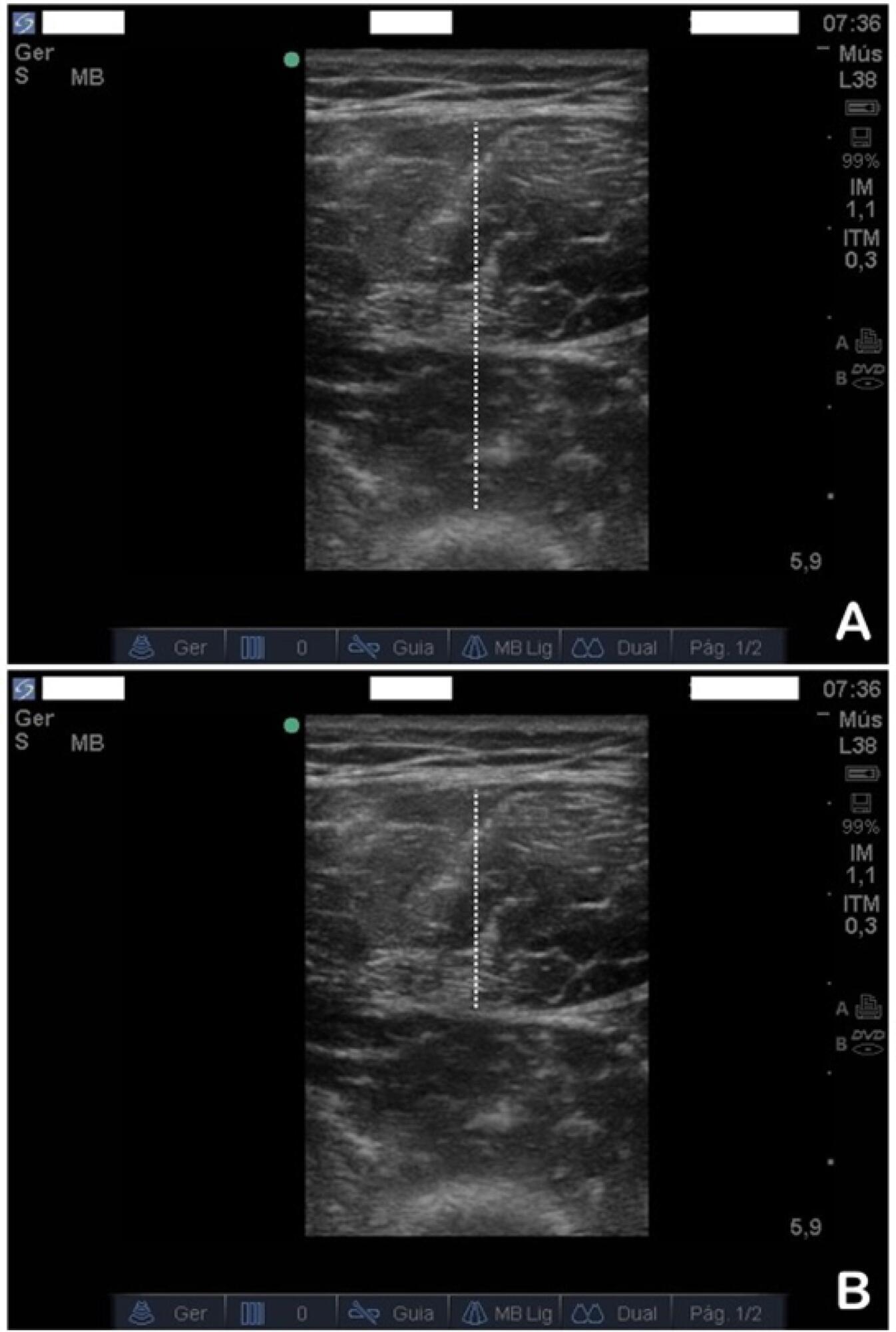
To evaluate the safety and feasibility of the ultrasound assessment of quadriceps in the emergency setting. To assess the intra- and interrater reliability for the acquisition and analysis of ultrasound images of muscle thickness and echogenicity in critically ill trauma patients between health professionals with different levels of expertise.
Diagnostic accuracy study. Two examiners (expert and novice) acquired ultrasound images from ten patients; an experienced, blinded analyst quantified the images. In a separate group of ten patients, two analysts (expert and novice) quantified quadriceps muscle thickness and echogenicity (square or trace method) from images acquired by one examiner.
Excellent reliability was found for image acquisition and analysis (intraclass correlation coefficients > 0.987; p < 0.001). The standard error of the measurement values ranged from 0.01 - 0.06cm for muscle thickness and from 0.75 - 2.04 arbitrary units for muscle echogenicity. The coefficients of variation were < 6% for thickness and echogenicity. The echogenicity values were higher when using the square technique than when using the tracing technique (p = 0.003).
Ultrasound is safe, feasible, and reliable for muscle assessment in critically ill trauma patients, regardless of the assessor’s level of expertise.
Search
Search in:


Comments