Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2010;22(2):125-132
DOI 10.1590/S0103-507X2010000200005
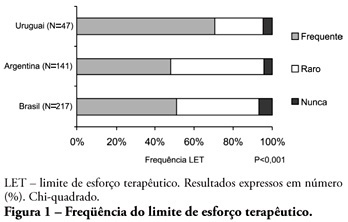
ABSTRACT OBJECTIVE: To evaluate end-of-life procedures in intensive care units. METHODS: A questionnaire was prepared by the End-of-Life Study Group of the Argentinean, Brazilian and Uruguayan Intensive Care societies, collecting data on the participants’ demographics, institutions and limit therapeutic effort (LTE) decision making process. During this cross sectional study, the societies’ multidisciplinary teams members completed the questionnaire either during scientific meetings or online. The variables were analyzed with the Chi-square test, with a p<0.05 significance level. RESULTS: 420 professionals completed the questionnaire. The Brazilian units had more beds, unrestricted visit was less frequent, their professionals were younger and worked more recently in intensive care units, and more non-medical professionals completed the questionnaire. Three visits daily was the more usual number of visits for the three countries. The most influencing LTE factors were prognosis, co-morbidities, and therapeutic futility. In the three countries, more than 90% of the completers had already made LTE decisions. Cardiopulmonary resuscitation, vasoactive drugs administration, dialysis and parenteral nutrition were the most suspended/refused therapies in the three countries. Suspension of mechanic ventilation was more frequent in Argentina, followed by Uruguay. Sedation and analgesia were the less suspended therapies in the three countries. Legal definement and ethical issues were mentioned as the main barriers for the LTE decision making process. CONCLUSION: LTE decisions are frequent among the professionals working in the three countries’ intensive care units. We found a more proactive LTE decision making trend In Argentina, and more equity for decisions distribution in Uruguay. This difference appears to be related to the participants’ different ages, experiences, professional types and genders.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2009;21(2):141-147
DOI 10.1590/S0103-507X2009000200005
OBJECTIVES: To evaluate the medical decisions at end-of-life of patients admitted at HU/UFSC and to compare these decisions and the profile of patients who died in the intensive care unit (ICU) to those who died in medical (MW) and surgical wards (SW). METHODS: This is a retrospective and observational study. Demographic data, clinical features, treatment and the end-of-life care decisions of adult patients who died in wards and the intensive care unit of HU/UFSC from July/2004 to December/2008 were analyzed . For statistical analysis the Student's t, χ2 and ANOVA tests were used: (significance p <0.05). RESULTS: An analysis was made of 1124 deaths: 404 occurred in ICU, 607 in MW and 113 in SW. The overall hospital mortality rate was 5.9% (ICU=24.49%, MW=7.2%, SW=1.69%). Mean ages of patients were: ICU=56.7, MW=69.3 and SW=70.4 years (p <0.01). Withholding/withdrawing life support was performed prior to 30.7% of deaths in the intensive care unit and 10% in the wards (p <0.01). Cardiopulmonary resuscitation was not carried out in 65% of cases in ICU, 79% in MW and 62% in SW. Besides cardiopulmonary resuscitation, the more frequent withholding/withdrawing life support in the intensive care unit were vasoactive drugs and in the wards refusal of admission to intensive care unit . Do-not-resuscitate order was documented in 2.4% of cases in ICU and 2.6% in MW. Palliative and comfort care were provided to 2% of patients in ICU, 11.5% in MW and 8% in SW. Terminality of the disease was recognized in 40% of cases in ICU, 34.6% in MW and 16.8% in SW. CONCLUSIONS: The profile of patients who died and medical decisions during the end-of-life process were different in the intensive care unit, clinical and surgical wards.