Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2022;34(1):107-115
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20220005-en
To evaluate clinical practices and hospital resource organization during the early COVID-19 pandemic in Brazil.
This was a multicenter, cross-sectional survey. An electronic questionnaire was provided to emergency department and intensive care unit physicians attending COVID-19 patients. The survey comprised four domains: characteristics of the participants, clinical practices, COVID-19 treatment protocols and hospital resource organization.
Between May and June 2020, 284 participants [median (interquartile ranges) age 39 (33 - 47) years, 56.3% men] responded to the survey; 33% were intensivists, and 9% were emergency medicine specialists. Half of the respondents worked in public hospitals. Noninvasive ventilation (89% versus 73%; p = 0.001) and highflow nasal cannula (49% versus 32%; p = 0.005) were reported to be more commonly available in private hospitals than in public hospitals. Mechanical ventilation was more commonly used in public hospitals than private hospitals (70% versus 50%; p = 0,024). In the Emergency Departments, positive endexpiratory pressure was most commonly adjusted according to SpO2, while in the intensive care units, positive end-expiratory pressure was adjusted according to the best lung compliance. In the Emergency Departments, 25% of the respondents did not know how to set positive end-expiratory pressure. Compared to private hospitals, public hospitals had a lower availability of protocols for personal protection equipment during tracheal intubation (82% versus 94%; p = 0.005), managing mechanical ventilation [64% versus 75%; p = 0.006] and weaning patients from mechanical ventilation [34% versus 54%; p = 0.002]. Finally, patients spent less time in the emergency department before being transferred to the intensive care unit in private hospitals than in public hospitals [2 (1 - 3) versus 5 (2 - 24) hours; p < 0.001].
This survey revealed significant heterogeneity in the organization of hospital resources, clinical practices and treatments among physicians during the early COVID-19 pandemic in Brazil.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2016;28(2):107-113
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20160024
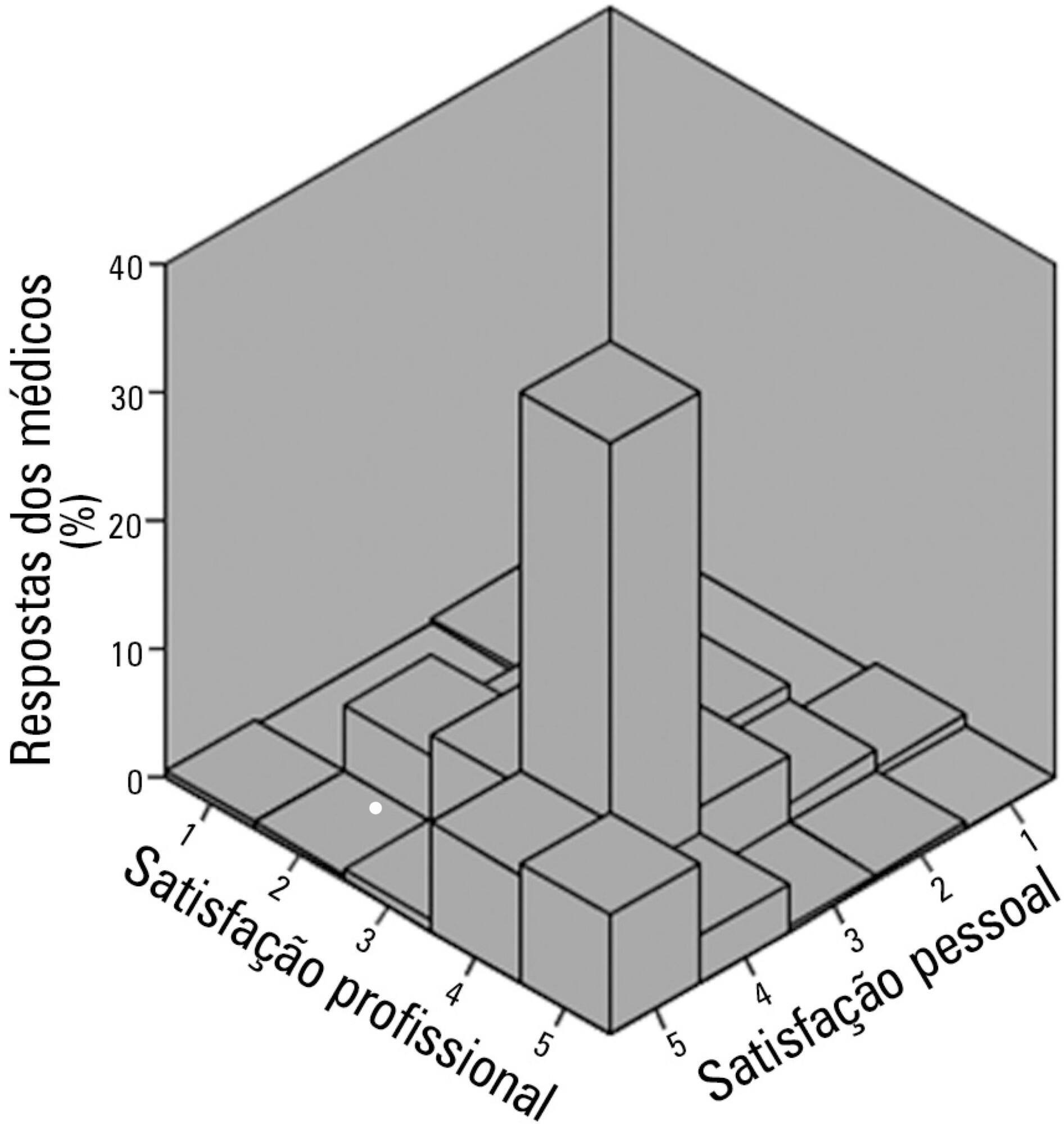
To evaluate job and personal satisfaction rates in physicians who work in adult intensive care units and to identify the factors associated with satisfaction.
A cross-sectional study performed with physicians who participated in two intensive medicine online discussion groups. A questionnaire designed to assess the physician's sociodemographic profile and job was available for both groups for 3 months. At the end of the questionnaire, the participants addressed their degrees of job and personal satisfaction using a Likert scale in which 1 represented "very dissatisfied" and 5 represented "very satisfied". The association between sociodemographic and job characteristics with job and personal satisfaction was evaluated. Variables independently associated with satisfaction were identified using a logistic regression model.
The questionnaire was answered by 250 physicians, of which 137 (54.8%) declared they were satisfied with their jobs and 34 (13.5%) were very satisfied. None of the evaluated characteristics were independently associated with job satisfaction. Regarding personal satisfaction, 136 (54.4%) physicians reported being satisfied, and 48 (19.9%) reported being very satisfied. Job satisfaction (OR = 7.21; 95%CI 3.21 - 16.20) and working in a university hospital (OR = 3.24; 95%CI 1.29 - 8.15) were factors independently associated with the personal satisfaction of the participants.
The participant physicians reported job and personal satisfaction with their work in intensive care. Job satisfaction and working in a university hospital were independently associated with greater personal satisfaction.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2008;20(3):261-266
DOI 10.1590/S0103-507X2008000300009
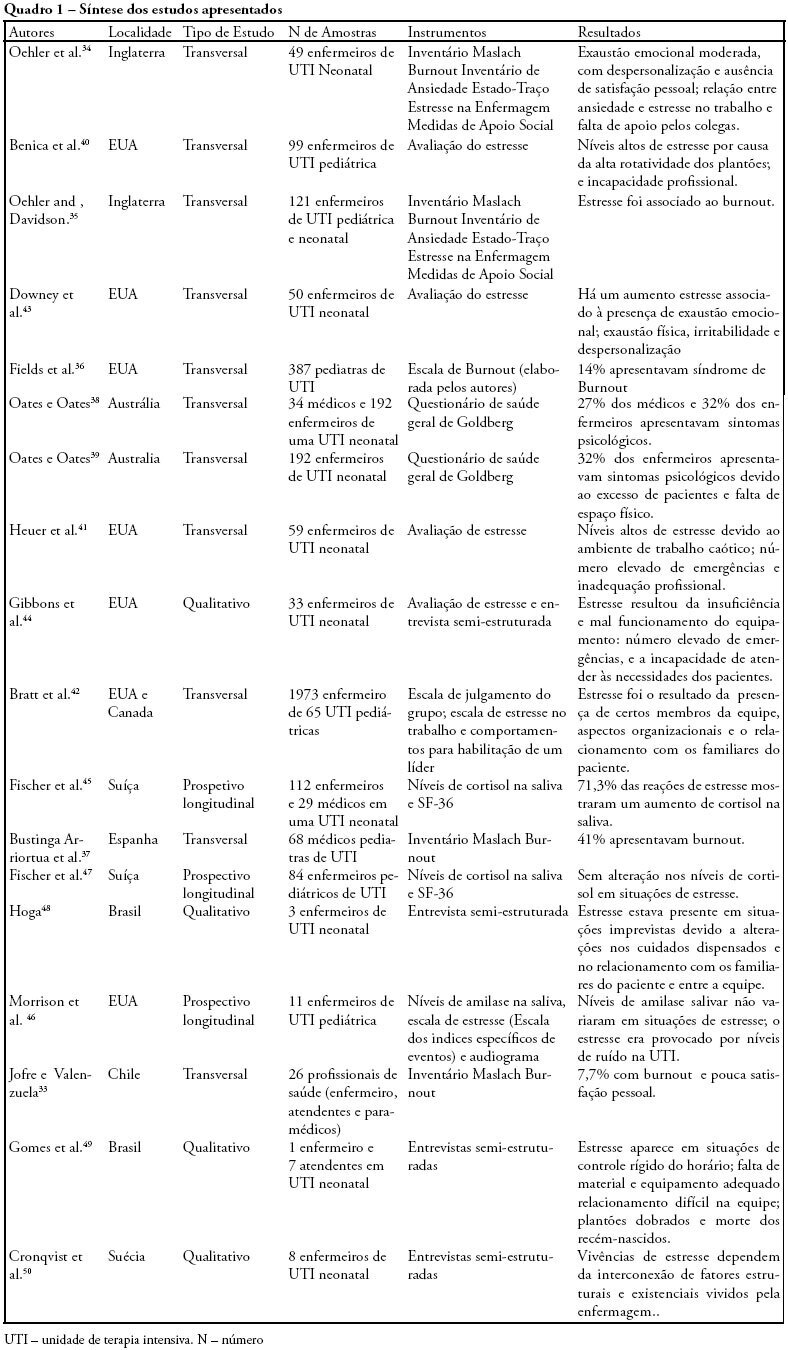
OBJECTIVES: Bibliographic review on occupational stress and burnout presence in physicians and nurses that work in pediatric and neonatal intensive care units. METHODS: The articles were selected from the MedLine, LILACS and SciElo data base using the key words: stress, burnout, physicians, nursing, intensive care unit, pediatric intensive care unit and neonatal intensive care unit. The studied period ranged from 1990 to 2007. RESULTS: Health professionals who work in pediatric and neonatal intensive care units are strong candidates for developing stress, psychological alterations and burnout syndrome. Researches on this subject identified important alterations suffered by these physicians and nurses, such as: work overload, burnout, desires of giving up their jobs, high levels of cortisol, among other alterations. CONCLUSIONS: Professionals, who work in pediatric and neonatal intensive care units, due to the specificity of their job, are liable to develop occupational stress, and consequently burnout. These results suggest the need for further research with the objective of developing preventive measures and intervention models.
Search
Search in:
Case reports (56) Child (53) Coronavirus infections (34) COVID-19 (46) Critical care (115) Critical illness (54) Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (26) Infant, newborn (27) Intensive care (72) Intensive care units (256) Intensive care units, pediatric (31) mechanical ventilation (38) Mortality (76) Physical therapy modalities (28) Prognosis (61) Respiration, artificial (119) Respiratory insufficiency (26) risk factors (34) SARS-CoV-2 (28) Sepsis (98)