Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2017;29(3):317-324
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20170047
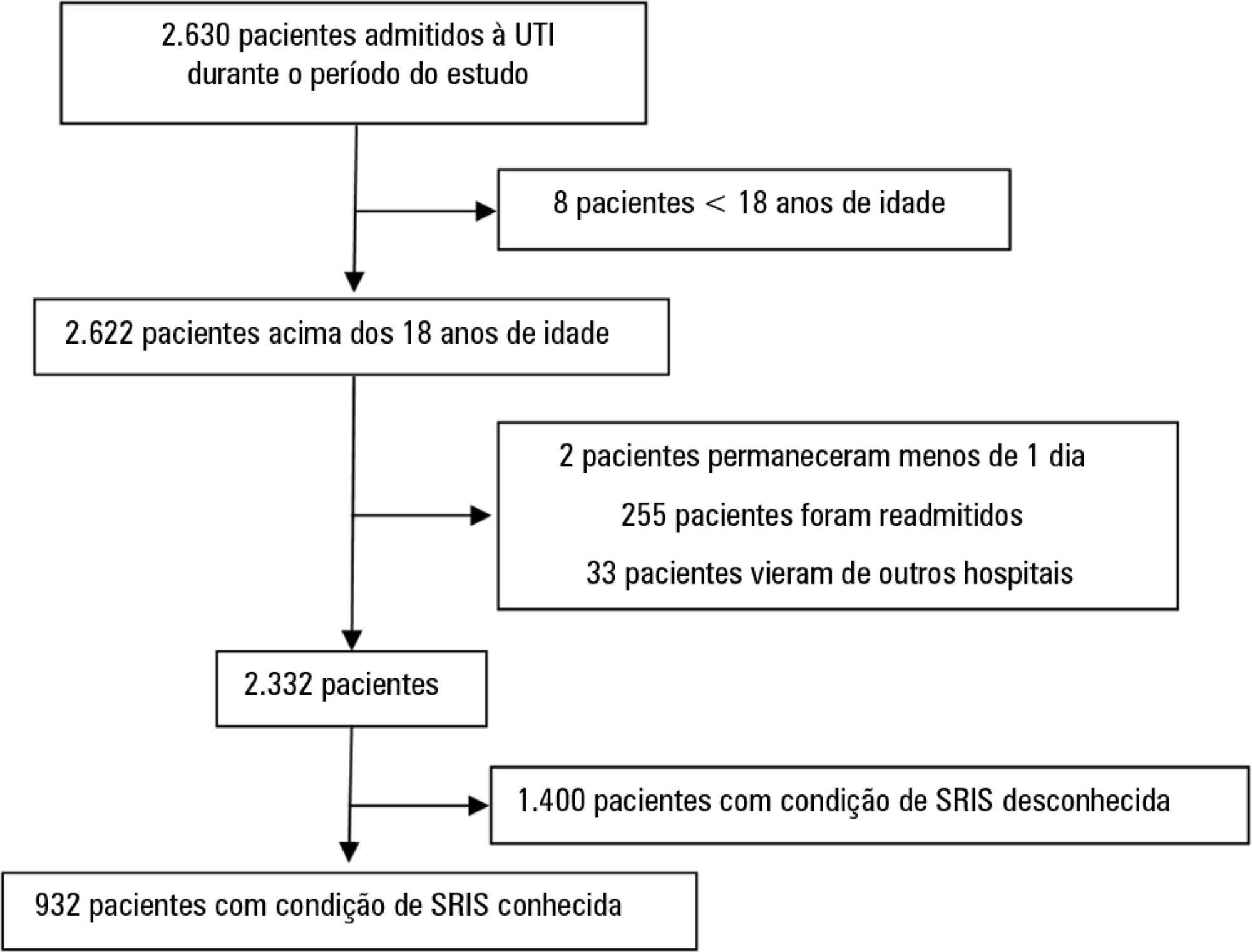
This study intended to determine whether the systemic inflammatory response syndrome criteria can predict hospital mortality in a Brazilian cohort of critically ill patients.
We performed a retrospective cohort study at a private tertiary hospital in São Paulo (SP), Brazil. We extracted information from the adult intensive care unit database (Sistema EpimedTM). We compared the SAPS 3 and the systemic inflammatory response syndrome model as dichotomous (≥ 2 criteria: systemic inflammatory response syndrome -positive versus 0 - 1 criterion: systemic inflammatory response syndrome -negative) and ordinal variables from 0 to 4 (according to the number of systemic inflammatory response syndrome criteria met) in the prediction of hospital mortality at intensive care unit admission. Model discrimination was compared using the area under the receiver operating characteristics (AUROC) curve.
From January to December 2012, we studied 932 patients (60.4% were systemic inflammatory response syndrome -positive). systemic inflammatory response syndrome -positive patients were more critically ill than systemic inflammatory response syndrome -negative patients and had higher hospital mortality (16.9% versus 8.1%, p < 0.001). In the adjusted analysis, being systemic inflammatory response syndrome -positive independently increased the risk of death by 82% (odds ratio 1.82; 95% confidence interval [CI] 1.12 - 2.96, p = 0.016). However, the AUROC curve for the SAPS 3 model was higher (0.81, 95%CI 0.78 - 0.85) compared to the systemic inflammatory response syndrome model with the systemic inflammatory response syndrome criteria as a dichotomous variable (0.60, 95%CI 0.55 - 0.65) and as an ordinal variable (0.62, 95%CI 0.57 - 0.68; p < 0.001) for hospital mortality.
Although systemic inflammatory response syndrome is associated with hospital mortality, the systemic inflammatory response syndrome criteria show low accuracy in the prediction of mortality compared with the SAPS 3.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2017;29(3):271-278
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20170048
This report aimed to describe the outcomes of the patients with severe H1N1 associated acute respiratory distress syndrome who were treated with extracorporeal membrane oxygenation therapy.
This retrospective review analyzed a single-center cohort of adult patients with H1N1-related acute respiratory distress syndrome who were managed with veno-venous extracorporeal membrane oxygenation during the winter of 2013/2014.
A total of 10 patients received veno-venous extracorporeal membrane oxygenation for H1N1 influenza between January 2013 and March 2014. Seven patients were transferred to our center for extracorporeal membrane oxygenation consideration (all within 72 hours of initiating mechanical ventilation). The median patient age was forty years, and 30% were female. The median arterial oxygen partial pressure to fraction of inspired oxygen ratio was 62.5, and the median RESP score was 6. Three patients received inhaled nitric oxide, and four patients were proned as rescue therapy before extracorporeal membrane oxygenation was initiated. The median duration of mechanical ventilation was twenty-two days (range, 14 - 32). The median length of stay in the intensive care unit was twenty-seven days (range, 14 - 39). The median hospital length of stay was 29.1 days (range, 16.0 - 46.9). Minor bleeding complications occurred in 6 of 10 patients. Eight of the ten patients survived to hospital discharge.
The survivors were relatively young and discharged with good functional status (i.e., enhancing quality-adjusted life-years-saved). Our experience shows that even a relatively new extracorporeal membrane oxygenation program can play an important role in that capacity and provide excellent outcomes for the sickest patients.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2017;29(3):331-336
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20170040
The goal was to determine the main drug-related problems in neonates who were using antimicrobials.
This was an observational, prospective and longitudinal study. Drug-related problems were classified according to version 6.2 of the Pharmaceutical Care Network Europe Foundation classification. A descriptive analysis was performed, in which the clinical and therapeutic variables were presented as absolute and relative frequencies or as the mean and standard deviation, as appropriate.
In total, 152 neonates with a predominance of males (58.5%), gestational age of 32.7 ± 4.2 weeks and weight of 1,903.1 ± 846.9g were included. The main diagnostic hypothesis of infection was early sepsis (66.5%), and 71.7% of the neonates had some risk factor for infection. Among the neonates, 33.6% had at least one drug-related problem. Of these, 84.8% were related to treatment effectiveness and 15.2% to adverse reactions. The main cause of drug-related problems was the selected dose, particularly for aminoglycosides and cephalosporins.
The use of antimicrobials in the neonatal intensive care is mainly associated with problems related to medication effectiveness, predominantly the prescription of subdoses of antimicrobials, especially aminoglycosides.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2017;29(3):303-309
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20170041
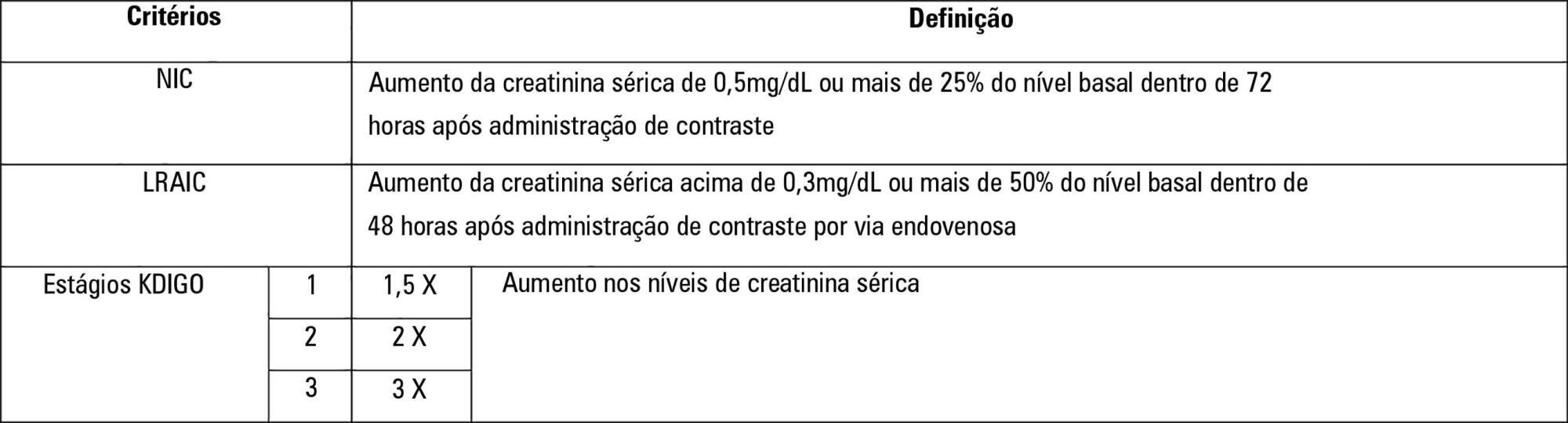
To establish whether there is superiority between contrast-induced acute kidney injury and contrast-induced nephropathy criteria as predictors of unfavorable clinical outcomes.
Retrospective study carried out in a tertiary hospital with 157 patients undergoing radiocontrast infusion for propaedeutic purposes.
One hundred forty patients fulfilled the inclusion criteria: patients who met the criteria for contrast-induced acute kidney injury (59) also met the criteria for contrast-induced nephropathy (76), 44.3% met the criteria for KDIGO staging, 6.4% of the patients required renal replacement therapy, and 10.7% died.
The diagnosis of contrast-induced nephropathy was the most sensitive criterion for renal replacement therapy and death, whereas KDIGO showed the highest specificity; there was no correlation between contrast volume and progression to contrast-induced acute kidney injury, contrast-induced nephropathy, support dialysis or death in the assessed population.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2017;29(3):310-316
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20170039
To phenotypically evaluate biofilm production by Pseudomonas aeruginosa clinically isolated from patients with ventilator-associated pneumonia.
Twenty clinical isolates of P. aeruginosa were analyzed, 19 of which were from clinical samples of tracheal aspirate, and one was from a bronchoalveolar lavage sample. The evaluation of the capacity of P. aeruginosa to produce biofilm was verified using two techniques, one qualitative and the other quantitative.
The qualitative technique showed that only 15% of the isolates were considered biofilm producers, while the quantitative technique showed that 75% of the isolates were biofilm producers. The biofilm isolates presented the following susceptibility profile: 53.3% were multidrug-resistant, and 46.7% were multidrug-sensitive.
The quantitative technique was more effective than the qualitative technique for the detection of biofilm production. For the bacterial population analyzed, biofilm production was independent of the susceptibility profile of the bacteria, demonstrating that the therapeutic failure could be related to biofilm production, as it prevented the destruction of the bacteria present in this structure, causing complications of pneumonia associated with mechanical ventilation, including extrapulmonary infections, and making it difficult to treat the infection.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2017;29(3):279-286
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20170038
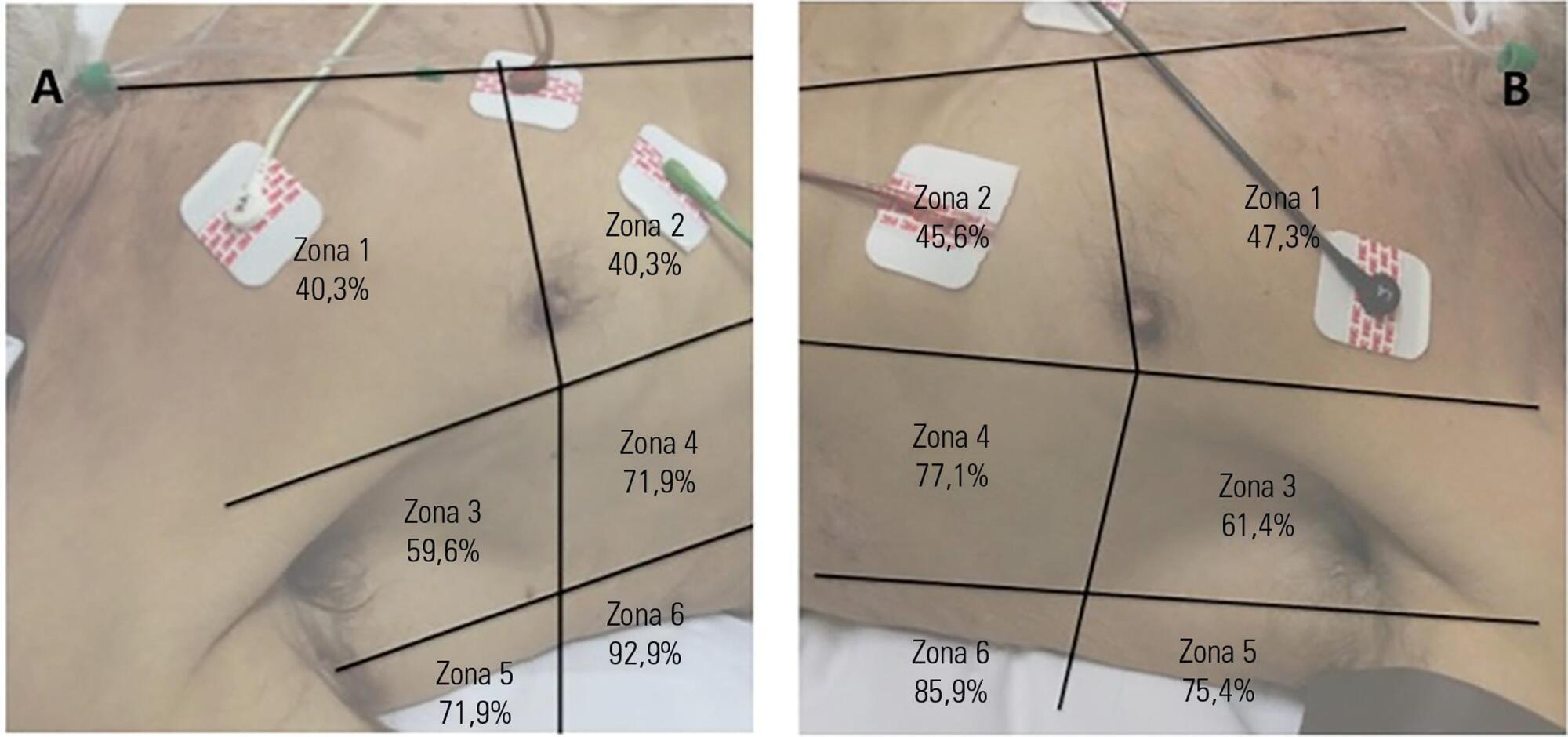
We aimed to investigate a potential association between B-lines and weaning failure.
Fifty-seven subjects eligible for ventilation liberation were enrolled. Patients with tracheostomy were excluded. Lung ultrasound assessments of six thoracic zones were performed immediately before and at the exnd of the spontaneous breathing trial. B-predominance was defined as any profile with anterior bilateral B-pattern. Patients were followed up to 48 hours after extubation.
Thirty-eight individuals were successfully extubated; 11 failed the spontaneous breathing trial and 8 needed reintubation within 48 hours of extubation. At the beginning of the T-piece trial, B-pattern or consolidation was already found at the lower and posterior lung regions in more than half of the individuals and remained non-aerated at the end of the trial. A trend toward loss of lung aeration during spontaneous breathing trials was observed only in the spontaneous breathing trial-failure group (p = 0.07), and there was higher B-predominance at the end of the trial (p = 0.01).
A loss of lung aeration during the spontaneous breathing trial in non-dependent lung zones was demonstrated in subjects who failed to wean.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2015;27(3):199-201
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20150036
Search
Search in:
Case reports (56) Child (53) Coronavirus infections (34) COVID-19 (46) Critical care (115) Critical illness (54) Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (26) Infant, newborn (27) Intensive care (72) Intensive care units (256) Intensive care units, pediatric (31) mechanical ventilation (38) Mortality (76) Physical therapy modalities (28) Prognosis (61) Respiration, artificial (119) Respiratory insufficiency (26) risk factors (34) SARS-CoV-2 (28) Sepsis (98)