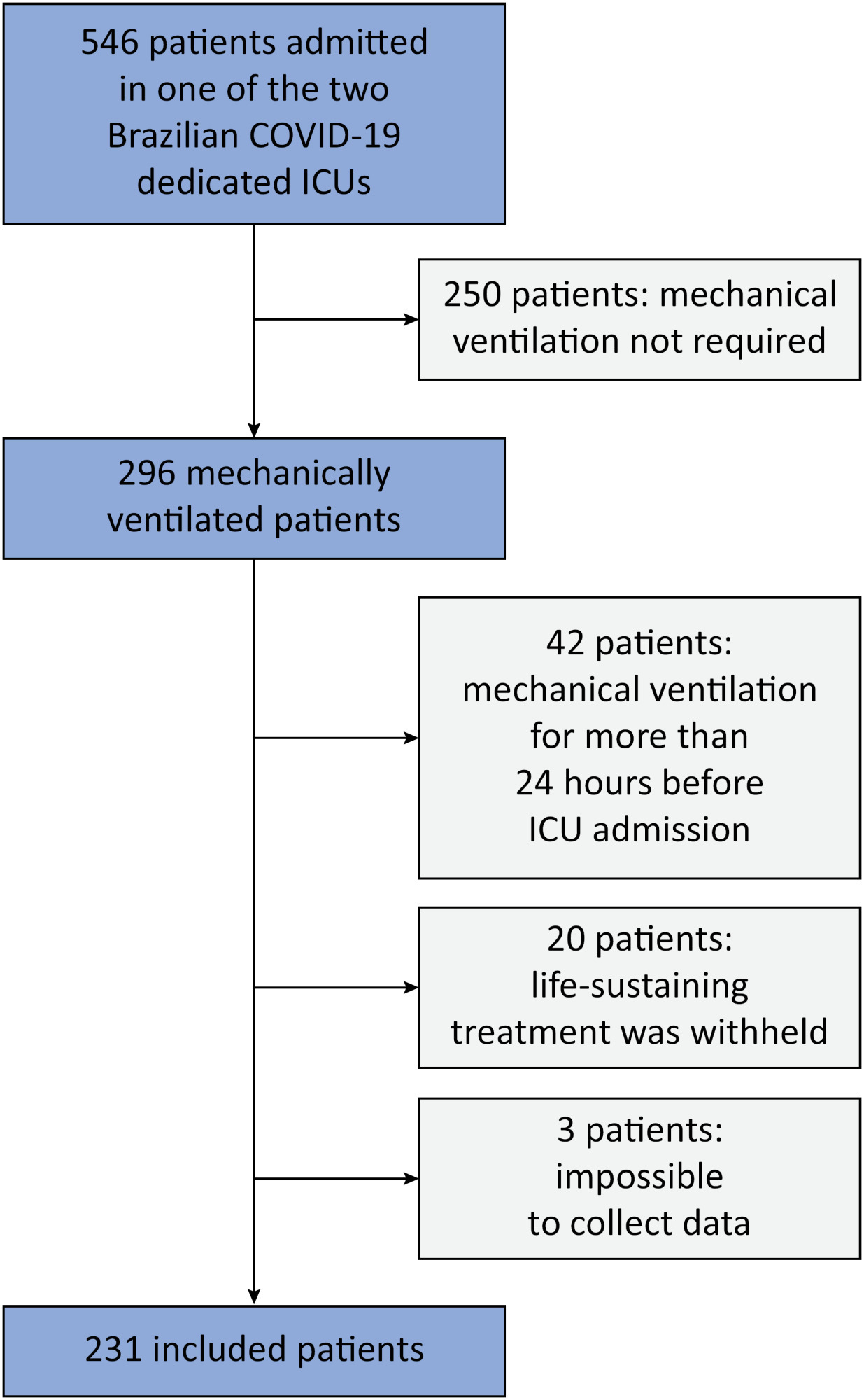
To evaluate the association between driving pressure and tidal volume based on predicted body weight and mortality in a cohort of patients with acute respiratory distress syndrome caused by COVID-19.
This was a prospective, observational study that included patients with acute respiratory distress syndrome due to COVID-19 admitted to two intensive care units. We performed multivariable analyses to determine whether driving pressure and tidal volume/kg predicted body weight on the first day of mechanical ventilation, as independent variables, are associated with hospital mortality.
We included 231 patients. The mean age was 64 (53 - 74) years, and the mean Simplified Acute and Physiology Score 3 score was 45 (39 - 54). The hospital mortality rate was 51.9%. Driving pressure was independently associated with hospital mortality (odds ratio 1.21, 95%CI 1.04 - 1.41 for each cm H2O increase in driving pressure, p = 0.01). Based on a double stratification analysis, we found that for the same level of tidal volume/kg predicted body weight, the risk of hospital death increased with increasing driving pressure. However, changes in tidal volume/kg predicted body weight were not associated with mortality when they did not lead to an increase in driving pressure.
In patients with acute respiratory distress syndrome caused by COVID-19, exposure to higher driving pressure, as opposed to higher tidal volume/kg predicted body weight, is associated with greater mortality. These results suggest that driving pressure might be a primary target for lung-protective mechanical ventilation in these patients.
Abstract
Crit Care Sci. 2024;36:e20240144en
DOI 10.62675/2965-2774.20240144-pt
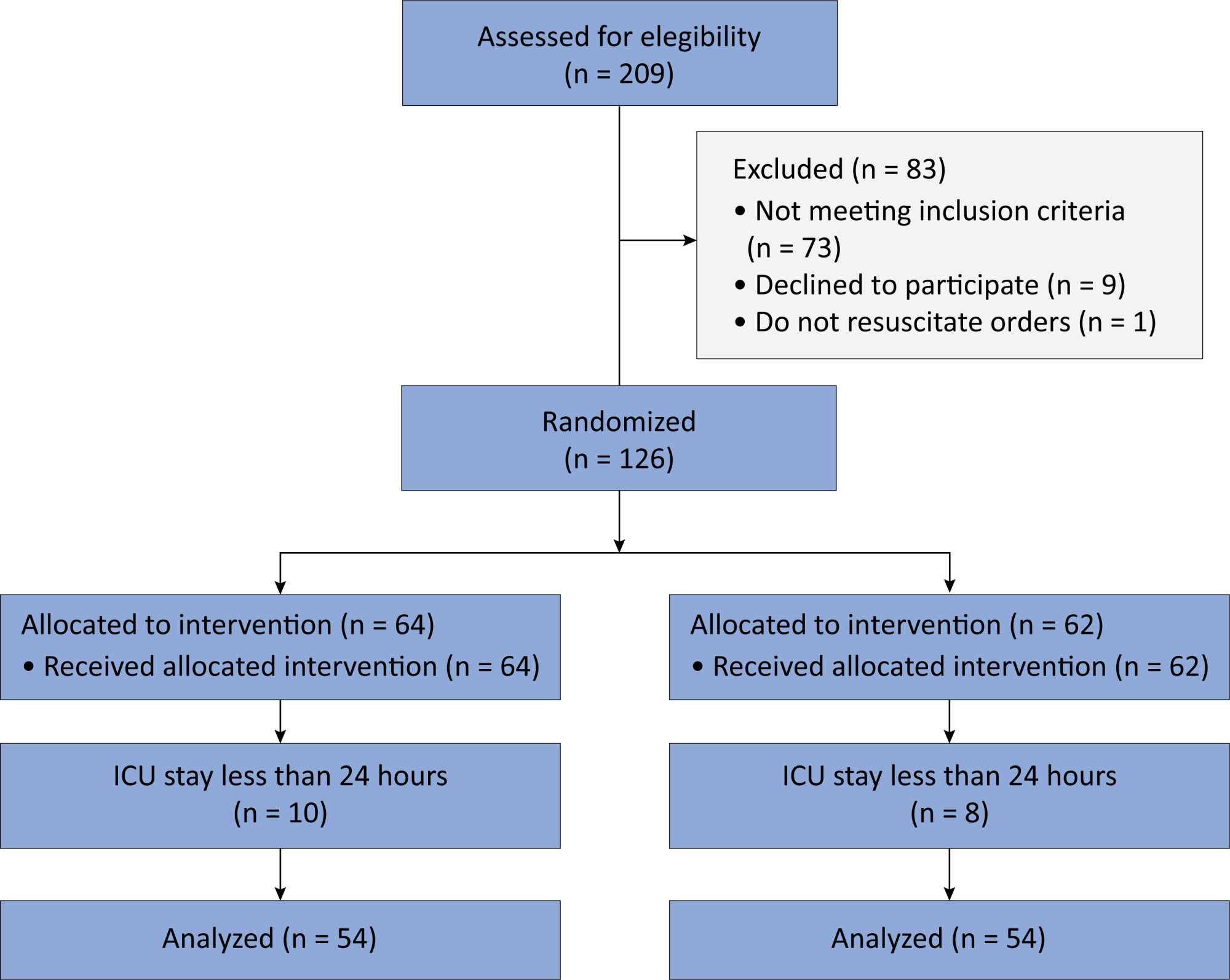
To determine whether enteral melatonin decreases the incidence of delirium in critically ill adults.
In this randomized controlled trial, adults were admitted to the intensive care unit and received either usual standard care alone (Control Group) or in combination with 3mg of enteral melatonin once a day at 9 PM (Melatonin Group). Concealment of allocation was done by serially numbered opaque sealed envelopes. The intensivist assessing delirium and the investigator performing the data analysis were blinded to the group allocation. The primary outcome was the incidence of delirium within 24 hours of the intensive care unit stay. The secondary outcomes were the incidence of delirium on Days 3 and 7, intensive care unit mortality, length of intensive care unit stay, duration of mechanical ventilation and Glasgow outcome score (at discharge).
We included 108 patients in the final analysis, with 54 patients in each group. At 24 hours of intensive care unit stay, there was no difference in the incidence of delirium between Melatonin and Control Groups (29.6 versus 46.2%; RR = 0.6; 95%CI 0.38 - 1.05; p = 0.11). No secondary outcome showed a statistically significant difference.
Enteral melatonin 3mg is not more effective at decreasing the incidence of delirium than standard care is in critically ill adults.
Abstract
Crit Care Sci. 2024;36:e20240158en
DOI 10.62675/2965-2774.20240158-en
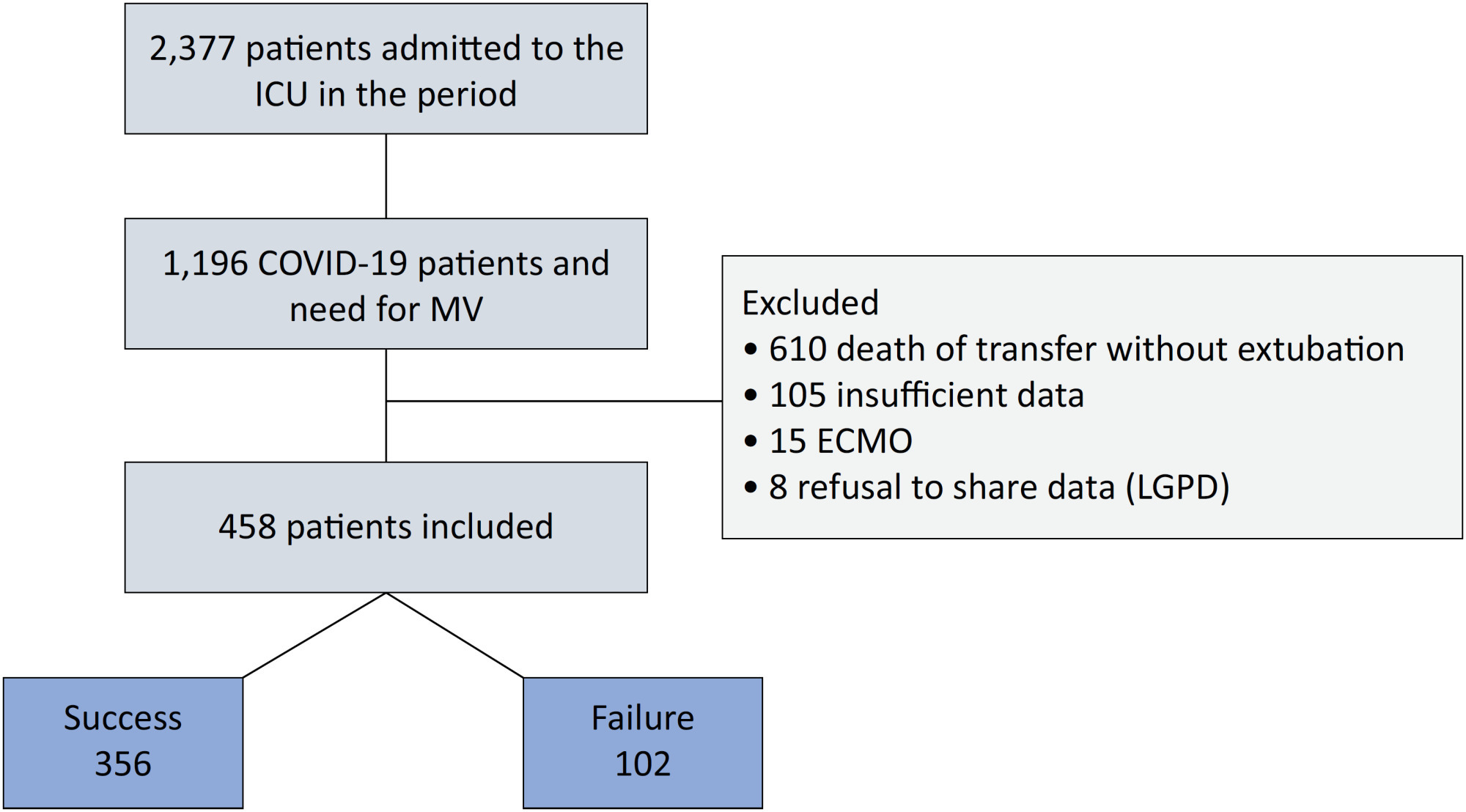
To evaluate the association of biomarkers with successful ventilatory weaning in COVID-19 patients.
An observational, retrospective, and single-center study was conducted between March 2020 and April 2021. C-reactive protein, total lymphocytes, and the neutrophil/lymphocyte ratio were evaluated during attrition and extubation, and the variation in these biomarker values was measured. The primary outcome was successful extubation. ROC curves were drawn to find the best cutoff points for the biomarkers based on sensitivity and specificity. Statistical analysis was performed using logistic regression.
Of the 2,377 patients admitted to the intensive care unit, 458 were included in the analysis, 356 in the Successful Weaning Group and 102 in the Failure Group. The cutoff points found from the ROC curves were −62.4% for C-reactive protein, +45.7% for total lymphocytes, and −32.9% for neutrophil/lymphocyte ratio. These points were significantly associated with greater extubation success. In the multivariate analysis, only C-reactive protein variation remained statistically significant (OR 2.6; 95%CI 1.51 – 4.5; p < 0.001).
In this study, a decrease in C-reactive protein levels was associated with successful extubation in COVID-19 patients. Total lymphocytes and the neutrophil/lymphocyte ratio did not maintain the association after multivariate analysis. However, a decrease in C-reactive protein levels should not be used as a sole variable to identify COVID-19 patients suitable for weaning; as in our study, the area under the ROC curve demonstrated poor accuracy in discriminating extubation outcomes, with low sensitivity and specificity.
Abstract
Crit Care Sci. 2023;35(4):355-366
DOI 10.5935/2965-2774.20230015-pt
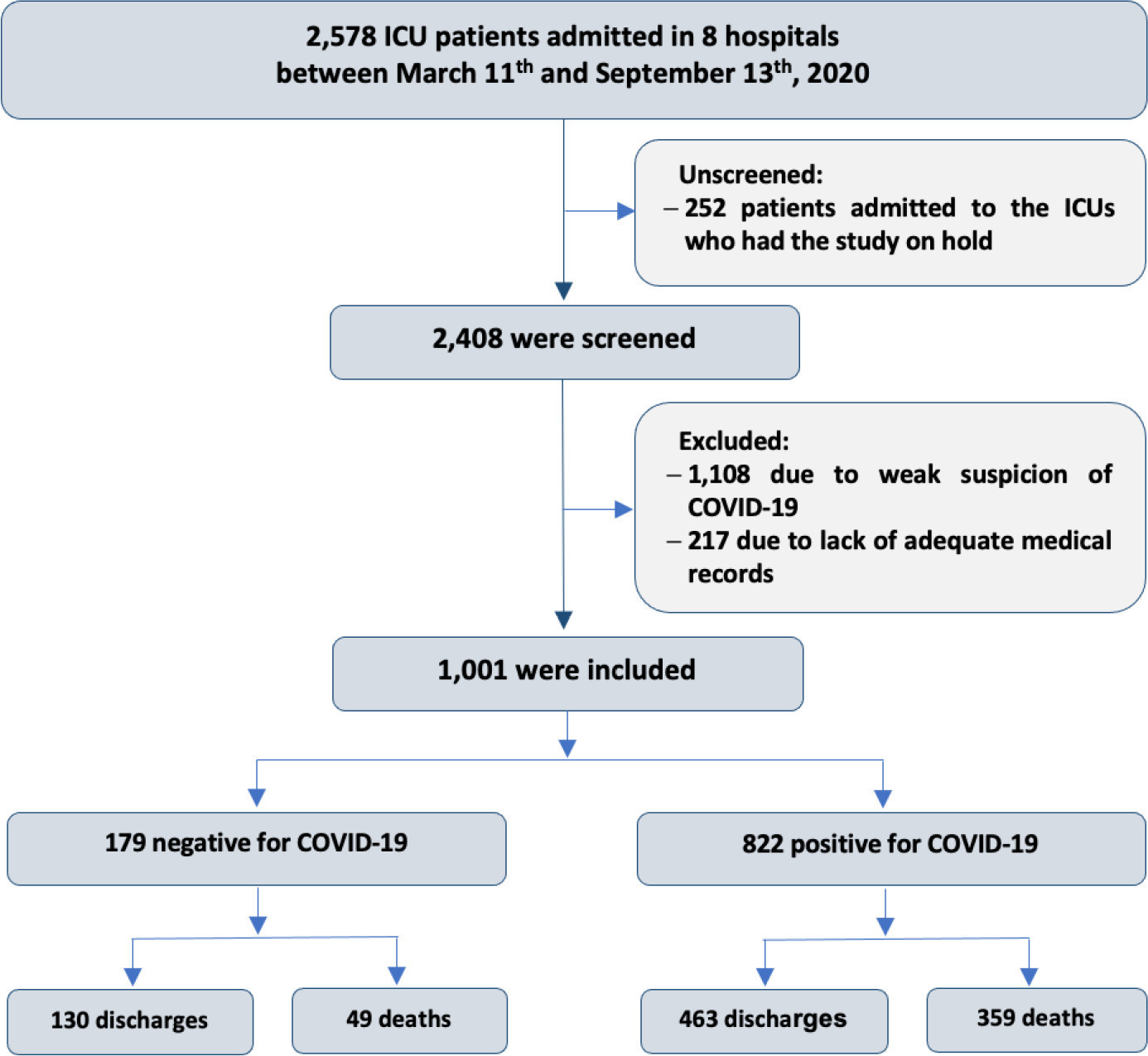
To compare, within a cohort of patients with acute respiratory failure, the phenotypes of patients with and without COVID-19 in the context of the pandemic and evaluate whether COVID-19 is an independent predictor of intensive care unit mortality.
This historical cohort study evaluated 1001 acute respiratory failure patients with suspected COVID-19 admitted to the intensive care unit of 8 hospitals. Patients were classified as COVID-19 cases and non-COVID-19 cases according to real-time polymerase chain reaction results. Data on clinical and demographic characteristics were collected on intensive care unit admission, as well as daily clinical and laboratory data and intensive care unit outcomes.
Although the groups did not differ in terms of APACHE II or SOFA scores at admission, the COVID-19 group had more initial symptoms of fever, myalgia and diarrhea, had a longer duration of symptoms, and had a higher prevalence of obesity. They also had a lower PaO2/FiO2 ratio, lower platelet levels than non-COVID-19 patients, and more metabolic changes, such as higher levels of blood glucose, C-reactive protein, and lactic dehydrogenase. Patients with non-COVID-19 acute respiratory failure had a higher prevalence of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease/asthma and cardiopathy. Patients with COVID-19 stayed in the hospital longer and had more complications, such as acute kidney failure, severe acute respiratory distress syndrome and severe infection. The all-cause mortality rate was also higher in this group (43.7% in the COVID-19 group versus 27.4% in the non-COVID-19 group). The diagnosis of COVID-19 was a predictor of intensive care unit mortality (odds ratio, 2.77; 95%CI, 1.89 - 4.07; p < 0.001), regardless of age or Charlson Comorbidity Index score.
In a prospective cohort of patients admitted with acute respiratory failure, patients with COVID-19 had a clearly different phenotype and a higher mortality than non-COVID-19 patients. This may help to outline more accurate screening and appropriate and timely treatment for these patients.
Abstract
Crit Care Sci. 2023;35(4):367-376
DOI 10.5935/2965-2774.20230069-pt
To assess the impact of different vertical positions on lung aeration in patients receiving invasive mechanical ventilation.
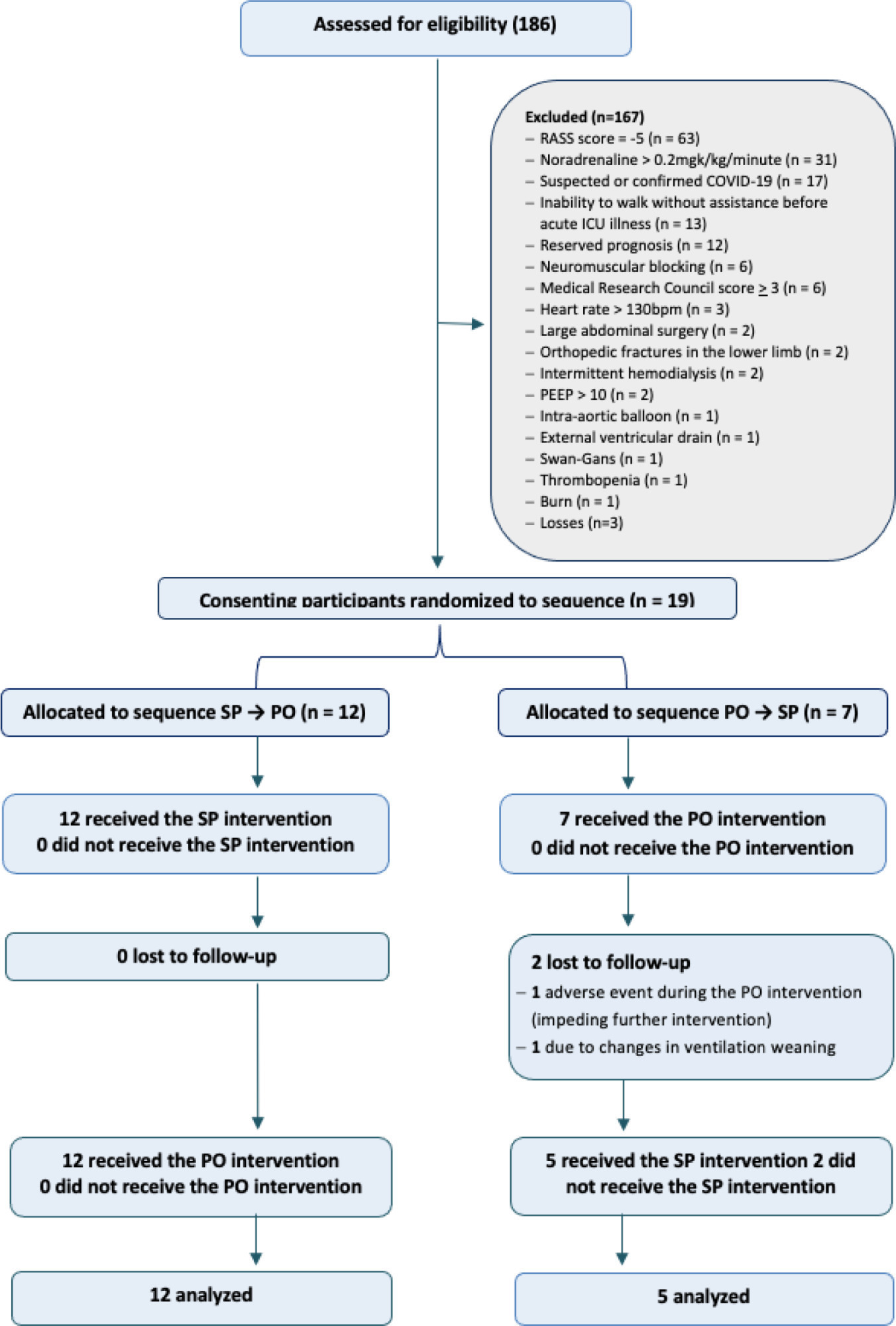
An open-label randomized crossover clinical trial was conducted between January and July 2020. Adults receiving invasive mechanical ventilation for > 24 hours and < 7 days with hemodynamic, respiratory and neurological stability were randomly assigned at a 1:1 ratio to the sitting position followed by passive orthostasis condition or the passive orthostasis followed by the sitting position condition. The primary outcome was lung aeration assessed using the lung ultrasound score (score ranges from 0 [better] to 36 [worse]).
A total of 186 subjects were screened; of these subjects, 19 were enrolled (57.8% male; mean age, 73.2 years). All participants were assigned to receive at least one verticalization protocol. Passive orthostasis resulted in mean lung ultrasound scores that did not differ significantly from the sitting position (11.0 versus 13.7; mean difference, -2.7; [95%CI -6.1 to 0.71; p = 0.11). Adverse events occurred in three subjects in the passive orthostasis group and in one in the sitting position group (p = 0.99).
This analysis did not find significant differences in lung aeration between the sitting and passive orthostasis groups. A randomized crossover clinical trial assessing the impact of vertical positioning on lung aeration in patients receiving invasive mechanical ventilation is feasible. Unfortunately, the study was interrupted due to the need to treat COVID-19 patients.
Abstract
Crit Care Sci. 2023;35(3):320-327
DOI 10.5935/2965-2774.20230165-pt
To translate and cross-culturally adapt the Cornell Assessment of Pediatric Delirium anchor points from English to Brazilian Portuguese.
For the translation and cross-cultural adaptation of the anchor points, all steps recommended internationally were followed after authorization for use by the lead author. The stages were as follows: translation of the original version into Portuguese by two bilingual translators who were native speakers of the target language, synthesis of the versions, reverse translation by two translators who were native speakers of the source language, review and synthesis of the back-translation, review by a committee of experts and preparation of the final version.
The translation and cross-cultural adaptation of the anchor points was conducted in accordance with recommendations. The linguistic and semantic issues that arose were discussed by a committee of judges, with 91.8% agreement, as determined using a Likert scale, after changes by consensus. After reanalysis by the authors, there were no changes, resulting in the final version, which was easy to understand and administer.
The translation and cross-cultural adaptation of the anchor points of the Cornell Assessment of Pediatric Delirium scale into Portuguese spoken in Brazil were successful, maintaining the linguistic and semantic properties of the original instrument. The table of anchor points is easy to understand and will be helpful during the assessment of children younger than 24 months using the Cornell Assessment of Pediatric Delirium scale.
Search
Search in:
Case reports (56) Child (53) Coronavirus infections (34) COVID-19 (46) Critical care (116) Critical illness (54) Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (26) Infant, newborn (27) Intensive care (72) Intensive care units (256) Intensive care units, pediatric (31) mechanical ventilation (38) Mortality (76) Physical therapy modalities (28) Prognosis (61) Respiration, artificial (119) Respiratory insufficiency (26) risk factors (34) SARS-CoV-2 (28) Sepsis (98)