Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2013;25(1):39-43
DOI 10.1590/S0103-507X2013000100008
OBJECTIVE: The objective of this study was to use a cycle ergometer to assess cardiorespiratory changes during active exercise and to verify patients' satisfaction with this type of activity. METHODS: A single intervention involving active lower limb exercise was performed with a cycle ergometer (without load) for 5 minutes. The following variables were measured before, during and immediately after exercise: heart rate, blood pressure, respiratory rate, peripheral oxygen saturation and the Borg dyspnea scale score. Following the exercise, the patients answered a questionnaire to evaluate their satisfaction with this type of activity. RESULTS: A total of 38 patients (65% male) with a mean age of 48 ± 16 years old participated in the study. Enrolled patients presented a sequential organ failure assessment (SOFA) score of 2 (0 - 5 scale). During the exercise, 16% of the patients used ventilation support and 55% of them were breathing at room air. A comparison of the initial and final values of the variables indicated increases in the heart rate (92±17 beats/min vs. 95±18 beats/min; p<0.05), the respiratory rate (19 ± 8 breaths/min vs. 23±8 breaths/min; p<0.05) and the Borg dyspnea scale score (1.3±1.8 vs. 2.8±2.2; p<0.05). In addition, 85% of the patients reported enjoying the activity. Only 25% of the patients reported some discomfort, and 100% of the patients wanted to repeat this type of activity in future treatments. CONCLUSION: During the cycle ergometer exercises, minor cardiorespiratory changes were observed in the patients. The evaluated patients reported high satisfaction with this type of activity.

Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2009;21(3):283-291
DOI 10.1590/S0103-507X2009000300008
OBJECTIVES: The intensive care unit emerged to improve and concentrate material and human resources for the care of critical patients, and need for constant observation and continuous assistance. However, patients in intensive care unit requires exceptional care, directed not only to the physiopathological problem, but also towards the psychosocial issue, now intimately interlinked to the physical disease. In this ambient, very demanding for capability of the multiprofessional team, presence of the physiotherapist has become more frequent. This study aims to verify if the attitude of an experienced physiotherapist in the intensive care unit is humanized. METHODS: To evaluate physiotherapy care humanization, a questionnaire was prepared and patients over 18 years of age, lucid and staying in intensive care unit for 24 hours or more were included. RESULTS: Forty four patients were interviewed and 95.5% of these considered the physiotherapy care as humanized. Positive association was observed between dissatisfaction with the items of dignity, communication, warranty and empathy, and a dehumannized physiotherapy care. Patients who evaluated warranty as negative had a twofold greater chance (0.7 - 5.3) of perceiving care as dehumanized. Patients who evaluated empathy as negative had a 1.6 (0.8 - 3.4) times greater chance of perceiving care as dehumanized. CONCLUSION: Physiotherapy care given in the intensive care unit was marked by good assistance, attention provided to the patient and quality of treatment, characterizing humanized care.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2006;18(1):34-37
DOI 10.1590/S0103-507X2006000100007
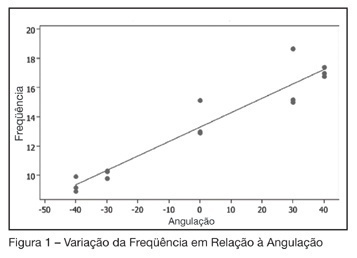
BACKGROUD AND OBJECTIVES: The high frequency oral oscillation therapy (HFOO) is carried through a plastic device which promotes the clearance of pulmonary sputum. This possesses a metallic sphere which, oscillates during the expiration, generating oscillatory positive expiratory pressure. The aim of this study was to verify the performance of the national device of HFOO (Shaker, NCS, São Paulo) in relation to frequency of oscillation and expiratory pressure with variation of flow and inclination. METHODS: The device was imprisoned to a circuit that consisted of a pneumotacograph and a mechanical ventilator. This had the varied flow and during this variation the expiratory pressure and the frequency of oscillation of the device were measured in angulations which, varied of +40º to -40º. RESULTS: Significant correlation between flow and expiratory pressure in each level of inclination was found. A bigger frequency of oscillation and pressure was evidenced in the positive angulations with the biggest flows (50 and 60 L/min). CONCLUSIONS: The high frequency oral oscillation device can be used as an assist for the air way clearance therapy during mechanical ventilation.
Search
Search in:
Case reports (56) Child (53) Coronavirus infections (34) COVID-19 (46) Critical care (116) Critical illness (54) Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (26) Infant, newborn (27) Intensive care (72) Intensive care units (256) Intensive care units, pediatric (31) mechanical ventilation (38) Mortality (76) Physical therapy modalities (28) Prognosis (61) Respiration, artificial (119) Respiratory insufficiency (26) risk factors (34) SARS-CoV-2 (28) Sepsis (98)