Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2021;33(1):119-124
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20210013
To assess the performance of Pediatric Risk of Mortality (PRISM) III and Pediatric Index of Mortality (PIM) 2 scores in the pediatric intensive care unit.
A retrospective cohort study. Data were retrospectively collected from medical records of all patients admitted to the pediatric intensive care unit of a cancer hospital from January 2017 to June 2018.
The mean PRISM III score was 15, and PIM 2, 24%. From the 338 studied patients, 62 (18.34%) died. The PRISM III estimated mortality was 79.52 patients (23.52%) and for PIM 2 80.19 patients (23.72%), corresponding to a standardized mortality ratio (95% confidence interval: 0.78 for PRISM II and 0.77 for PIM 2). The Hosmer-Lemeshow chi-square test was 11.56, 8df, 0.975 for PRISM II and 0.48, 8df, p = 0.999 for PIM 2. The area under the Receiver Operating Characteristic curve was 0.71 for PRISM III and 0.76 for PIM 2.
Both scores overestimated mortality and have shown a regular ability to discriminate between survivors and non-survivors. Models should be developed to quantify the severity of cancer pediatric patients in Pediatric Intensive Care Units and to predict the mortality risk accounting for their peculiarities.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2019;31(1):27-33
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20190006
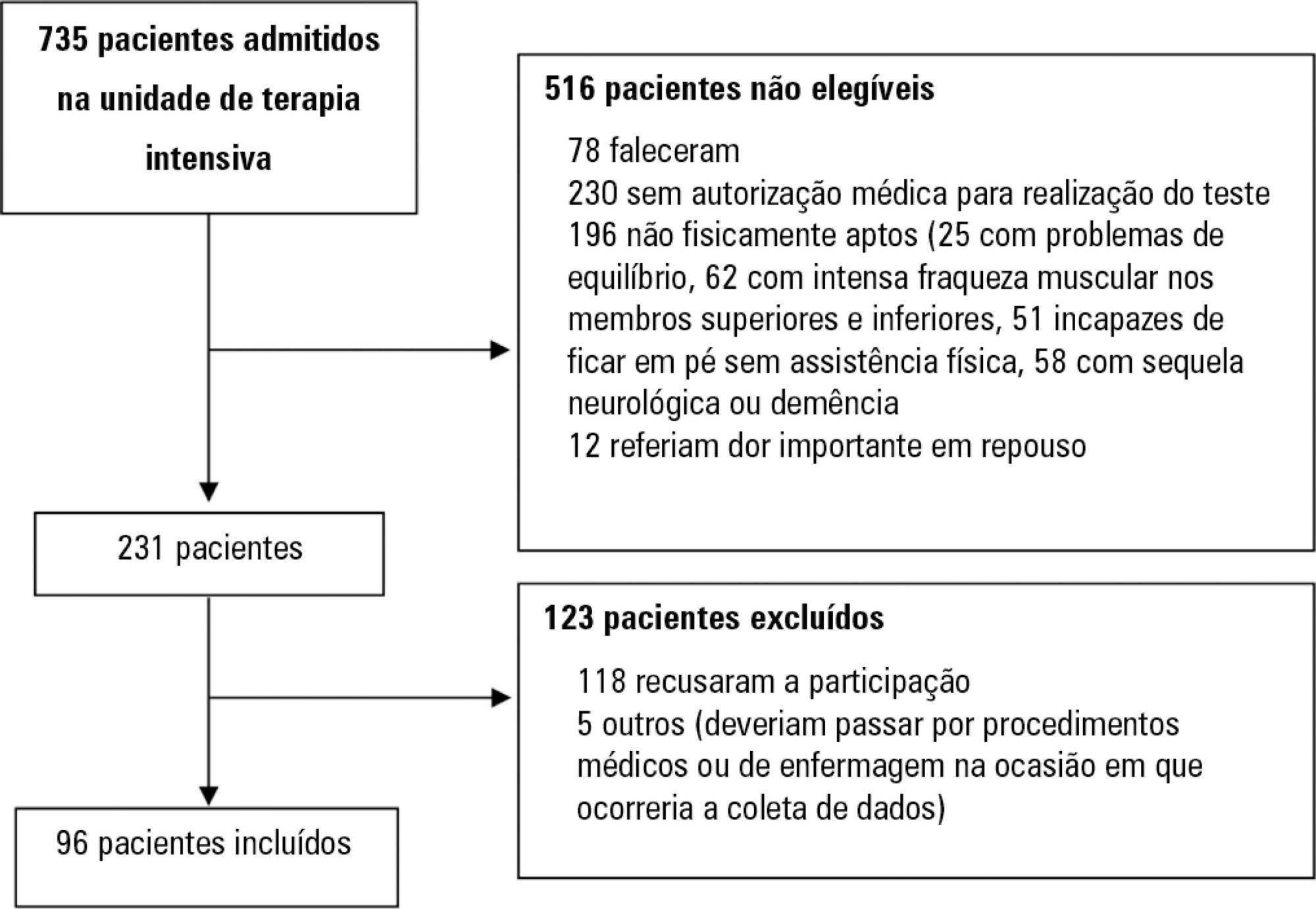
Assess the Five Times Sit-to-Stand Test safety and clinimetric properties in older patients hospitalized in an intensive care unit.
Test safety was assessed according to the incidence of adverse events and through hemodynamic and respiratory data. Additionally, reliability properties were investigated using the intraclass correlation coefficients, standard error of measurement, standard error percentage change, Altman-Bland plot and a survival agreement plot.
The overall suitability of the Five Times Sit-to-Stand Test was found to be low, with 29.8% meeting the inclusion criteria. Only 44% of the hospitalized patients who met the inclusion criteria performed the test, with no need for discontinuation in any patient. Heart rate (79.7 ± 10.2bpm/86.6 ± 9.7bpm; p = 0.001) and systolic blood pressure (118 ± 21.4mmHg/129 ± 21.5mmHg; p = 0.031) were the only variables that presented a significant statistical increase, with no evidence of exacerbated response to the test. Additionally, no adverse events were reported from participating and both test-retest and interrater reliability were high (intraclass correlation coefficient ≥ 0.99).
The Five Times Sit-to-Stand Test was proven to be safe and to have excellent reliability. Its clinical use, however, may be restricted to high-functioning older adults in hospital settings.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2017;29(3):303-309
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20170041
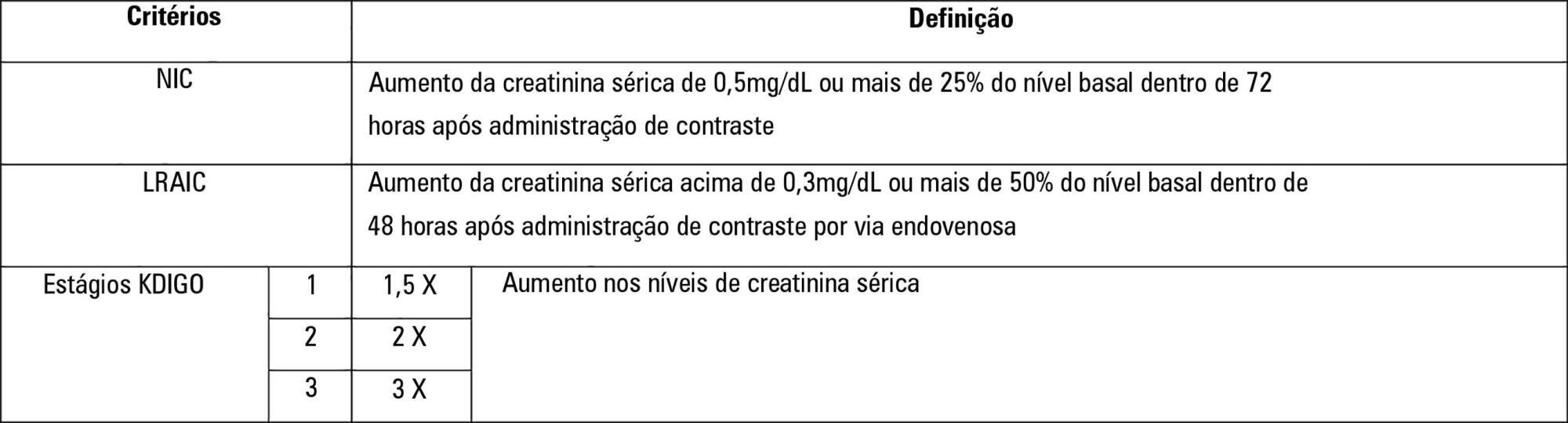
To establish whether there is superiority between contrast-induced acute kidney injury and contrast-induced nephropathy criteria as predictors of unfavorable clinical outcomes.
Retrospective study carried out in a tertiary hospital with 157 patients undergoing radiocontrast infusion for propaedeutic purposes.
One hundred forty patients fulfilled the inclusion criteria: patients who met the criteria for contrast-induced acute kidney injury (59) also met the criteria for contrast-induced nephropathy (76), 44.3% met the criteria for KDIGO staging, 6.4% of the patients required renal replacement therapy, and 10.7% died.
The diagnosis of contrast-induced nephropathy was the most sensitive criterion for renal replacement therapy and death, whereas KDIGO showed the highest specificity; there was no correlation between contrast volume and progression to contrast-induced acute kidney injury, contrast-induced nephropathy, support dialysis or death in the assessed population.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2017;29(4):453-459
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20170069
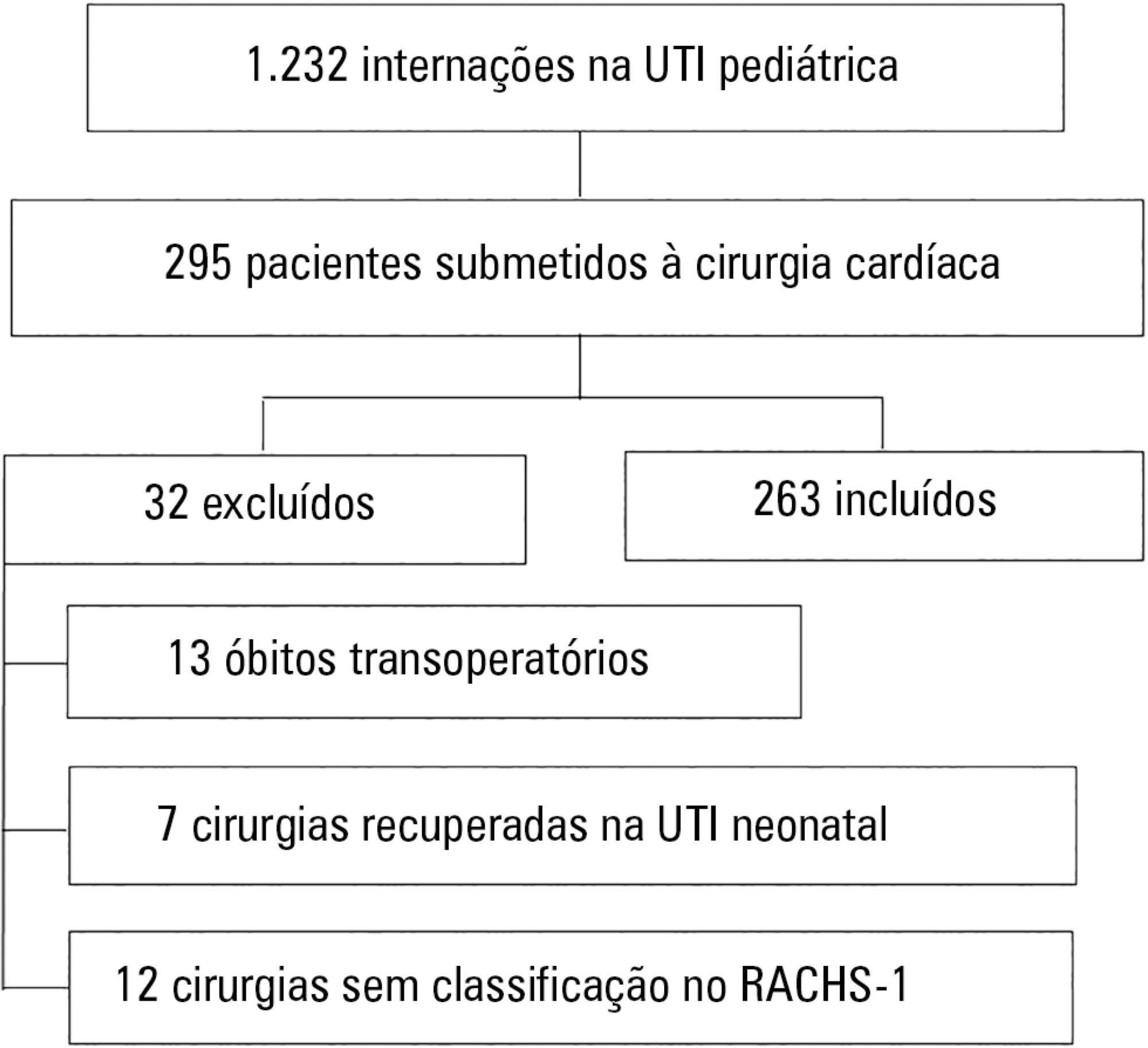
To assess the performance of the Pediatric Index of Mortality (PIM) 2 and the Risk Adjustment for Congenital Heart Surgery (RACHS) in the postoperative period of congenital heart disease patients.
Retrospective cross-sectional study. Data were collected from patient records to generate the scores and predictions using recommended techniques, demographic data and outcomes. The Mann-Whitney test, Hosmer-Lemeshow test, standardized mortality rate, area under the receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve, chi square test, Poisson regression with robust variance and Spearman's test were used for statistical analysis.
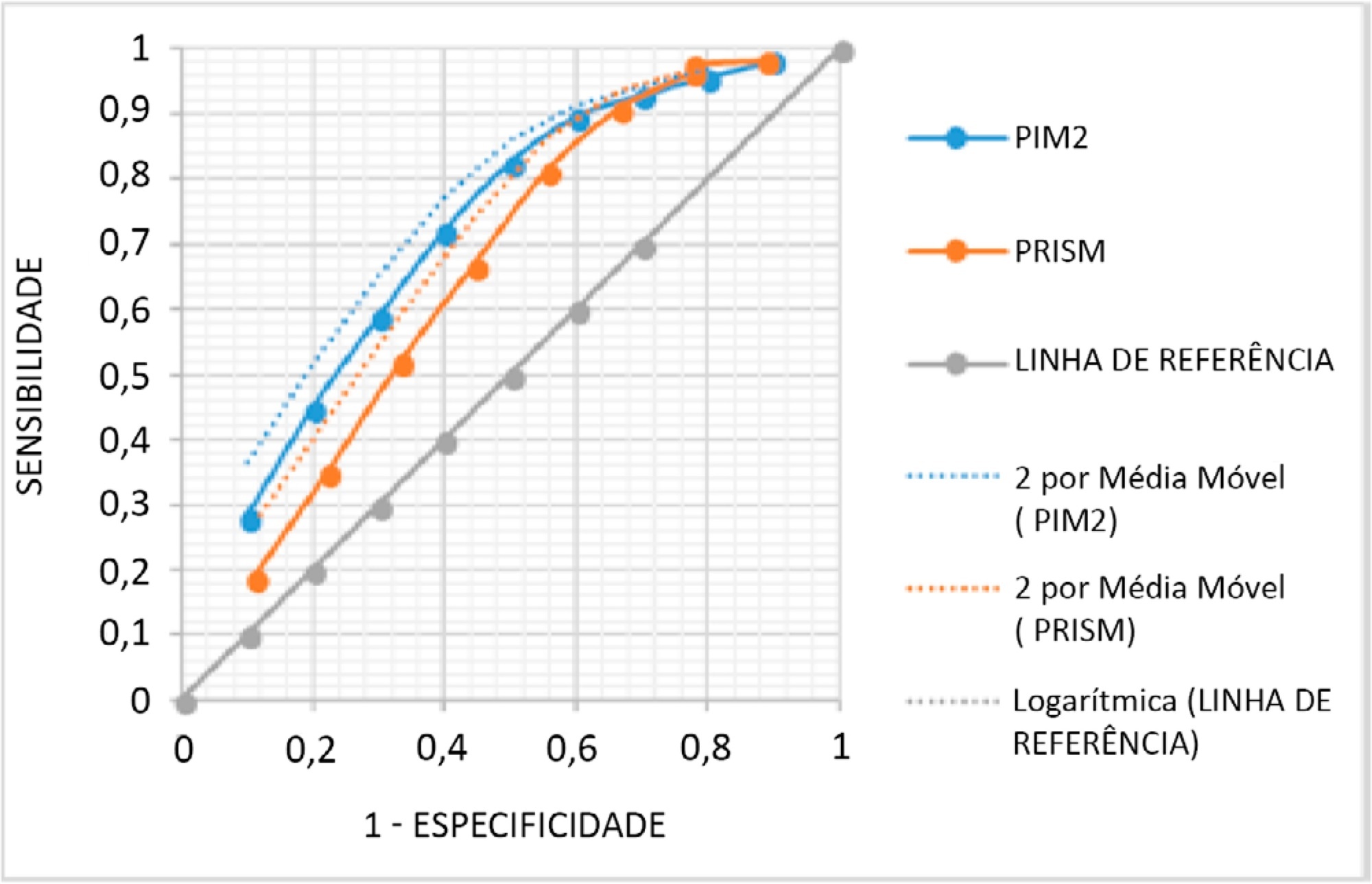
A total of 263 patients were evaluated, and 72 died (27.4%). These patients presented significantly higher PIM-2 values than survivors (p < 0.001). In the RACHS-1 classification, mortality was progressively higher according to the complexity of the procedure, with a 3.24-fold increase in the comparison between groups 6 and 2. The area under the ROC curve for PIM-2 was 0.81 (95%CI 0.75 - 0.87), while for RACHS-1, it was 0.70 (95%CI 0.63 - 0.77). The RACHS presented better calibration power in the sample analyzed. A significantly positive correlation was found between the results of both scores (rs = 0.532; p < 0.001).
RACHS presented good calibration power, and RACHS-1 and PIM-2 demonstrated good performance with regard to their discriminating capacities between survivors and non-survivors. Moreover, a positive correlation was found between the results of the two risk scores.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2015;27(1):57-63
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20150010
This study aimed to evaluate Brazilian physicians’ perceptions regarding the diagnosis, severity assessment, treatment and risk stratification of severe community-acquired pneumonia patients and to compare those perceptions to current guidelines.
We conducted a cross-sectional international anonymous survey among a convenience sample of critical care, pulmonary, emergency and internal medicine physicians from Brazil between October and December 2008. The electronic survey evaluated physicians’ attitudes towards the diagnosis, risk assessment and therapeutic interventions for patients with severe community-acquired pneumonia.
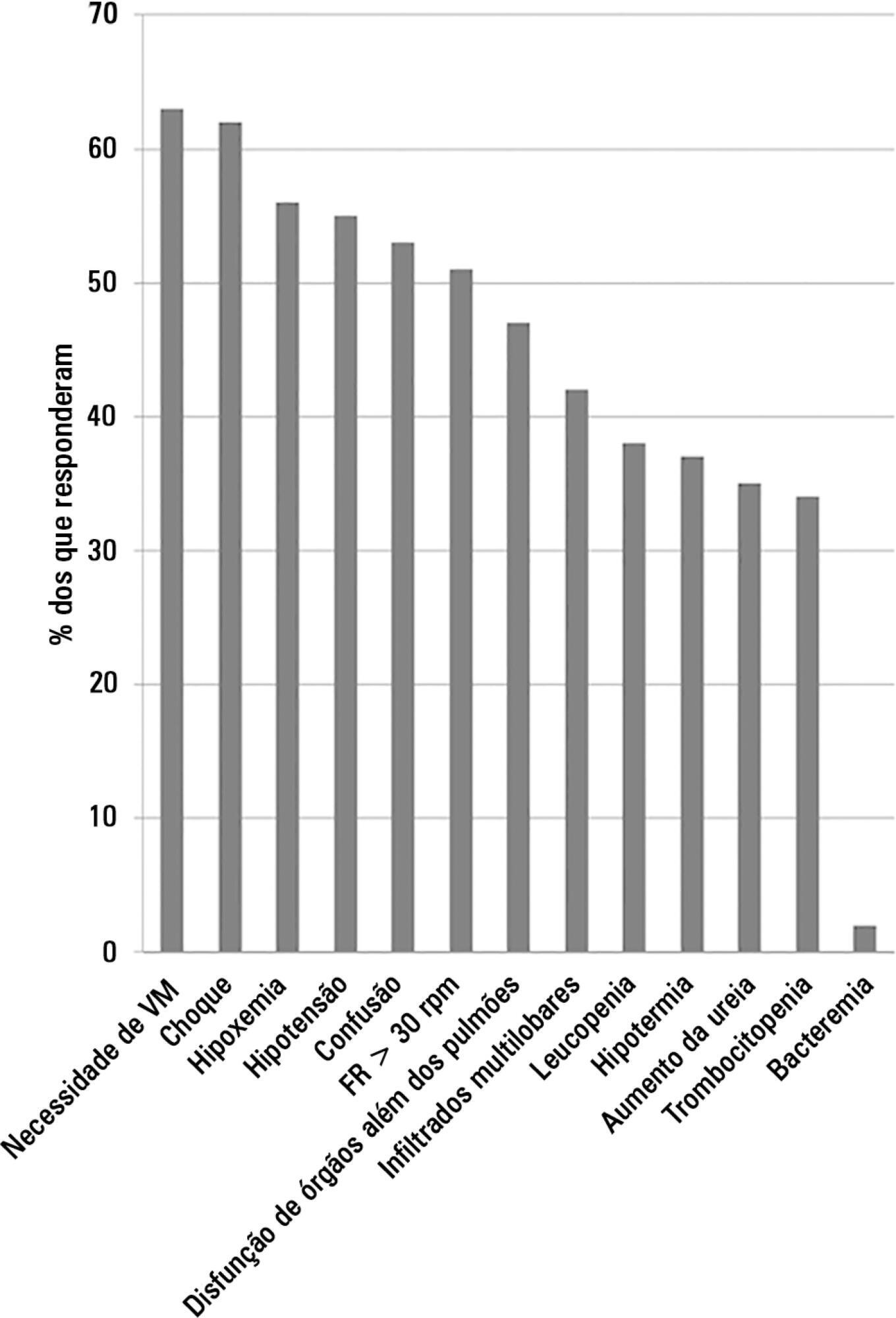
A total of 253 physicians responded to the survey, with 66% from Southeast Brazil. The majority (60%) of the responding physicians had > 10 years of medical experience. The risk assessment of severe community-acquired pneumonia was very heterogeneous, with clinical evaluation as the most frequent approach. Although blood cultures were recognized as exhibiting a poor diagnostic performance, these cultures were performed by 75% of respondents. In contrast, the presence of urinary pneumococcal and Legionella antigens was evaluated by less than 1/3 of physicians. The vast majority of physicians (95%) prescribe antibiotics according to a guideline, with the combination of a 3rd/4th generation cephalosporin plus a macrolide as the most frequent choice.
This Brazilian survey identified an important gap between guidelines and clinical practice and recommends the institution of educational programs that implement evidence-based strategies for the management of severe community-acquired pneumonia.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2014;26(1):44-50
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20140007
To assess the discrimination and calibration of the Pediatric Index of Mortality 2 in patients admitted to a pediatric intensive care unit.
The study was conducted with a contemporary cohort from November 2005 to November 2006. Patients aged 29 days to 18 years were included in the study. Patients who died within 12 hours of admission and cases of readmission were excluded from the study. The performance of the Pediatric Index of Mortality 2 was assessed by means of the Hosmer-Lemeshow goodness-of-fit test, the standardized mortality ratio and the area under receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve with 95% confidence interval. The significance level was established as 5%.
A total of 276 admissions to the pediatric intensive care unit were included in the analysis. The mortality rate was 14.13%, and the efficiency of admission 0.88%. The median age of the sample was 42.22 months, and most participants were male (60.1%). Most admissions were referrals from the emergency department. The mean duration of stay in pediatric intensive care unit was 6.43±5.23 days. Approximately 72.46% of admissions were for clinical reasons and exhibited an association with the outcome death (odds ratio: 2.9; 95%CI: 1.09-7.74; p=0.017). Calibration of the Pediatric Index of Mortality 2 with the chi-square statistic was 12.2686 (p=0.1396) in the Hosmer-Lemeshow goodness-of-fit test, and the standardized mortality ratio was 1.0. The area under the ROC curve assessing model discrimination was 0.778.
Pediatric Index of Mortality 2 exhibited satisfactory performance.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2013;25(2):106-114
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20130021
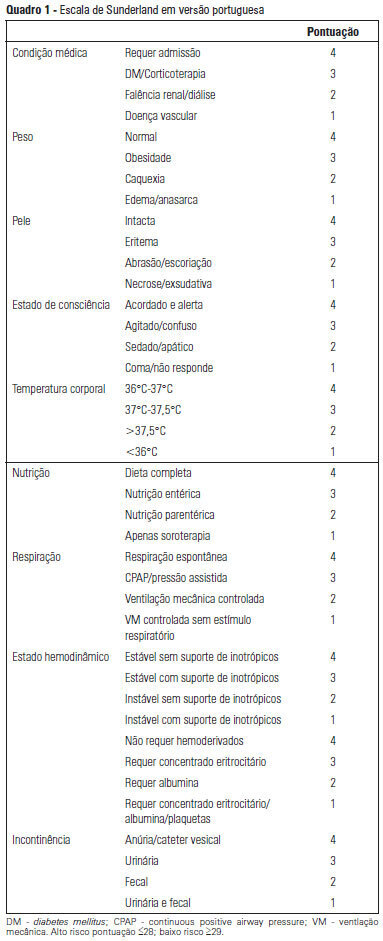
OBJECTIVE: To Translate into Portuguese and evaluate the measuring properties of the Sunderland Scale and the Cubbin & Jackson Revised Scale, which are instruments for evaluating the risk of developing pressure ulcers during intensive care. METHODS: This study included the process of translation and adaptation of the scales to the Portuguese language, as well as the validation of these tools. To assess the reliability, Cronbach alpha values of 0.702 to 0.708 were identified for the Sunderland Scale and the Cubbin & Jackson Revised Scale, respectively. The validation criteria (predictive) were performed comparatively with the Braden Scale (gold standard), and the main measurements evaluated were sensitivity, specificity, positive predictive value, negative predictive value, and area under the curve, which were calculated based on cutoff points. RESULTS: The Sunderland Scale exhibited 60% sensitivity, 86.7% specificity, 47.4% positive predictive value, 91.5% negative predictive value, and 0.86 for the area under the curve. The Cubbin & Jackson Revised Scale exhibited 73.3% sensitivity, 86.7% specificity, 52.4% positive predictive value, 94.2% negative predictive value, and 0.91 for the area under the curve. The Braden scale exhibited 100% sensitivity, 5.3% specificity, 17.4% positive predictive value, 100% negative predictive value, and 0.72 for the area under the curve. CONCLUSIONS: Both tools demonstrated reliability and validity for this sample. The Cubbin & Jackson Revised Scale yielded better predictive values for the development of pressure ulcers during intensive care.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2013;25(3):233-238
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20130040
The objective of this study was to assess the correlation between the European System for Cardiac Operative Risk Evaluation (EuroSCORE) score and the risk of developing acute kidney injury in cardiac surgery patients.
This retrospective study was conducted at a tertiary hospital on consecutive cardiac surgery patients (e.g., valvular, ischemic and congenital heart diseases) between October 2010 and July 2011.
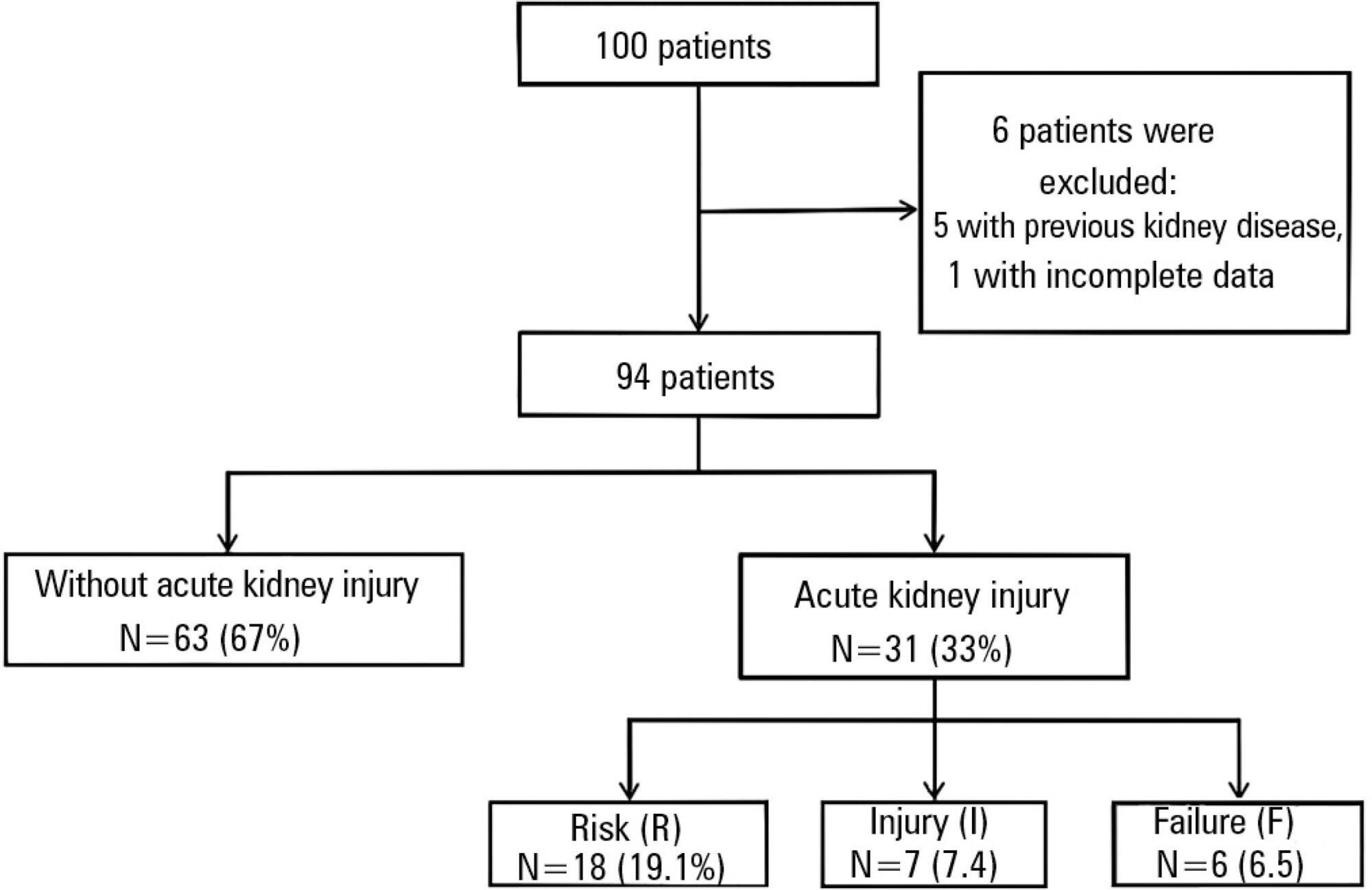
One hundred patients were assessed. Among the 100 patients, six were excluded, including five because of prior kidney disease or dialysis therapy and one because of incomplete medical records. The primary surgical indications were myocardial revascularization in 55 patients (58.5% of cases) and valve replacement in 28 patients (29.8%). According to the EuroSCORE, 55 patients were classified as high risk (58.5%), 27 patients as medium risk (28.7%) and 12 patients as low risk (12.8%). In the postoperative period, patients were classified with the Risk, Injury, Failure, Loss and End-stage kidney disease (RIFLE) score. Among the 31 patients (33%) who displayed an increase in serum creatinine, 18 patients (19.1%) were classified as RIFLE "R" (risk), seven patients (7.4%) were classified as RIFLE "I" (injury) and six patients (6.5%) were classified as RIFLE "F" (failure). Among the patients who were considered to be high risk according to the EuroSCORE criteria, 24 patients (43.6%) showed acute kidney injury. Among the patients who were classified as medium or low risk, acute kidney injury occurred in 18.5 and 16.6% of the cases, respectively. The correlations between risk stratification (low, medium and high) and the EuroSCORE and postoperative RIFLE scores were statistically significant (p=0.03).
In the studied population, there was a statistically significant correlation between the EuroSCORE and the risk of developing acute kidney injury in the postoperative period after cardiac surgery.
Search
Search in:
Case reports (56) Child (53) Coronavirus infections (34) COVID-19 (46) Critical care (116) Critical illness (54) Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (26) Infant, newborn (27) Intensive care (72) Intensive care units (256) Intensive care units, pediatric (31) mechanical ventilation (38) Mortality (76) Physical therapy modalities (28) Prognosis (61) Respiration, artificial (119) Respiratory insufficiency (26) risk factors (34) SARS-CoV-2 (28) Sepsis (98)