You searched for:"Augusto Savi"
We found (8) results for your search.-
Original Articles
Association between electromyographical findings and intensive care unit mortality among mechanically ventilated acute respiratory distress syndrome patients under profound sedation
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2019;31(4):497-503
Abstract
Original ArticlesAssociation between electromyographical findings and intensive care unit mortality among mechanically ventilated acute respiratory distress syndrome patients under profound sedation
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2019;31(4):497-503
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20190087
Views0ABSTRACT
Objective:
To evaluate whether electromyographical findings could predict intensive care unit mortality among mechanically ventilated septic patients under profound sedation.
Methods:
A prospective cohort study that consecutively enrolled moderate-severe acute respiratory distress syndrome (partial pressure of oxygen/fraction of inspired oxygen < 200) patients who were ≥ 18 years of age, dependent on mechanical ventilation for ≥ 7 days, and under profound sedation (Richmond Agitation Sedation Scale ≤ -4) was conducted. Electromyographic studies of the limbs were performed in all patients between the 7th and the 10th day of mechanical ventilation. Sensory nerve action potentials were recorded from the median and sural nerves. The compound muscle action potentials were recorded from the median (abductor pollicis brevis muscle) and common peroneal (extensor digitorum brevis muscle) nerves.
Results:
Seventeen patients were enrolled during the seven months of the study. Nine patients (53%) had electromyographic signs of critical illness myopathy or neuropathy. The risk of death during the intensive care unit stay was increased in patients with electromyographical signs of critical illness myopathy or neuropathy in comparison to those without these diagnostics (77.7% versus 12.5%, log-rank p = 0.02).
Conclusion:
Electromyographical signs of critical illness myopathy or neuropathy between the 7th and the 10th day of mechanical ventilation may be associated with intensive care unit mortality among moderate-severe acute respiratory distress syndrome patients under profound sedation, in whom clinical strength assessment is not possible.
Keywords:Critical illnessElectromyographyIntensive care unitsMortalityPolyneuropathiesPrognosisRespiration, artificialRespiratory distress syndromesedationSee more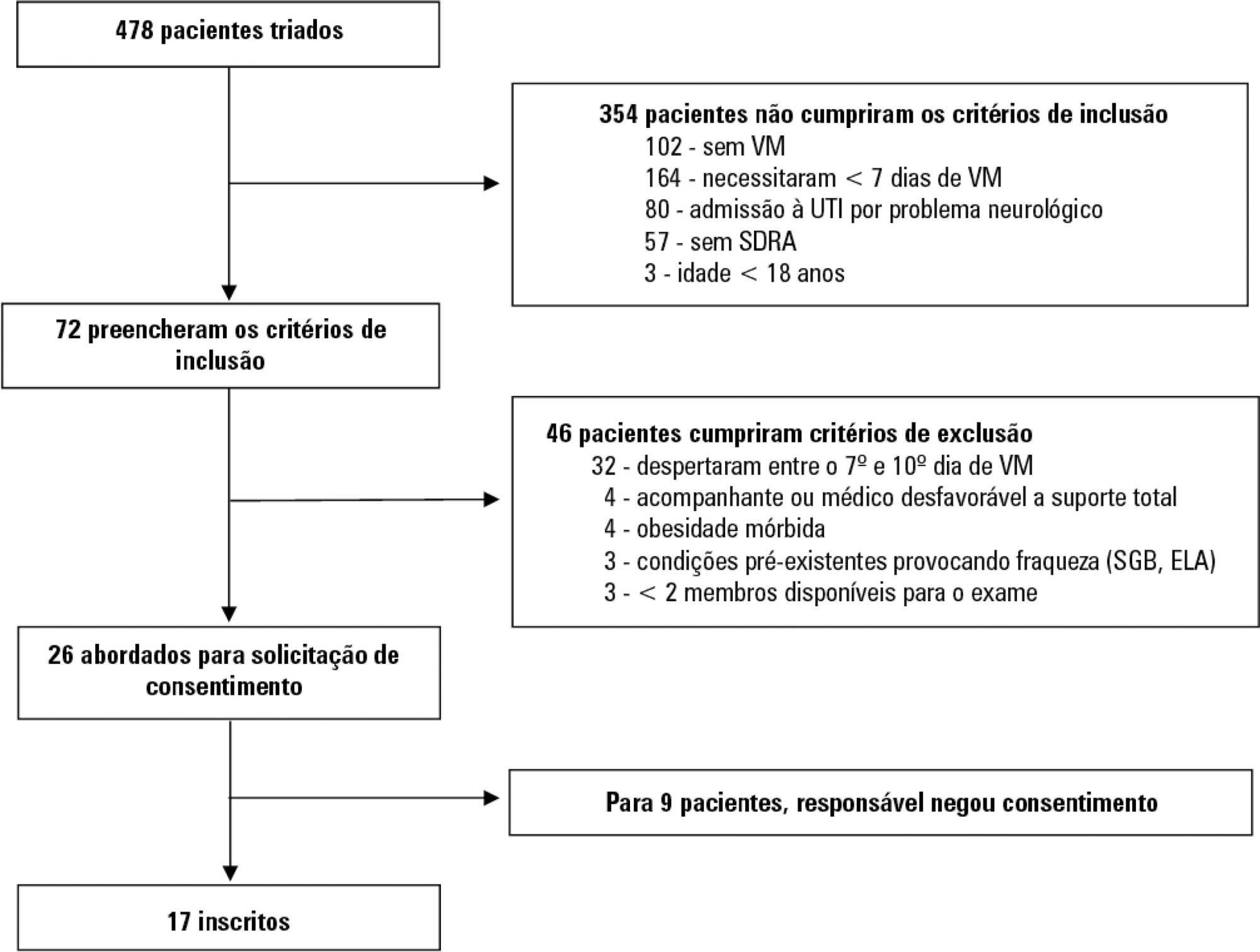
-
Articles
Behavior of lung ultrasound findings during spontaneous breathing trial
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2017;29(3):279-286
Abstract
ArticlesBehavior of lung ultrasound findings during spontaneous breathing trial
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2017;29(3):279-286
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20170038
Views0See moreABSTRACT
Objective:
We aimed to investigate a potential association between B-lines and weaning failure.
Methods:
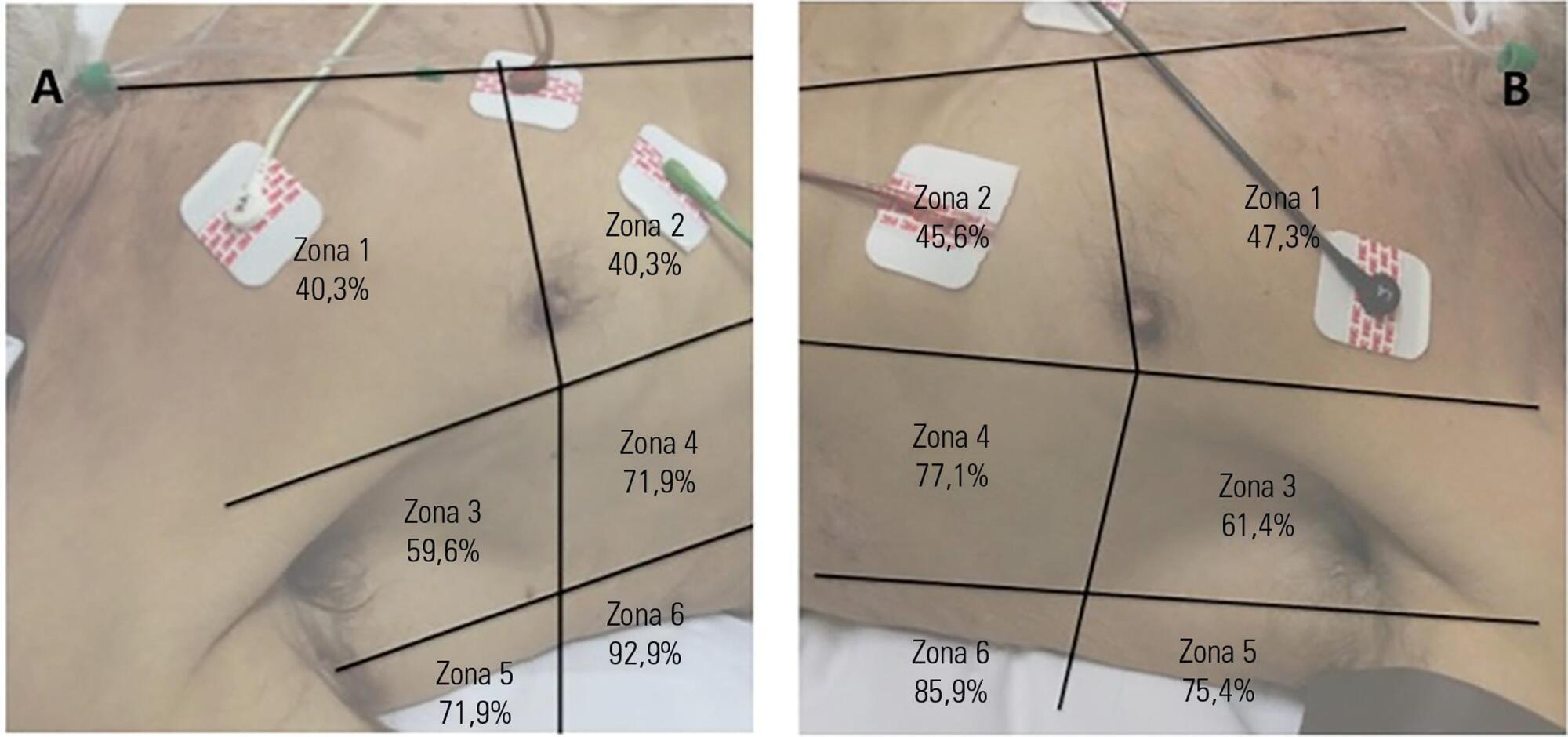
Fifty-seven subjects eligible for ventilation liberation were enrolled. Patients with tracheostomy were excluded. Lung ultrasound assessments of six thoracic zones were performed immediately before and at the exnd of the spontaneous breathing trial. B-predominance was defined as any profile with anterior bilateral B-pattern. Patients were followed up to 48 hours after extubation.
Results:
Thirty-eight individuals were successfully extubated; 11 failed the spontaneous breathing trial and 8 needed reintubation within 48 hours of extubation. At the beginning of the T-piece trial, B-pattern or consolidation was already found at the lower and posterior lung regions in more than half of the individuals and remained non-aerated at the end of the trial. A trend toward loss of lung aeration during spontaneous breathing trials was observed only in the spontaneous breathing trial-failure group (p = 0.07), and there was higher B-predominance at the end of the trial (p = 0.01).
Conclusion:
A loss of lung aeration during the spontaneous breathing trial in non-dependent lung zones was demonstrated in subjects who failed to wean.
-
Original Articles
The reality of patients requiring prolonged mechanical ventilation: a multicenter study
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2015;27(1):26-35
Abstract
Original ArticlesThe reality of patients requiring prolonged mechanical ventilation: a multicenter study
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2015;27(1):26-35
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20150006
Views5See moreObjective:
The number of patients who require prolonged mechanical ventilation increased during the last decade, which generated a large population of chronically ill patients. This study established the incidence of prolonged mechanical ventilation in four intensive care units and reported different characteristics, hospital outcomes, and the impact of costs and services of prolonged mechanical ventilation patients (mechanical ventilation dependency ≥ 21 days) compared with non-prolonged mechanical ventilation patients (mechanical ventilation dependency < 21 days).
Methods:
This study was a multicenter cohort study of all patients who were admitted to four intensive care units. The main outcome measures were length of stay in the intensive care unit, hospital, complications during intensive care unit stay, and intensive care unit and hospital mortality.
Results:
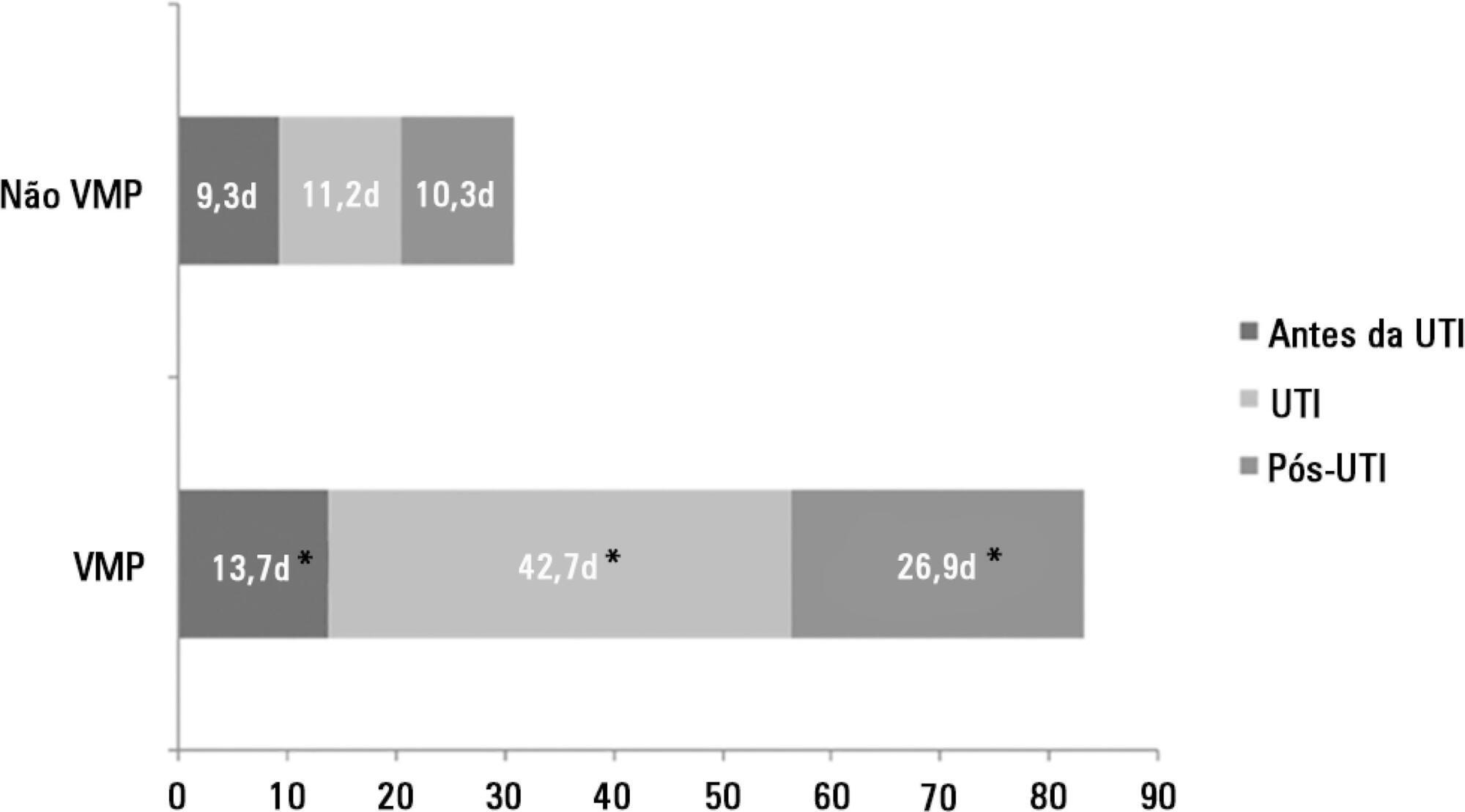
There were 5,287 admissions to the intensive care units during study period. Some of these patients (41.5%) needed ventilatory support (n = 2,197), and 218 of the patients met criteria for prolonged mechanical ventilation (9.9%). Some complications developed during intensive care unit stay, such as muscle weakness, pressure ulcers, bacterial nosocomial sepsis, candidemia, pulmonary embolism, and hyperactive delirium, were associated with a significantly higher risk of prolonged mechanical ventilation. Prolonged mechanical ventilation patients had a significant increase in intensive care unit mortality (absolute difference = 14.2%, p < 0.001) and hospital mortality (absolute difference = 19.1%, p < 0.001). The prolonged mechanical ventilation group spent more days in the hospital after intensive care unit discharge (26.9 ± 29.3 versus 10.3 ± 20.4 days, p < 0.001) with higher costs.
Conclusion:
The classification of chronically critically ill patients according to the definition of prolonged mechanical ventilation adopted by our study (mechanical ventilation dependency ≥ 21 days) identified patients with a high risk for complications during intensive care unit stay, longer intensive care unit and hospital stays, high death rates, and higher costs.
-
Original Articles
Changes in respiratory mechanics during respiratory physiotherapy in mechanically ventilated patients
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2015;27(2):155-160
Abstract
Original ArticlesChanges in respiratory mechanics during respiratory physiotherapy in mechanically ventilated patients
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2015;27(2):155-160
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20150027
Views0See moreABSTRACT
Objective:
To evaluate the changes in ventilatory mechanics and hemodynamics that occur in patients dependent on mechanical ventilation who are subjected to a standard respiratory therapy protocol.
Methods:
This experimental and prospective study was performed in two intensive care units, in which patients dependent on mechanical ventilation for more than 48 hours were consecutively enrolled and subjected to an established respiratory physiotherapy protocol. Ventilatory variables (dynamic lung compliance, respiratory system resistance, tidal volume, peak inspiratory pressure, respiratory rate, and oxygen saturation) and hemodynamic variables (heart rate) were measured one hour before (T-1), immediately after (T0) and one hour after (T+1) applying the respiratory physiotherapy protocol.
Results:
During the period of data collection, 104 patients were included in the study. Regarding the ventilatory variables, an increase in dynamic lung compliance (T-1 = 52.3 ± 16.1mL/cmH2O versus T0 = 65.1 ± 19.1mL/cmH2O; p < 0.001), tidal volume (T-1 = 550 ± 134mL versus T0 = 698 ± 155mL; p < 0.001), and peripheral oxygen saturation (T-1 = 96.5 ± 2.29% versus T0 = 98.2 ± 1.62%; p < 0.001) were observed, in addition to a reduction of respiratory system resistance (T-1 = 14.2 ± 4.63cmH2O/L/s versus T0 = 11.0 ± 3.43cmH2O/L/s; p < 0.001), after applying the respiratory physiotherapy protocol. All changes were present in the assessment performed one hour (T+1) after the application of the respiratory physiotherapy protocol. Regarding the hemodynamic variables, an immediate increase in the heart rate after application of the protocol was observed, but that increase was not maintained (T-1 = 88.9 ± 18.7 bpm versus T0 = 93.7 ± 19.2bpm versus T+1 = 88.5 ± 17.1bpm; p < 0.001).
Conclusion:
Respiratory therapy leads to immediate changes in the lung mechanics and hemodynamics of mechanical ventilation-dependent patients, and ventilatory changes are likely to remain for at least one hour.
-
Original Articles
Functional and psychological features immediately after discharge from an Intensive Care Unit: prospective cohort study
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2013;25(3):218-224
Abstract
Original ArticlesFunctional and psychological features immediately after discharge from an Intensive Care Unit: prospective cohort study
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2013;25(3):218-224
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20130038
Views0See moreOBJECTIVE:
To assess the functional and psychological features of patients immediately after discharge from the intensive care unit.
METHODS:
Prospective cohort study. Questionnaires and scales assessing the degree of dependence and functional capacity (modified Barthel and Karnofsky scales) and psychological problems (Hospital Anxiety and Depression Scale), in addition to the Epworth Sleepiness Scale, were administered during interviews conducted over the first week after intensive care unit discharge, to all survivors who had been admitted to this service from August to November 2012 and had remained longer than 72 hours.
RESULTS:
The degree of dependence as measured by the modified Barthel scale increased after intensive care unit discharge compared with the data before admission (57±30 versus 47±36; p<0.001) in all 79 participants. This impairment was homogeneous among all the categories in the modified Barthel scale (p<0.001) in the 64 participants who were independent or partially dependent (Karnofsky score ≥40) before admission. The impairment affected the categories of personal hygiene (p=0.01) and stair climbing (p=0.04) only in the 15 participants who were highly dependent (Karnofsky score <40) before admission. Assessment of the psychological changes identified mood disorders (anxiety and/or depression) in 31% of the sample, whereas sleep disorders occurred in 43.3%.
CONCLUSIONS:
Patients who remained in an intensive care unit for 72 hours or longer exhibited a reduced functional capacity and an increased degree of dependence during the first week after intensive care unit discharge. In addition, the incidence of depressive symptoms, anxiety, and sleep disorders was high among that population.
-
Original Articles – Clinical Research
Use of a noninvasive ventilation device following tracheotomy: an alternative to facilitate ICU discharge?
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2012;24(2):167-172
Abstract
Original Articles – Clinical ResearchUse of a noninvasive ventilation device following tracheotomy: an alternative to facilitate ICU discharge?
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2012;24(2):167-172
DOI 10.1590/S0103-507X2012000200012
Views0See moreOBJECTIVE: We aimed to assess the use of noninvasive ventilation devices in patients with prolonged weaning following tracheotomy. METHODS: We performed a retrospective observational study using data collected from the clinical records of tracheotomized patients diagnosed with prolonged weaning. The participants were hospitalized in the adult intensive care unit of Moinhos de Vento Hospital, Porto Alegre (RS) between December 2007 and December 2008. RESULTS: In the data collection period, 1,482 patients were admitted to the intensive care unit. In total, 126 patients underwent tracheotomies, and 26 of these patients met the inclusion criteria for participating in the study. The average age of the patients in our sample was 73 ± 12 years. In our sample, 57.7% of the participants were female, and 80.8% were admitted as a result of acute hypoxemic respiratory failure. After the tracheotomy, the patients remained under mechanical ventilation for an average of 29.8 days. After the initiation of the experimental protocol, the tracheotomized patients remained under ventilation for an average of 53.5 days on a portable noninvasive device connected to the tracheotomy. There were three possible outcomes for the patients. They were discharged, were weaned from the noninvasive ventilation, or died in the intensive care unit or hospital ward. In total, 76.9% (20/26) of the patients were discharged from the intensive care unit, and 53.8% (14/26) of the patients were discharged from the hospital. CONCLUSION: The use of noninvasive portable ventilators connected to the tracheotomy may represent an alternative for discontinuing ventilationand discharging tracheotomized patients with prolonged ventilatory weaning from intensive care unit.
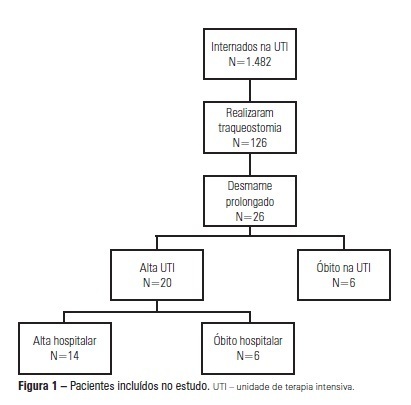
-
Hemodynamic and metabolic effects of passive leg movement in mechanically ventilated patients
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2010;22(4):315-320
Abstract
Hemodynamic and metabolic effects of passive leg movement in mechanically ventilated patients
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2010;22(4):315-320
DOI 10.1590/S0103-507X2010000400001
Views0See moreOBJECTIVE: Limb movements, passively performed by a physiotherapist, have been shown to result in significant increases in critically ill patients’ metabolic and hemodynamic variables. This study objective was to determine whether passive cycling leg movement increases hemodynamic and metabolic variables in sedated mechanical ventilation dependent patients. METHODS: Five sedated mechanical ventilation dependent patients in a 18-bed intensive care unit of a university hospital were evaluated. Passive cycling leg movements were performed for 10min at a 30 movements/min rate. Complete hemodynamical data were recorded and arterial and mixed venous blood sample were collected 5 minutes before and after 5 minutes after the maneuver completion. RESULTS: All patients had increased oxygen consumption (VO2). The VO2 increase occurred with a concomitant drop in mixed venous blood saturation (SvO2), likely from both oxygen extraction ratio (O2ER) and cardiac index (CI) increase. CONCLUSION: passive cycling leg movements may influence hemodynamical and metabolic status in sedated mechanical ventilation-dependent patients.
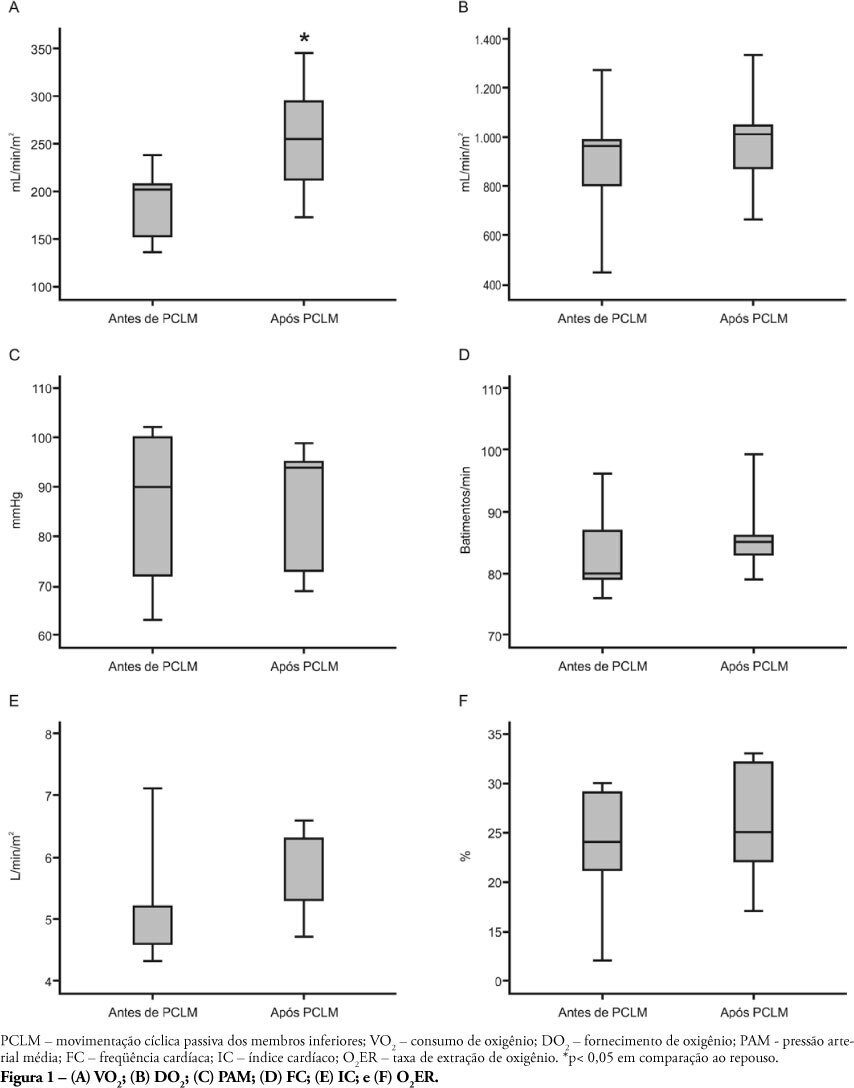
-
Artigos originais
Behavior of the lung mechanics after the application of protocol of chest physiotherapy and aspiration tracheal in patients with invasive mechanical ventilation
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2007;19(2):170-175
Abstract
Artigos originaisBehavior of the lung mechanics after the application of protocol of chest physiotherapy and aspiration tracheal in patients with invasive mechanical ventilation
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2007;19(2):170-175
DOI 10.1590/S0103-507X2007000200005
Views0See moreBACKGROUND AND OBJECTIVES: The chest physiotherapy (CP) in patients submitted to invasive support ventilation acts directly in the breathing system, and it could alter the lung mechanics through the dynamic lung compliance (DynC) and resistance of the breathing system (Rbs). However the alterations after the accomplishment of CP are still controversy. The objective of this study was to evaluate the alterations of the lung mechanics in patients in invasive mechanical ventilation (IMV). METHODS: It was a prospective, randomized, and controlled and crossover study, with patient with more than 48 hours in IMV. The protocol of chest physiotherapy and isolated tracheal aspiration they were randomized for the application order with a window of 24 hours among them. Data of lung mechanics and its varied cardiorespiratory were collected moments before the protocol, immediately after the application of the protocol, 30 minutes and 120 minutes after the application of the protocols. RESULTS: Twelve patients completed the study. Pneumonia was the mean cause respiratory failure (RF). There was not statistical difference among the groups in relation to Cdyn, volume tidal (Vt) and volume minute (Ve). Rbs decreased in a significant way immediately after (of 10.4 ± 3 cmH2O/L/seg for 8.9 ± 2 cmH2O/L/seg; p < 0.02), 30 minutes after (of 10.4 ± 3 cmH2O/L/seg for 9 ± 2 cmH2O/L/seg; p < 0.01) and 120 minutes after (of 10.4 ± 3 cmH2O/L/seg for 9 ± 2 cmH2O/L/seg; p < 0.03) application the protocol of chest physiotherapy. When compared with the protocol of isolated tracheal aspiration it was significantly smaller in the 30 (9 ± 2 cmH2O/L/seg versus10.2 ± 2 cmH2O/L/seg; p < 0.04) and 120 minutes (9 ± 2 cmH2O/L/seg versus 10.4 ± 3 cmH2O/L/seg; p < 0.04). CONCLUSIONS: The protocol of chest physiotherapy was effective in the decrease of Rsr when compared with the aspiration protocol. That decrease was maintained for two hours after its application, what did not happen when only the just accomplished the tracheal aspiration was performed isolated.
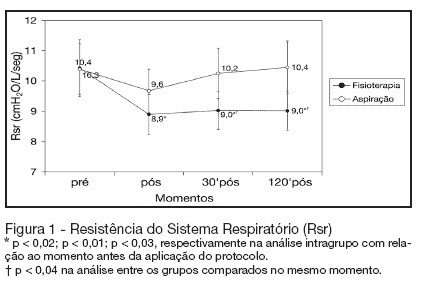
Search
Search in:
KEY WORDS
Case reports Child Coronavirus infections COVID-19 Critical care Critical illness Infant, newborn Intensive care Intensive care units Intensive care units, pediatric mechanical ventilation Mortality Physical therapy modalities Prognosis Respiration, artificial Respiratory insufficiency risk factors SARS-CoV-2 Sepsis Septic shock




