Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2019;31(4):504-510
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20190067
To evaluate the risk factors for protein-caloric inadequacy in critically ill patients.
Prospective cohort study of patients hospitalized in an adult intensive care unit between February and November 2017. Patients were followed for 7 days. The conditional probability of inadequacy was calculated using the Kaplan-Meier method and the 95% log-rank test. To assess the risk of inadequacy, crude and adjusted hazard ratios (HR) were calculated using Cox regression with a 95% confidence interval.
Of the 130 patients, 63.8% were male, 73.8% were <60 years of age, and 49.2% were diagnosed with trauma. The mean APACHE II score was 24 points, and 70.0% of the patients had a protein-caloric adequacy >80%. In the univariate analysis, the significant variables for inadequacy were use of vasoactive drugs, interruptions of diet and failure to initiate nutrition early. In the final model, patients who presented with vomiting/gastric residue (adjusted HR = 22.5; 95%CI 5.14 - 98.87) and fasting for extubation (adjusted HR = 14.75; 95%CI 3.59 - 60.63) and for examinations and interventions (adjusted HR = 12.46; 95%CI 4.52 - 34.36) had a higher risk of not achieving protein-caloric adequacy.
Achievement of nutritional goals > 80.0% occurred in 70.0% of patients. The risk factors for protein-caloric inadequacy were nutritional interruptions, especially due to vomiting/gastric residue and fasting for extubation, exams and surgical procedures.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2019;31(4):511-520
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20190088
To characterize patients with chronic critical illness and identify predictors of development of chronic critical illness.
Prospective data was collected for 1 year in the intensive care unit of a general hospital in Southern Brazil. Three logistic regression models were constructed to identify factors associated with chronic critical illness.
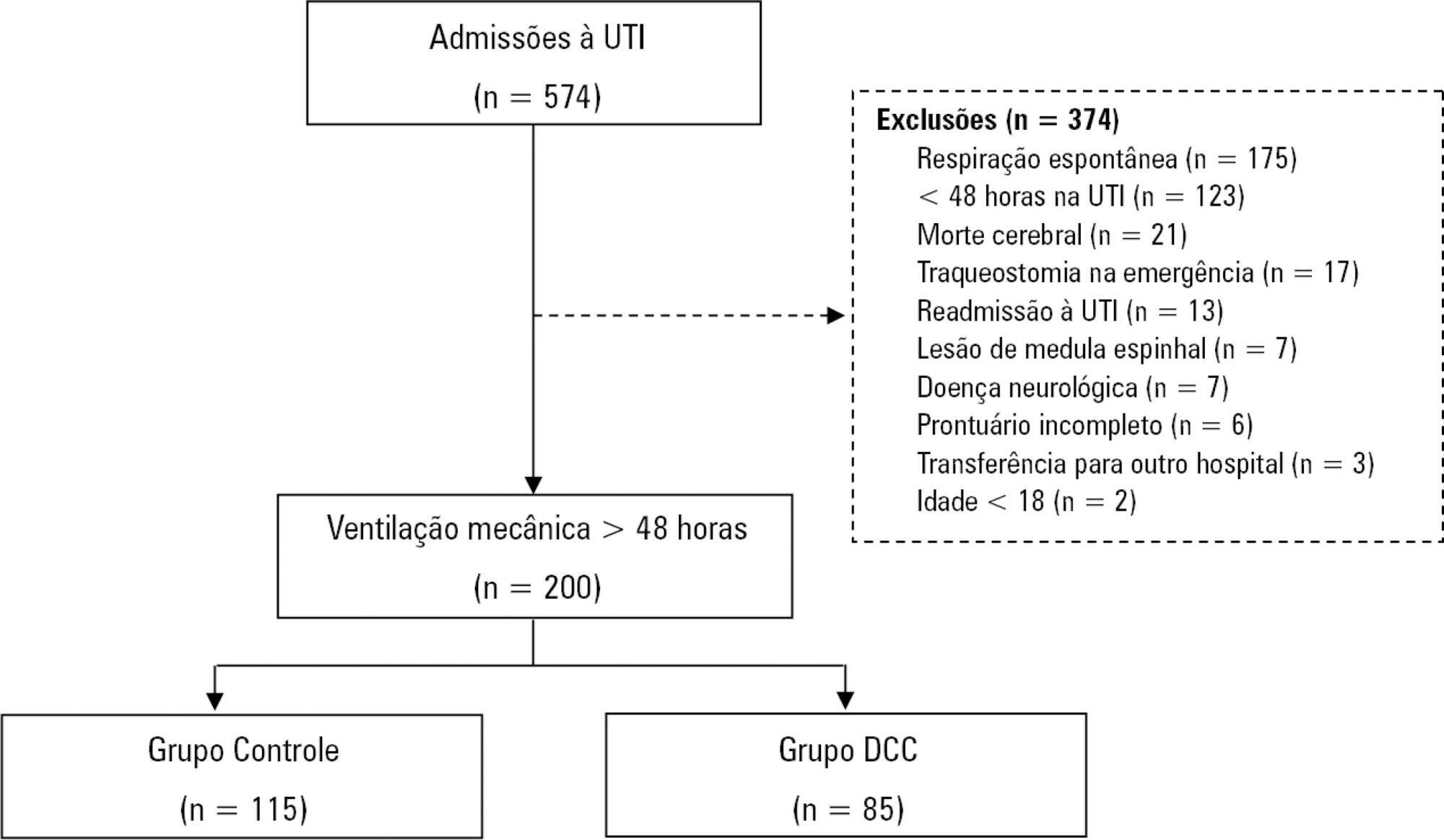
Among the 574 subjects admitted to the intensive care unit, 200 were submitted to mechanical ventilation. Of these patients, 85 (43.5%) developed chronic critical illness, composing 14.8% of all the patients admitted to the intensive care unit. The regression model that evaluated the association of chronic critical illness with conditions present prior to intensive care unit admission identified chronic renal failure in patients undergoing hemodialysis (OR 3.57; p = 0.04) and a neurological diagnosis at hospital admission (OR 2.25; p = 0.008) as independent factors. In the model that evaluated the association of chronic critical illness with situations that occurred during intensive care unit stay, muscle weakness (OR 2.86; p = 0.01) and pressure ulcers (OR 9.54; p < 0.001) had the strongest associations. In the global multivariate analysis (that assessed previous factors and situations that occurred in the intensive care unit), hospital admission due to neurological diseases (OR 2.61; p = 0.03) and the development of pressure ulcers (OR 9.08; p < 0.001) had the strongest associations.
The incidence of chronic critical illness in this study was similar to that observed in other studies and had a strong association with the diagnosis of neurological diseases at hospital admission and chronic renal failure in patients undergoing hemodialysis, as well as complications developed during hospitalization, such as pressure ulcers and muscle weakness.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2019;31(4):521-528
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20190065
To compare the measurement properties (internal consistency, intra and interrater reliability, construct validity, and ceiling and floor effects) of the Functional Status Score for the ICU (FSS-ICU) and the Functional Independence Measure (FIM-motor domain).
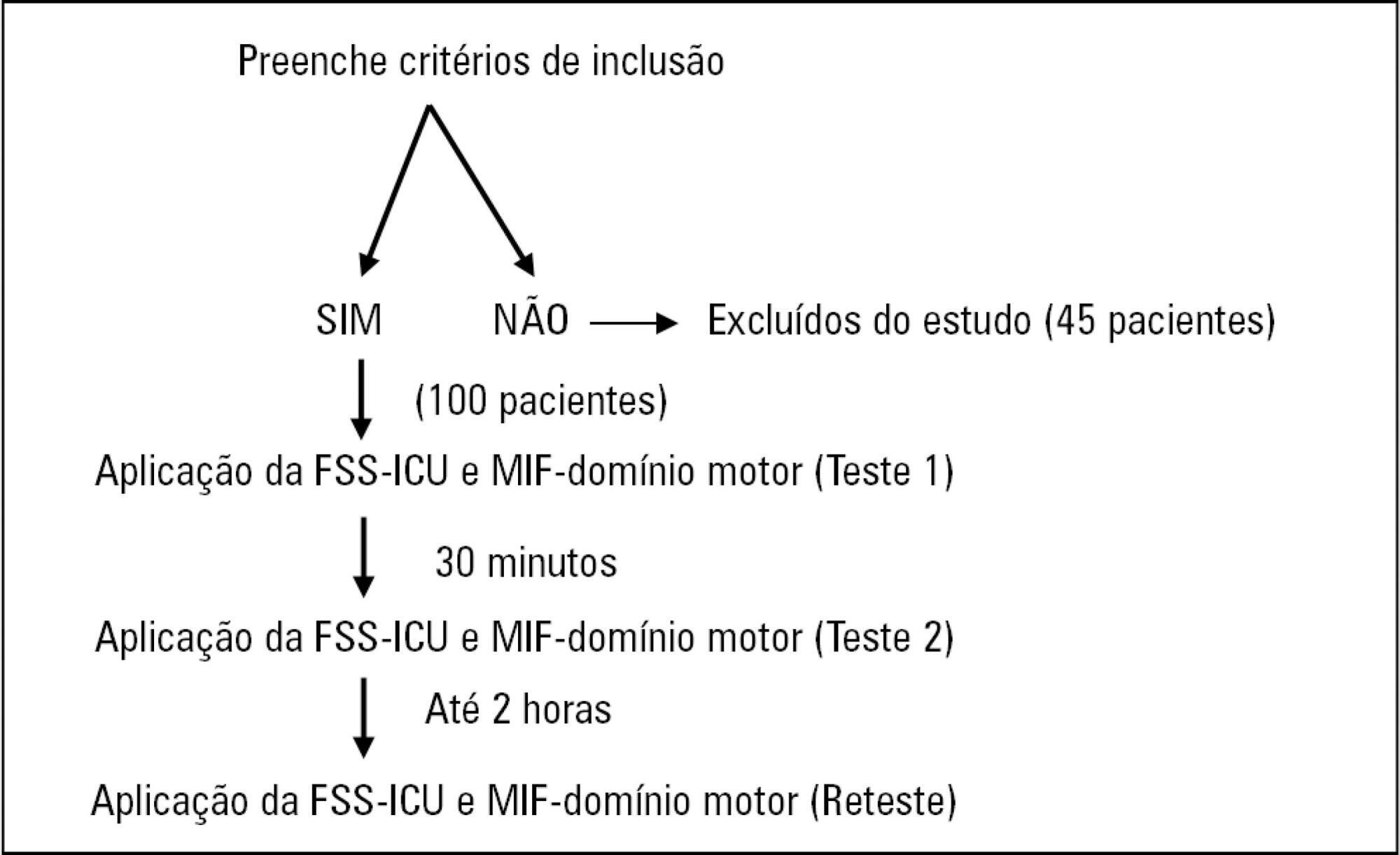
In this study of measurement properties, the FSS-ICU and FIM were applied to 100 patients (72.1 ± 15.9 years; 53% male; Sequential Organ Failure Assessment = 11.0 ± 3.5 points, Simplified Acute Physiology Score 3 = 50.2 ± 16.8 points) in an intensive care unit at baseline and after 2 hours by physiotherapist 1 (test and retest) and 30 minutes after baseline by physiotherapist 2. The measurement properties evaluated were internal consistency (Cronbach's alpha), intra- and interrater reliability (intraclass correlation coefficient), agreement (standard error of measurement) and minimum detectable change at a 90% confidence level, ceiling and floor effects (frequency of maximum and minimum scores) and construct validity (Pearson's correlation).
The FSS-ICU and FIM presented adequate internal consistency (Cronbach's alpha, FSS-ICU = 0.95 and FIM = 0.86), intra-and interrater reliability for overall FSS-ICU and FIM score (ICC > 0.75), agreement (minimum detectable change at a 90% confidence level: FSS-ICU and FIM = 1.0 point; standard error of measurement: FSS-ICU = 2% and FIM = 1%) and construct validity (r = 0.94; p < 0.001). However, the FSS-ICU and FIM presented ceiling effects (maximum score for 16% of patients for the FSS-ICU and 18% for the FIM).
The FSS-ICU and FIM present adequate measurement properties to assess functionality in critically ill patients, although they present ceiling effects.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2019;31(4):529-535
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20190066
To measure and compare the functionality of patients after discharge from the intensive care unit and at the time of hospital discharge.
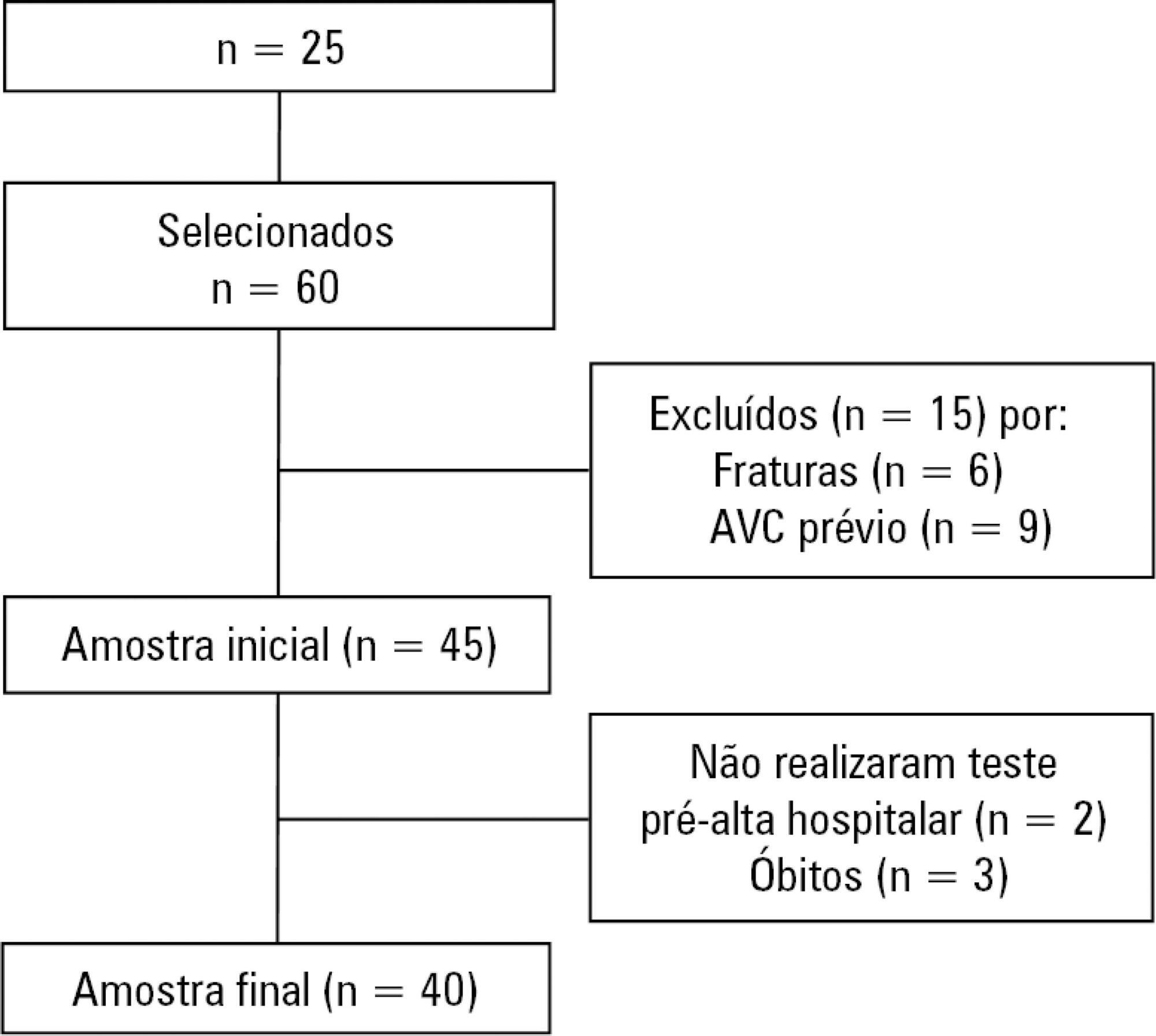
Quantitative study of a prospective cohort performed between August of 2016 and December of 2017 at a university hospital. A 10-meter walk test was performed at 2 timepoints: after discharge from the intensive care unit and prior to hospital discharge. The data were analyzed using Student's t-test and Pearson or Spearman correlation. Statistical Package for Social Science (SPSS) version 21.0 was used for the analysis, and p ≤ 0.05 was adopted as the level of significance.
Forty patients, with a mean age of 57.1 ± 12.2 years and with a predominance of males (60%), were evaluated. For the post-intensive care unit test, a mean speed of 0.48m/s was observed, and for the pre-hospital discharge test, there was an increase to 0.71m/s, evidencing functional evolution during the hospital stay (p < 0.001).
There was significant improvement in walking speed at the time of hospital discharge when compared to the walking speed at the time of intensive care unit discharge.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2019;31(4):447-455
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20190085
To evaluate the impact of an opioid-sparing pain management protocol on overall opioid consumption and clinical outcomes.
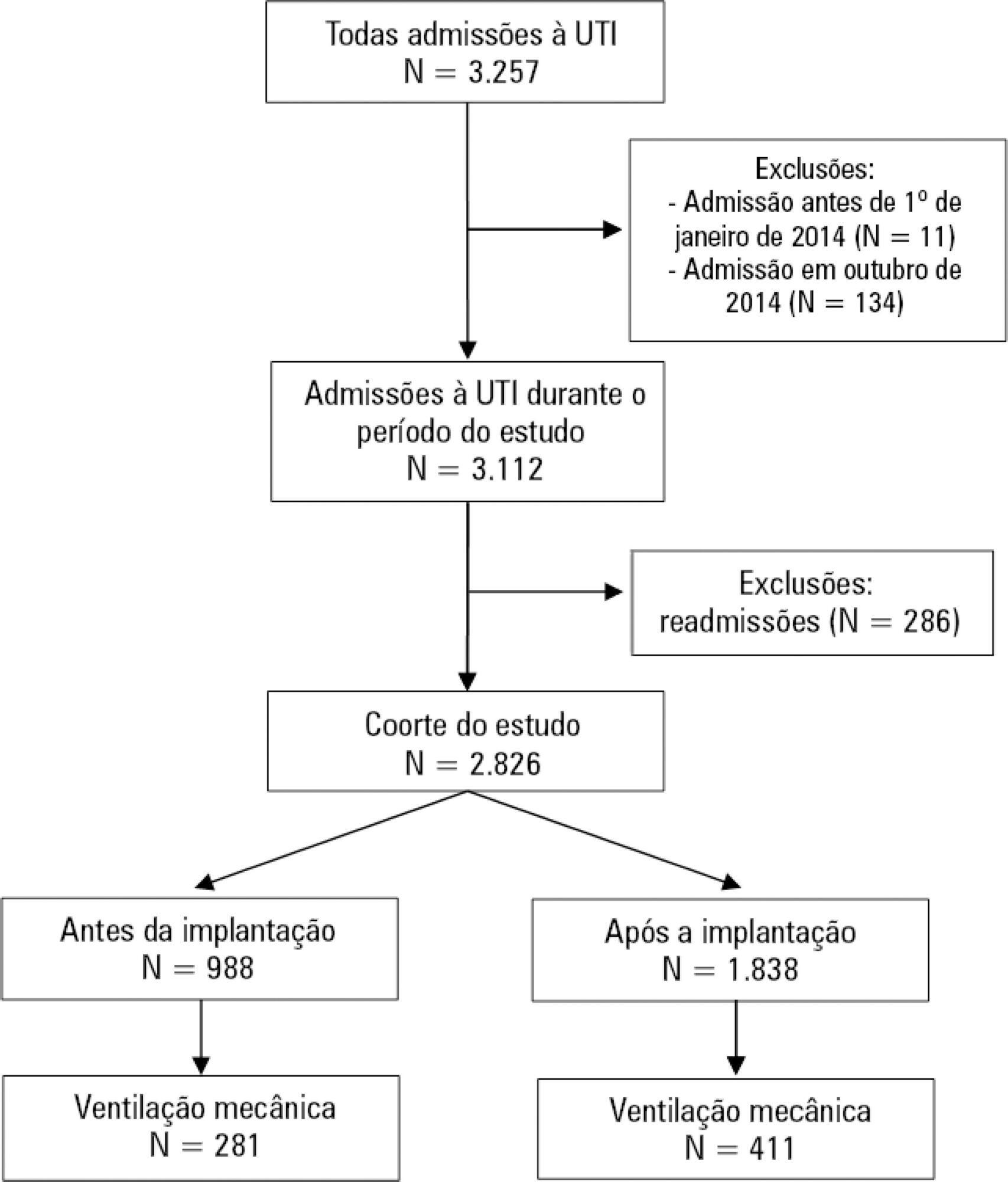
This was a single-center, quasi-experimental, retrospective, before and after cohort study. We used an interrupted time series to analyze changes in the levels and trends of the utilization of different analgesics. We used bivariate comparisons in the before and after cohorts as well as logistic regression and quantile regression for adjusted estimates.
We included 988 patients in the preintervention period and 1,838 in the postintervention period. Fentanyl consumption was slightly increasing before the intervention (β = 16; 95%CI 7 - 25; p = 0.002) but substantially decreased in level with the intervention (β = - 128; 95%CI -195 - -62; p = 0.001) and then progressively decreased (β = - 24; 95%CI -35 - -13; p < 0.001). There was an increasing trend in the utilization of dipyrone. The mechanical ventilation duration was significantly lower (median difference: - 1 day; 95%CI -1 - 0; p < 0.001), especially for patients who were mechanically ventilated for a longer time (50th percentile difference: -0.78; 95%CI -1.51 - -0.05; p = 0.036; 75th percentile difference: -2.23; 95%CI -3.47 - -0.98; p < 0.001).
A pain management protocol could reduce the intensive care unit consumption of fentanyl. This strategy was associated with a shorter mechanical ventilation duration.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2019;31(4):456-463
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20190078
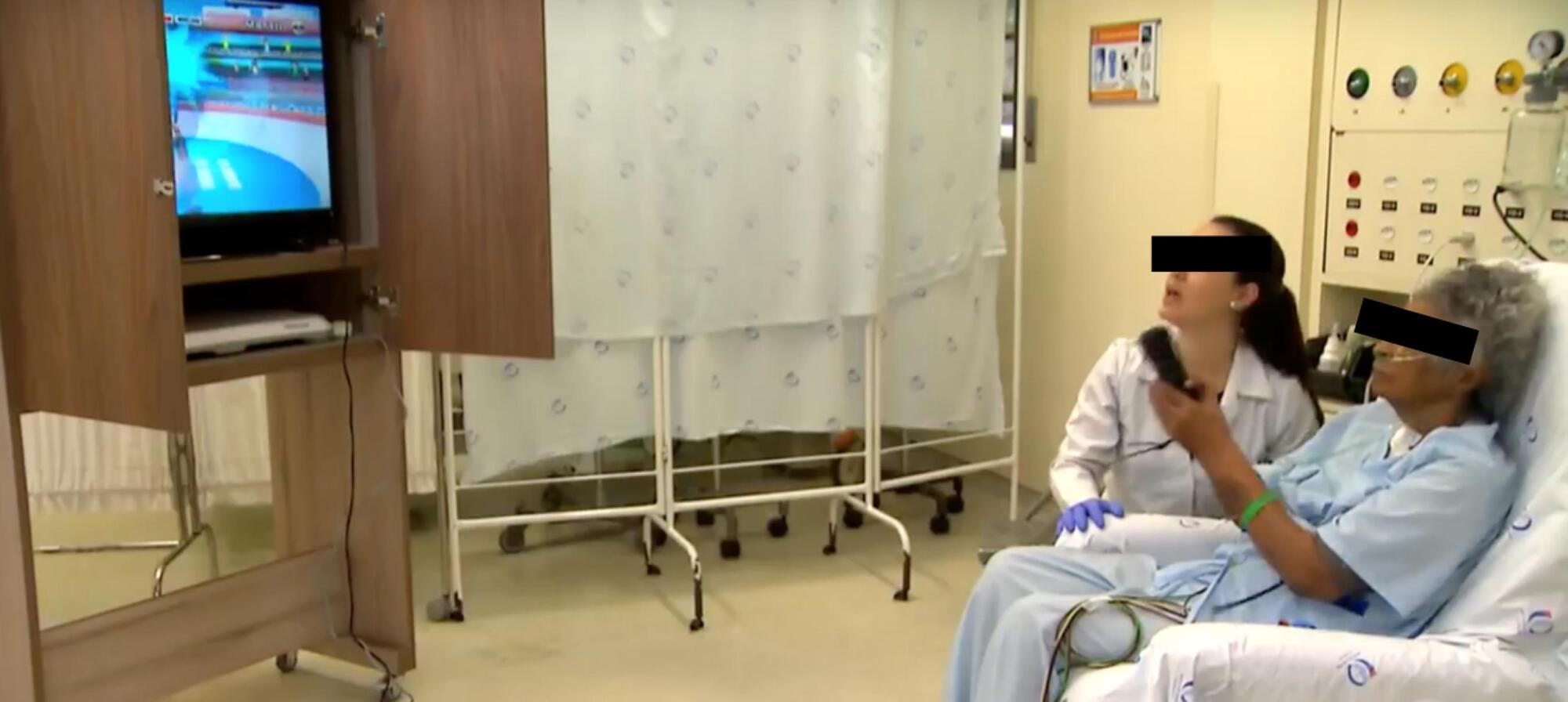
To evaluate the level of activity that Nintendo WiiTM can elicit in intensive care unit patients and its associated safety and patient satisfaction.
Experimental, single-center study performed at a tertiary care hospital. Patients ≥ 18 years old who were admitted to the intensive care unit, participated in videogames as part of their physical therapy sessions and did not have mobility restrictions were included. Th exclusion criteria were the inability to comprehend instructions and the inability to follow simple commands. We included n = 60 patients and performed 100 sessions. We used the Nintendo WiiTM gaming system in the sessions. An accelerometer measured the level of physical activity of patients while they played videogames. We evaluated the level of activity, the modified Borg scale scores, the adverse events and the responses to a questionnaire on satisfaction with the activity.
One hundred physical therapy sessions were analyzed. When the patients played the videogame, they reached a light level of activity for 59% of the session duration and a moderate level of activity for 38% of the session duration. No adverse events occurred. A total of 86% of the patients reported that they would like to play the videogame in their future physical therapy sessions.
Virtual rehabilitation elicited light to moderate levels of activity in intensive care unit patients. This therapy is a safe tool and is likely to be chosen by the patient during physical therapy.

Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2019;31(4):464-473
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20190072
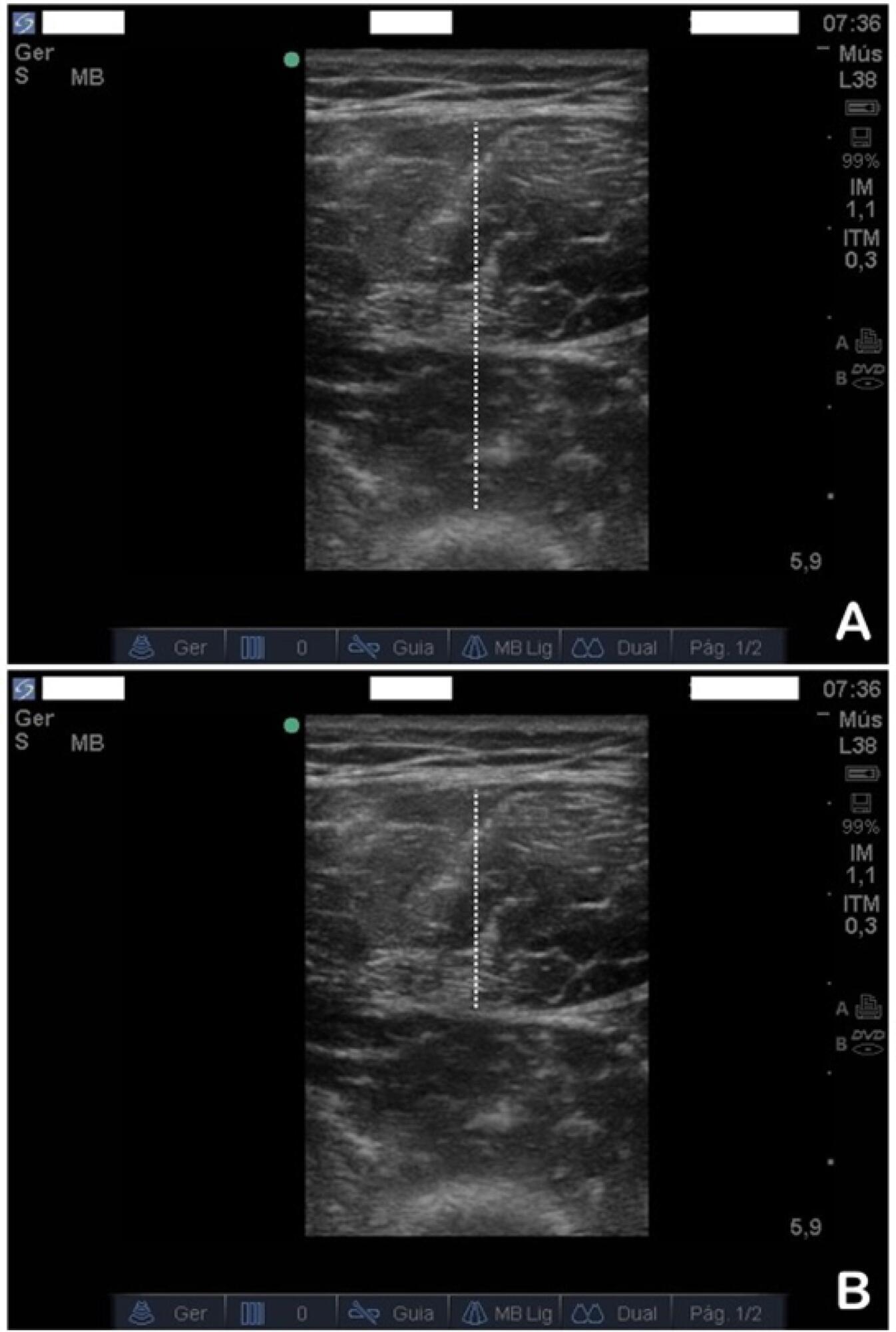
To evaluate the safety and feasibility of the ultrasound assessment of quadriceps in the emergency setting. To assess the intra- and interrater reliability for the acquisition and analysis of ultrasound images of muscle thickness and echogenicity in critically ill trauma patients between health professionals with different levels of expertise.
Diagnostic accuracy study. Two examiners (expert and novice) acquired ultrasound images from ten patients; an experienced, blinded analyst quantified the images. In a separate group of ten patients, two analysts (expert and novice) quantified quadriceps muscle thickness and echogenicity (square or trace method) from images acquired by one examiner.
Excellent reliability was found for image acquisition and analysis (intraclass correlation coefficients > 0.987; p < 0.001). The standard error of the measurement values ranged from 0.01 - 0.06cm for muscle thickness and from 0.75 - 2.04 arbitrary units for muscle echogenicity. The coefficients of variation were < 6% for thickness and echogenicity. The echogenicity values were higher when using the square technique than when using the tracing technique (p = 0.003).
Ultrasound is safe, feasible, and reliable for muscle assessment in critically ill trauma patients, regardless of the assessor's level of expertise.
Search
Search in:
Case reports (56) Child (53) Coronavirus infections (34) COVID-19 (46) Critical care (116) Critical illness (54) Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (26) Infant, newborn (27) Intensive care (72) Intensive care units (256) Intensive care units, pediatric (31) mechanical ventilation (38) Mortality (76) Physical therapy modalities (28) Prognosis (61) Respiration, artificial (119) Respiratory insufficiency (26) risk factors (34) SARS-CoV-2 (28) Sepsis (98)