Abstract
Crit Care Sci. 2023;35(1):73-83
DOI 10.5935/2965-2774.20230374-pt
To understand the perception of medical communication and needs of family members with loved ones in intensive care.
The study was mainly qualitative and exploratory, with thematic analysis of comments made by 92 family members with loved ones in intensive care units when answering in-person interviews comprising the Quality of Communication Questionnaire (QoC) and open-ended questions about their need for additional help, the appropriateness of the place where they received information, and additional comments.
The participants’ mean age was 46.8 years (SD = 11.8), and most of them were female, married and had incomplete or completed elementary education. The following themes were found: perception of characteristics of medical communication; feelings generated by communication; considerations about specific questions in the QoC; family members’ needs; and strategies to overcome needs regarding communication. Characteristics that facilitated communication included attention and listening. Characteristics that made communication difficult included aspects of information sharing, such as inaccessible language; lack of clarity, objectivity, sincerity, and agreement among the team; limited time; and inadequate location. Feelings such as shame, helplessness, and sadness were cited when communication was inadequate. Family members’ needs related to communication included more details about the loved one’s diagnosis, prognosis, and health condition; participation in decisionmaking; and being asked about feelings, spirituality, dying and death. Others were related to longer visitation time, psychological support, social assistance, and better infrastructure.
It is necessary to enhance medical communication and improve hospital infrastructure to improve the quality of care for family members.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2017;29(2):188-194
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20170018
This study aims to identify the satisfaction levels of the family members of patients in intensive care units.
This is a cross-sectional analytical study. General intensive care units offer a variety of services to clinical and surgical patients. For the purpose of this study, a trained interviewer communicated with the families of patients, either before or after visiting hours.
The study included 208 participants: 119 (57.2%) males and 89 (42.8%) females. Seventy-three (35.1%) of the patients attended a private hospital, and 135 (64.9%) attended a public hospital in the city of Al Madinah Al- Munawarah. All of the participants were either family members or friends of patients admitted to the intensive care units at the hospitals. The responses of both groups yielded low scores on the satisfaction index. However, a relatively high score was noted in response to questions 2, 6, and 10, which concerned the care that was extended by the hospital staff to their patients, the courteous attitude of intensive care unit staff members towards patients, and patients' satisfaction with the medical care provided, respectively. A very low score was obtained for item 11, which was related to the possibility for improvements to the medical care that the patients received. Overall, greater satisfaction with the services offered by the public intensive care units was reported compared to the satisfaction with the services offered by the private intensive care units.
An overall low score on the satisfaction index was obtained, and further studies are recommended to assess the current situation and improve the satisfaction and quality of care provided by intensive care units.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2014;26(4):339-346
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20140052
This study aimed to determine which visitation policy was the most predominant in Brazilian intensive care units and what amenities were provided to visitors.
Eight hundred invitations were sent to the e-mail addresses of intensivist physicians and nurses who were listed in the research groups of the Brazilian Association of Intensive Care Network and the Brazilian Research in Intensive Care Network. The e-mail contained a link to a 33-item questionnaire about the profile of their intensive care unit.
One hundred sixty-two questionnaires from intensive care units located in all regions of the country, but predominantly in the Southeast and South (58% and 16%), were included in the study. Only 2.6% of the intensive care units reported having liberal visitation policies, while 45.1% of the intensive care units allowed 2 visitation periods and 69.1% allowed 31-60 minutes of visitation per period. In special situations, such as end-of-life cases, 98.7% of them allowed flexible visitation. About half of them (50.8%) did not offer any bedside amenities for visitors. Only 46.9% of the intensive care units had a family meeting room, and 37% did not have a waiting room.
Restrictive visitation policies are predominant in Brazilian intensive care units, with most of them allowing just two periods of visitation per day. There is also a lack of amenities for visitors.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2011;23(1):78-86
DOI 10.1590/S0103-507X2011000100013
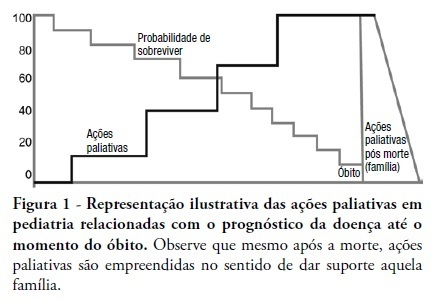
This review discusses the main dilemmas and difficulties related to end-of-life decision's in children with terminal and irreversible diseases and propose a rational sequence for delivering palliative care to this patients' group. The Medline and Lilacs databases were searched using the terms 'end of life', 'palliative care', 'death' and 'terminal disease' for articles published in recent years. The most relevant articles and those enrolling pediatric patients were selected and compared to previous authors' studies in this field. The current Brazilian Medical Ethics Code (2010) was analyzed regarding end-oflife practices and palliative care for terminal patients. Lack of knowledge, insufficient specific training, and legal concerns are the main reasons why end-of-life decisions in terminal children are based on medical opinion with scarce family participation. The current Brazilian Medical Ethics Code (2010) fully supports end-of-life decisions made consensually with active family participation. Honest dialogue with the family regarding diagnostic, prognostic, therapeutic and palliative care measures should be established gradually to identify the best strategy to meet the child's end-of-life needs. Treatment focused on the child's welfare combined with the family's participation is the basis for successful palliative care of children with terminal diseases.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2009;21(1):32-37
DOI 10.1590/S0103-507X2009000100005
OBJECTIVES: To know the needs and level of family members' satisfaction is an essential part of the care provided to critically ill patients in intensive care units. The objective of this study was to identify the level of family members' satisfaction in an intensive care unit. METHODS: A descriptive survey was carried out in the general adult intensive care unit of the Hospital Português (Salvador - BA) from November 2007 to January 2008. Jonhson's 14-question modified version of the Critical Care Family Needs Inventory was used to evaluate satisfaction of family members. RESULTS: Fifty three family members were included, mean age was 44 years and 68% were female. The median of family members satisfaction level was 11 (IQI = 9-13). Critical Care Family Need Inventory, questions with higher percentiles of satisfaction were those stating that family members felt that the patient was receiving the best possible care (96%) and that the information provided was honest (96%). The questions with lower percentiles of satisfaction were those stating that family members believed that someone in the intensive care unit had shown interest in their feelings (45%) and that a healthcare professional had explained how the intensive care unit equipment was used (41%). CONCLUSIONS: Most family members positively evaluated the intensive care unit professionals in the questions related to communication, attitude and patient care. However, there was a lower level of satisfaction in the questions related to the intensive care unit professionals' ability to comfort family members.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2008;20(4):370-375
DOI 10.1590/S0103-507X2008000400009
OBJECTIVE: The aim of this study was to understand the experience of family members, during a patient's stay in the intensive care unit of public and private hospitals using an approximation to the phenomenology referential. METHODS: We interviewed 27 relatives of adult patients, 10 from a public institution and 17 from a private one. RESULTS: From analyses of interviews in a public institution, four thematic categories emerged. In a private institution six categories were identified. Searching for differences and similarities, four similar thematic categories were perceived in both institutions and two categories were absent in the public hospital. CONCLUSION: There are no significant differences between categories in private and public hospitals. This indicates that family behavior and reactions to patient's admission to the ICU are not associated with social or financial aspects. However, a greater knowledge of government policies and programs is necessary, because they favor humanization by allowing family members to accompany the patient in tertiary services.
Search
Search in:
Case reports (56) Child (53) Coronavirus infections (34) COVID-19 (46) Critical care (116) Critical illness (54) Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (26) Infant, newborn (27) Intensive care (72) Intensive care units (256) Intensive care units, pediatric (31) mechanical ventilation (38) Mortality (76) Physical therapy modalities (28) Prognosis (61) Respiration, artificial (119) Respiratory insufficiency (26) risk factors (34) SARS-CoV-2 (28) Sepsis (98)