Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2021;33(1):167-171
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20210018
The natural history of the disease, and the treatment of post-COVID-19 patients, are still being built. Symptoms are persistent, even in mild cases, and the infection consequences include fatigue, dyspnea, tachycardia, muscle loss, and reduced functional capacity. Regarding cardiopulmonary rehabilitation, there seems to be an improvement in functional capacity, quality of life, and prognosis with the 6-Minute Walk Test used as a prognostic and therapeutic evaluator. Therefore, this case series report aims to present our experience with four cases of different severity levels, involved in a post-COVID-19 cardiopulmonary rehabilitation program. These patients were assessed with the 6-Minute Walk Test, peripheral muscle strength, and double product at rest, to assess the results after a three-month rehabilitation protocol of at least 300 minutes per week. The four patients had their distance covered during the walk test increased between 16% and 94%. Peripheral muscle strength was improved by 20% to six times the baseline values, and double product at rest was reduced by 8% to 42%. The cardiopulmonary rehabilitation program had a positive impact on these cases, improving functional capacity despite the different severity levels in these post-COVID-19 cases.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2019;31(4):529-535
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20190066
To measure and compare the functionality of patients after discharge from the intensive care unit and at the time of hospital discharge.
Quantitative study of a prospective cohort performed between August of 2016 and December of 2017 at a university hospital. A 10-meter walk test was performed at 2 timepoints: after discharge from the intensive care unit and prior to hospital discharge. The data were analyzed using Student's t-test and Pearson or Spearman correlation. Statistical Package for Social Science (SPSS) version 21.0 was used for the analysis, and p ≤ 0.05 was adopted as the level of significance.
Forty patients, with a mean age of 57.1 ± 12.2 years and with a predominance of males (60%), were evaluated. For the post-intensive care unit test, a mean speed of 0.48m/s was observed, and for the pre-hospital discharge test, there was an increase to 0.71m/s, evidencing functional evolution during the hospital stay (p < 0.001).
There was significant improvement in walking speed at the time of hospital discharge when compared to the walking speed at the time of intensive care unit discharge.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2019;31(1):57-62
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20190016
To assess the Perme mobility scale score as a predictor of functional status and complications in the postoperative period in patients undergoing liver transplantation.
The sample consisted of 30 patients who underwent liver transplantation. The patients were evaluated at two time points to determine their perception of pain, degree of dyspnea, peripheral muscle strength, and functional status according to the Perme scale. The collected data were analyzed by descriptive and inferential statistics. To compare the means between the evaluations, Student's t test for paired samples was applied. In case of asymmetry, the Wilcoxon test was used. In the evaluation of the association between the quantitative variables, the Pearson or Spearman correlation tests were applied.
A total of 30 individuals who underwent liver transplantation were included. The patients were predominantly male, and the mean age was 58.4 ± 9.9 years. The most prevalent underlying pathology was cirrhosis C virus (23.3%). Significant associations of the time on mechanical ventilation with the Perme scale score at discharge from the intensive care unit (r = -0.374; p = 0.042) and the number of physical therapy treatments (r = -0.578; p = 0.001) were recorded. When comparing the results of the initial evaluation and the evaluation at hospital discharge, there was a significant improvement in functional status (p < 0.001).
Functional mobility, peripheral muscle strength, pain perception, and dyspnea are significantly improved at hospital discharge compared with those at inpatient unit admission.
Abstract
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2018;30(4):479-486
DOI 10.5935/0103-507X.20180069
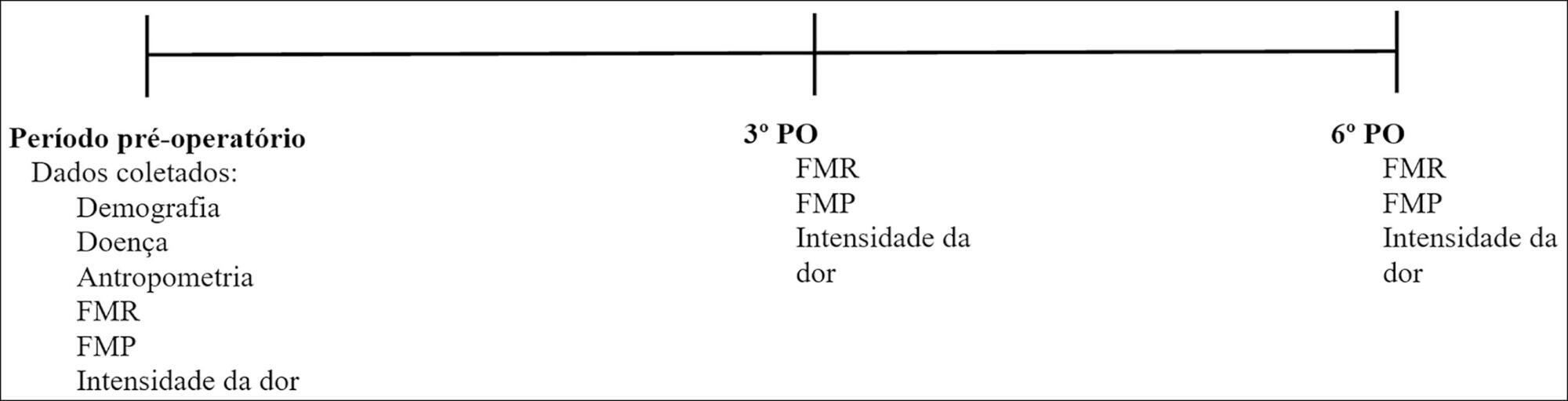
To evaluate respiratory and peripheral muscle strength after cardiac surgery. Additionally, we compared the changes in these variables on the third and sixth postoperative days.
Forty-six patients were recruited, including 17 women and 29 men, with a mean age of 60.50 years (SD = 9.20). Myocardial revascularization surgery was performed in 36 patients, replacement of the aortic valve in 5 patients, and replacement of the mitral valve in 5 patients.
A significant reduction in respiratory and peripheral muscle strength and a significant increase in pain intensity were observed on the third and sixth postoperative days (p < 0.05), except for the variable maximal inspiratory pressure; on the sixth postoperative day, maximal inspiratory pressure values were already similar to the preoperative and predicted values (p > 0.05). There was an association between peripheral muscle strength, specifically between maximal expiratory pressure preoperatively (rs = 0.383; p = 0.009), on the third postoperative day (rs = 0.468; p = 0.001) and on the sixth postoperative day (rs = 0.311; p = 0.037). The effect sizes were consistently moderate-to-large for respiratory muscle strength, the Medical Research Council scale and the visual analog scale, in particular between preoperative assessment and the sixth postoperative day.
There is a decrease in respiratory and peripheral muscle strength after cardiac surgery. In addition, maximal expiratory pressure is the variable that is most associated with peripheral muscle strength. These variables, especially respiratory and peripheral muscle strength, should be considered by professionals working in the intensive care setting.
Search
Search in:
Case reports (56) Child (53) Coronavirus infections (34) COVID-19 (46) Critical care (116) Critical illness (54) Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (26) Infant, newborn (27) Intensive care (72) Intensive care units (256) Intensive care units, pediatric (31) mechanical ventilation (38) Mortality (76) Physical therapy modalities (28) Prognosis (61) Respiration, artificial (119) Respiratory insufficiency (26) risk factors (34) SARS-CoV-2 (28) Sepsis (98)