Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2019;31(4):497-503
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20190087
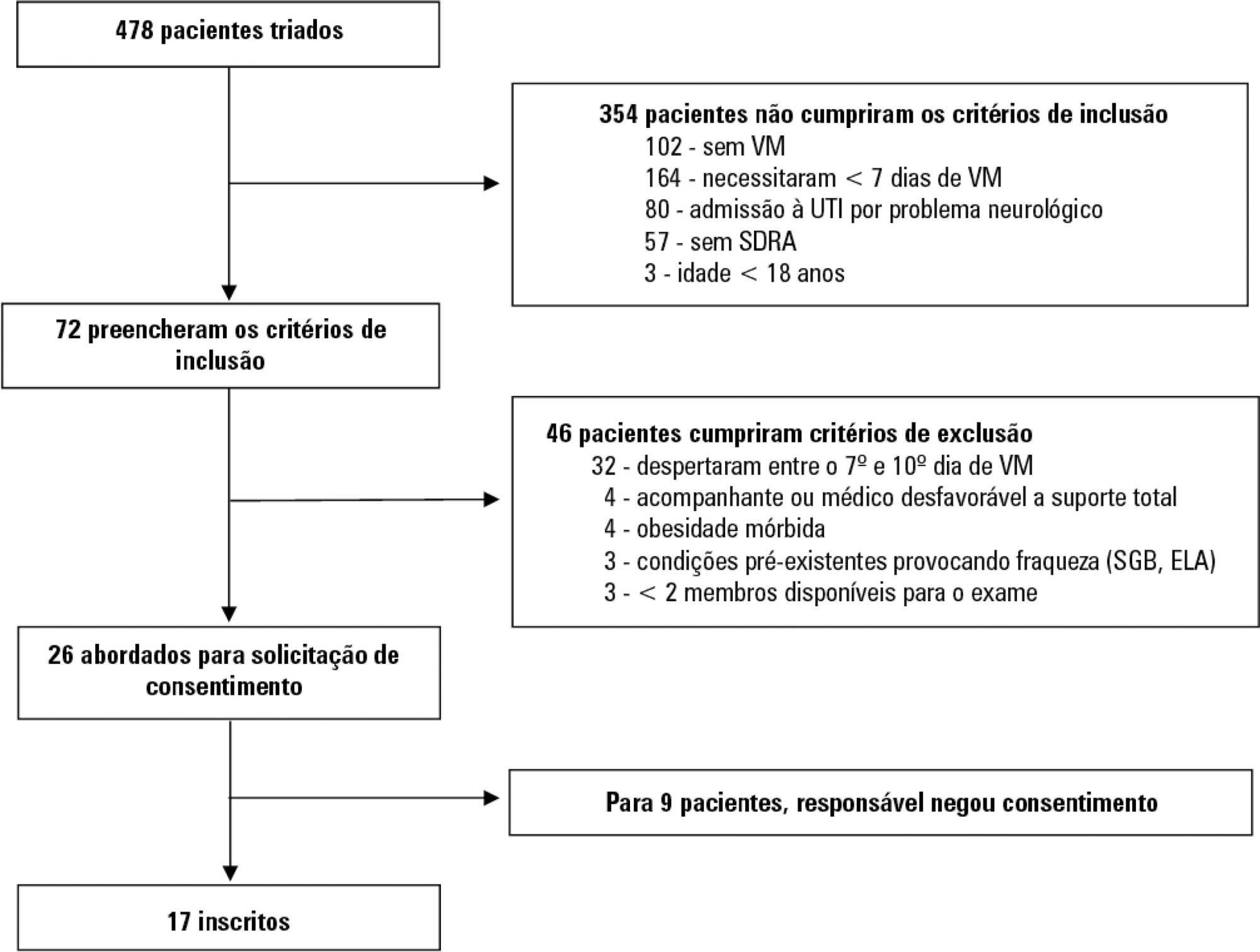
To evaluate whether electromyographical findings could predict intensive care unit mortality among mechanically ventilated septic patients under profound sedation.
A prospective cohort study that consecutively enrolled moderate-severe acute respiratory distress syndrome (partial pressure of oxygen/fraction of inspired oxygen < 200) patients who were ≥ 18 years of age, dependent on mechanical ventilation for ≥ 7 days, and under profound sedation (Richmond Agitation Sedation Scale ≤ -4) was conducted. Electromyographic studies of the limbs were performed in all patients between the 7th and the 10th day of mechanical ventilation. Sensory nerve action potentials were recorded from the median and sural nerves. The compound muscle action potentials were recorded from the median (abductor pollicis brevis muscle) and common peroneal (extensor digitorum brevis muscle) nerves.
Seventeen patients were enrolled during the seven months of the study. Nine patients (53%) had electromyographic signs of critical illness myopathy or neuropathy. The risk of death during the intensive care unit stay was increased in patients with electromyographical signs of critical illness myopathy or neuropathy in comparison to those without these diagnostics (77.7% versus 12.5%, log-rank p = 0.02).
Electromyographical signs of critical illness myopathy or neuropathy between the 7th and the 10th day of mechanical ventilation may be associated with intensive care unit mortality among moderate-severe acute respiratory distress syndrome patients under profound sedation, in whom clinical strength assessment is not possible.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2017;29(2):253-258
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20170035
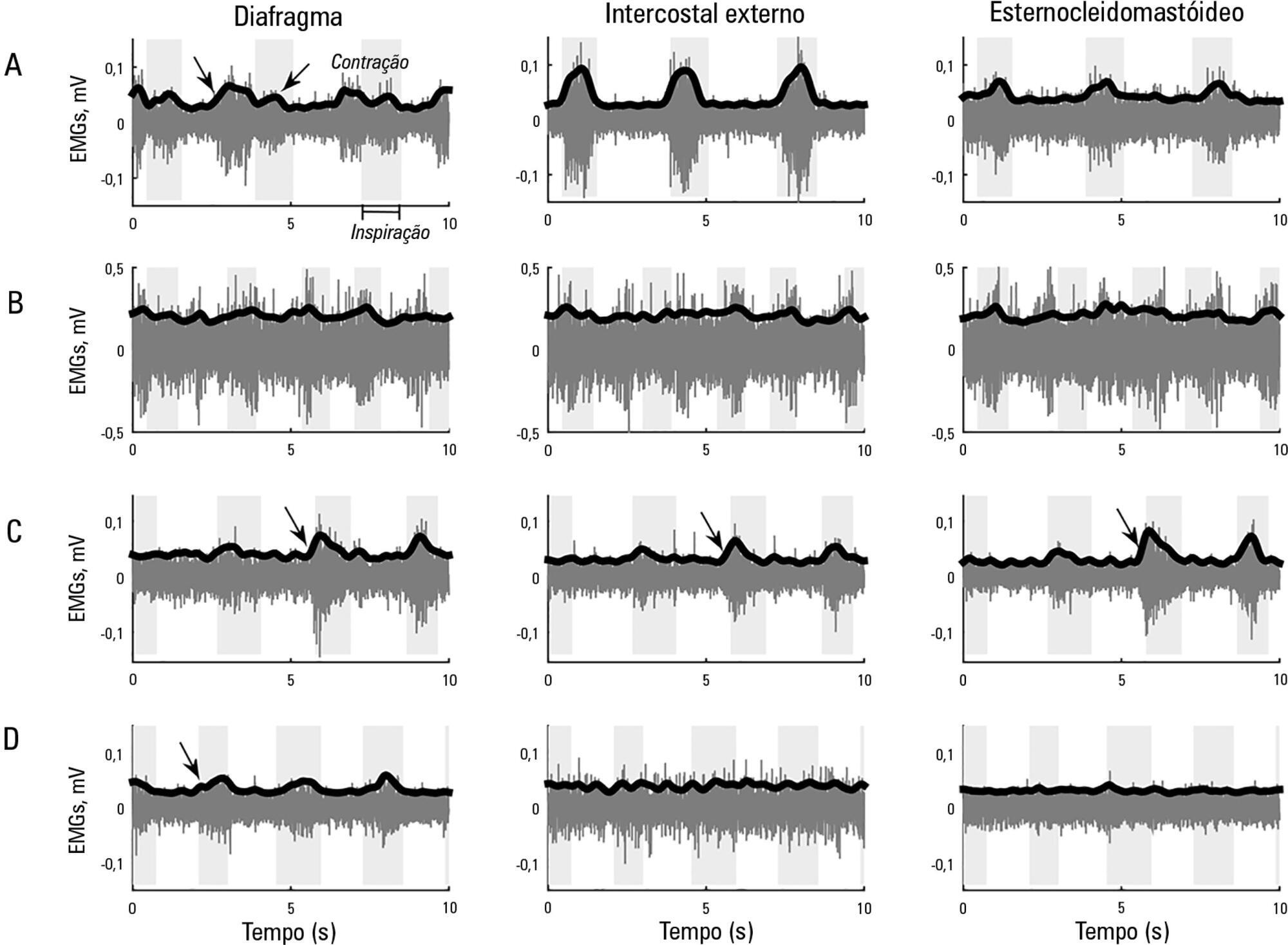
This study aimed to explore the usefulness of measuring respiratory muscle activity in mechanically ventilated patients suffering from acute organophosphate poisoning, with a view towards providing complementary information to determine the best time to suspend ventilatory support. Surface electromyography in respiratory muscles (diaphragm, external intercostal and sternocleidomastoid muscles) was recorded in a young man affected by self-poisoning with an unknown amount of parathion to determine the muscle activity level during several weaning attempts from mechanical ventilation. The energy distribution of each surface electromyography signal frequency, the synchronization between machine and patient and between muscles, acetylcholinesterase enzyme activity, and work of breathing and rapid shallow breathing indices were calculated in each weaning attempt. The work of breathing and rapid shallow breathing indices were not correlated with the failure/success of the weaning attempt. The diaphragm gradually increased its engagement with ventilation, achieving a maximal response that correlated with successful weaning and maximal acetylcholinesterase enzyme activity; in contrast, the activity of accessory respiratory muscles showed an opposite trend.
Search
Search in:
Case reports (56) Child (53) Coronavirus infections (34) COVID-19 (46) Critical care (115) Critical illness (54) Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (26) Infant, newborn (27) Intensive care (72) Intensive care units (256) Intensive care units, pediatric (31) mechanical ventilation (38) Mortality (76) Physical therapy modalities (28) Prognosis (61) Respiration, artificial (119) Respiratory insufficiency (26) risk factors (34) SARS-CoV-2 (28) Sepsis (98)