Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2016;28(2):107-113
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20160024
To evaluate job and personal satisfaction rates in physicians who work in adult intensive care units and to identify the factors associated with satisfaction.
A cross-sectional study performed with physicians who participated in two intensive medicine online discussion groups. A questionnaire designed to assess the physician's sociodemographic profile and job was available for both groups for 3 months. At the end of the questionnaire, the participants addressed their degrees of job and personal satisfaction using a Likert scale in which 1 represented "very dissatisfied" and 5 represented "very satisfied". The association between sociodemographic and job characteristics with job and personal satisfaction was evaluated. Variables independently associated with satisfaction were identified using a logistic regression model.
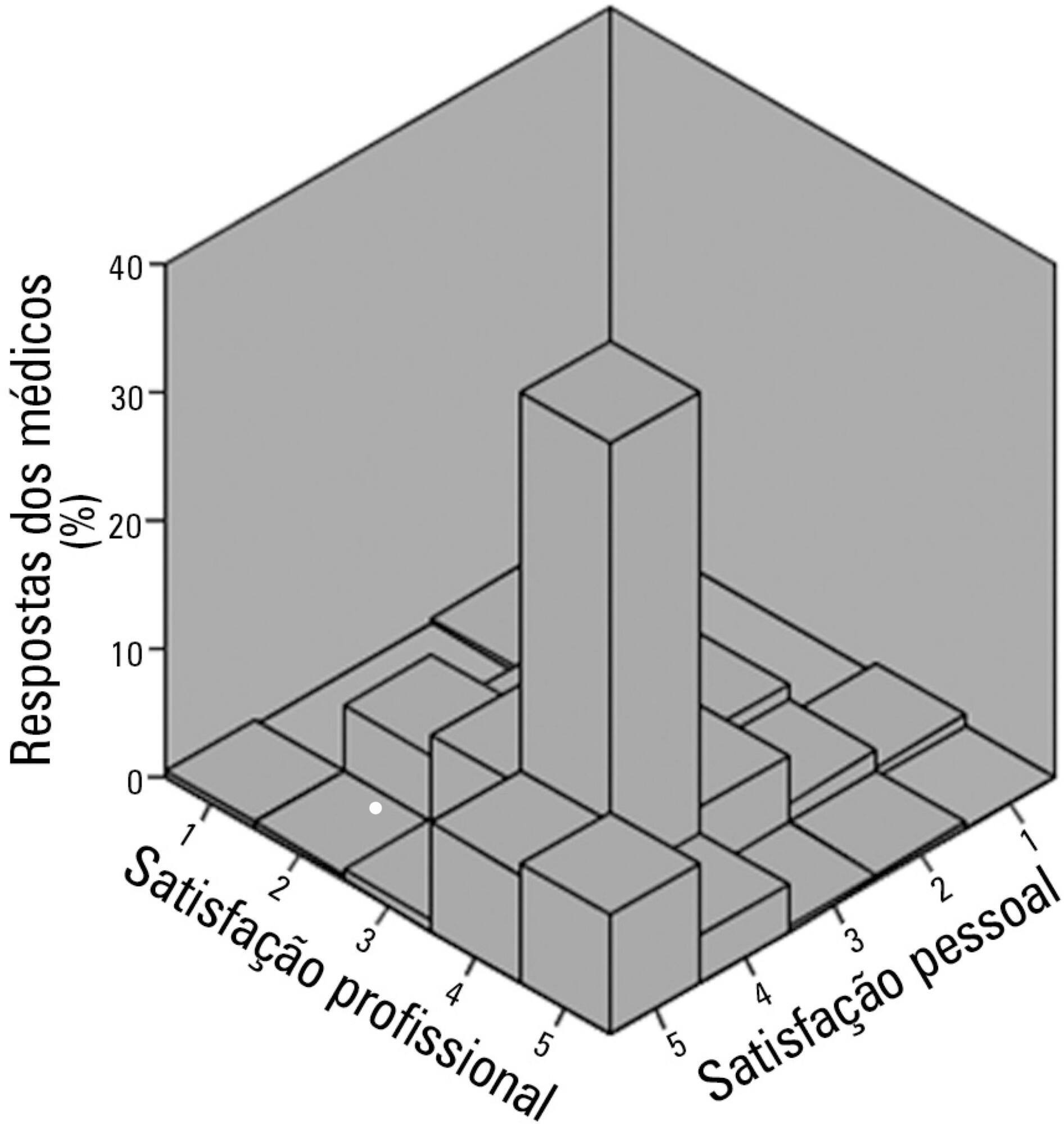
The questionnaire was answered by 250 physicians, of which 137 (54.8%) declared they were satisfied with their jobs and 34 (13.5%) were very satisfied. None of the evaluated characteristics were independently associated with job satisfaction. Regarding personal satisfaction, 136 (54.4%) physicians reported being satisfied, and 48 (19.9%) reported being very satisfied. Job satisfaction (OR = 7.21; 95%CI 3.21 - 16.20) and working in a university hospital (OR = 3.24; 95%CI 1.29 - 8.15) were factors independently associated with the personal satisfaction of the participants.
The participant physicians reported job and personal satisfaction with their work in intensive care. Job satisfaction and working in a university hospital were independently associated with greater personal satisfaction.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2015;27(1):57-63
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20150010
This study aimed to evaluate Brazilian physicians’ perceptions regarding the diagnosis, severity assessment, treatment and risk stratification of severe community-acquired pneumonia patients and to compare those perceptions to current guidelines.
We conducted a cross-sectional international anonymous survey among a convenience sample of critical care, pulmonary, emergency and internal medicine physicians from Brazil between October and December 2008. The electronic survey evaluated physicians’ attitudes towards the diagnosis, risk assessment and therapeutic interventions for patients with severe community-acquired pneumonia.
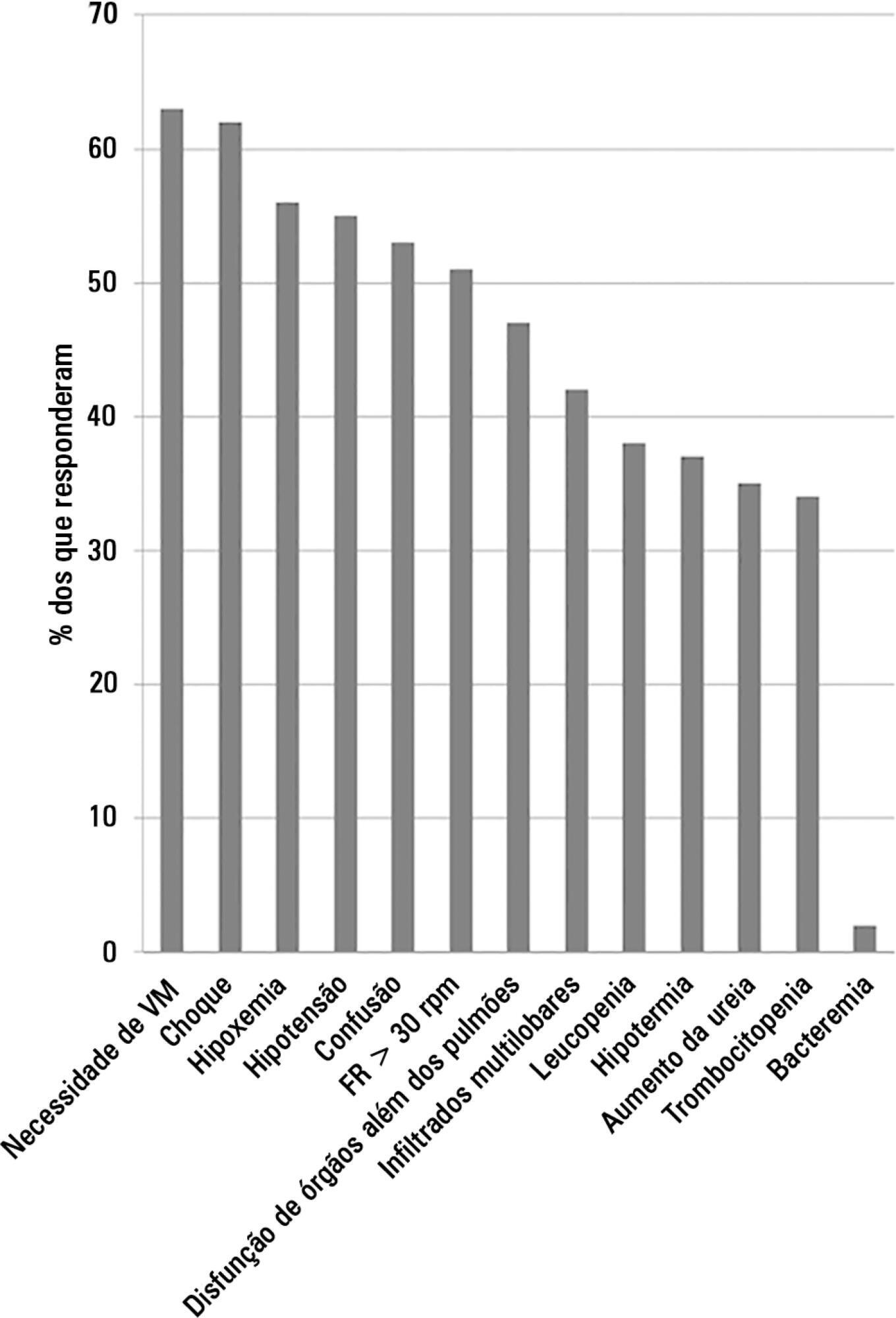
A total of 253 physicians responded to the survey, with 66% from Southeast Brazil. The majority (60%) of the responding physicians had > 10 years of medical experience. The risk assessment of severe community-acquired pneumonia was very heterogeneous, with clinical evaluation as the most frequent approach. Although blood cultures were recognized as exhibiting a poor diagnostic performance, these cultures were performed by 75% of respondents. In contrast, the presence of urinary pneumococcal and Legionella antigens was evaluated by less than 1/3 of physicians. The vast majority of physicians (95%) prescribe antibiotics according to a guideline, with the combination of a 3rd/4th generation cephalosporin plus a macrolide as the most frequent choice.
This Brazilian survey identified an important gap between guidelines and clinical practice and recommends the institution of educational programs that implement evidence-based strategies for the management of severe community-acquired pneumonia.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2015;27(4):360-368
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20150061
To conduct a multinational survey of intensive care unit professionals to determine the practices on delirium assessment and management, in addition to their perceptions and attitudes toward the evaluation and impact of delirium in patients requiring noninvasive ventilation.
An electronic questionnaire was created to evaluate the profiles of the respondents and their related intensive care units, the systematic delirium assessment and management and the respondents' perceptions and attitudes regarding delirium in patients requiring noninvasive ventilation. The questionnaire was distributed to the cooperative network for research of the Associação de Medicina Intensiva Brasileira (AMIB-Net) mailing list and to researchers in different centers in Latin America and Europe.
Four hundred thirty-six questionnaires were available for analysis; the majority of the questionnaires were from Brazil (61.9%), followed by Turkey (8.7%) and Italy (4.8%). Approximately 61% of the respondents reported no delirium assessment in the intensive care unit, and 31% evaluated delirium in patients under noninvasive ventilation. The Confusion Assessment Method for the intensive care unit was the most reported validated diagnostic tool (66.9%). Concerning the indication of noninvasive ventilation in patients already presenting with delirium, 16.3% of respondents never allow the use of noninvasive ventilation in this clinical context.
This survey provides data that strongly reemphasizes poor efforts toward delirium assessment and management in the intensive care unit setting, especially regarding patients requiring noninvasive ventilation.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2014;26(4):339-346
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20140052
This study aimed to determine which visitation policy was the most predominant in Brazilian intensive care units and what amenities were provided to visitors.
Eight hundred invitations were sent to the e-mail addresses of intensivist physicians and nurses who were listed in the research groups of the Brazilian Association of Intensive Care Network and the Brazilian Research in Intensive Care Network. The e-mail contained a link to a 33-item questionnaire about the profile of their intensive care unit.
One hundred sixty-two questionnaires from intensive care units located in all regions of the country, but predominantly in the Southeast and South (58% and 16%), were included in the study. Only 2.6% of the intensive care units reported having liberal visitation policies, while 45.1% of the intensive care units allowed 2 visitation periods and 69.1% allowed 31-60 minutes of visitation per period. In special situations, such as end-of-life cases, 98.7% of them allowed flexible visitation. About half of them (50.8%) did not offer any bedside amenities for visitors. Only 46.9% of the intensive care units had a family meeting room, and 37% did not have a waiting room.
Restrictive visitation policies are predominant in Brazilian intensive care units, with most of them allowing just two periods of visitation per day. There is also a lack of amenities for visitors.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2014;26(4):360-366
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20140055
In Brazil, there are no data on the preferences of intensivists regarding hemodynamic monitoring methods. The present study aimed to identify the methods used by national intensivists, the hemodynamic variables they consider important, the regional differences, the reasons for choosing a particular method, and the use of protocols and continued training.
National intensivists were invited to answer an electronic questionnaire during three intensive care events and later, through the Associação de Medicina Intensiva Brasileira portal, between March and October 2009. Demographic data and aspects related to the respondent preferences regarding hemodynamic monitoring were researched.
In total, 211 professionals answered the questionnaire. Private hospitals showed higher availability of resources for hemodynamic monitoring than did public institutions. The pulmonary artery catheter was considered the most trusted by 56.9% of the respondents, followed by echocardiograms, at 22.3%. Cardiac output was considered the most important variable. Other variables also considered relevant were mixed/central venous oxygen saturation, pulmonary artery occlusion pressure, and right ventricular end-diastolic volume. Echocardiography was the most used method (64.5%), followed by pulmonary artery catheter (49.3%). Only half of respondents used treatment protocols, and 25% worked in continuing education programs in hemodynamic monitoring.
Hemodynamic monitoring has a greater availability in intensive care units of private institutions in Brazil. Echocardiography was the most used monitoring method, but the pulmonary artery catheter remains the most reliable. The implementation of treatment protocols and continuing education programs in hemodynamic monitoring in Brazil is still insufficient.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2014;26(3):299-304
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20140042
To assess the opinions and practices of intensive care professionals with regard to diarrhea in critically ill patients.
A multicenter cross-sectional study was conducted among health care professionals working at three adult intensive care units. Participants responded individually to a self-administered questionnaire about their length of work experience in intensive care; the definition, characterization, and causes of diarrhea; types of records in the patient's medical record; and training received.
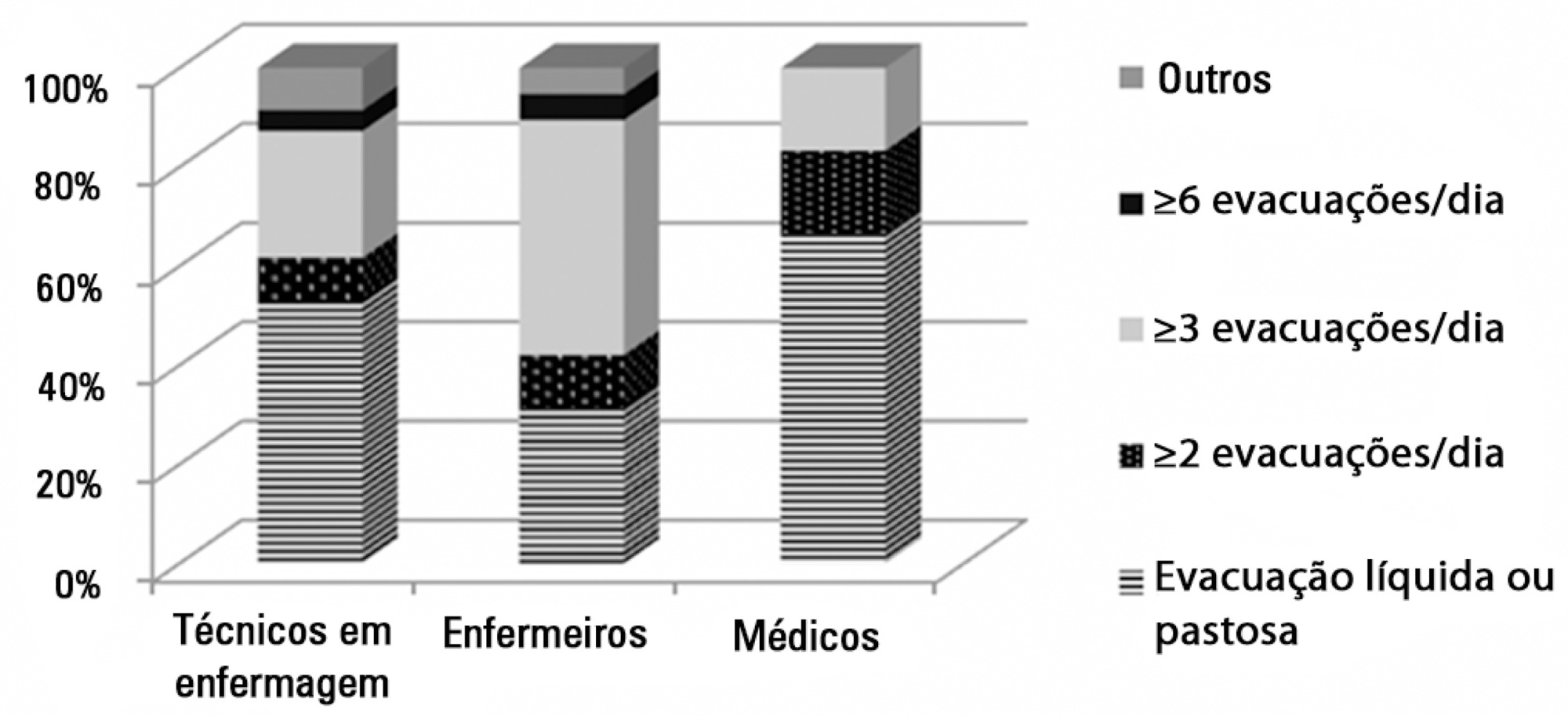
A total of 78 professionals participated in this study, of whom 59.0% were nurse technicians, 25.7% were nurses, and 15.3% were physicians; 77.0% of them had worked in intensive care for over 1 year. Only 37.2% had received training on this topic. Half of the interviewees defined diarrhea as "liquid and/or pasty stools" regardless of frequency, while the other 50.0% defined diarrhea based on the increased number of daily bowel movements. The majority of them mentioned diet as the main cause of diarrhea, followed by "use of medications" (p<0.001). Distinct nutritional practices were observed among the analyzed professionals regarding episodes of diarrhea, such as discontinuing, maintaining, or reducing the volume of enteral nutrition; physicians reported that they do not routinely communicate the problem to other professionals (for example, to a nutritionist) and do not routinely record and quantify diarrhea events in patients' medical records.
Different opinions and practices were observed in intensive care professionals with regard to diarrhea.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2010;22(2):125-132
DOI 10.1590/S0103-507X2010000200005
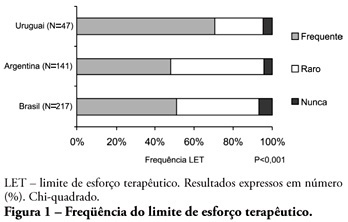
ABSTRACT OBJECTIVE: To evaluate end-of-life procedures in intensive care units. METHODS: A questionnaire was prepared by the End-of-Life Study Group of the Argentinean, Brazilian and Uruguayan Intensive Care societies, collecting data on the participants’ demographics, institutions and limit therapeutic effort (LTE) decision making process. During this cross sectional study, the societies’ multidisciplinary teams members completed the questionnaire either during scientific meetings or online. The variables were analyzed with the Chi-square test, with a p<0.05 significance level. RESULTS: 420 professionals completed the questionnaire. The Brazilian units had more beds, unrestricted visit was less frequent, their professionals were younger and worked more recently in intensive care units, and more non-medical professionals completed the questionnaire. Three visits daily was the more usual number of visits for the three countries. The most influencing LTE factors were prognosis, co-morbidities, and therapeutic futility. In the three countries, more than 90% of the completers had already made LTE decisions. Cardiopulmonary resuscitation, vasoactive drugs administration, dialysis and parenteral nutrition were the most suspended/refused therapies in the three countries. Suspension of mechanic ventilation was more frequent in Argentina, followed by Uruguay. Sedation and analgesia were the less suspended therapies in the three countries. Legal definement and ethical issues were mentioned as the main barriers for the LTE decision making process. CONCLUSION: LTE decisions are frequent among the professionals working in the three countries’ intensive care units. We found a more proactive LTE decision making trend In Argentina, and more equity for decisions distribution in Uruguay. This difference appears to be related to the participants’ different ages, experiences, professional types and genders.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2009;21(3):283-291
DOI 10.1590/S0103-507X2009000300008
OBJECTIVES: The intensive care unit emerged to improve and concentrate material and human resources for the care of critical patients, and need for constant observation and continuous assistance. However, patients in intensive care unit requires exceptional care, directed not only to the physiopathological problem, but also towards the psychosocial issue, now intimately interlinked to the physical disease. In this ambient, very demanding for capability of the multiprofessional team, presence of the physiotherapist has become more frequent. This study aims to verify if the attitude of an experienced physiotherapist in the intensive care unit is humanized. METHODS: To evaluate physiotherapy care humanization, a questionnaire was prepared and patients over 18 years of age, lucid and staying in intensive care unit for 24 hours or more were included. RESULTS: Forty four patients were interviewed and 95.5% of these considered the physiotherapy care as humanized. Positive association was observed between dissatisfaction with the items of dignity, communication, warranty and empathy, and a dehumannized physiotherapy care. Patients who evaluated warranty as negative had a twofold greater chance (0.7 - 5.3) of perceiving care as dehumanized. Patients who evaluated empathy as negative had a 1.6 (0.8 - 3.4) times greater chance of perceiving care as dehumanized. CONCLUSION: Physiotherapy care given in the intensive care unit was marked by good assistance, attention provided to the patient and quality of treatment, characterizing humanized care.
Search
Search in:
Case reports (56) Child (53) Coronavirus infections (34) COVID-19 (46) Critical care (116) Critical illness (54) Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (26) Infant, newborn (27) Intensive care (72) Intensive care units (256) Intensive care units, pediatric (31) mechanical ventilation (38) Mortality (76) Physical therapy modalities (28) Prognosis (61) Respiration, artificial (119) Respiratory insufficiency (26) risk factors (34) SARS-CoV-2 (28) Sepsis (98)